Chapter 15 Traveling Waves and Sound
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
A mechanical wave
A traveling displacement of some material. The medium itself does not travel. Since the disturbance travels it can transfer energy.
Longitudinal waves move ______ to the direction of motion, whereas transverse waves move ______ to the direction of motion
parallel; perpendicular
The velocity of a traveling wave depends on _____ and ______. Velocity is proportional the the square root of _____ and inversely proportional to the square root of ________.
Tension and Linear density
Tension; linear density
A wave transfers energy, but does NOT transfer _____
any particles or materials of the medium outward from the source
A transverse wave
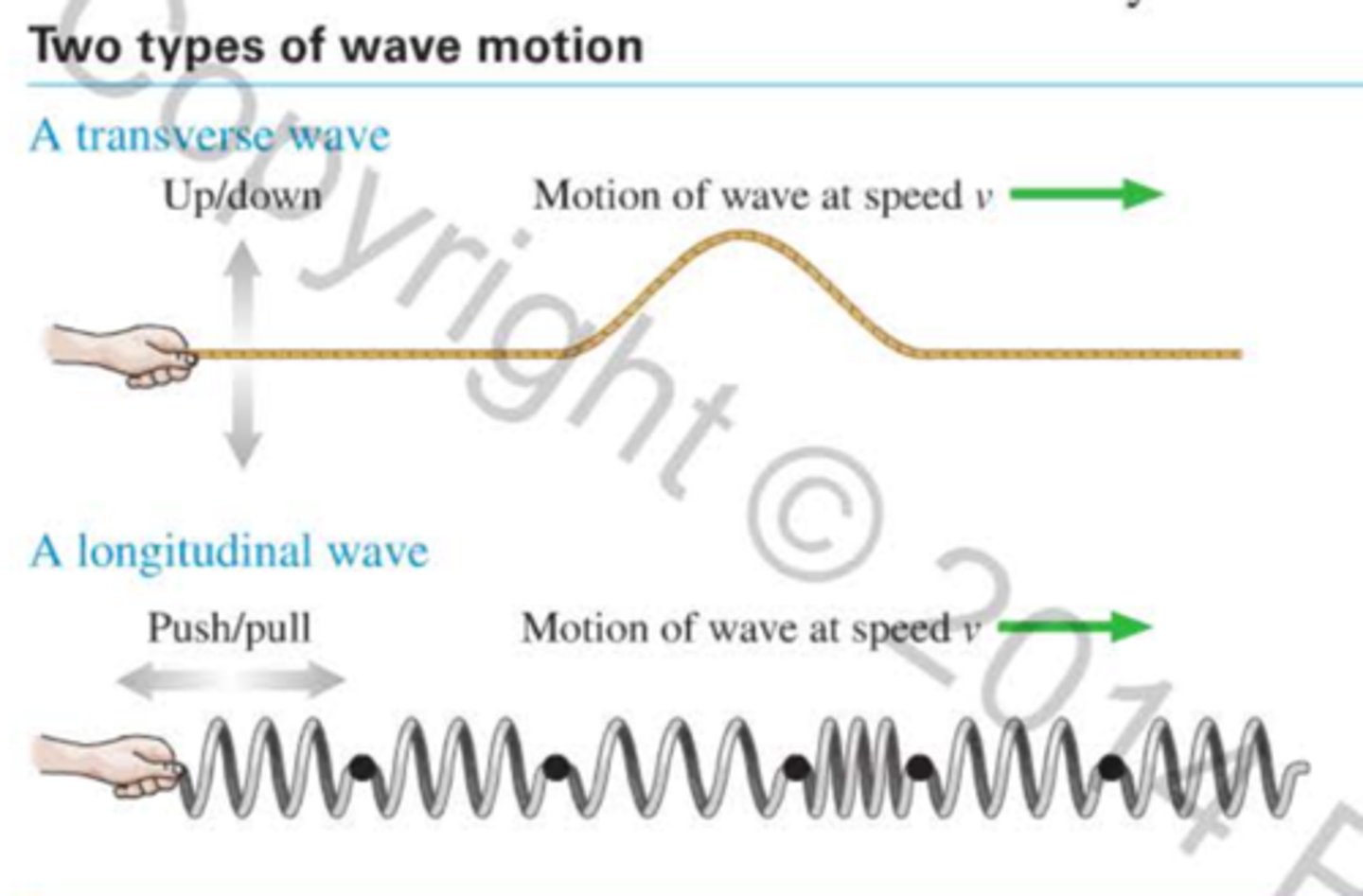
For mechanical waves, a transverse wave is a wave in which the particles in the medium move perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. Shaking the end of a stretched string up and down creates a wave that travels along the string in a horizontal direction while the particles that make up the string oscillate vertically.
