Unit Three- Venous History and Physical/Pharmacology
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CVS 115- Vascular Sonography II, Unit Three- Venous History and Physical/Pharmacology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Why do we do venous testing? (4)
Presence of thrombus
Evaluate valve competence
Vein Mapping
Pre-Op AV Fistula
Presence of thrombus (3)
R/O DVT
R/O SVT
Assess embolism risk
What does SVT stand for
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
DVT: Etiology (3)
Virchow’s Triad
Causes of clot formation within the intact venous system
“Discovered” by Rudolf Virchow in 1856
“Discovered” by Rudolf Virchow in 1856 (3)
Stasis
Vein Wall Injury
Hypercoagulability
ALL HISTORY AND PHYSICAL QUESTIONS RELATED TO DVT/VENOUS STUDIES SHOULD ALL REVOLVE AROUND THESE THREE THINGS!!
1. STASIS
2. VEIN WALL INJURY
3. HYPERCOAGULABILITY
3
STASIS
VEIN WALL INJURY
HYPERCOAGULABILITY
Virchow’s Triad: STASIS (5)
Blood that remains stagnant for any period will clot with minimal stimulus
Immobilization
Obstruction/Extrinsic Compression
Previous DVT History
CHF
IMMOBILIZATION (6)
Surgery
Acute Stroke
Bedrest
Obesity
Paraplegic
Etc.
Obstruction/Extrinsic Compression (7)
Tumors
Late Trimester Pregnancy
Hematomas
Trauma
Paget-Schroetter Syndrome
May-Thurner Syndrome
Nutcracker Syndrome (we will learn about this Summer Semester!)
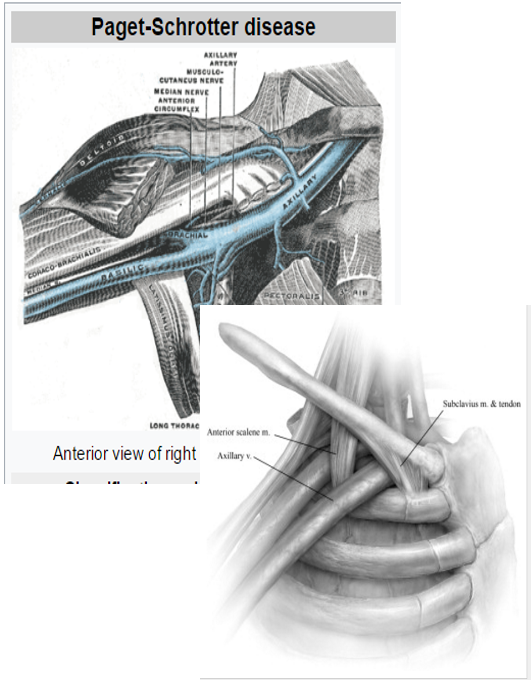
PAGET-SCHROTTER DISEASE: “Effort Thrombosis” (5)
