Major Depressive Disorder- Krysiak
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a _____ disorder compared to schizophrenia which is a thought disorder.
mood
What is the monoamine hypothesis for MDD?
decreased brain levels of NE, 5-HT, DA associated with depressive symptoms
What hypothesis is now emphasized for MDD, focusing on a molecular problem with signal transduction rather than neurotransmitter depletion?
Dysregulation hypothesis
What is Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)? How does it relate to depression?
BDNF—> growth factor protein that regulates neuronal survival—> its dysregulation is connected with depression
What are 3 main classifications of depression based on severity and duration?
bipolar/ unipolar depression—> opposite ends of an affective or mood spectrum
major depression—> most common, single episode or recurrent episodes
dysthymia—> less severe but often longer lasting form of depression (>2yrs)
What are some drugs that can cause depression?
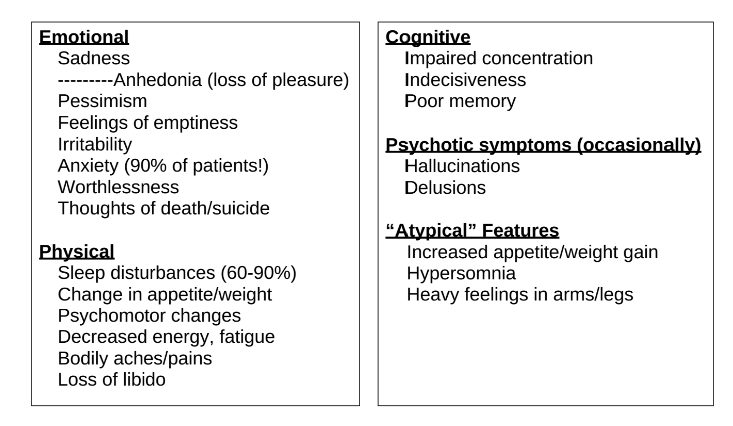
What are the emotional, physical, cognitive, psychotic, and atypical symptoms of depression?
i would just recognize> memorizing
According to DSM-5, what are the criteria for diagnosing MDD?
5 or more of the following symptoms have been present during the same 2 week period and is a change from previous functioning, at least one of the symptoms must be the red/underlined ones:
depressed mood
markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all/almost all activities
significant weight loss or weight gain (can also be increase/decrease in appetite)
insomnia or hypersomnia
psychomotor agitation or retardation
fatigue/ loss of energy
feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt
diminished ability to think or concentrate or indecisiveness
recurrent thought of death, recurrent suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, or plan to commit suicide
What does the “SIG E CAPS” mnemonic for depression symptoms stand for?
S- sleep disorder
I- interest deficit
G- guilt
E- energy deficit
C- concentration deficit
A- appetite disorder
P- psychomotor
S- suicide
What does the IS PATH WARM mnemonic for suicide stand for?

Depression rating scales are useful for what? What are some examples of scales?
idk how imp
useful for taking subjective info and making it more objective
helps establish a baseline for the pt.
examples: HAM-D, MADRS, BDI

What are the three phases of depression treatment?
how long (weeks/month) is each phase?
goal of each phase?
acute phase (6-12 weeks)—> goal to achieve remission (absence of sx)
continuation phase (4-9 months)—> goal to eliminate residual symptoms, prevent relapse
maintenance phase (12-36 months)—> goal is to prevent recurrence
Duration of antidepressant therapy depends on the risk of recurrence.
Lifelong maintenance is used for what age groups?
pts. <40 w/ 2+ episodes
any age with 3+ episodes
Definition of each of the following in the context of depression tx:
nonresponse
partial response
response
remission
recovery
relapse
recurrence
nonresponse: <25% decrease in baseline symptoms
partial response: 26-49% decrease in baseline symptoms
response: 50% reduction in symptoms
remission: at least 3w of the absence of sad mood+ reduced interest and no more than 3 symptoms
recovery: removal of all symptoms for >6-12m
relapse: depression returns within 6m of remission
recurrence: returns after recovery
What is treatment resistance in the context of MDD?
