Organic Chemistry 1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reaction mechanisms and conditions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Addition of hydrogen halides to alkynes
H+ is the electrophile, catalysts are:HF,HBr,HCl,HI
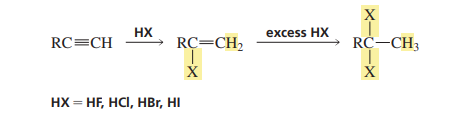
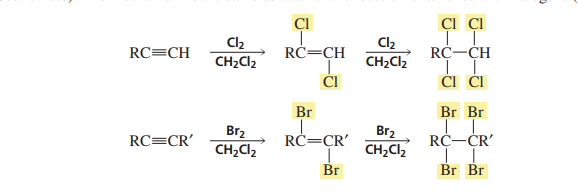
Additions of halogens to alkynes
Acid catalyzed hydration/hydroboration of an alkyne (INTERNAL ALKYNE)
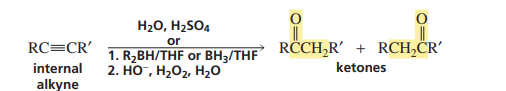
Acid catalysed hydration/hydroboration of an alkyne (TERMINAL ALKYNE)
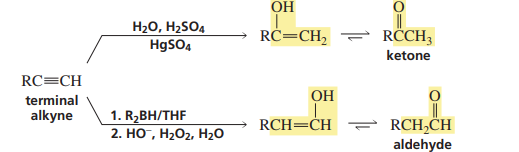
Addition of hydrogen to an alkyne
3 different mechanisms
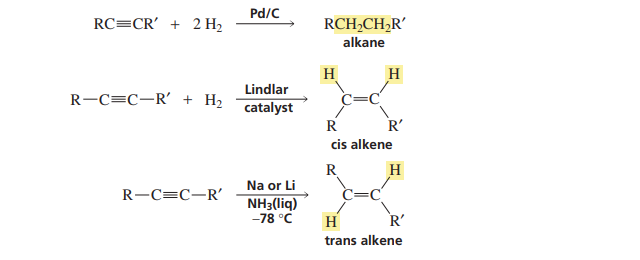