Effort Subclavian Vein Thrombosis
Blood clot occurring in the Subclavian Vein under the Collarbone
Extrinsic compression of the vein
Annual Incidence: 1 and 2 out of 100,000
Continuous flow would be demonstrated distally
Extrinsic compression of the vein
Aching, numbness, or tiredness with positional changes of the shoulder
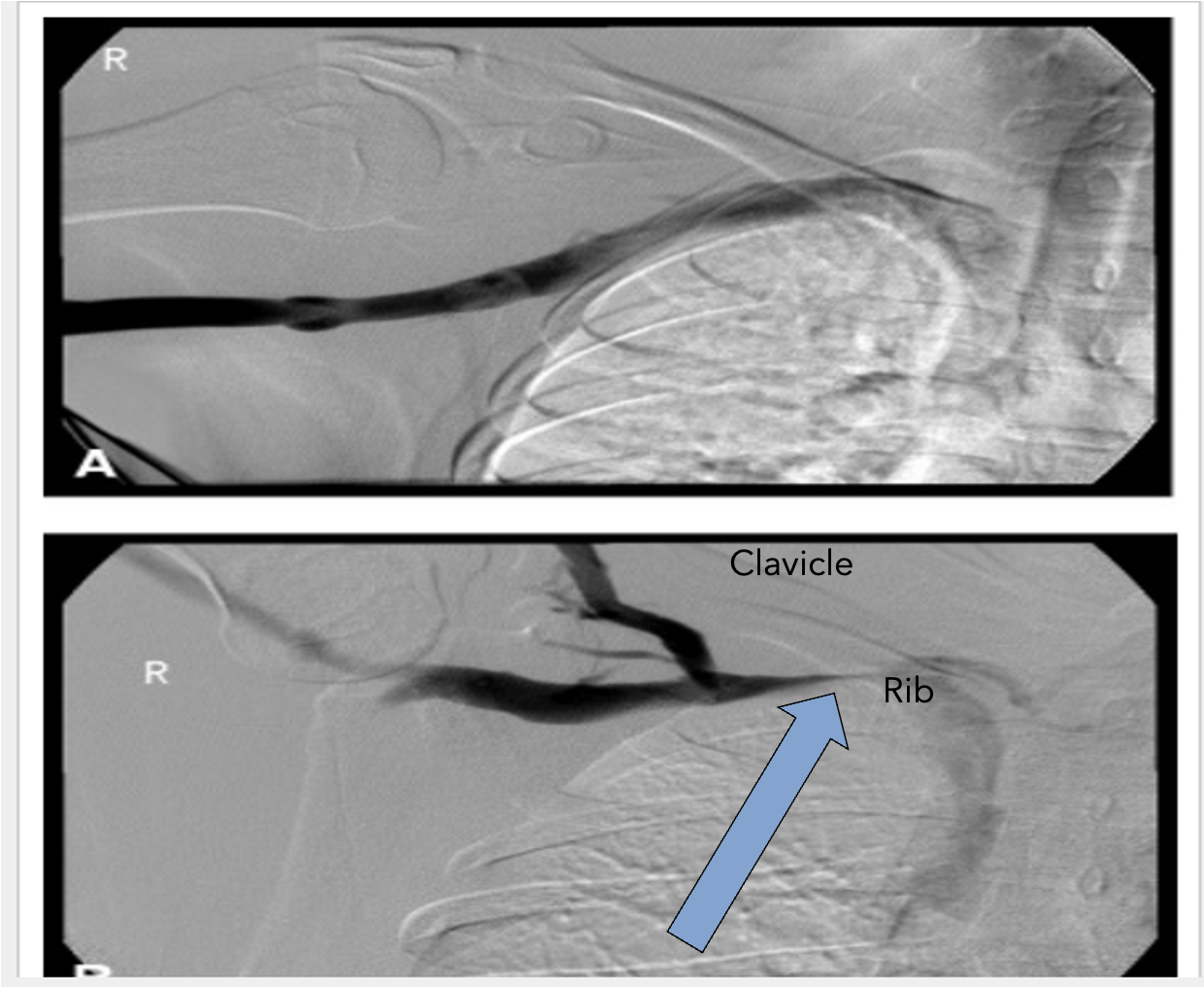
Most common place- interscalene triangle (4)
Shoulder is raised causing compression of the subclavian vein
1st rib & clavicle pinching the vein
Axillary/Brachial veins become dilated and enlarged – Collateral veins start to appear
Flow in the Superior Vena Cava is decreased slightly
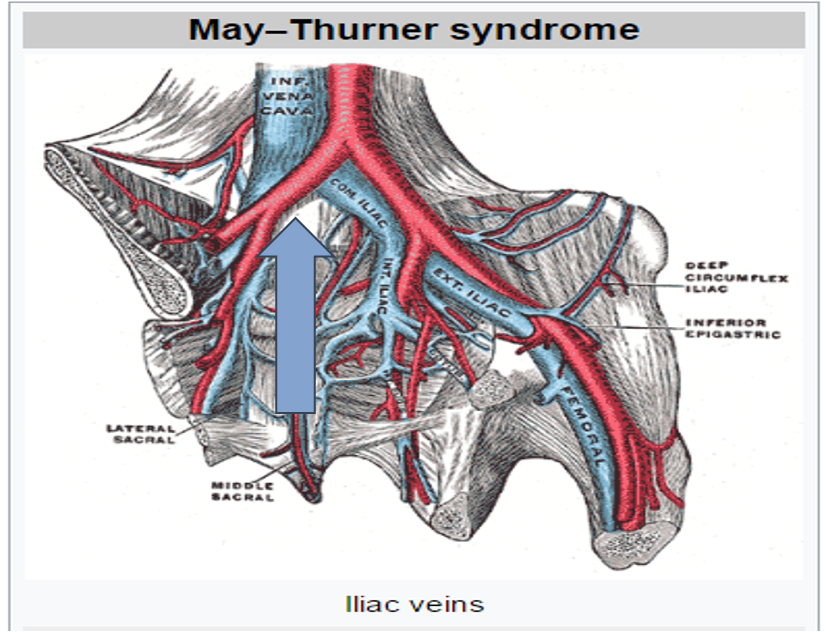
MAY-THURNER SYNDROME: “Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome” (3)
The left Iliac Vein is compressed by the Right Common Iliac Artery
Increased risk of endothelial injury to Iliac Vein
Undetected until pathology is present
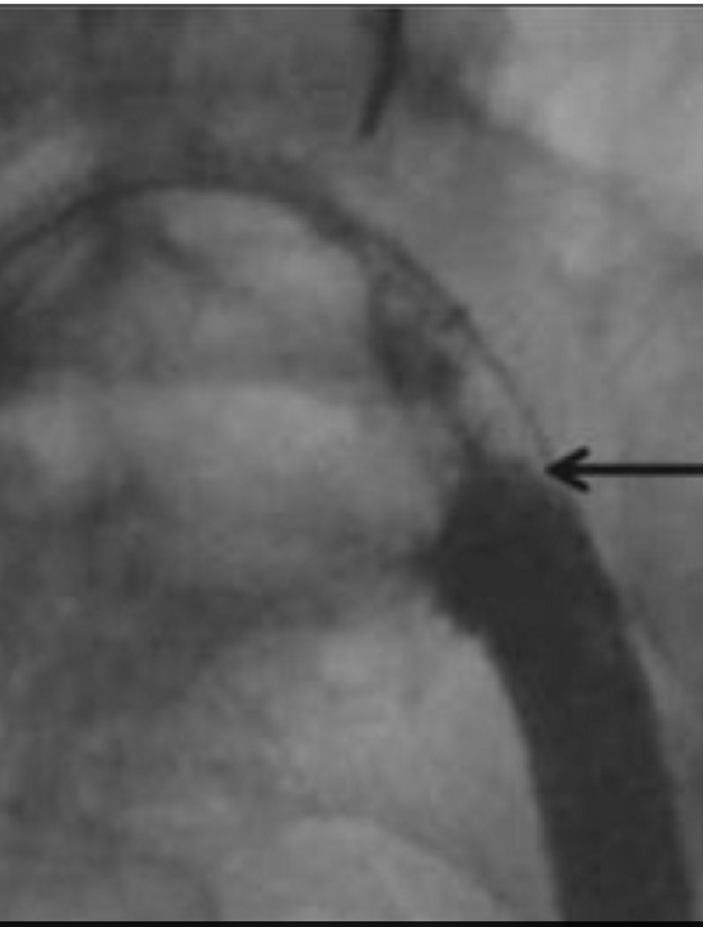
MTS: (2)
*Endovenous stenting to treat MTS
*Early thrombus removal would be beneficial in reducing the development of post thrombotic syndrome
Virchow’s Triad: VEIN WALL INJURY (3)
Normal Venous Endothelium
Luminal surface of these cells contain various substances in their membrane to prevent adhesion of platelets and clotting factors
Mild to moderate injury can alter this
Normal Venous Endothelium:
Intact single layer of non-thrombogenic cells
VEIN WALL INJURY DUE TO: (5)
