Antibody Detection and Identification
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Antibody Screen
Test used to detect Abs
Used pts plasma or serum against reagent RBCs to detect unexpected Abs
Unexpected Abs are a result of RBC stimulation
Transfusion
HDFN
When are Antibody Screens used?
Pts needing a transfusion
Pregnant women
Pts who have had transfusion rxns
Blood and plasma donors
Which unexpected Ab is clinically significant?
Clinically significant (IgG)
Not clinically significant (immunoglobulin M [IgM]
Clinically Significant Antibodies
Usually IgG
React best at 37° C and during the antihuman globulin (AHG) phase (indirect antiglobulin test [IAT])
are associated with hemolytic transfusion reactions
(HTRs) and HDFN
Performing an Antibody Screen
pt’s plasma or serum is incubated with screening cells
After incubation, an IAT is performed using AHG reagent
Want to detect any IgG antibodies
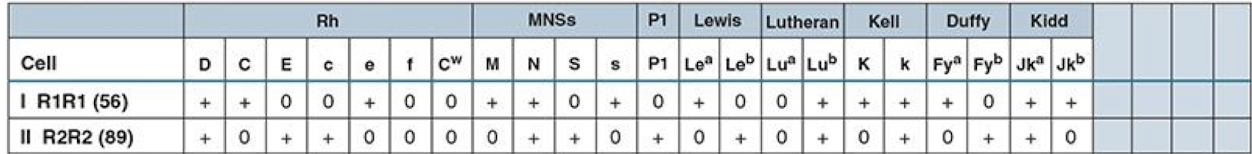
Screening Cells
are single or pooled donor group O cells
however, single-donor vials offer increased sensitivity