Stereo chemistry hydroboration
syn adition
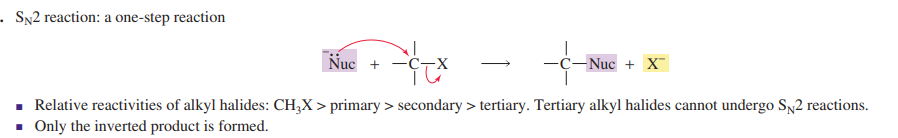
Sn2
back attack
polar aprotic solvent
inversion of stereochemsitry
strong nucleophile
good leaving group
needs space for nucleophile to attack
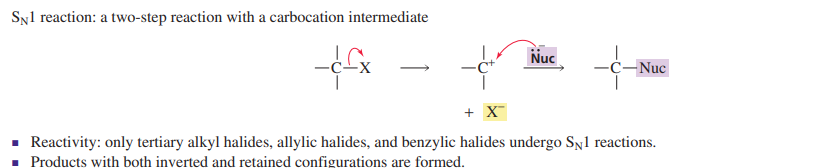
Sn1
carbocation intermediate
2 step
racemization
polar protic solvent
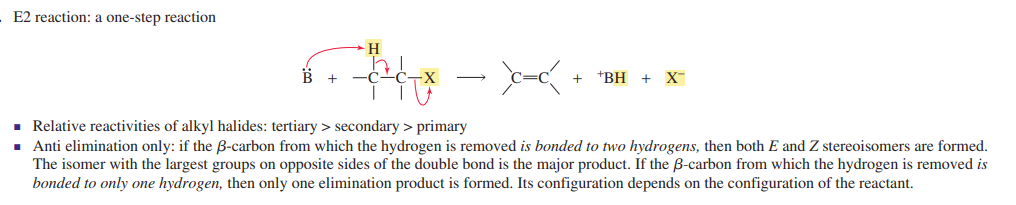
E2
one step reaction
Base removes proton and leaving group leaves in one step
Tertiary>secondary>primary
Only anti elimination if 2 hydrogens, (consequence is it must be antiplanar product)
strong base
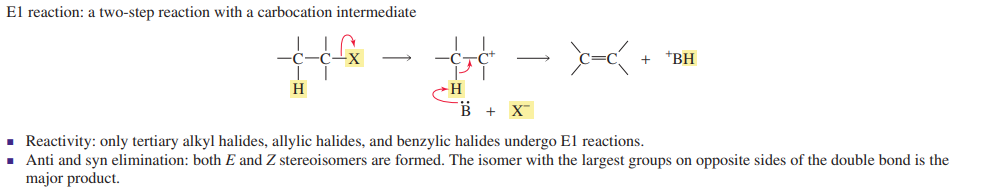
E1 reactions
two step reaction
