Anatomy Chapter 4 Flashcards
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the 4 basic types of tissues
Epithelial: covers body surfaces and lines hollow organs, body caivties, ducts, and forms glands
Found at boundary btwn 2 environments
always has a free surface
Little to no EC matriz
Connective: Protects, supports and binds organs; stores E as fat, provides immunity
Muscular
Nervous: generates nerve impulses
What are the 2 general types of epithelium
Covering and lining epithelium
Covers outer surfaces: skin
Lines inner surfaces: stomach
Glandular Epithelium
Forms most glands of the body: sweat glands, oil glands, etc
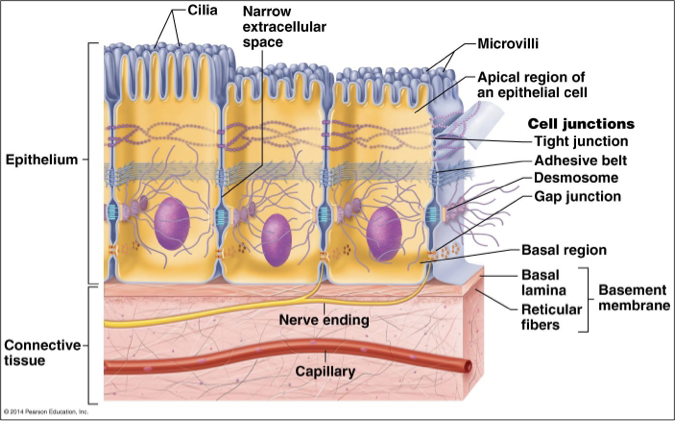
What are some special features of Epithelia
High cellularity
Specialized contacts
Polarity
Apical surface: faces body surface
Basal surface: adheres to basement membrane
Support by connective tissue: Basement membrane
Avascular
Nervous innervation
High Regeneration
What are two 2 layers of the basement membrane
The basement membrane has 2 layers
The basal laminal is secreted by the epithelium
The reticular lamina is part of the underlying connective tissue
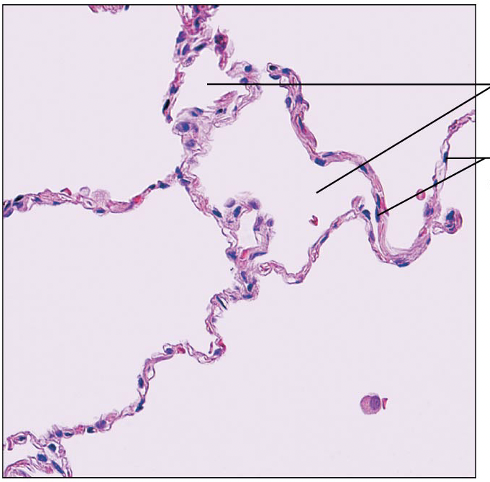
Identify this type of Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium: allows for diffusion most readily
Kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, serosae
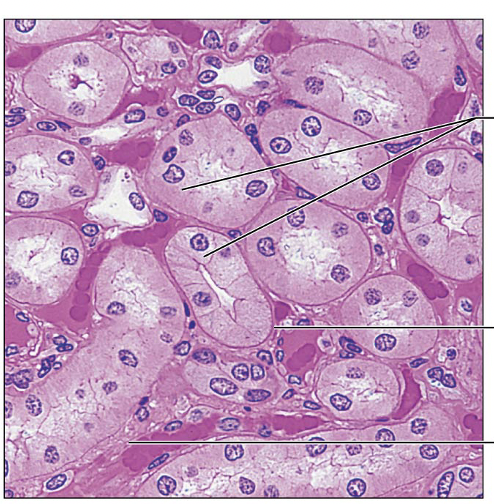
Identify this type of Epithelium
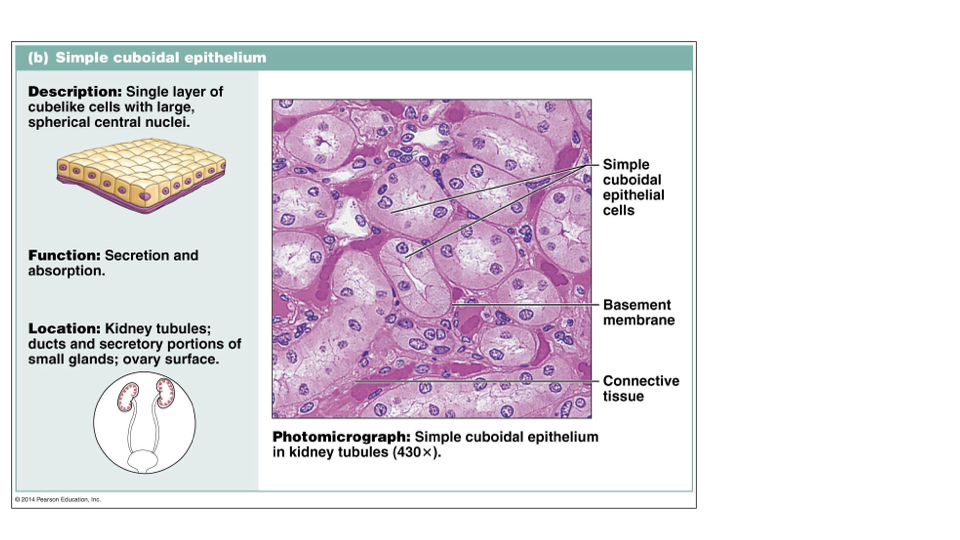
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: secretion and absorption
kidney tubules, ducts, ovary surface
Identify this type of Epithelium
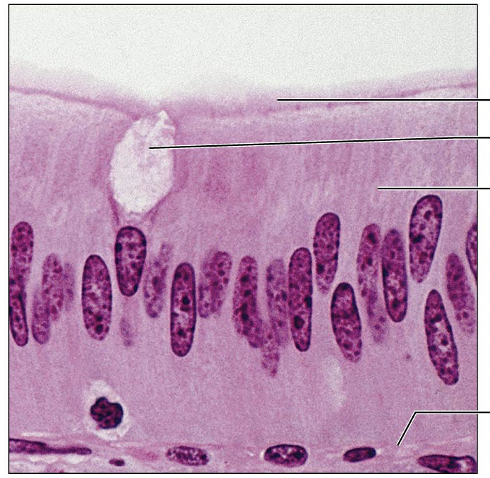
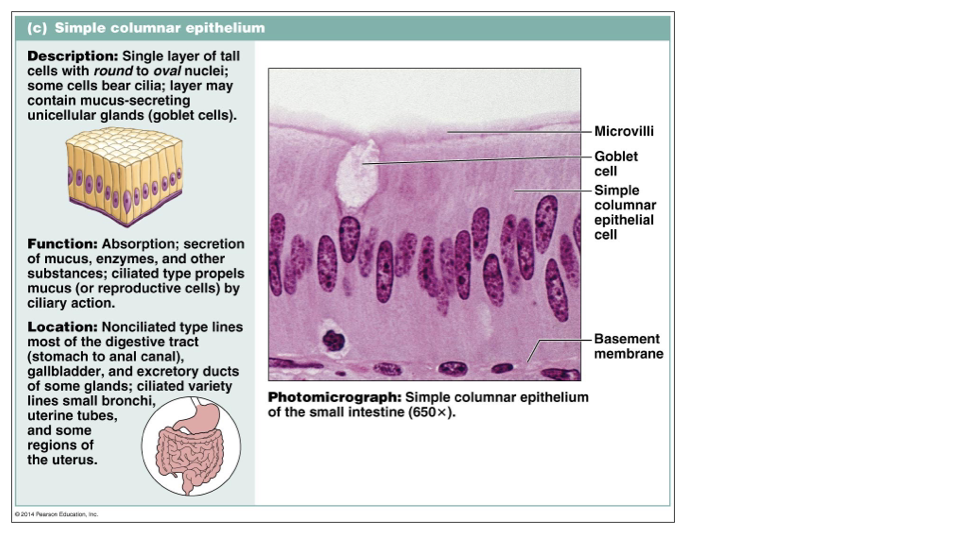
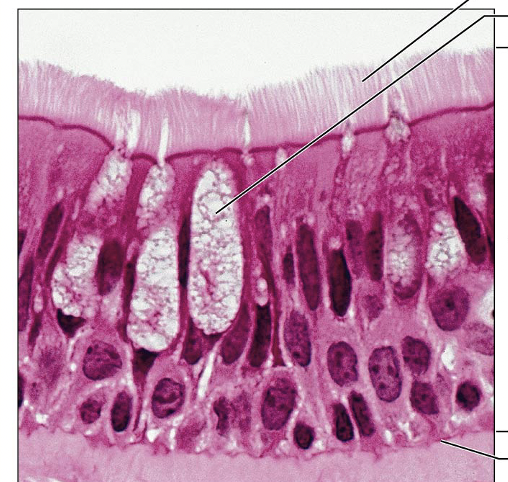
Simple Columnar Epithelium: absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus
Nonciliated type: digestive tract, gallbladder, ducts
Ciliated type: bronchi, uterine tubes
Identify this type of Epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar: all cells attached to basement membrane; secretion, particularly of mucus and propulsion of mucus
Repoductive tracts of males, parts of upper respiratory tract
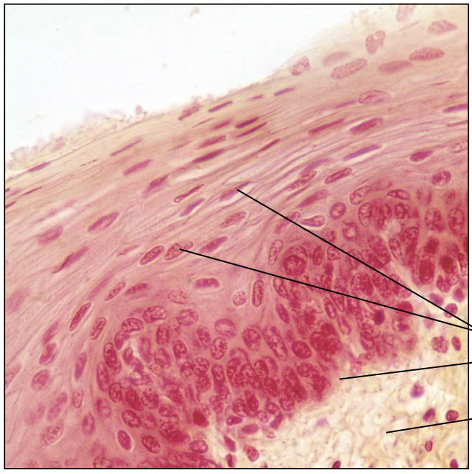
Identify this type of Epithelium
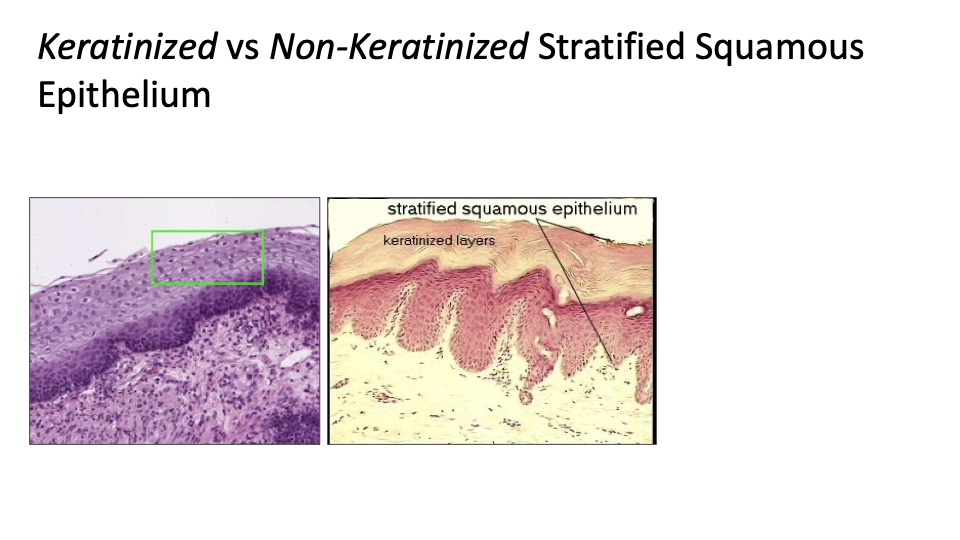
Stratified Squamous Epithelium: protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
Nonkeratinized type: moist linings of esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Keratinized type: skin
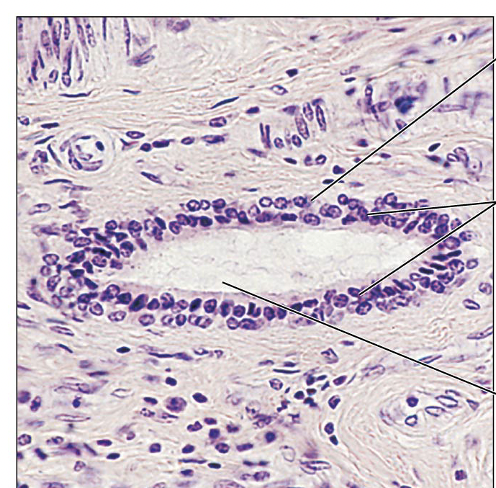
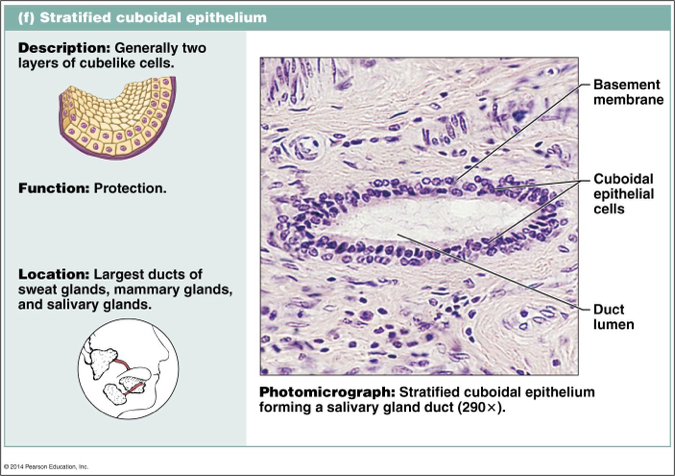
Identify this type of Epithelium
