03 Infection control in hospital settings. Multiresistant pathogens
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is infection control in general?
population/community level data collection and intervention in relation to infectious diseases
What is infection control in a hospital setting?
hospital hygiene
primary target population in a hospital setting
patients
health care staff
secondary target population in a hospital setting
visitors
non-health care staff (administrative, janitorial, etc.)
Classic approaches to infection control?
Isolation of infectious patient
Isolation of susceptible patient (protective or reverse isolation)
Disinfection (germ reduction)
Sterilization (germ elimination)
Hazardous waste management
Disinfective cleaning
Hygiene in food service/catering
Hygiene in laundering
Pest control (insects, rodents)
Advanced approaches to infection control? (aka surveillance)
Data collection to identify hospital infections (aka. nosocomial infections)
Built on evidence-based definitions
Field work carried out by infection control nurses
Managed by hospital epidemiology/preventive medicine/public health specialist physicians
Computer analysis of data
Action response planning and implementation
What is an example of surveillance?
general microbiological monitoring
What is general microbiological monitoring?
Daily evaluation of microbiological findings
Identification of positive blood cultures and multiresistant pathogens
Microbiological analysis of the most commonly found pathogens
Antibiotic resistance monitoring
Most common types in ICU patients
respiratory tract and bloodstream infections
Why is ICUs a hotbed of nosocomial infections?
Invasive interventions are a key causal factor
Colonization
microorganism permanently lives and multiplies on body surface without causing disease
Infection
when there are risk factors, infectious disease can develop from colonization
Normal flora versus Nosocomial flora
more Gram negatives, more resistant bacteria in latter
Nosocomial infection
infection acquired in a health care setting
Standard isolation
designated room and equipment; involvement and impact on staff, patient, and visitors/relatives
Contact isolation
staff must wear protective equipment
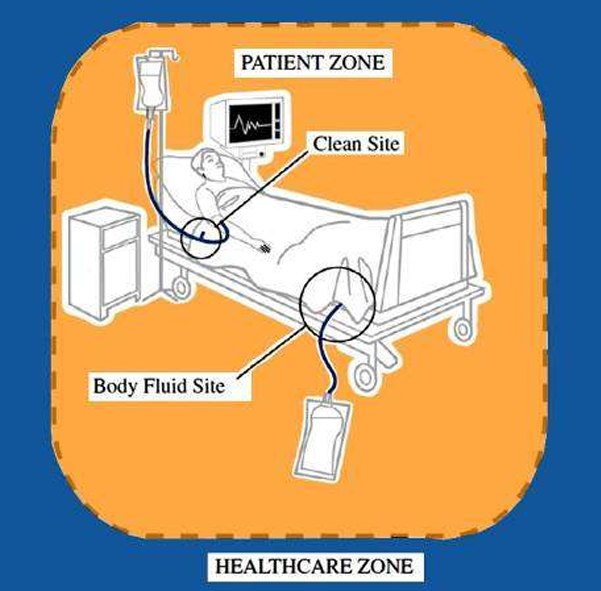
patient zone
assumed to be rapidly contaminated by patient’s flora
must be cleaned between patients
two critical sites: clean site & body fluid site
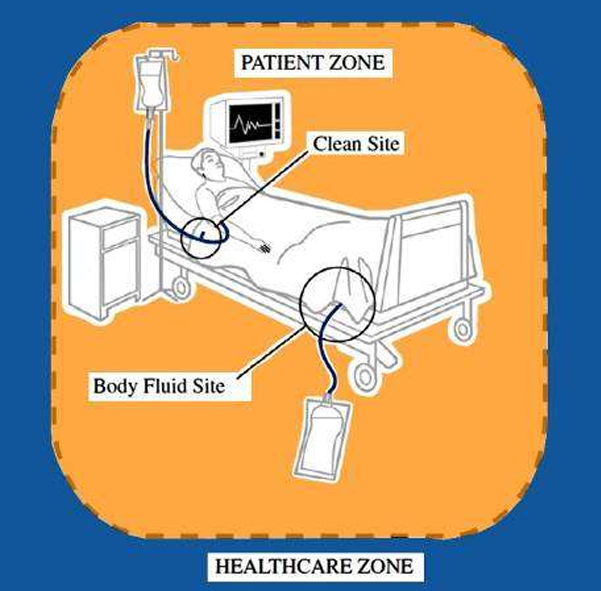
Healthcare zone
assumed to contain hospital germ strains source of exogenous infection
5 moments for hand hygiene by WHO
before touching a patient
before a procedure
after a procedure or body fluid exposure risk
after touching a patient
after touching a patient’s surroundings
Polyresistance (PDR)
resistance to at least 2 antibiotic groups effective against the wild type
Multiresistance (MDR)
resistance to at least 3 antibiotic groups effective against the wild type
Panresistance (extended drug resistance, XDR)
resistance to all (or all but one) known antibiotics
What is the cause of emerging multiresistance?
antibiotic (ab) misuse
low adherence to institutional ab policy
ab without prescription
ab in viral infection
poor compliance by patients
ab overuse in animal farming
exceeds human medical use
preventive use against infections
greater weight yield
poor infection control
What can we do against the increasing tendency of nosocomial infection?
screening
risk group awareness: e.g. medical devices inserted for a long time
proper infection control practice
appropriate, rational antibiotic policy
MRSA types
CA-MRSA (community-acquired/associated)
HA-MRSA (hospital-acquired)
LA-MRSA (livestock-acquired)
CA-MRSA (community-acquired/associated)
lower levels of antibiotic resistance
highly pathogenic (may even cause serious infections in healthy young persons)
severe tissue damage (Panton-Valentine leukocidin)
HA-MRSA (hospital-acquired)
higher levels of resistance
relatively less pathogenic