Episode that has failed to respond to 2 separate trials of different antidepressants of adequate dose and duration
What are non-pharmacologic treatment options for MDD?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
psychotherapy
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
CAM
St. John’s Wort
S-adenosyl Methionine (SAMe)
Folate and L-methylfolate
What are the recommended uses for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)?
Severe depression, depression with psychosis or catatonic features, and treatment of choice for patients with severe suicide ideation or food refusal.
What are the common side effects of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)?
Headache and transient scalp discomfort.
What is the indication for VNS?
adjuctive long-term chronic/recurrent depression lasting at least 2 yrs and not responding to 4 trials of antidepressants (not for pts <18)
What is the indication for Psychotherapy?
How does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) address depression?
idk how imp
How does Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) address depression?
idk how imp
indication: monotherapy for mild/acute depression or in combo with pharm tx for severe depression
CBT—> Aims to address psychosocial stressors and psychological factors associated with mood episodes by focusing on the impact of thoughts on emotions and actions
IPT—> improves communication skills and dealing with difficult emotions or relationships by focusing on building current interpersonal relationships
SSRIs are only FDA approved for what?
only approved for use in OCD, rarely used alone for depression
List the SSRIs:
citalopram
escitalopram
fluoxetine
fluvoxamine
paroxetine
sertraline
vilazodone
MOA of SSRIs
inhibit presynaptic serotonin reuptake (but each SSRI has it’s unique properties)
Difference between citalopram and escitalopram?
which enantiomer is responsible for efficacy? ADRs?
which is more efficacious?
citalopram—> R and S enantiomer
escitalopram—> ONLY S enantiomer—> most efficacious, best tolerated SSRI ❤
R enantiomer= mild antihistaminic properties
S enantiomer= blocks 5-HT reuptake
Answer the following about Citalopram (an SSRI):
max dose <60 yr old
max dose >60 yr old
FDA MEDWATCH and BBW for what?
max dose <60 yr old= 40mg
max dose >60 yr old= 20mg
FDA MEDWATCH for QT prolongation
BBW for warning dose-dependent QTc prolongation and increased risk of torsades de pointes
Answer the following about Fluoxetine (Prozac) (an SSRI):
helpful for what pt. population?
recommended as continuation or initial tx?
IDK HOW IMP IDK HOW IMP
helpful with pts. suffering from hypersomnia and fatigue
recommended as continuation therapy vs. initial
Paroxetine is preferred for what symptoms?
anxiety symptoms
Vilazodone and Vortioxetine are thought to have what advantage compared to other SSRIs? (even tho there isn’t a lot of evidence)
thought to have faster ONSET of therapeutic response (and for Vortioxetine lower GI ADRs)
MOA of Vilazodone and Vortioxetine?
i don’t think imp—> austin covers this
Vilazodone—> 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist
Vortioxetine—> 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 5-HT3 antagonist
What is the ONLY SSRI with an active metabolite?
Which SSRI has the longest t ½ ?
FLUOXETINE!!!!!!!!!!!!!—> t ½ of 4-6 days
SSRIs interact with what drugs?
NSAIDs
antiplatelets
anticoagulants
With SSRIs, which are potent CYP inhibitors? of what enzyme?
Fluvoxamine—> CYP1A2
Fluoxetine, Paroxetine—> CYP2D6
BBW for all SSRIs and SNRIs?
increased risk of suicide in children, adolescents, and young adults age 24 or younger
ADRs of SSRIs:
common
GI (n/d, anorexia)
neurologic (anxiety, insomnia, HA)
sexual dysfunction (decreased libido, delayed ejaculation, anorgasmia, ED)
withdrawal syndrome
hyponatremia
List the SNRIs:
Venlafaxine
Desvenlafaxine
Duloxetine
Levomilnacipran
MOA of SNRIs
results?
