Immunity and Internal Defense
1/169
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology 200 - Exam 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
phagocytic cells (internal defense)
phagocytic cell brings the pathogen inside and it’s in a vacuole
vacuole fuses with lysosome and pathogen is destroyed
phagocyte cell spits out destroyed pathogen
toll-like receptors
phagocytic cells (WBC) have
phagocytic cells
recognize fragments of molecules found on a set of pathogens
recognized molecules normally ABSENT from vertebrate body and an essential component of a class of pathogens
ex: flaggelin (main protein of bacterial flagella)
two phagocytic cell types
neutrophils
macrophages
neutrophils
circulate in blood, attracted to infected tissue, destroy pathogens
macrophages
big eaters
some move around body
others live permanently in tissues
likely to encounter pathogens
natural killer cells
circulate body
detect abnormal array of surface proteins typically of virus-infected or cancerous cells
release chemicals that lead to cell death
inflammatory response
damage to body (splinters)
-
histamines released by mast cells = vasodilation of capillaries
-
vasodilation delivers phagocytes to area
-
pus: fluid filled with WBC’s and dead microbes
histamines
mast cells released by
pus
fluid filled with WBC’s and dead microbes
lymphatic system
lymph vessels + structure that trap foreign substances
-
lymph = fluid that flows through lymphatic system
-
intersitial fluid + WBC’s continually enter lympth vessels
-
within lymph nodes, high concentrations of defense cells
lymph
fluid that flows through the lymphatic system
adaptive immunity
found only in vertebrates
develops more slowly than innate
detects pathogens with specificity
B and T cells
lymphocytes made in bone marrow
T cells mature in Thymus; B cells in Bone marrow
recognize antigen with antigen receptors
T cells
mature in thymus
B cells
mature in bone marrow
lymphocytes (B and T cells)
made in bone marrow
Antigens (protein or polysaccaharides)
foreign substances that elicits a B or T cell response
usually - or - that protrude from surface of foreign cells or viruses
major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules
proteins that display antigen fragments on cell surface
MHC I
on most body cells
MHC I
bind and display fragments of foreign antigens made WITHIN cells
MHC II
on antigen-presenting cells (eg. cells, macrophages)
MHC II
bind and display antigens internalized through phagocytosis
helper T cells
activate humoral and cell-mediated immunity
must themselves be activated by antigen-presenting cell that is displaying an antigen
role of antibodies
neutralization
blocking of ability of a virus to bind to a host cell
opsonization
promotion of phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages and neutrophils
neutralization
blocking of ability of a virus to bind to a host cell
opsonization
promotion of phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages and neutrophils
primary immune response
1st time B and T cells encounter antigen
secondary immune response
2nd time B and T cells encounter antigen
secondary response
2nd time B and T cells encounter antigen
antibodies increase faster and with greater magnitude because of memory cells
passive immunity
short term immunity conferred by transfer of antibodies (maternal antibodies transferred to fetus or nursing infant, blood transfusions)
active immunity
defenses that arise when a pathogen infects body and prompts a primary or secondary immune response
-
vaccination introduces antigens into body (dead microbes, parts of microbes) - induces a primary response
-
results from the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen
vaccination programs
successful against many infectious diseases
worldwide eradication of smallpox in the 1970’s
studies do not make a link with autism
osmoregulation
process of how animals control solute concentration and balance water loss/gain
relative concentrations of water and solutes must be kept in a narrow range (homeostasis)
osmolarity
total [solute] expressed as (moles of solute)/L
mOsm/L = milliosmoles/L
reference values → sea water (1000 mOsm/L) and blood (300 mOsm/L)
isoosmotic
same solute concentration on both sides
hyperosmotic
higher solute concentration
hypoosmotic
lower solute concentration
antibody
soluble form of the B-cell antigen receptor
osmoconformer
isoosmotic with surroundings (marine invertebrates)
ex: jellyfish, sea slugs
osmoregulator
control its internal osmolarity independent of its environment
marine osmoregulator (hypoosmotic)
lower [solute] than ocean
animals constantly losing water
balance water loss by drinking water and ridding excess salt through kidneys/gills
freshwater osmoregulator (hyperosmotic)
higher [solute] than river
constantly gaining water
drinks little water, excretes LOTS of dilute urine
anhydrobiosis
dormant state involving loss of almost all body water
tardigrades (invertebrate)
land animals
body coverings help prevent dehydration
desert organisms are nocturnal
drink water, eat moist foods, generate water through respiration
nitrogenous waste
breakdown product of protein and nucleic acid
enzymes remove nitrogen in form of ammonia (NH3)
Ammonia (NH3)
tolerated at low concentrations (in the bloodstream)
need access to lots of water
fish - _________ lost across gills
Urea
