Anatomy: The Tissues/cells
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/71
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
200 different cell types
How many different types of cell does the human body have
2
New cards
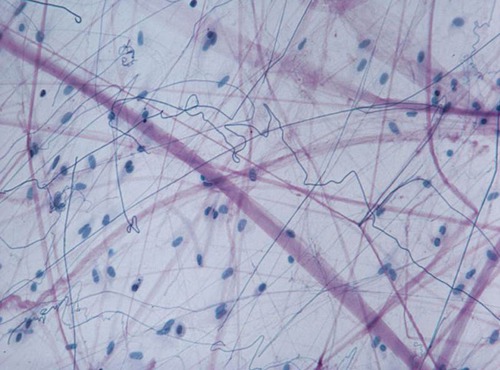
Firbroblasts
produce ( secrete) cable like fibers
3
New cards
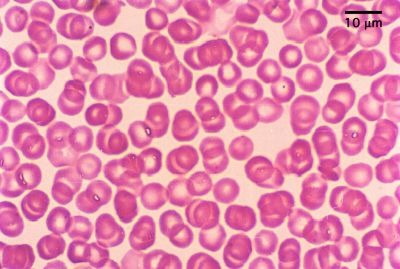
Erythrocytes ( red blood cells)
Carries oxygen to the blood stream
4
New cards
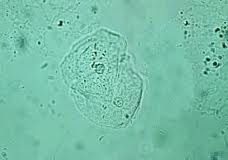
epithelial cells
skin cells that packs together in sheets. Intermediate fibers resist tearing during rubbing of pulling
5
New cards
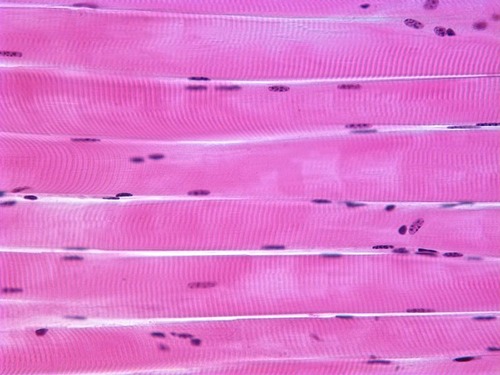
skeletal muscle
contractile filaments allow cells to shorten forcefully
6
New cards
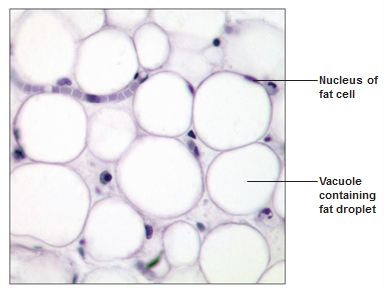
Fat cells
Stores nutrients, lipid droplets stored in cytoplasm
7
New cards
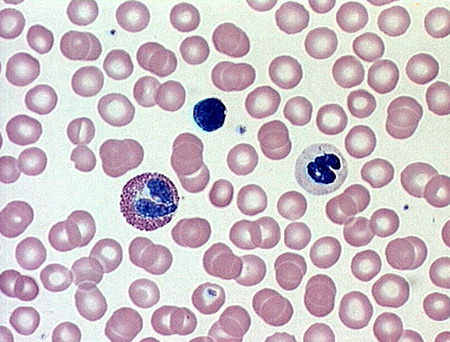
White blood cells
Digests infectious microorganisms
8
New cards
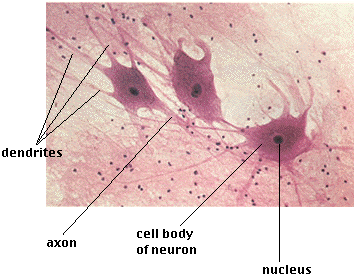
Nerve cells (neuron)
Receives and transmits messages to other body structures
9
New cards
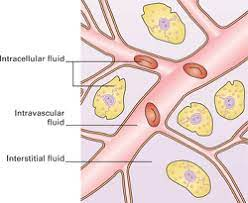
Intracellular fluid
Nucleoplasm and cytosol
Solution containing gasses, nutrients, and salts dissolved in water
Solution containing gasses, nutrients, and salts dissolved in water
10
New cards
Extracellular fluid ( interstitial fluid)
Fluid on the exterior of the cell
Contains thousands of ingredients, such as nutrients, hormones, neurotransmitters, salts, and waste products
Contains thousands of ingredients, such as nutrients, hormones, neurotransmitters, salts, and waste products
11
New cards
selective permable
The plasma membrane is a ------------ barrier
12
New cards
Passive processes
substances are transported across the membrane without any input from the cell ( NO ENERGY REQUIRED)
13
New cards
Active process
the cell provides the metabolic energy (ATP) to drive the transport process.