Group O cells are used so that anti-A and anti-B antibodies will not react
Screening cells come in sets of 2 or 3 vials (donor) each
Each vial has been phenotyped for each antigen

Antigram
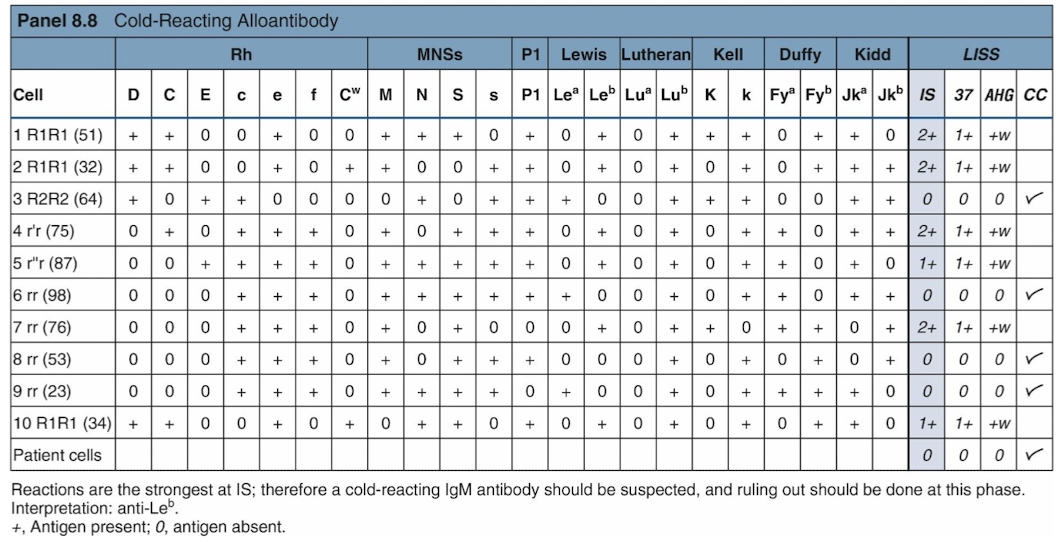
A reaction to one or more cells indicates the presence of an atypical antibody,
Autocontrol
Tests a patient’s serum with his or her own RBCs
incubated with the Ab screen (or Ab panel)
if AC w/ a screen and it is (+), can run a DAT (patient cells plus AHG) to detect in vivo coating
help determine if Abs are directed against the pt’s cells or transfused cells (allo- or autoantibody)
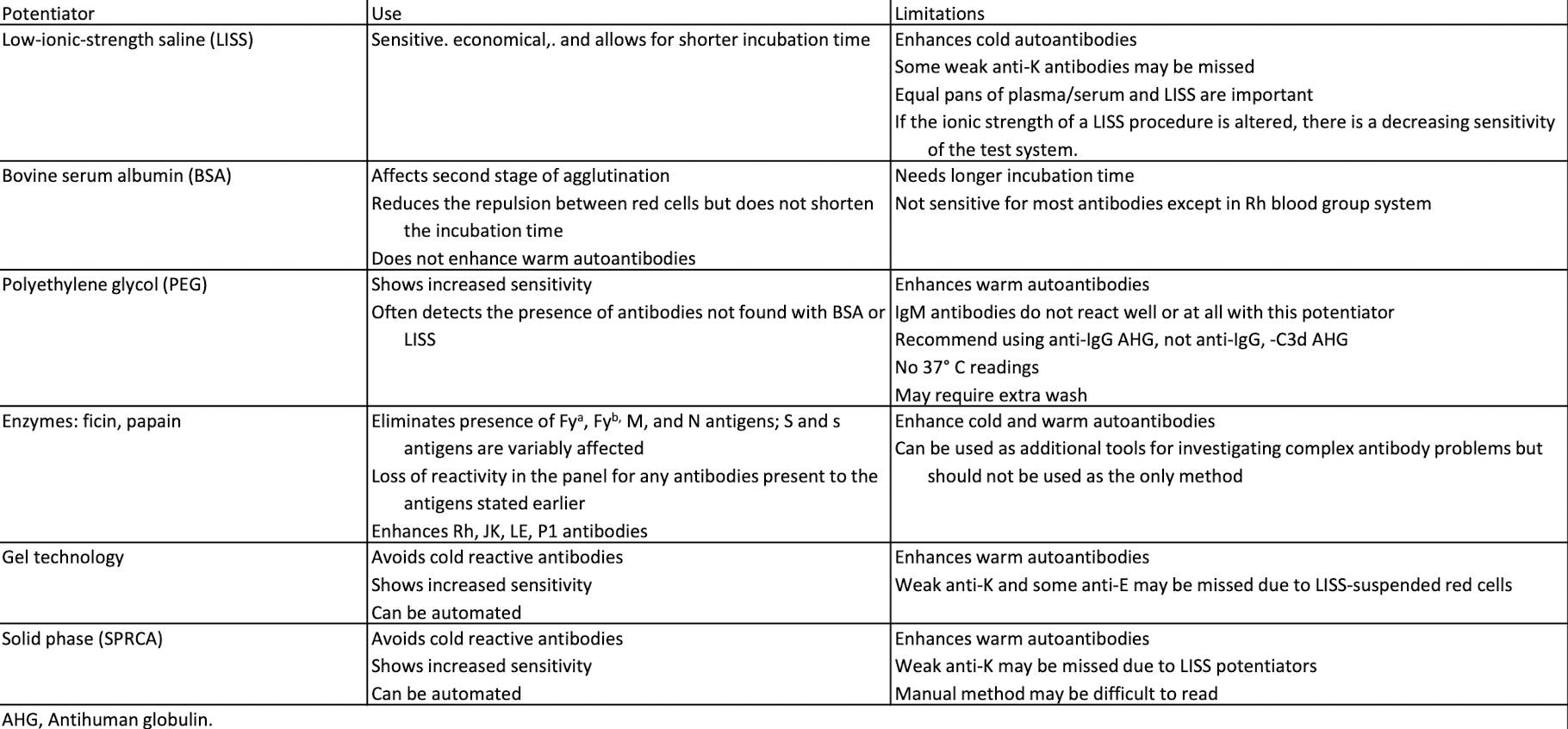
Potentiators
Used in Ab detection and identification to enhance an Ag–Ab rxn
Saline (may only enhance if incubated for a long time)
Low-ionic-strength solution (LISS): common
Bovine serum albumin (BSA)
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)
Proteolytic enzymes (can destroy some antigens)
Comparison of Potentiators and Methods
Patient History Significance
GET THE HISTORY!