A longitudinal wave
ln a longitudinal wave, the particles in the medium move parallel to the direction in which the wave travels. Here we see a chain of masses connected by springs. lf you give the first mass in the chain
a sharp push, a disturbance travels down the chain by compressing and expanding the springs.
Wave speed does NOT depend on
the shape or size of the wave pulse, how the pulse was started, or how far the pulse has traveled; it only depends on the medium that carries the wave.
Wave speed increases with increasing ____ and decreasing with increasing ______
Tension; linear density
Wave speed increases with increasing ____ and decreases with increasing ______
Tension; linear density
What is a snapshot graph and why is needed to describe wave motion?
A snapshot graph shows the displacement as a function of wave position at a single instant in time.
Waves are not localized. It is spread out through space in each instant of time. We need a function that tells us what a wave is doing at an instant of time (when) at a particular point in space (where). We need a function that depends on both position and time.
What is a history graph?
A record of the motion of one point in the medium over time.
The motion of a point along a string carrying a sinusoidal wave is in
simple harmonic motion
Before we can specify the displacement of a wave, we need to know both _____ and _____
position and time
During a time interval of exactly one period T, each crest of a sinusoidal wave travels a distance lambda, exactly one _____
wavelength
Sound waves create regions of high and low pressure, called ______ and ________, respectively.
Compressions and rarefactions
Compressions are crests and rarefactions are troughs
A circular wave is a _____ wave that spreads across a surface from a source. The distance between the crests are known as ____ and are separated by a distance _____
two dimensional
wave fronts
lambda (Wavelength)
A spherical wave is a _____ wave whose wavelength is the distance between two __________
three dimensional
wave fronts
Quantities such as brightness and loudness depend not only on the rate of energy transfer, or ______, but also on the ________ that receives that _______.
Power
area; power
Why is the intensity of a sound weaker further away from the source?
The inverse-square dependence of r is really just a statement of energy conservation. The energy is spread over a larger and larger area as the wave moves outward. Consequently, the energy per area must decrease in proportion to the surface area of a sphere.
increasing the sound intensity by a factor of 10 results in an increase in perceived loudness by a factor of approximately
2
A normal conversation has I0,000 times the sound intensity of a whisper, but it sounds only about 16 times as loud.
The difference in perceived loudness is much less than the actual difference in intensity, the sound intensity level is measured on a logarithmic scale.
True or False.
The motion of a source can affect a wave that has already been emitted.
False.
The change in frequency of a sound when a source moves relative to an observer is called
The Doppler Effect.
In the Doppler Effect, expanding wave fronts get ________ in the direction of motion and _________ in the direction opposite the motion.
compressed; stretched/expanded
In the Doppler Effect, the stationary observer from whom the source is receding will perceive a _____ frequency, whereas the stationary observer towards whom the source is approaching will perceive a _____ frequency.
A lower frequency; a higher frequency
red shift and blue shift
red shift: when wavelengths expand (receding source),
blue shift: when wavelengths shorten (approaching source)
A wave bounces back and forth on a guitar string; this is responsible for making the sound of the guitar. As the
temperature of the string rises, the tension ______.
This ______ the speed of the wave on the string.
decreases; decreases
An oscillator creates periodic waves on a stretched string.
If the period of the oscillator doubles, what happens to the wavelength and wave speed?
The wavelength doubles but the wave speed is unaffected.
Doubling the period will halve the frequency, and halving the frequency while keeping wave speed constant requires the wavelength to double.
An oscillator creates periodic waves on a stretched string.
If the amplitude of the oscillator doubles, what happens to the wavelength and wave speed?
Both are unchanged.
An oscillator creates periodic waves on two strings made of the same material. The tension is the same in both strings.
If the strings have different thicknesses, which of the following parameters, if any, will be different in the two strings?