Statified cuboidal: protection (rare)
Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, salivary glands
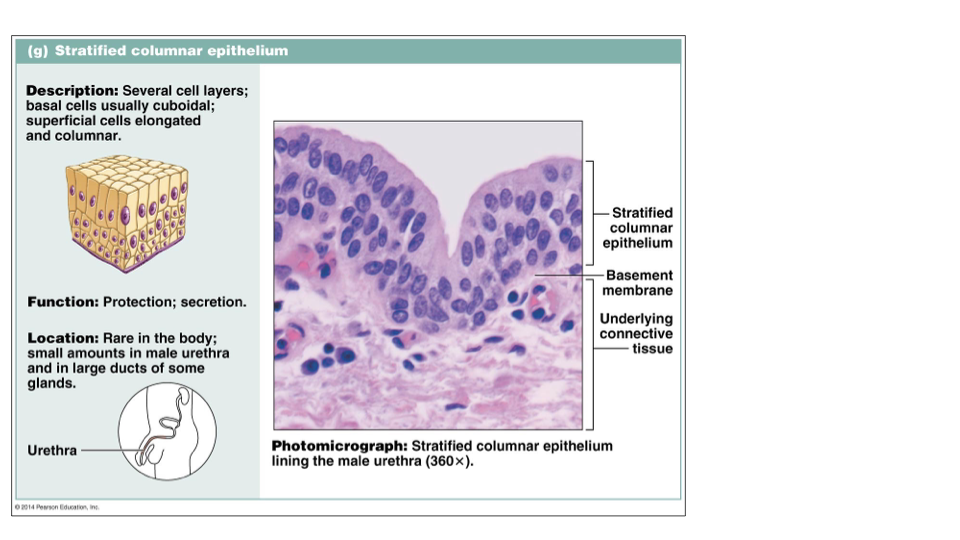
Identify this type of Epithelium
Stratified columnar epithelium: protection, secretion (rare)
small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
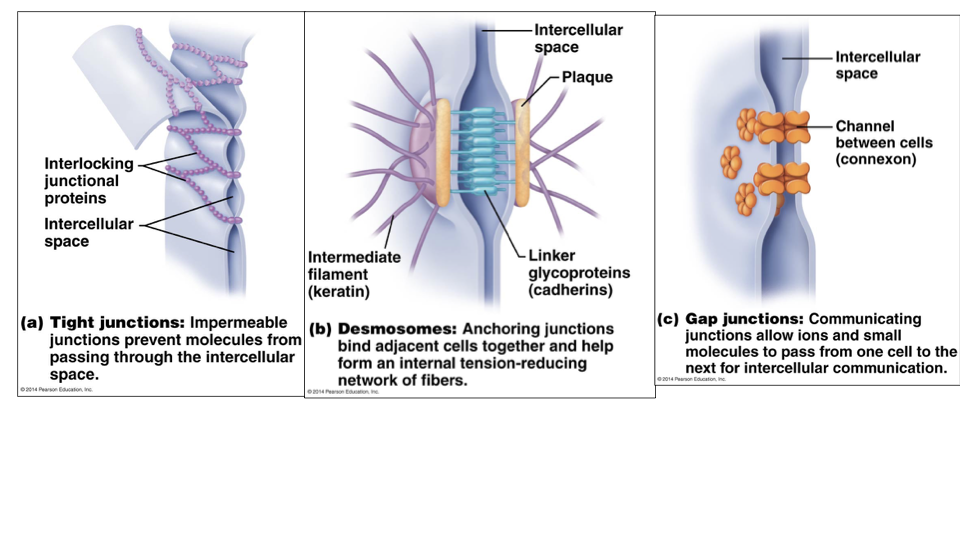
Explain the differences btwn the 3 types of cell junctions
Tight Junctions: impermeable; prevents molecules from passing through intercellular space
Interlocking junctional proteins fuses plasma membrane of 2 cells together
Desmosomes: Anchoring junctions; form internal tension-reducing network of fibers
Linker glycoproteins (cadherins) interdigitize like a zipper
Intermediate filament (keratin)
Gap Junctions: allow for intercellular communication;
channel between cells is called a connexon
What are the 2 classifications of Glands
Endocrine Glands: Hormones are released directly into ECF and then diffuse into blood stream without a duct
Secretions = hormones
Effector organs are far away
Exocrine Glands: Secretions flow onto body surfaces or into cavities; secretions act locally
Multicellular: multiple cells form a gland
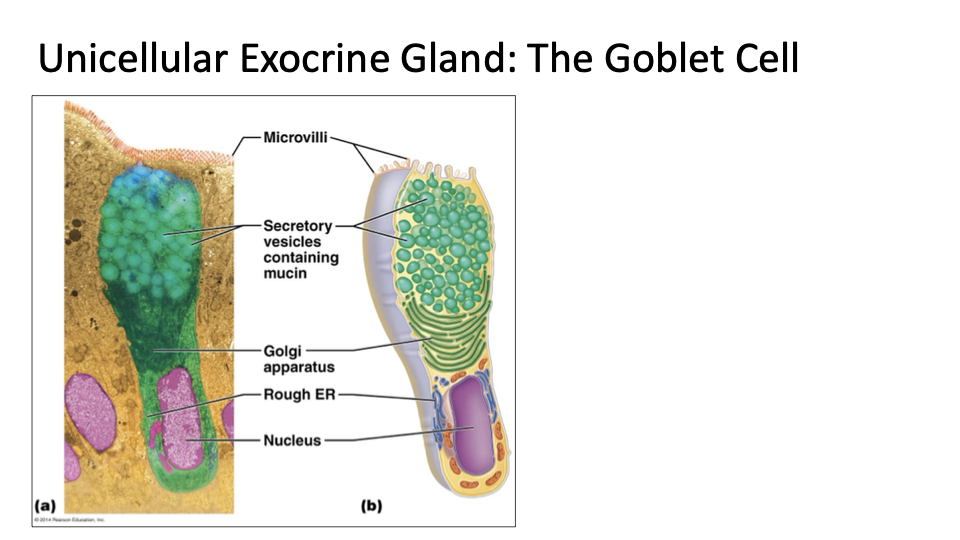
Unicellular: one-celled gland
Ex: Globlet cells: produce mucin which is a glycoprotein
Mucin + water = mucus