Mixed RBC pop. from a prev. transfusion can remain for up to 3 months
Pt may have come from another hospital
Some diseases are associated with Abs
Some Abs occur at a higher frequency in some races
Learn about the diagnosis, age, and race of the patient
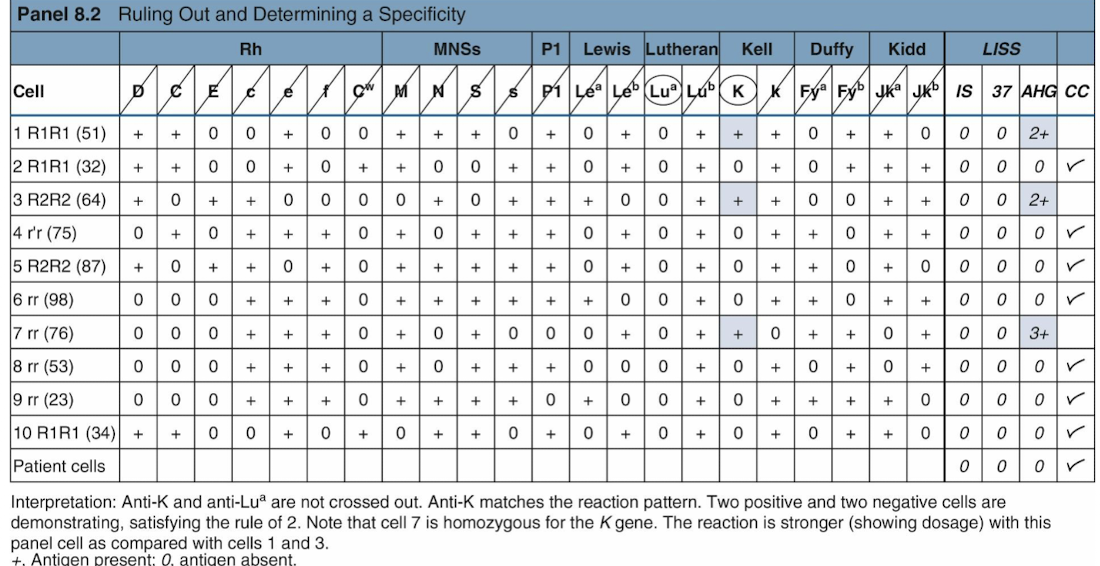
Antibody ID: Initial Panel
an extended version of an antibody screen (10 to 20 cells)
Group O cells
Each panel cell is antigen typed
its antigram lists the phenotypes of each panel cell
used to record and interpret results
Interpretation Guidelines
Autocontrol: A (+) autocontrol suggests autoantibodies or alloantibodies to transfused cells, while (-) result = alloantibodies.
Phases: IgM reacts at room temp/IS phase, IgG reacts at 37°C/AHG phase.
Reaction Strength: Varying strengths suggest multiple Abs or dosage effects.
Ruling Out Antibodies: Use fully (-) panel cells to rule out Abs, avoiding heterozygous exclusions.
Matching the Pattern: A single antibody shows a clear pattern; multiple Abs show mixed patterns.
Rule of Three: Confirm AB ID with 3 antigen-positive and 3 antigen-negative cell reactions.
Autocontrol (AC) interpretation
Positive autocontrol or DAT:
Autoantibody or alloantibody present to recently transfused cells
Negative autocontrol: indicates alloantibody
Positive autocontrol + negative DAT:
Indicates false positive test
Phases Interpretation
IgM Abs react at room temp. or during immediate-spin (IS) crossmatching
anti-Lea, anti-Leb, anti-M, anti-N, anti-I, anti-P1 Abs
IgG antibodies usually react at 37° C or with AHG
Rxn at diff phases may indicate IgM AND IgG
Reaction strength Interpretation
Rxns w/ varying strengths can indicate multiple Abs
Strength also affected by dosage
Ruling Out Antibodies Interpretation
Use panel cells (-) in all phases to rule out Abs.