14
New cards
Isotonic solutions
have the same solute and water concentrations as cells and cause no visible changes in the cell.
15
New cards
Hypertonic solutions
contain more solutes than the cells do; the cells will begin to shrink.
16
New cards
Hypotonic solutions
contain fewer solutes (more water) than the cells do; cells will plump
17
New cards
Vesicular transport
substances are moved across the membrane "in bulk" without actually crossing the plasma membrane
18
New cards
Exocytosis
bulk items are removed from a cell
19
New cards
Endocytosis
bulk items are brought into a cell
20
New cards
Phagocytosis
solids
21
New cards
Pinocytosis
liquids
22
New cards
Body coverings, body linings, glandular tissue
Location of epithelial tissue
23
New cards
protection, absorption, filtration, secretion
functions of epithelial tissue
24
New cards
Cover and line body surface
Often form sheets with free surface, the apical surface, and a basel -scorched surface, the basement membrane.
Avascular (no blood supply).
Regenerate easily if well nourished
Often form sheets with free surface, the apical surface, and a basel -scorched surface, the basement membrane.
Avascular (no blood supply).
Regenerate easily if well nourished
Hallmarks of epithelial tissue
25
New cards
free surface
Part of the epithelial tissue that is exposed to an open area (either the external environment or to the inside of a hollow organ).
26
New cards
basement membrane
Cells at the base of an epithelial layer are attached to this.
27
New cards
simple
one layer
28
New cards
stratified
multiple layers
29
New cards
Squamous
flattened, like fish scales (squished)
30
New cards
Cuboidal
cube-shaped, like dice
31
New cards
Columnar
shaped like columns
32
New cards
Simple epithelia
Functions in absorption, secretion, and filtration
Very thin (so not suited for protection)
Very thin (so not suited for protection)
33
New cards
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells
Locations - usually forms membranes
Lines air sacs of the lungs
Forms walls of capillaries
Forms serous membranes (serosae) that line and cover organs in ventral cavity
Functions in diffusion, filtration, or secretion in membranes
Locations - usually forms membranes
Lines air sacs of the lungs
Forms walls of capillaries
Forms serous membranes (serosae) that line and cover organs in ventral cavity
Functions in diffusion, filtration, or secretion in membranes
34
New cards
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single layer of cubelike cells
Locations
Common in glands and their ducts
Forms walls of kidney tubules
Covers the surface of ovaries
Functions in secretion and absorption; ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells.
Locations
Common in glands and their ducts
Forms walls of kidney tubules
Covers the surface of ovaries
Functions in secretion and absorption; ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells.
35
New cards
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall cells
Goblet cells secrete mucus
Locations
Lining of the digestive tract from stomach to anus
Mucous membranes (mucosae) line body cavities opening to the exterior
Functions in secretion and absorption; ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells.
Goblet cells secrete mucus
Locations
Lining of the digestive tract from stomach to anus
Mucous membranes (mucosae) line body cavities opening to the exterior
Functions in secretion and absorption; ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells.
36
New cards
goblet cells
secrete mucus
37
New cards
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
All cells rest on a basement membrane
Single layers, but some cells are shorter than others giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification
Location
Respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Single layers, but some cells are shorter than others giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification
Location
Respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
38
New cards
Stratified squamous epithelium
Most common stratified epithelium
Named for cells present at the free (apical) surface, which are squamous
Functions as a protective covering where friction is common
Named for cells present at the free (apical) surface, which are squamous
Functions as a protective covering where friction is common
39
New cards
Lining of Skin (Outer Portion), Mouth, and Esophagus
location of stratified squamous ep
40
New cards
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two layers of cuboidal cells; functions in protection
41
New cards
Stratified columnar epithelium
surface cells are columnar, and cells underneath vary in size and shape; functions in protection
42
New cards
Stratified cuboidal and columnar
Rare in human body
Found mainly in ducts of large glands
Found mainly in ducts of large glands
43
New cards
Transitional epithelial
Composed of modified stratified squamous epithelium
Shape of cells depends upon the amount of stretching
Functions in stretching and the ability to return to normal shape
Location: lining of urinary system organs
Shape of cells depends upon the amount of stretching
Functions in stretching and the ability to return to normal shape
Location: lining of urinary system organs
44
New cards
Glandular epithelia
One or more cells responsible for secreting a particular product
45
New cards
Endocrine glands
Ductless; secretions (hormones) diffuse into blood vessels
Ex. include thyroid, adrenals, and pituitary
Ex. include thyroid, adrenals, and pituitary
46
New cards
Exocrine glands
Secretions empty through ducts to the epithelial surface
Ex. include sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas (both internal and external)
Ex. include sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas (both internal and external)
47
New cards
connective tissue
Found everywhere in the body parts, includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues. It is used for protection, support and binding.