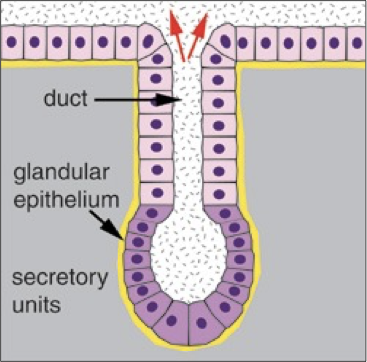
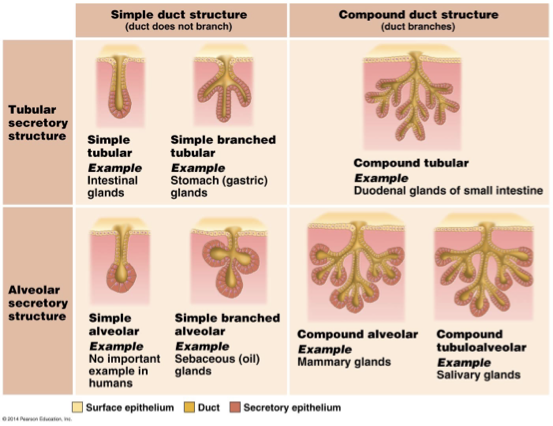
Explain the general characteristics and different types of multicellular exocrine glands
Duct: form passageway of the exocrine gland
Secretory units: secrete product
Simple: Duct does not branch
Compound: duct does branch
Branched: many branches of secretory structure
Tubular: tubular secretory structure
Alveolar: spherical secretory structure
Explain the general characteristics of Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant type of tissue
Few cells
Lots of EC Matrix
Ground substance (gel)
fibers: collagen, elastic, reticular
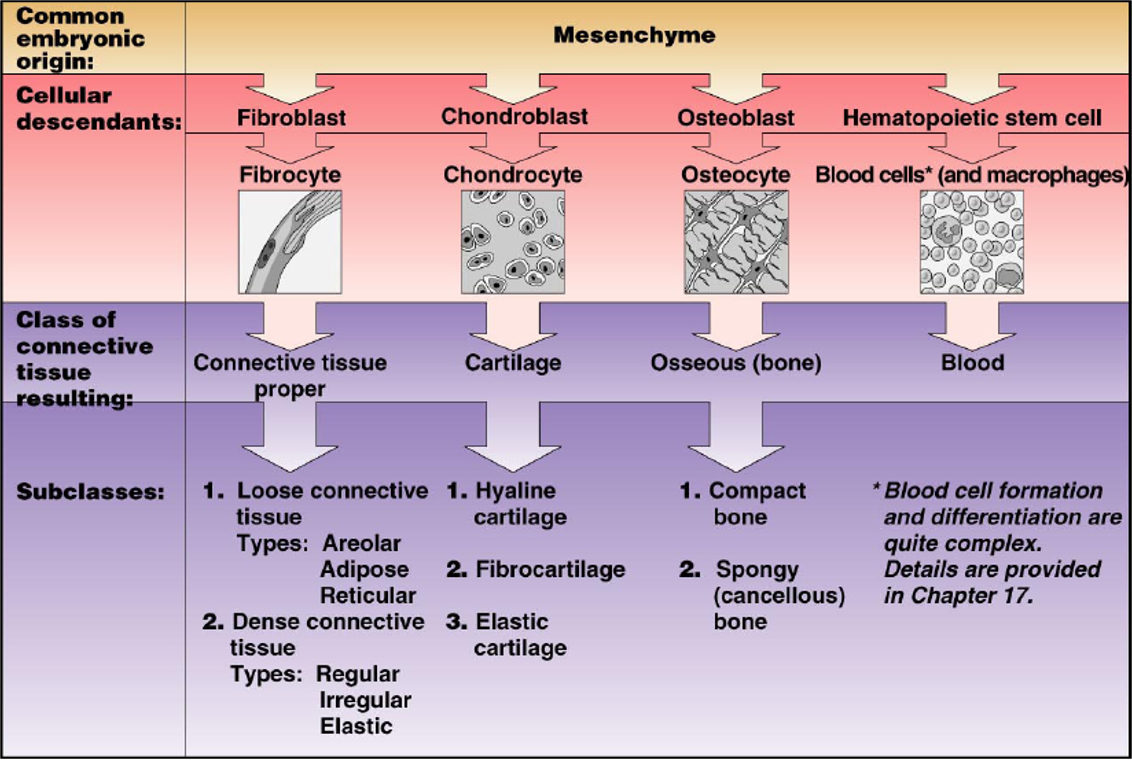
What are the main types of Connective Tissue Cells
All Connective Tissues come from a common embryonic origin: Mesenchyme
Immature Cells of each type of CT have names that end in -blast; retain capacity for mitosis & secrete the matrix
Fibroblasts: losse and dense CT Proper
Chondroblasts: in cartilage
Osteoblasts: in bone
Mature cells have reduced capacity for cell division; mostly involved in matrix maintenance
Fibrocyte
Chondrocyte
Osteocyte
What are other tissue cells in Connective Tissue
Adipocytes (fat cells)
Mast cells: produce histamine (increase blood flow) and heparin (prevents blood clotting)