Start with the first (-) panel cell and cross out present Ags.
Do not cross out heterozygous panel cells; Abs may be too weak to react.
Matching the Pattern Interpretation
pattern of rxns matches one of the Ag columns when a single Ab is present
Multiple Abs show varying patterns
Rule of Three Interpretation
To ensure valid results, 3 Ag (+) cells must react and 3 Ag (-) cells must not react with the pt’s serum or plasma
If this does not occur, additional panel cells (selected cells) are used
Example of Ruling Out and Matching the Pattern
Phenotyping the patient
confirm the presence of Abs is to determine the pt’s phenotype for Ags
Individuals do not make alloantibodies toward Ags on their own RBCs
If the patient has recently been transfused, RBC separation techniques should be used before phenotyping is done
Multiple Antibodies
Special techniques can be used to help identify multiple Abs
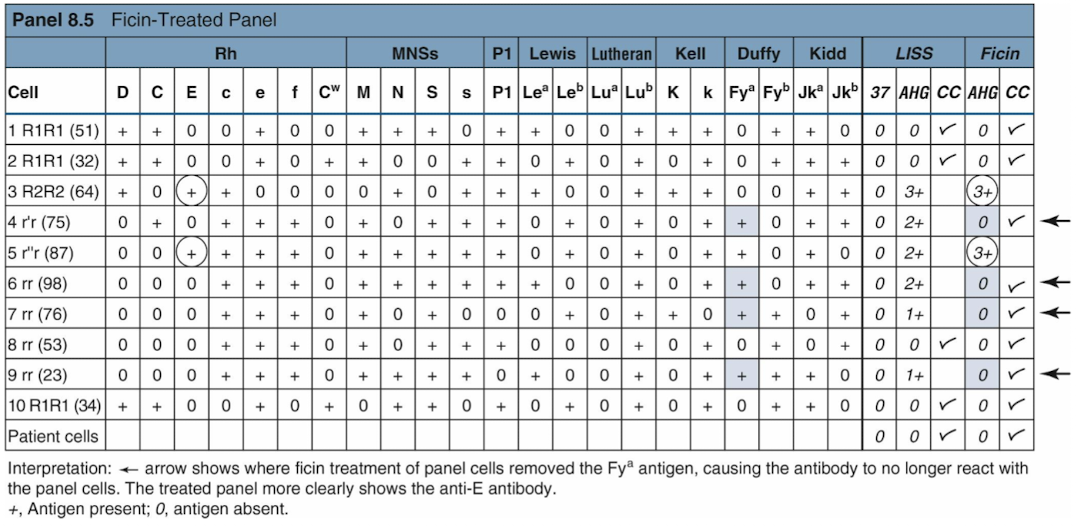
Selected cells
Proteolytic enzymes
Other chemicals (e.g., dithiothreitol)
Dithiothreitol = denature Kell antigen
Proteolytic Enzymes
used to eliminate or enhance Ab activity
Duffy and MNS Ags are destroyed
Decrease
Rh, Kidd, and Lewis antigens are enhanced
Increase
One-stage test: Enzymes, RBCs, and serum are simultaneously incubated
Two-stage test: Panel cells are pretreated with enzymes, washed, and then used as usual
Proteolytic Enzymes Examples
include papain, bromelain, and ficin, used to alter antigen expression on red blood cells.