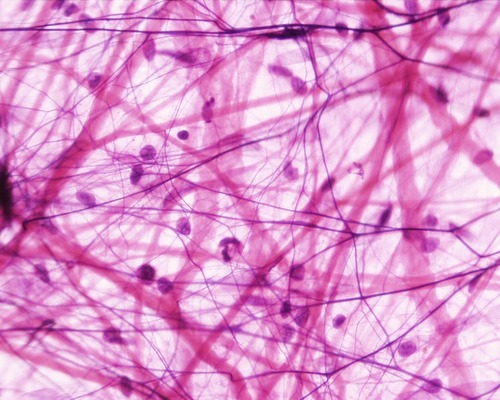
48
New cards
Characteristics of connective tissue
Variation in blood supply, some tissues are well vascularized and some have a poor blood supply or are avascular ( none)
49
New cards
extracellular matrix
nonliving material that surrounds living cells. there are two main elements.
50
New cards
Ground substance
mostly water along with adhesion proteins and polysaccharide molecules ( part of extracellular matrix)
51
New cards
Fibers
collagen, elastic, reticular ( part of extracellular)
52
New cards
Bone
Most rigid of connective tissue, composed of Osteocytes ( bone cells) sitting in lacunae( cavities), Hard matrix of calcium salts. Large number of collagen fibers. It is suppose to support the body
53
New cards
Cartilage
Less hard then bone, found in only a few places in the body. Chondrocyte (cartilage cell) is the major cell type
54
New cards
hyaline cartilage
Most widespread type of cartilage, Abundant collagen fibers hidden by a glassy rubbery matrix. It is located in the trachea, attaches to the ribs to the breast bone, and covers the ends of long bones, the entire fetal skeleton prior to birth and epiphyseal (growth) plates in long bones.
55
New cards
elastic cartilage
provides elasticity, supports the external ear
56
New cards
Fibrocartilage
highly compressible, forms cushion-like discs between vertebrae of spinal coloumn
57
New cards
dense connective tissue
main matrix element is collagen fiber, fibroblasts are cells that make fibers. Located in the tendons and ligaments and dermis
58
New cards
Dermis
Inner layer of skin
59
New cards
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
60
New cards
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
61
New cards
loose connective tissue
softer and have more cells and fewer fibers than any other connective tissue type except blood, types include areloar, adipose and reticular
62
New cards
areloar tissue
Loose soft more cells fewer fiber more cushion and protection
63
New cards
adipose tissue
Tissue that stores fat.
64
New cards
reticular
delicate network of interwoven fibers with reticular cells ( like fibroblasts) Forms stroma ( internal framework) of organs. Location in the lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow
65
New cards
Blood (vascular tissue)
Blood cells surrounded by fluid matrix called blood plasma, Fibers are visible during clotting, Functions as the transport vehicle for materials ( wastes, nutrients and respiratory gases)
66
New cards
muscle tissue
contract, or shorten, to produce movement
67
New cards
skeletal muscle tissue
Voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements. ( straiations, multinucleate, long cylindrical shape)
68
New cards
cardiac muscle tissue
involuntarilly controlled, found only in the heart (one nucleus, striations, short branching cells, contains gap junctions to connect cells)
69
New cards
smooth (visceral) muscle tissue
involuntarily controlled, found in walls of hollow organs (stomach, uterus, blood vessels, etc) peristalsis (wave like), spindle shaped, 1 nucleus per cell, no visible stripes
70
New cards
tissues that are replaced largely with scar tissue
cardiac muscle and nerve tissue in the brain and spinal cord
71
New cards
tissue that regions poorly
skeletal muscle
72
New cards
regens easily
epithelial tissue, fibrous connective tissue and bone