5-HT reuptake inhibition + NE reuptake inhibition
boosts 5-HT and NE in the brain
boosts DA in the brain bc of NE inhibition
Answer the following about Venlafaxine (an SNRI):
what are the dose dependent effects?
metabolized to what?
MAY CAUSE DOSE-RELATED WHAT?
low doses—> most potent 5HT reuptake inhibition
high doses—> inhibits DA transporter
metabolized to DESvenlafaxine
May cause dose-related INCREASE in blood pressure
Answer the following about Duloxetine (Cymbalta):
MECHANISM IN ADDITION TO 5-HT and NE effects
FDA approved for what?
C/I?
Mechanism
FDA approved for MDD, DPN, fibromyalgia, and chronic musculoskeletal pain
not used in hepatic insufficiency or severe renal impairment (CrCl <30ml/min)
avoid in pts. with history of heavy alcohol use as well
Why is Levomilnacipran (SNRI) not really used in practice?
risk of seizures, urinary retention
associated with tachycardia/palpitations
Drug and CYP interactions with SNRIs?
LIKE SSRIs!!!!!!!—> NSAIDs, antiplatelets, anticoagulants
CYP
Duloxetine, Venlafaxine, CYP2D6
Desvenlafaxine—> no CYP interactions
Levomilnacipran—> CYP3A4
SNRIs should be used in caution in pts. with a history of…
hypertension and narrow angle glaucoma
ADRs of SNRIs:
common
similar to SSRIs—> nausea, sexual dysfunction, insomnia
neuro (sedation, somnolence, hypersomnia, dizzy)
anticholinergic
withdrawal syndrome
diaphoresis
CV (increase BP)
List the Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs):
Amitriptyline
Clomipramine
Doxepin
Imipramine
Desipramine
Active metabolite of Amitriptyline is…
nortriptyline
ALL TCAs are substrates of WHAT CYP?
CYP2D6
Interactions with TCAs:
idk how imp
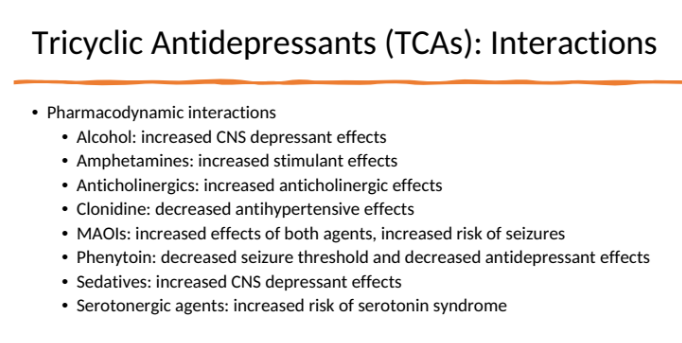
BBW and warnings associated with TCAs:
BBW: increased risk of suicidality
warning: TCAs are lethal in overdose—> don’t use if severely suicidal
overdose sym: hypotension, confusion, hyperthermia, arrhythmias, seizure, coma etc.
TCAs ADRs:
common:
sedation
anticholinergic effects
CV effects (cardiotoxicity, ortho hypotension, tachycardia,)
note: secondary amines are better tolerated!!!—> tertiary are more sedative and anticholinergic than secondary
List the MAOIS:
Phenelzine
Selegiline transdermal
tranylcypromine
Isocarboxazid
MOA of MAOIs:
difference between MAO-A and MAO-B?