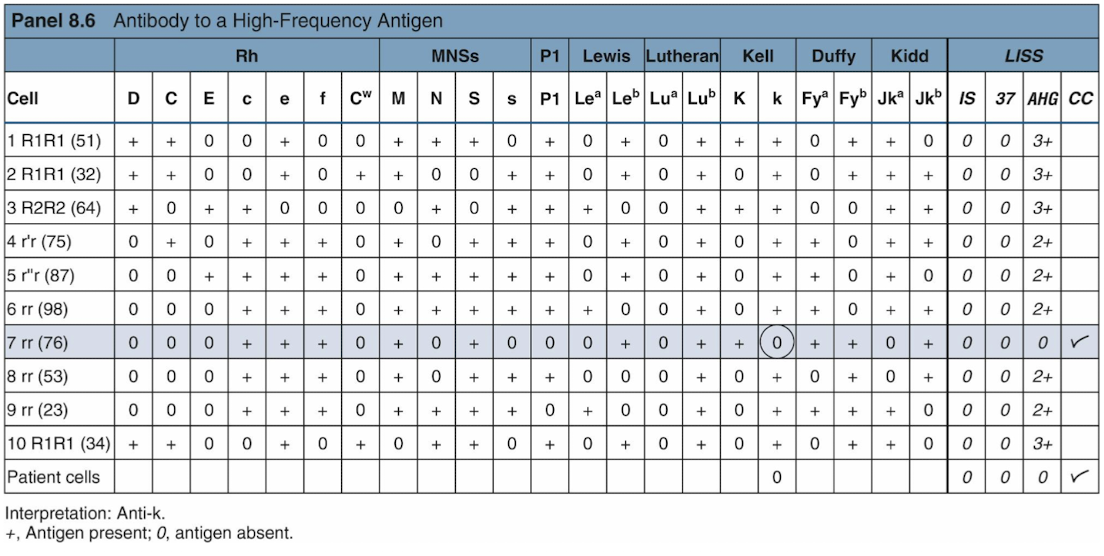
Antibodies to High-Frequency Antigens
High-frequency Ags occur in the pop. at a frequency of 98% or higher
Suspect an alloantibody to a high-frequency Ag if most panel cells are positive
Testing to confirm include:
Enzymes to enhance or destroy Ags
Dithotheritol to destroy Kell Ags
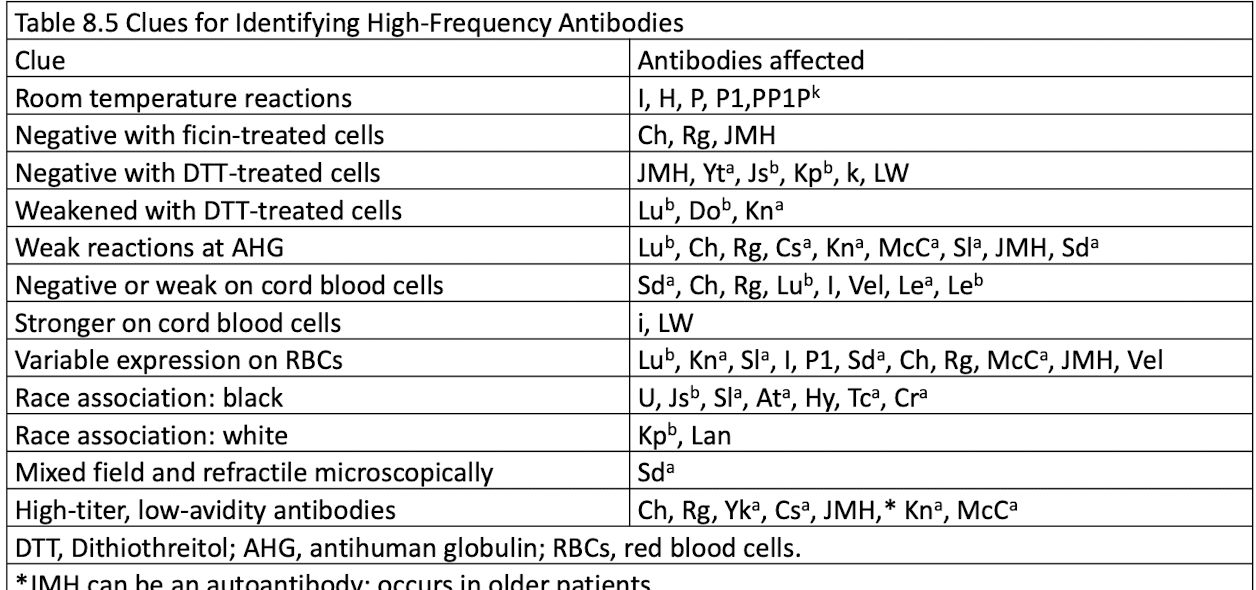
Clues for Identifying High Frequency Antibodies
High-Titer, Low-Avidity Antibodies
Antibodies to high frequency antigens that react weakly
React at AHG phase
Not implicated in transfusion reactions of HDFN

Anitbodies to Low-Frequency Antigens
may occur alone or suspect when screen is negative and crossmatching is positive
one one reactive cell suggest this
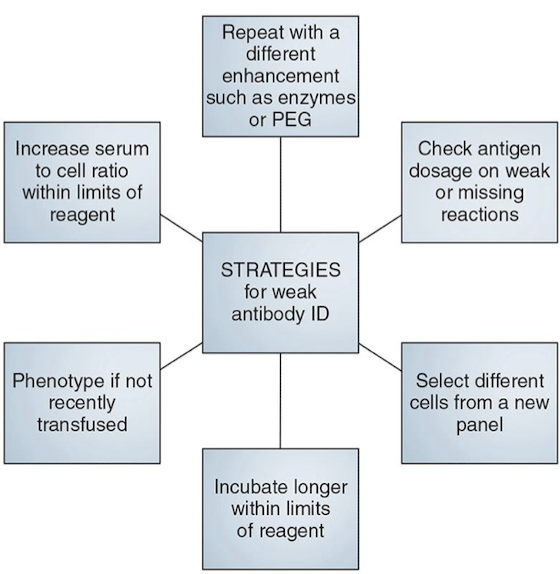