White Blood Cells: immune response; Neutrophils and Eosinophils
Macrophages: engulf bacteria and cellular debris by phagocytosis
Plasma cells: secrete antibodies
Explain in detail the Connective Tissue Matrix
Matrix contains protein fibers embedded in a fluid, gel, or solid ground substance
Ground substance: material that fills space btwn cells and fibers
functions to support and bind cells, store H2O, and act as a medium for exchange btwn blood and cells
Combination of proteins and polysaccharides
Fibers: provides strength and support for tissues
Synthesized by fibroblasts
Collagen: tensile strength
Largest in diameter, strongest
Elastic: recoil
Intermediate diameter, branches form networks
Reticular Fibers: support
smallest diameter, special collagen fibrils, cluster into networks
How does Scurvy Happen
Vitamin C is necessary for cross-linkage of callagen Fibrils to make collagen fibers
Collagen helps: hold teeth in place, reinforce blood vessels, wound healing
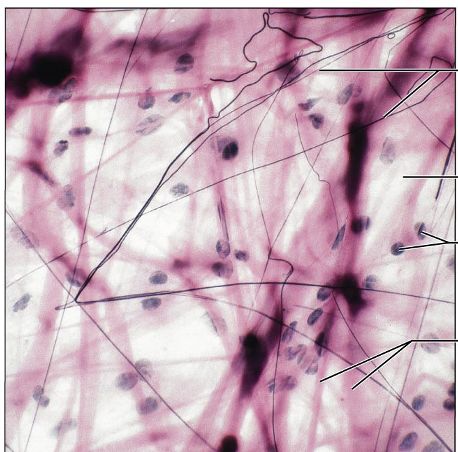
Identify this type of Tissue
Connective Tissue Proper Loose Areolar: gel like matrix w all 3 fiber types
Wraps and cushions organs, plays important role in inflammation, holds and conveys tissue fluid
Widely distributed under epithelia of body. Forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs, surrounds capillaries
