Read-out Devices
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
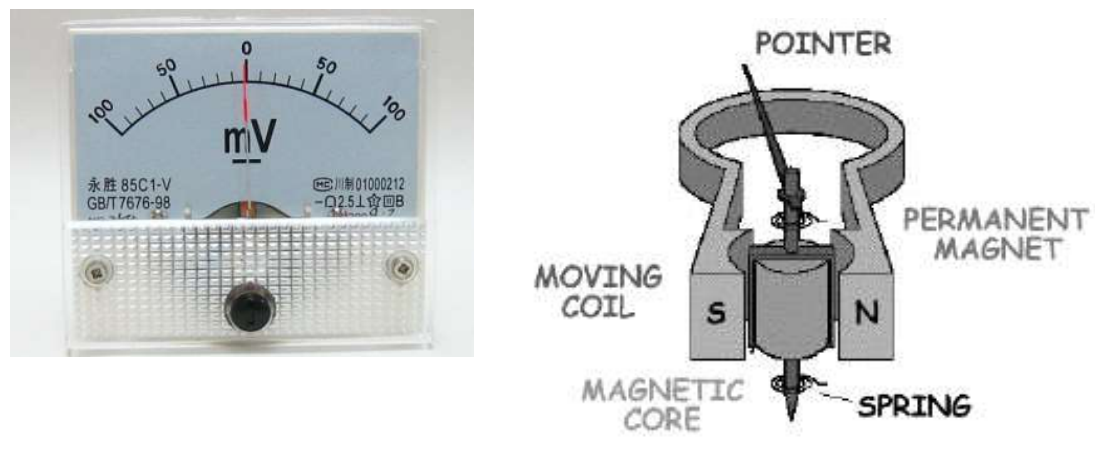
Moving-Coil System
connected to the output of the signal processor
As the signal changes, the pointer deflects
The amount of deflection is proportional to the signal and thus represents the variable being measured
Plotters definition (2)
A type of printer used for drawing or creating large-scale images, diagrams, and graphics
Often uses a moving-coil system to control the movement of the pointer (pen, inkjet nozzle, or heated stylus) for precise drawing or printing
Plotters types (2)
Ink-jet plotters
Thermal plotters
Ink-jet plotters
Uses capillary action with a ‘pointer’ and ink pump to spray ink onto the paper

Thermal plotters
Uses a heated pointer to transfer heat onto heat-sensitive paper, creating marks without ink

7 Segment Digital Display Systems based on (2)
LED (Light Emitting Diode) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) based

Advantages of 7 Segment Digital Display Systems
Direct readout
LCD displays
Direct readout
The numbers are clearly displayed, allowing immediate reading of the values - even in low-light situations
LCD displays
Use liquid crystals that respond to electrical currents, typically requiring backlighting for visibility, but are energy-efficient
Monitors types (2)
CRT (Cathode Ray Tube)
LCD-TFT (Flat Screen)
CRT general (3)
Uses a cathode ray tube to display images by shooting electron beams at phosphorescent screens
producing light to form the image
Older technology, typically bulkier and less energy-efficient
CRT electrobeam
responsible for exciting phosphors on the screen, producing the light that creates the image
LCD-TFT general (6)
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display):
uses liquid crystals that are manipulated by electrical currents to display images
TFT (Thin Film Transistor):
a type of LCD that uses a thin film of transistors to improve the display quality
provides sharper images and better color contrast
Common in flat-screen monitors due to its slim design and energy efficiency.
LCD how it works? (3)
The liquid crystals are manipulated by electrical currents to control light passing through them
When an electric field is applied, the liquid crystals align in a way that either blocks or allows light to pass through
creating images or text on the screen
Footprint for CRT vs LCD-TFT (outlied is preffered)
CRT: larger, bulky, thick
LCD-TFT: smaller, slim/flat
Image brightness for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: higher brightness
LCD-TFT: lower brightness
Colour for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: rich, natural colours
LCD-TFT: not that colourful + not vibrant
bc/ of crystals
Size - weight for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: large, heavy
LCD-TFT: slim, lightweight
Screen burn-in for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: prone to it
LCD-TFT: Minimal
“ghost”/ lining of image on screen
Viewing angle for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: any direction
LCD-TFT: straight on - 1D
Response time for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: ultra-fast
LCD-TFT: slower
Screen-flicker for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT:prone to flicker
refreshed by the electron beam scanning the screen at a certain refresh rate - slow rate
LCD-TFT: flicker-free viewing
image remains stable
Magnetic interference for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: prone to magnetic interference
bc/ electron beam can be distorted by external magnetic fields
leading to image or color distortions
LCD-TFT: immune
not rely on electrobeams
Power consumption for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: High
LCD-TFT: Low - energy efficient
Dead-pixels for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: none
LCD-TFT: crystals show black spots
Contrast for CRT vs LCD-TFT
CRT: Excellent black&white
LCD-TFT: lower contrast
Medical Printers types (4)
ink-jet
colour laser
thermal sublimation
video printers