Indwelling catheters (most common in upper extremity)
Venography
Stretching or twisting injuries
Blunt trauma
Chemical injury
Virchow’s Triad: HYPERCOAGUABILITY
Increase in clotting factors and platelets/Condition that causes blood to clot more easily
Causes of Virchow’s Triad: HYPERCOAGUABILITY (2)
Congenital
Acquired
Congenital causes of Virchow’s Triad: HYPERCOAGUABILITY (5)
Decreased antithrombin III
Protein C Deficiency
Protein S Deficiency
Disorders of plasminogen and plasminogen activator
Factor V Leiden
Congenital
1. there is a lower than normal amount of this protein in the blood, which plays a crucial role in preventing blood clots by inhibiting the clotting cascade
Factor V Leiden is a genetic disorder that increases the risk of blood clots. It's caused by a mutation in the F5 gene, which controls the production of factor V, a protein that helps blood clot
Acquired causes of Virchow’s Triad: HYPERCOAGUABILITY (7)
Carcinoma (Cancer)
Estrogen Replacements
Oral Contraceptives
Pregnancy and Postpartum
Liver Disease
Smoking
Nephrotic Syndrome
Acquired
Liver disease; Cannot produce enough clotting proteins; Kidney disease lose important anticoagulant proteins in the urine
ONCE THROMBUS HAS FORMED… (3)
STABILIZE
PROPAGATE
EMBOLIZE
Stabilize
adhere to wall without changing location or propagating
Propagate
growth in size and location
Embolize
a portion breaks free and travels elsewhere within vascular system