weak base
anti and syn elimination
largest substituted isomer is major product
Common protic solvents
H2O
HCOOH
CH3OH
HC3HC2OH
CH3COOH
Common aprotic solvents
DMF
DMSO
Acetone
THF
Toluene
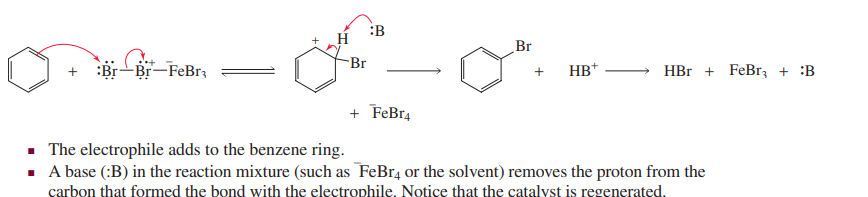
Halogenation (electrophilic aromatic substitution)
each carbocation has three resonance structures
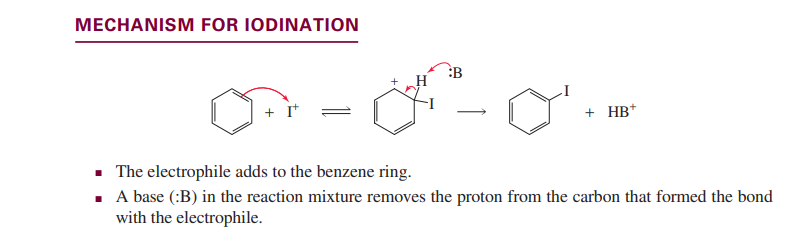
Iodination(electrophilic aromatic substitution)
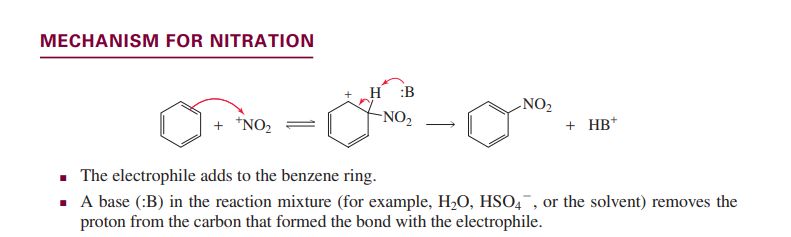
Nitration of benzene
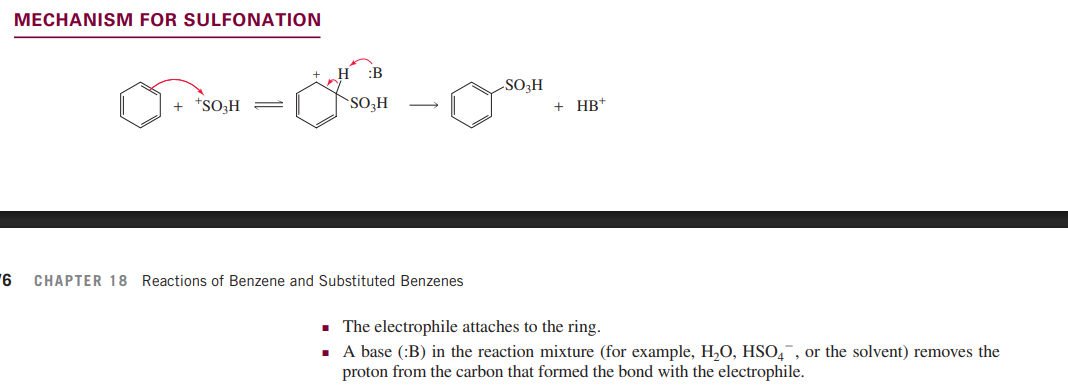
Sulfonation of benzene
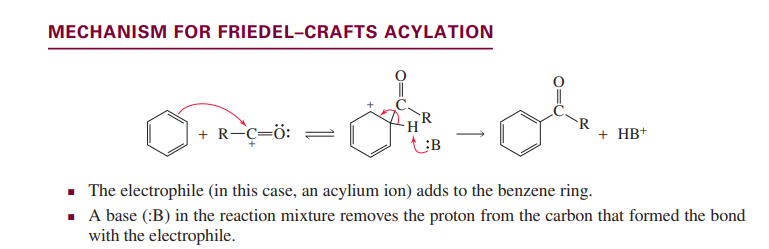
Fiedel-Crafts acylation
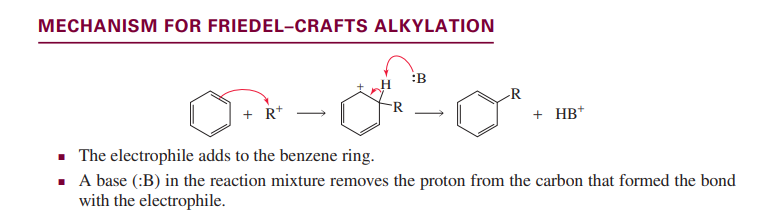
Fiedel-Crafts alkylation
