sustainable energy chp. 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
economic assessment goal
to provide useful financial insight and enable comparison between various energy objections
objectives of energy flow analysis and resource accounting
conceptualize and compare different energy system investments, account for external costs and identify sustainability issues
largest renewable
hydropower
sustainable energy engineering approach
use quantitative analysis to understand the end use, environmental and social requirements, and resource availability
unit cost of energy
Cs= Co/Q x t
Cs- unit cost of energy produced
Co- intial construction and installation cost
Q- units of energy
T- time
payback period (pp)
time required for the system to payback initial costs
found by comparing total cost to annual benefit- energy produced or energy saved
PP= Co/BiCs
Co- total cost of equipment and installation
Bi- value of energy saved/yr
Cs- unit cost of energy ($/kWh)
assumes no loans, which is generally not the case
time value of money
when money is invested and financed through bonds/stock, rate of return on investment is expected
if you borrow money you owe interest
present worth
fixed monetary value, future value of that flow, accounting for the time value of that money
future value of money
F= P(1+i)^t
F- future value
P- sum of money
invested today at annual interest rate i
t- time interval
disregarding monetary inflation
present worth factor (PWF)
i,t key for discounted cash flow analysis
used for comparing different options for investing in different energy management or conservation opportunities
revenues in future worth less money than earned in the present
PWF= 1/(1+i)^t
discount rate
interest rate used in discounted cash flow analysis to determine present value of future cash flows
annuity
future cash flows are fixed in size (A) and regularly occur over specific number of periods
inflation rate (j)
current dollars= actual cash flow
constant dollars around base year (F0), then future dollar equivalent after t years of inflation rate
not constant or know- add extra percent to account for future inflation rate
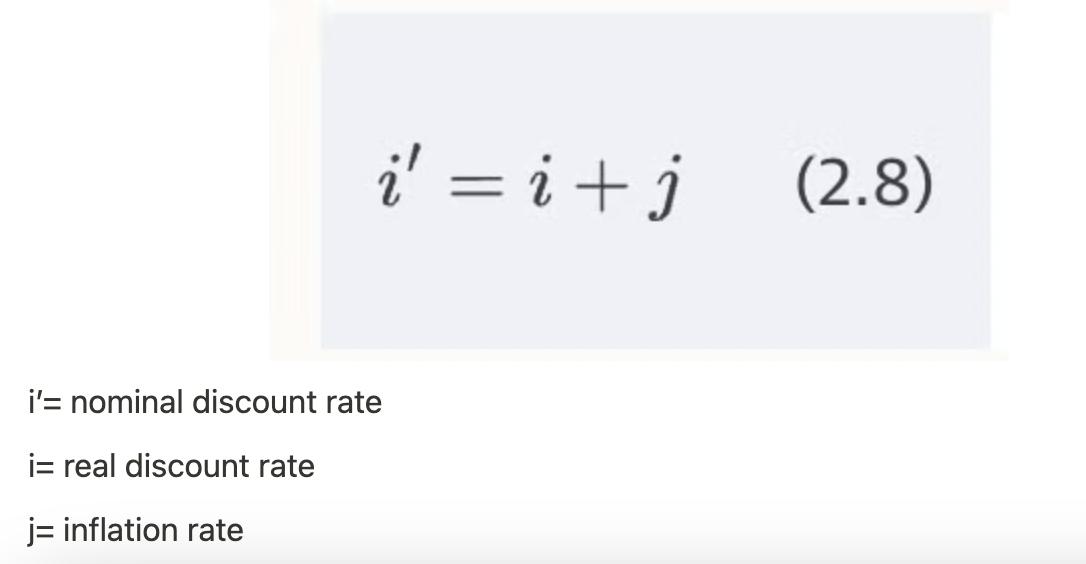
real vs. nominal discount rates
real- excludes inflation, used if cash flow is in constant dollars
nominal- includes inflation, used if cash flow is in current dollars
nominal discount rate
= real discount rate + inflation rate
return on investment required to invest in a project
present value analysis
can take into effects of inflation
determines current value of future cash flows- idea that money today is worth more than in the future
9 factors that investors and companies use to evaluate risk and rewards for projects
unit cost of energy
payback period
time value of money
discount rate
inflation
nominal discount rate
present value analysis
total life cycle costs
internal rate of return
capital recovery factor
levelized cost of energy
societal and environmental costs
total life cycle costs
considers all significant dollar costs over the life of a project
costs are discounted to base year using present value analyses
TLCC+ C0 + PVOM (nonprofit, residential, govt)
C0- initial investment
PVOM- precent value of all O&M costs
taxes must be included for by rpfoit companies- T
internal rate of return (IRR)
compare variety of investment activities
commonly used for accept/reject decisions by comparing IRR with minimal acceptable rate (hurdle rate)
rate of return that will make net present value (NPV) equal to zero, summation of discounted cash flows that equal initial investment
capital recovery factor (CRF)
ratio of uniform payment (annuity) to present value of receiving that annuity for a given length of time
each payment is a mix of interest and principal repayment
self amortizing loan
periodic payments include both principal and interest
payments made on predetermined schedule
loan will be fully paid off by end of agreed upon term
ex: home mortgage, solar energy by private companies
levelized cost of energy (LCOE)
used for comparing different energy generation technologies
present value of all investment costs plus operation and maintenance, fuel costs, in each future year per unit power generation- will equal to TLCC when discounted back to base year
LCOE formula
total lifetime costs/total lifetime energy production
LCOE= (TLCC/Q) x CRF
TLCC- total life cycle costs
Q- electricity generated
CRF- capital recovery factor (interest, time)
externalities
hidden societal and environmental costs or activity of one agent that affects the well being of another agent
not included in conventional energy economics
hard to pinpoint values- human health or life, global warming
externalities example
ExternE focuses on air pollutant emissions, human health effects, effects on crops, materials and climate
40-50% of costs from climate change
costs will change based on proximity to population