produced in liver
low toxicity
must spend energy to make
mammals excrete ____
Uric Acid
non-toxic
doesn’t dissolve in water, excreted as paste
more energy to make than urea, but very little water lost with its excretion
reptiles/birds/land snails
nephrons
long tubules weave back and forth across cortex and medulla
ball of capillaries = glomerulus
Bowman’s capsule surrounds glomerulus
filtration of blood
blood pressure forces fluid from the blood in glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule
blood cells and large molecules stay in blood
filtrate contains small molecules (salts, nitrogenous waste, amino acids)
blood cells and large molecules
stay in blood
blood pressure forces fluid from the blood in glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule
antidiuretic hormone (AHD)
made in hypothalamus, stored in posterior pituitary gland
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus monitor blood osmolarity and regulate release of ADH
collecting ducts
receives filtrate from many nephrons
renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, urethra
filtrate flows to ____ _____ to ______ to _______ to ______
blood osmolarity
> 300 mOsm/L
salty foods
trigger ADH release; ADH targets the collecting duct
epithelium
ADH makes __________ MORE permeable to water; water reabsorbed; urine concentrations
results in our blood osmolarity going back to 300 mOsm/L (drink water to dilute blood)
hormone
molecule secreted into extracellular fluid
circulates in blood/hemolymph
communicates regulatory messages
target cells
have appropriate receptors (for specific hormones)
hormones maintain homeostasis
regulate growth, development, and reproduction
hormones
maintain homeostasis
regulate growth, development, and reproduction
hormones and the endocrine system
proximal tubule
reabsorption of valuable nutrients
ions, water
wastes (like urea) remain in the filtrate
distal tubule
regulates [K+] and [NaCl]
ascending limb
permeable to salt, but not H20
NaCl* is actively being transported out of the filtrate
maintains a concentration gradient in kidney
collecting duct
permeable to water
water pilled out of _________ ____
want concentrated urine, so body doesn’t loose excess water
concentration gradients
do not occur spontaneously
polypeptide
amine
steroid
chemical classes of hormones
polypeptide
cleavage (chopping) of longer protein chains
water soluble
amine
made from single amino acid
some water soluble
some fat soluble
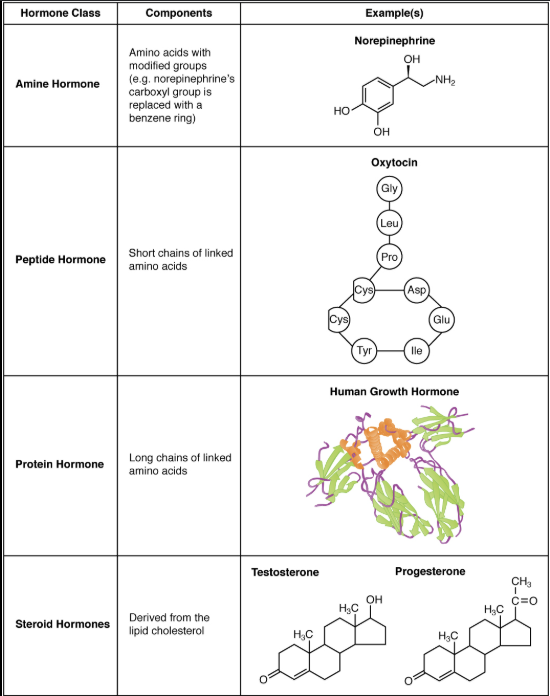
steroid (fat soluble)
fused C-rings derived from cholesterol
water-soluble hormones
travel freely in the bloodstream
bind to cell surface signal receptors
signal transduction!
fat-soluble hormones
travel in bloodstream bound to transport proteins
bind to intracellular receptors (change gene transcription)
epinephrine
water-soluble amine
liver - hormone binds to receptor in plasma membrane
activates protein kinase (phosphate)
activate enzyme for glycogen breakdown to glucose
estradiol
steroid (fat-soluble)
liver cell → female bird/frog
-
hormone binds to intracellular receptor → activates transcription of gene for protein vitellogenin
translation = protein in egg yolk
vitellogenin
egg yolk protein
hormones can have multiple effects
different signal transduction pathways in different cells
different receptors in/on cells
ex: epinephrine
pheromones
signaling molecule → not a hormone
chemicals release into external environment
local regulators
signaling molecule → not a hormone
-
secreted molecules that act over short distances
-
act on target cells faster than hormones
-
ex: cytokines, nitric oxide, prostaglandin, and histamines
cytokines
immune cell communication
nitric oxide (NO)
endothelial cells in blood vessels release NO when O2 in blood falls
stimulates vasodilation
viagra
interferes with NO breakdown
blood vessels stay dilated for longer
prostaglandins
promote fever and inflammation
aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit ______________ synthesis
pancreas
regulates blood glucose
pancreatic islets
scattered through pancreas are clusters of endocrine cells
Langerhans
pancreatic islets
within _________ ____ there are two types of cells
(cluster of endocrine cells)
alpha cells
beta cells
alpha cells
make glycogen
which promotes the release of glucose into blood (glycogen to glucose in liver)
beta cells
makes insulin, which triggers uptake of glucose from blood; all cells respond
70-110
normal blood glucose range = __ - __ glucose/100mL
type 1 diabetes mellitus
autoimmune disorder, body destroys beta cell
without beta cells, can’t make insulin
type 2 diabetes mellitus
failure of target cells to respond normally to insulin
functioning beta cells, make insulin
body cells ignore it
result of obsesity and lack of exercise
blood glucose
both I and II have elevated _____ ______ levels
hypothalmus
endocrine gland in brain
receives info from nerve throughout body and from brain
initiates endocrine response
lymph vessels + structure
that trap foreign substances
interstitial fluid + WBCs
continually enter lymph vessles
within lymph nodes
high concentrations of defense cells
posterior pituitary
stores and secretes 2 hormones by hypothalamus
ADH
Oxytocin
oxytocin
regulates milk release during nursing (positive feedback)
-mammary glands have correct receptpr
antidiuretic hormone
helps regulate blood osmolarity