Choices: wave frequency, wave speed, wavelength, none of these.
wave speed and wavelength.
Wave speed is a function of linear density, which is affected by string thickness. Wavelength depends on wave speed and frequency/
An oscillator creates periodic waves on two strings made of the same material. The tension is the same in both strings.
If the strings have the same thickness but different lengths, which of the following parameters, if any, will be different in the two strings?
Choices: wave frequency, wave speed, wavelength, none of these.
Each parameter will be the same.
Since the strings are made of the same material and have the same thickness, they will have the same mass per unit length.
When a wave travels along a string, the wave speed depends exclusively on the properties of the ______ whereas the wave frequency is set by the ______ that creates the waves.
The wavelength is a quantity that can vary if either the _________ or the _________ is changed. Thus, it can be modified by changing either the motion of the oscillator or the properties of the string.
string; oscillator
wave speed; wave frequency
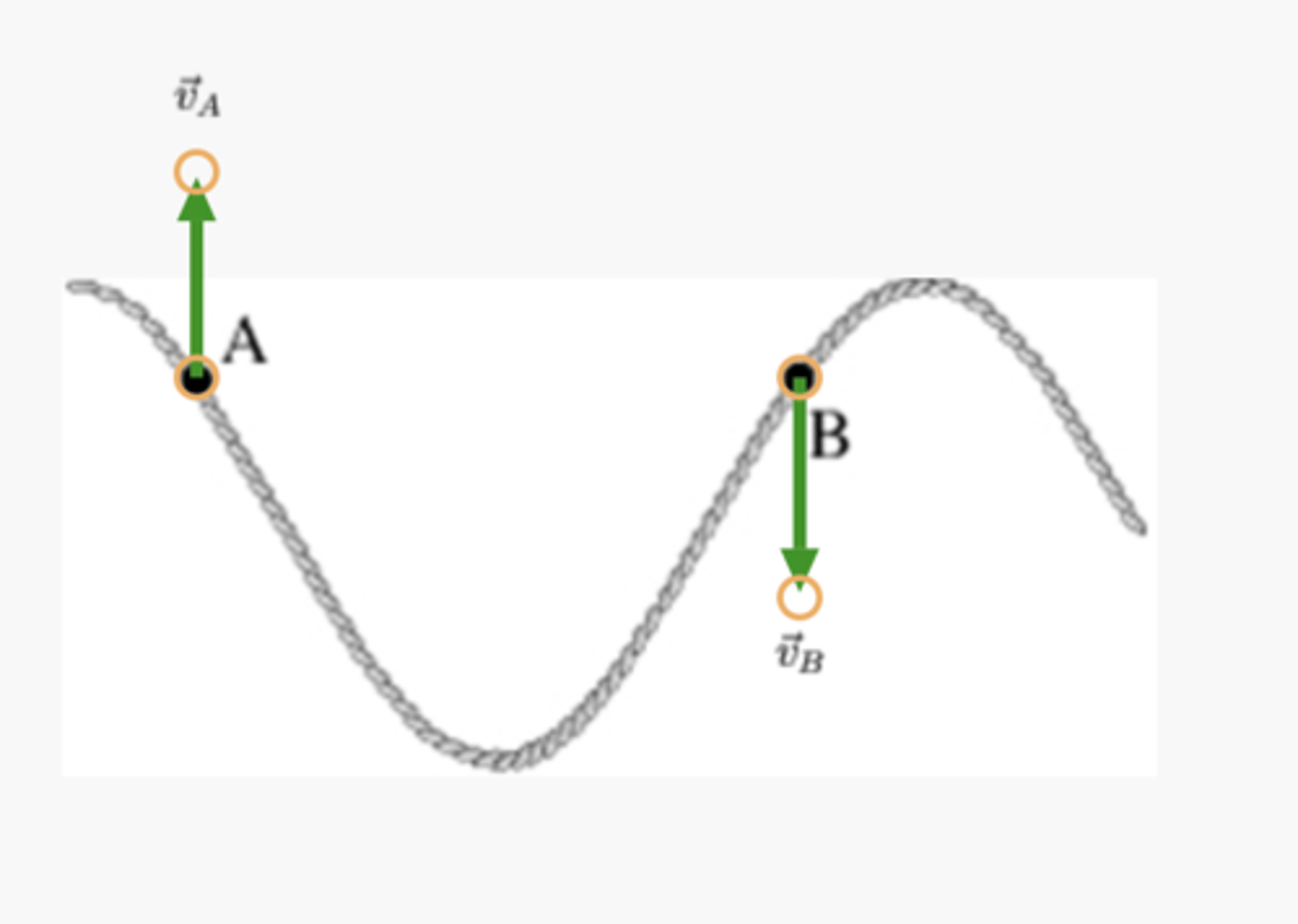
A long string is stretched and its left end is oscillated upward and downward. Two points on the string are labeled A and B.