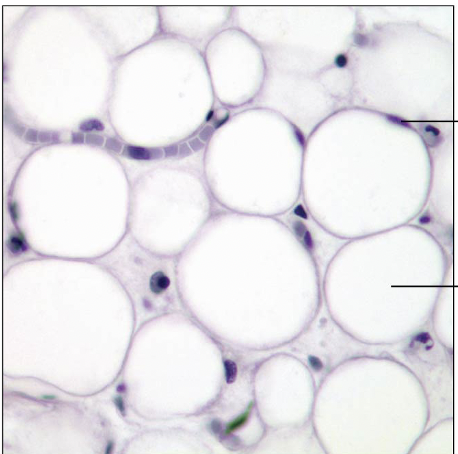
Identify this Tissue Type
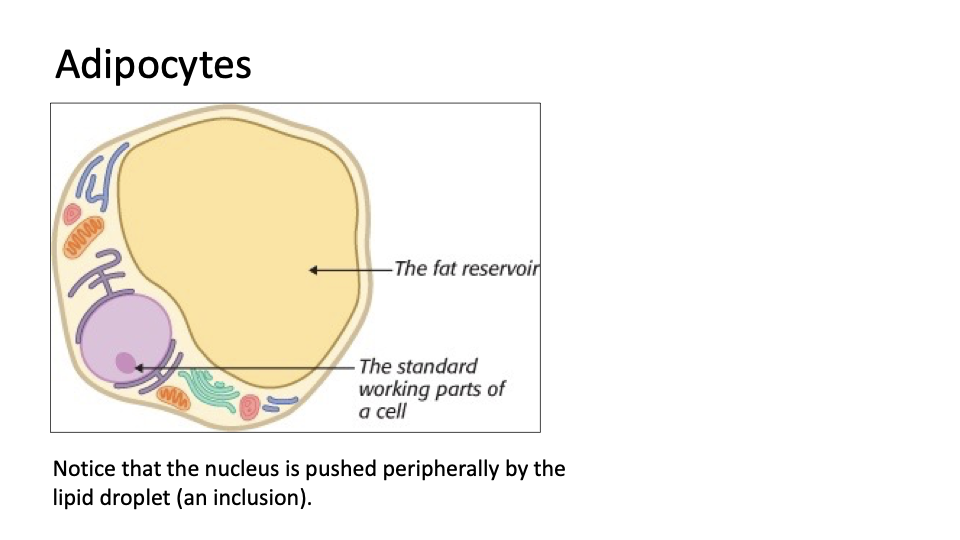
Connective Tissue Proper Loose Adipose: gel like matrix w all 3 fiber types; very sparse fibers; closely packed adipocytes have nucleus pushed to side by large fat droplet
Under skin of hypodermis, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, in breasts
Identify this tissue type
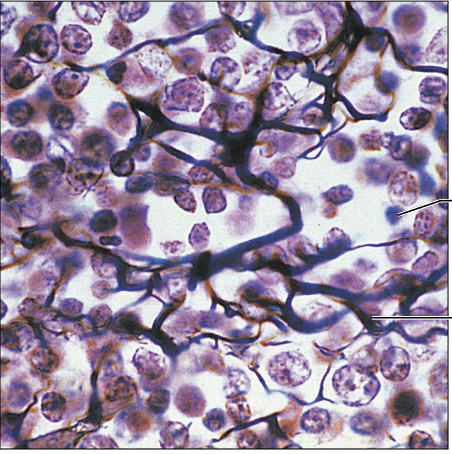
Connective Tissue Proper Loose Reticular: loose network of reticular fibers in a gel-like substance; reticular cells lie on the fibers
Bibers form a soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types including WBC's, mast cells, and macrophages
Lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen
Identify this type of Tissue
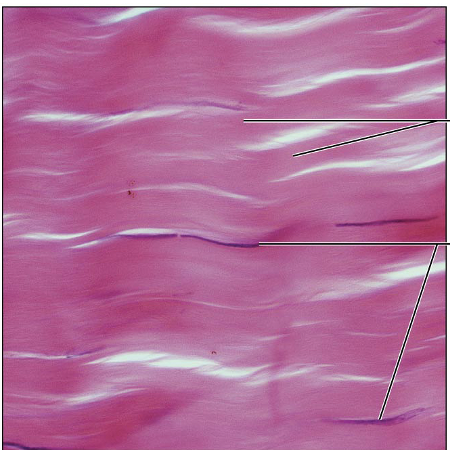
Connective Tissue Proper Dense Regular: primarily parallel collagen fibers; major cell type is fibroblast
withstands great tensile stress when pullling force is applied in one direction
Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
Identify this type of Tissue
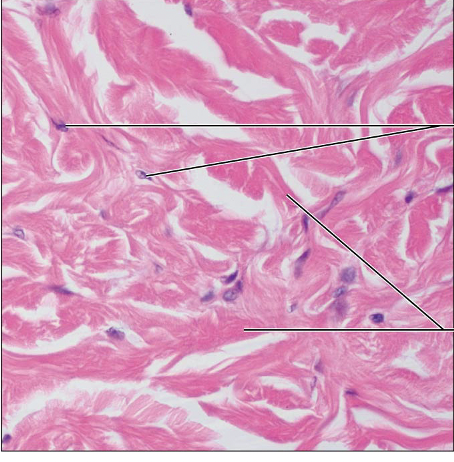
Connective Tissue Proper Dense Irregular: primarily irregularly arranged collagen fibers; some elastic fibers; defense cells and fast cells also present