Enhancing Weak IgG Antibodies
Cold Alloantibodies
IgM antibodies that react during IS crossmatching (sometimes 37 C)
Not clinically significant
Anti-P, anti M, and anti-N antibodies have variable rxns
to enhance rxns: incubation < 37 C
to avoid rxns: neutralize to allow for detection of clinically sig, Abs
Autoantibodies
react w/ all reagents & self & donor RBCs, regardless of present Abs
AC & DAT (+)
must identify underlying AlloAb when autoAbs present
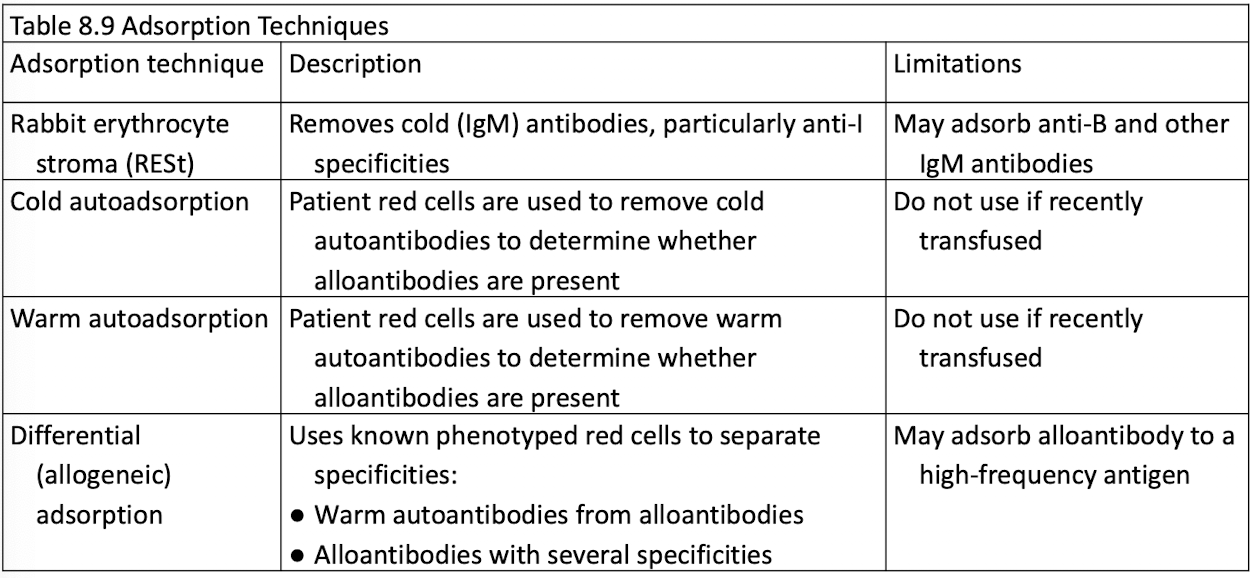
Adsorption used for removal of AutoAbs
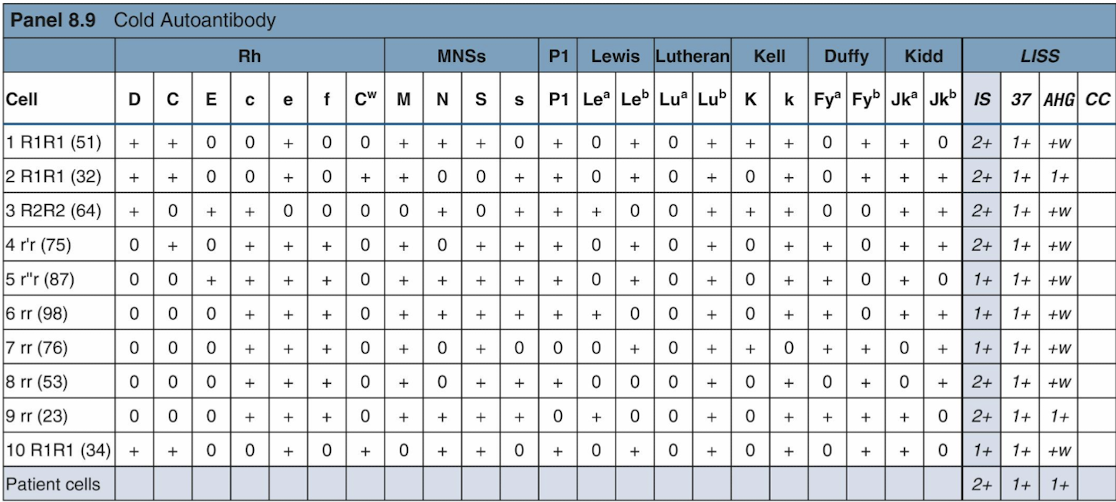
Cold Autoantibodies
React during IS crossmatching
Positive autocontrol and DAT (to C3)
May occur with:
Mild anemia
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
Infectious mononucleosis