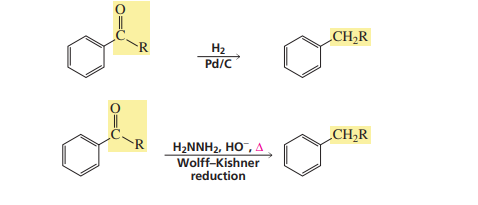
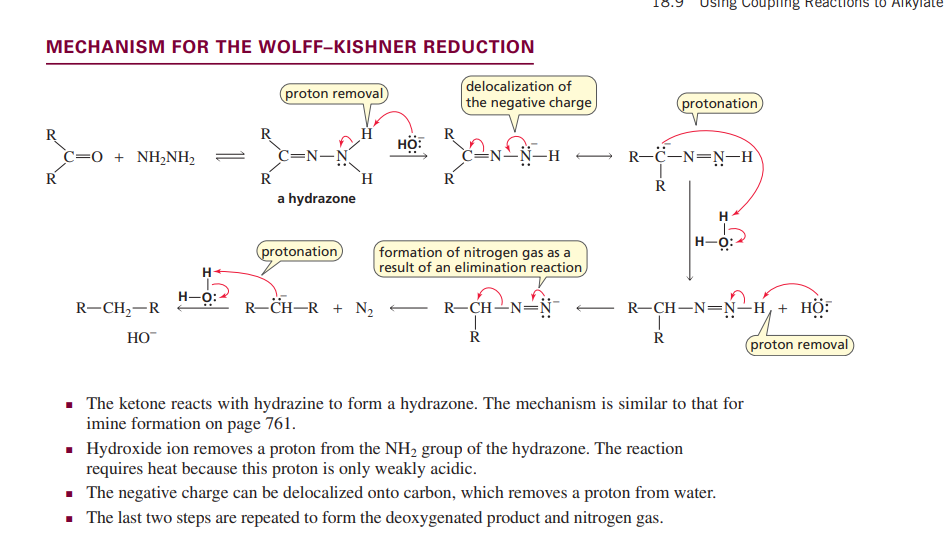
Wolf-kishner reduction
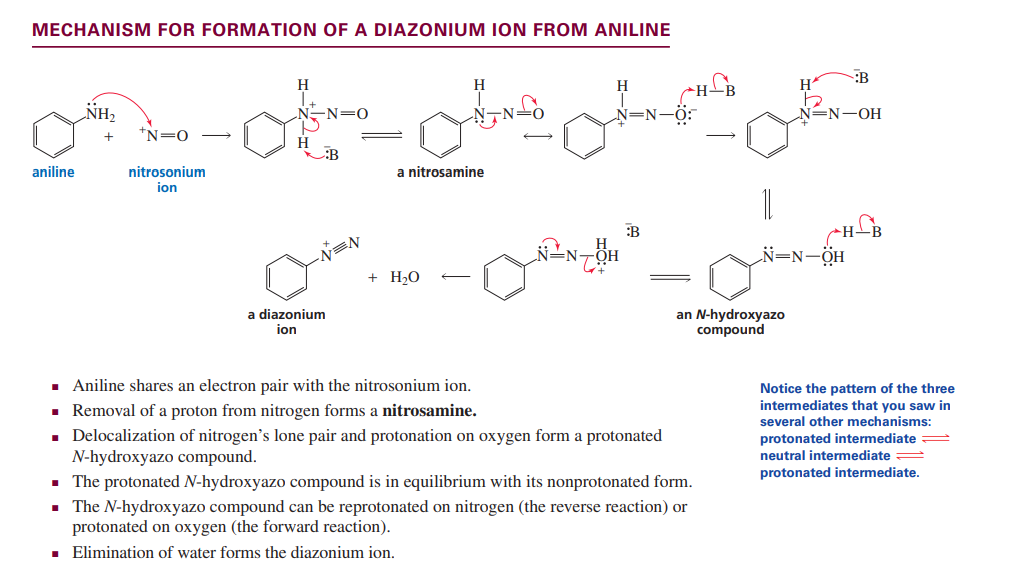
Formation of diazonium ion from aniline
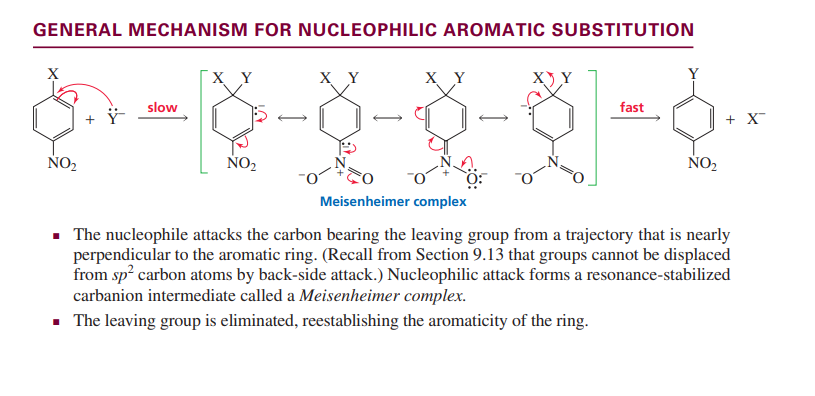
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
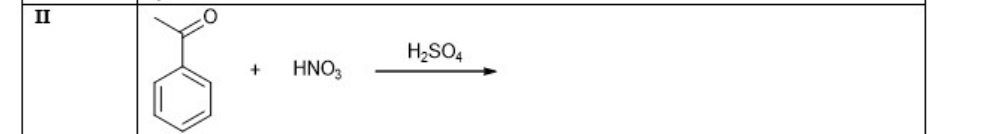
What is the major product of
Nitration
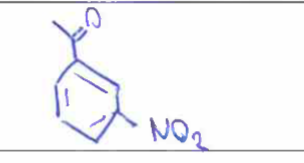
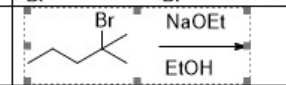
What is the major product of
strong base
E2 reaction

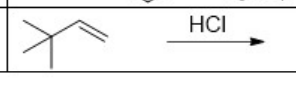
What is the major product of

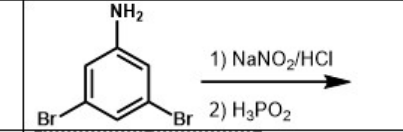
What is the major product of

reduction of acyl group on benzene