Able to withstand tension exerted in many directions
Fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of skin; submucosa of digestive tract
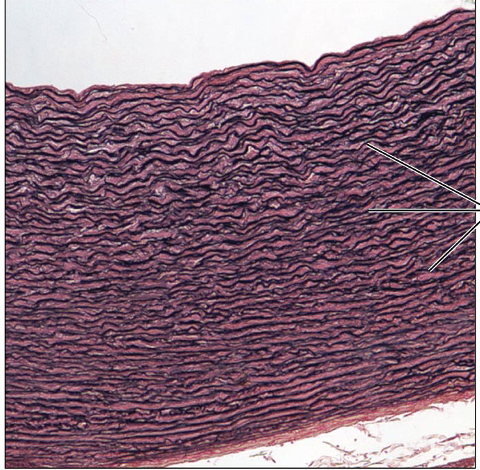
Identify this Type of Tissue
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense elastic: dense regular connective tissue containing a high proportion of elastic fibers
Allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
Walls of large arteries, within cerain ligaments of vertebral column; within walls of the bronchial tubes
Identify this type of tissue
Hyaline Cartilage: Amorphous but firm matrix; collegen fibers form an inperceptible network; chondroblasts produce matrix while chondrocytes lie in lacunae
Supports and reinforces; serves as resilient cushion; resists compressive stress
Forms most of embryonic skeleton; covers long bones in joint cavities; forms costal cartilages of the ribs; cartilages of the nose trachea and larynx
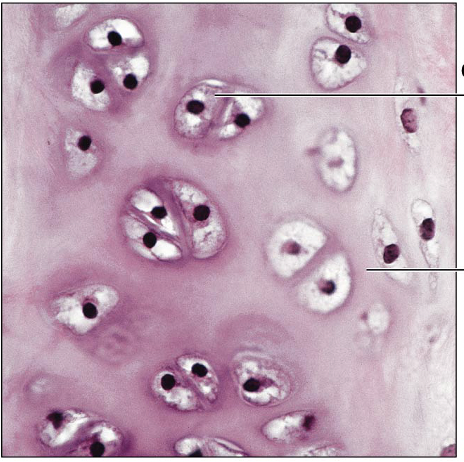
Identify this type of Tissue
Elastic Cartilage: similar to hyaline cartilage but more elastic fibers in matrix
Maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
Supports the external ear (pinna), epiglottis
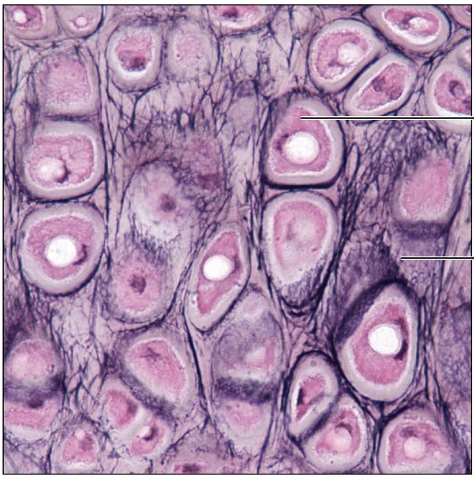
Identify this type of tissue
Fibrocartilage: matrix similar to but less firm than that in hyaline cartilage; thick collagen fibers predominate
Tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
Intervertebral discs; pubic symphysis; discs of knee joint
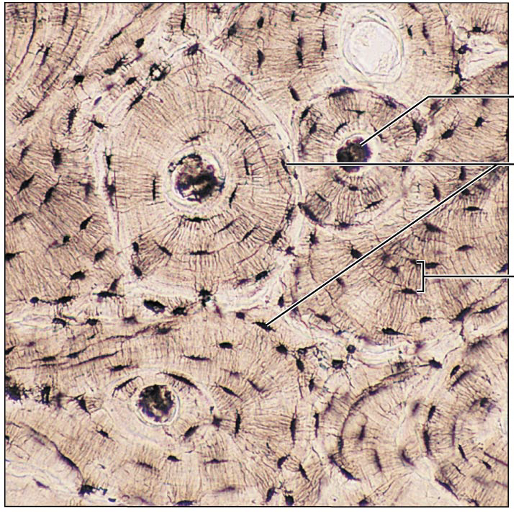
Identify this type of tissue
Bone: hard calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in lacunae; very well vascularized
Hard calcified matrix forms lamellae: surrounding central canal
Central canal has blood vessels
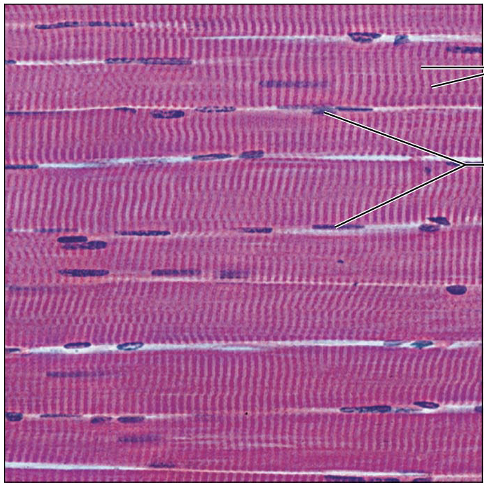
Identify this type of Tissue
Skeletal muscle; Long cylindrical multinucleate cells; obvious striations
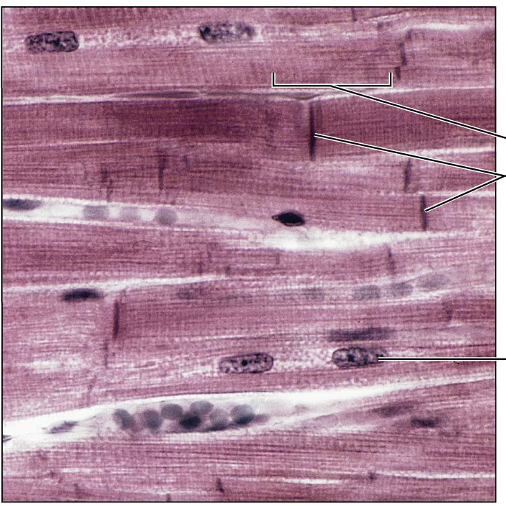
Identify this type of tissue
Cardiac muslce; Branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that inerdigitize at specialized junctions called intercalated discs
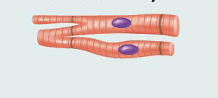
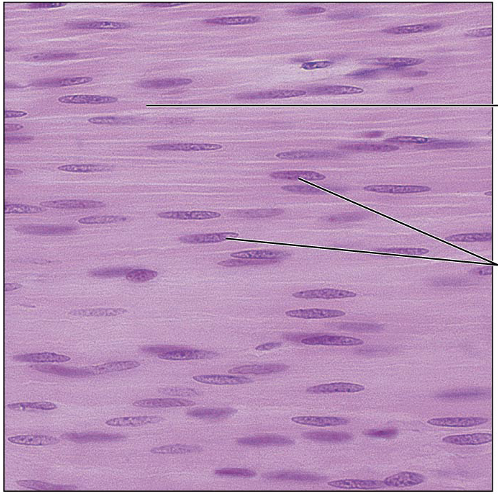
Identify this type of tissue
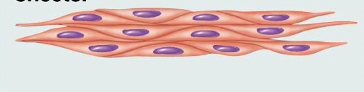
Smooth Muscle: spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets
Classify diferent tissues by their regenerative capacities
Good regenerators: bone, areolar and dense irregular CT, blood
Mediocre regenerators: smooth muscle, dense regular CT
Poor Regenerators: skeletal muscle, tendons, ligaments, cartilage
Almost no regeneration: cardiac muscle, nervous tissue