Most are anti-I, anti-H, and anti-IH
"Cold panels" can aid identification
Avoiding Cold Autoantibody Reactions
Use a monospecific IgG AHG reagent rather than a polyspecific reagent
Skip IS crossmatching and testing at 37° C
Use 22% bovine serum albumin instead of LISS
Prewarming all tubes to 37° C will avoid reactivity
Washing with warm saline is not advised when prewarming the tubes
Use adsorption techniques if all else fails
Adsorption techniques
Warm Autoantibodies
More common than cold autoantibodies
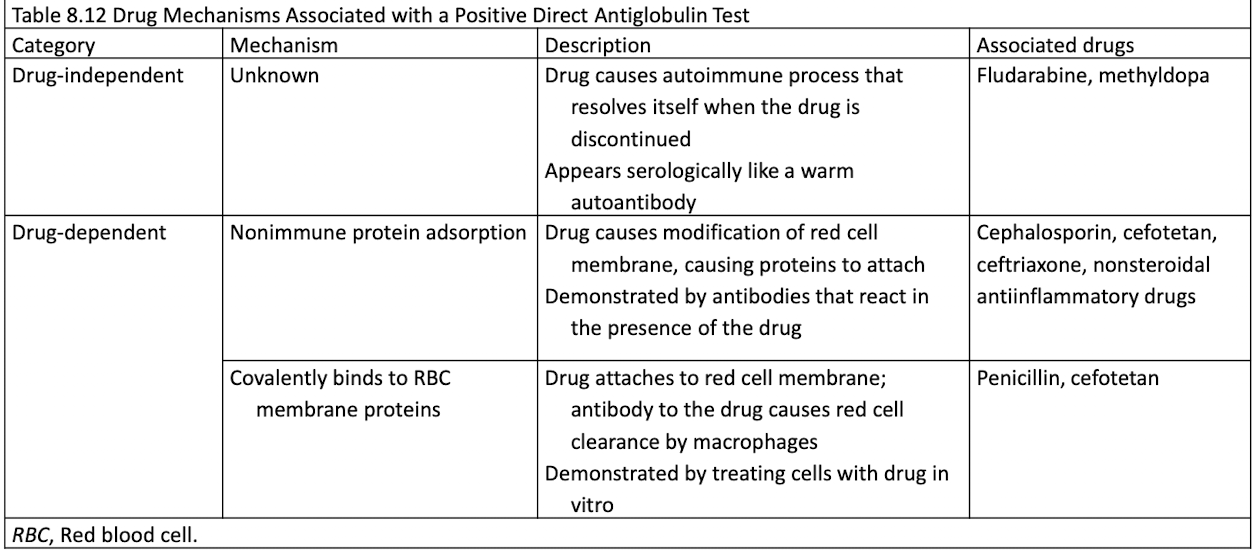
May result from autoimmune hemolytic anemia, disease, or drug.
Most panel cells and the AC are (+)
22% albumin decreases reactivity
Determine if underlying alloantibodies exist
Specificity
Warm autoantibodies often target Rh system, esp. e antigen.
