Biology (triple content) topic 2 - Year 9
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are stem cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to become specialised cells that you need to build a human
What are the advantages with stem cells
They can be cloned and made to differentiate into specialised cells to be used in medicine or research
Help repair damaged tissues
Used to replace damaged cells
Hoped in the future to be able to grow a replacement organ from an adults stem cells = getting rid of need for a donor so no chance that body eject the donated organ
What are the disadvantages with stem cells
if not inserted properly they can lead to cancer
When grown in a lab they could get contaminated with a virus
An embryo is a human life and should not be used for experiments
What is the practical for investigating enzyme activity affected on PH
Blend potatoes with water and filter to make a potatoe extract full of all the catalase from the cells
Add this to various pH buffers and hydrogen peroxide in a test tube
and using a test flask fill it with water and attach a tube from the test tube to the flask and measure the bubble of oxygen produced per minute from the reaction
Method of measuring the energy content of a food sample
Weigh the food sample
Place 20cm³ of water in a boiling tube
Measure the temperature of the water
Light the food and hold it under the boiling tube
Continue this until it will to longer burn
Stir the water and measure the final temperature
There are two things you need to know to work out how much energy is in the sample =
1. Amount of joules of energy that raises the temperature of 1g of water by 1 degree
2. How much 1cm³ of water mass is
= therefore you can work out the equation for energy = (final temp - start temp) x 20 (g) x 4.2/ mass of food (g)
4.2 joules of energy raises the temperature of 1g water by 1 degree
1cm³ of water has a mass of 1g
What is the equation for energy 1/g
Energy in 1g = (final temp - start temp) x 20 (g) x 4.2/ mass of food (g)
How can you work out how much energy is in a food
Burn it in a calorimeter
What is the total energy content measured in
Kilojoules KJ
what is the role of diffusion in gaseous exchange for plants
gaseous exchange in plants occurs through the stomata in the leaves
the gases move by diffusion (high concentration to a low concentration)
what happens between carbon dioxide and oxygen = during photosynthesis
carbon dioxide enters the leaf
oxygen exits the leaf
what happens between carbon dioxide and oxygen = during respiration
oxygen enters the leaf
carbon dioxide exits the leaf
how is the structure of the leaf adapted for gaseous exchange
broad so large surface area for diffusion
thin so short diffusion distance
air spaces allow gases to easily move to all cells
lots of stomata
plants can control the opening and closing of the stomata using guard cells
what is the role of stomata in gas exchange
allow movement of gases in and out of the air spaces by diffusion
what is the method to investigating the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf using hydrogen carbonate indicator = start of with what the indicator does
hydrogen carbonate indicator starts of orange
if it turns purple there is low CO2 meaning photosynthesis occurred
if it turns yellow there is high CO2 meaning respiration occurred
using 4 test tubes place one leaf (all the same size) in 3 of them with all 4 having the same volume of hydrogen carbonate indicator in each one.
the empty one is used as a control experiment
wrap one tube (with a leaf in) in aluminium foil
wrap one tube (with a leaf in) in muslin
leave the remaining tubes bare
shine a bright light onto the tubes and leave them for 45 minutes
what is the results to investigating the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf using hydrogen carbonate indicator
the control one = indicator stays orange = no change in CO2
the tube covered in foil = no light = no photosynthesis could of occurred = leaf was respiring = indicator turns yellow = producing CO2
the tube with no cover = photosynthesis occurred = indicator turns purple = used up CO2 in the tube
the tube covered in muslin = had some light = no change in CO2 = indicator stays orange
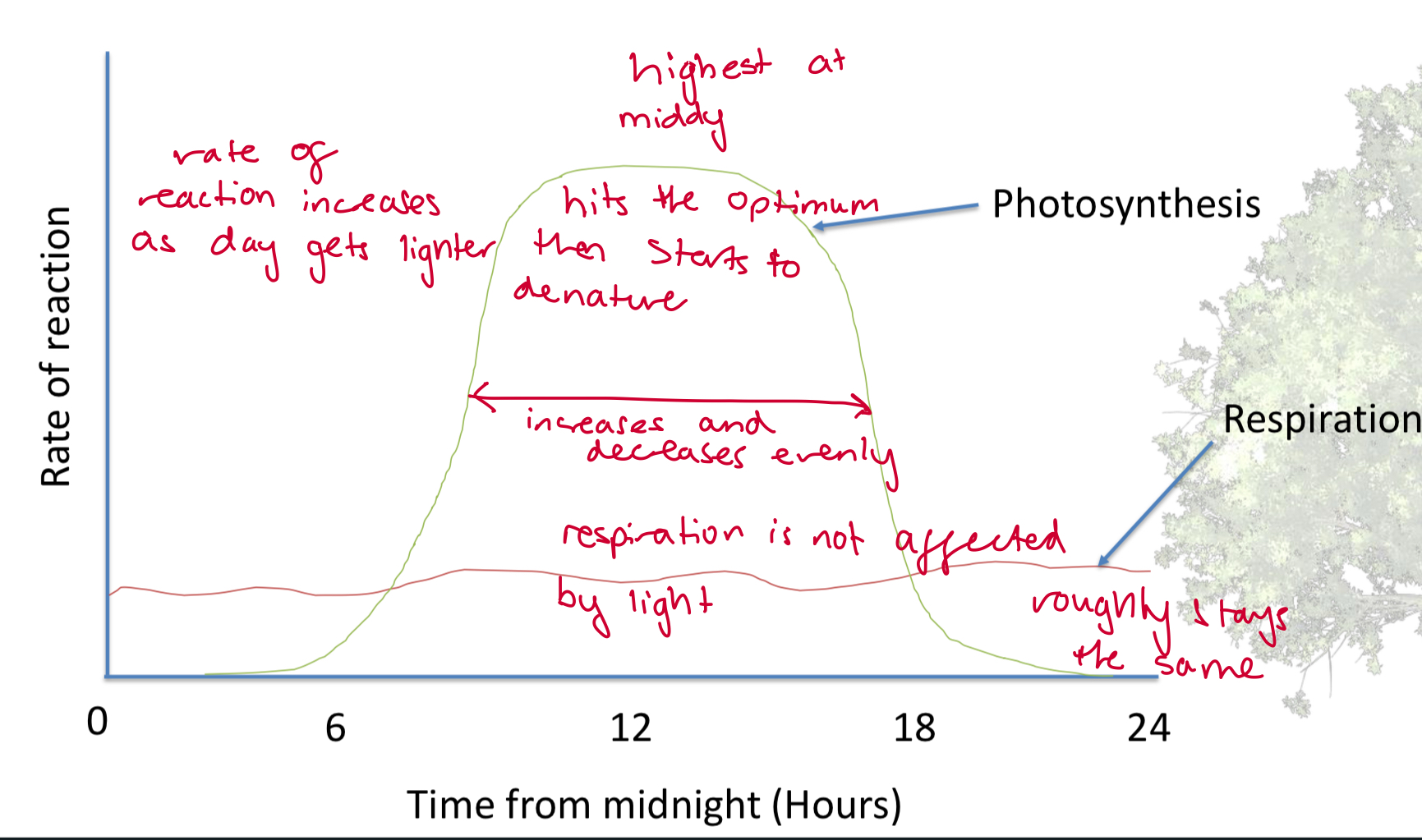
how long does respiration occur in plants
24 hours
when does photosynthesis occur
during when sunlight is available
what does the net exchange of gases depend on
how much light is available
describe this graph on what happens with gas exchange during hours of the day