Points A and B are indicated on the string. Orient the two vectors, v⃗ A and v⃗ B, to correctly represent the direction of the wave velocity at points A and B.
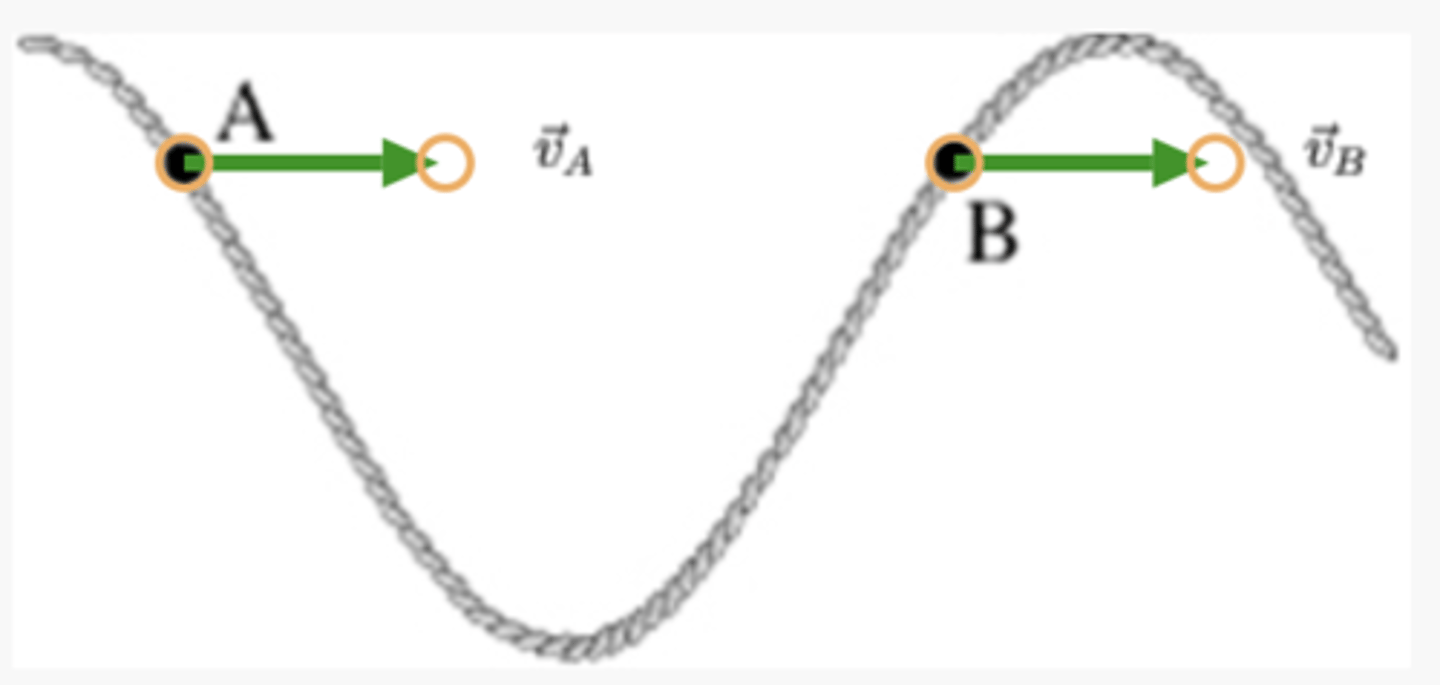
A long string is stretched and its left end is oscillated upward and downward. Two points on the string are labeled A and B.
At the instant shown, orient the given vectors, v⃗ A and v⃗ B, to correctly represent the direction of the velocity of the small pieces of the string at points A and B