Patient has anti-e antibody and e antigen
Positive DAT.
e-negative blood may improve RBC survival in chronic hemolysis.
Medications can induce warm autoantibodies.
Drug Mechanisms Associated w/ Positive DAT
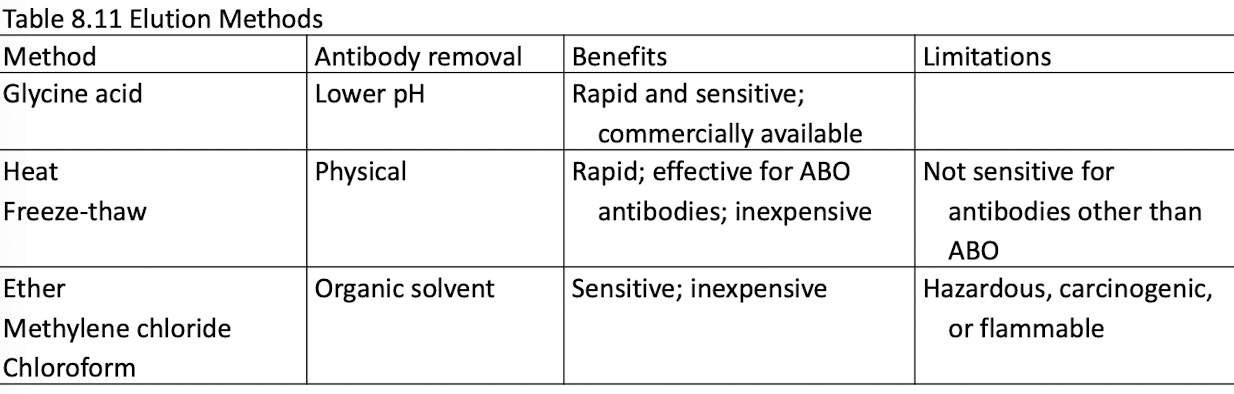
What is Elution? What are its methods?
Used to identify antibodies when the DAT is positive.
IgG must be detached by using the elution technique
The recovered antibody is called the eluate
Eluate is used in an antibody panel to identify antibody
Elution is performed in suspected cases of HDFN; may not be reactive in all cases of warm autoantibodies
Adsorption
Remove warm autoantibodies to test for underlying alloantibodies
Cells pretreated with dithiothreitol or ZZAP to remove in vivo attached antibodies