block MAO enzyme—> which is responsible for breakdown of 5-HT, NE, DA
inhibits BOTH subtypes MAO-A, MAO-B
MAO-A—> located in intestinal epithelium and is responsible for breakdown of tyramine and prevents absorption
MAO-B—> metabolizes trace amines
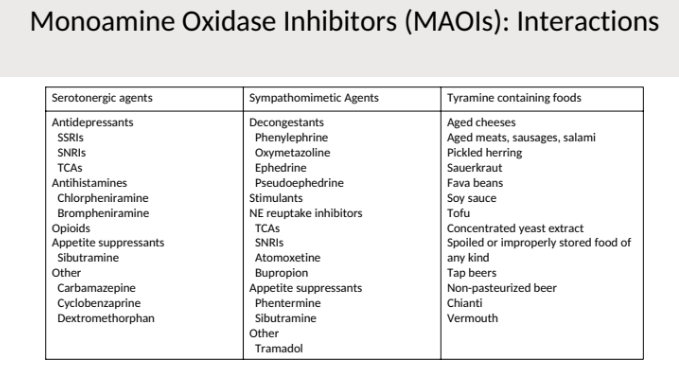
Why do we never use MAOIs?
interactions?
foods?
INTERACTS WITH EVERYTHING
sympathomimetics
HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS
serotonin syndrome
dietary restrictions
foods with tyramine—> MAO-A destroys it—> then we can’t increase NE
BBW with MAOIs:
increased risk of suicidality
List the Triazolopyridines:
trazodone
nefazodone
Although Trazodone isn’t really used in practice for depression, and is more used for sleep/sedation it’s still an option in depression, what is it’s MOA?
i don’t think that important!
weakly inhibits 5-HT and NE reuptake
weak a1 antagonist
serotonin 5HT2 antagonist
BBW, warnings, and interactions with Trazodone and Nefazodone:
interactions:
serotonin syndrome
nefazodone—> CYP3A4 inhibitor
Trazodone—> CYP3A4 substrate
BBW: increased suicide risk
BBW: nefazodone and live threatening liver failure—> must monitor LFTs
others:
ortho hypotension
increased QTc prolongation
risk of priapism
HOW IS THE MOA OF BUPROPION UNIQUE? benefits to use?
UNIQUE—> NO EFFECT ON SEROTONIN
MOA: weak reuptake inhibitors of DA and NE
benefits:
generally activating—> good for pts. with sedation
DOES NOT CAUSE SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
BBW, warnings, risks, interactions with Bupropion (Wellbutrin)?
what CYP?
risk of what?
BBW
C/I
monitor?
CYP2D6 substrate and inhibitor—> D/I
RISK OF SEIZURES increased
BBW—> increased risk of suicidality
C/I in seizures and anorexia
must monitor BP
HOW IS THE MOA OF MIRTAZAPINE UNIQUE? benefits to use?
UNIQUE: increases 5HT release BUT DOES NOT CAUSE SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
MOA: increases 5HT and NE through a2 antagonism + 5HT2 and 3 receptor antagonist
benefits: no sexual dysfunction, reduce n and GI problems, relieves insomnia
ADRs of Mirtazapine:
sedation
weight gain
hypertriglyceridemia
dry mouth
For MAOIs you MUST have a wash-out period due to risk of serotonin syndrome.
What is the wash-out period if d/c a MAOI and wanting to start a serotonin agent?
What is the wash-out period if you are on a SSRI and want to start a MAOI?
exception?
2 weeks after d/c a MAOI—> may start serotonergic agent
2-4 weeks after d/c a SSRI—> may start MAOI
exception: 5 WEEKS for FLUOXETINE
What is the triad of symptoms seen with serotonin syndrome
(I don’t like the way Krysiak described the triad of symptoms for serotonin syndrome so I’m taking from Austin’s lectures)
cognitive- mental status change, HA, hallucinations
somatic- hyperreflexia, tremor, myoclonus
autonomic: hyperthermia, n/v/d, tachycardia, sweating
Are there any lab findings used to confirm Serotonin syndrome?
no!!!
Tx for serotonin syndrome?
removal of precipitating agents- most important
supportive care
control agitation
administer 5HT2A antagonist
cyproheptadine
atypical antipsychotic
control hyperthermia
Augmenting agents are used in depression in addition to an antidepressant to improve response. What are some agents used?
Which is considered the gold standard?
LITHIUM—> gold standard for augmenting
thiiothyronine
SGAs—>FDA approved ones include:
Aripiprazole
brexipiprazole
olanzapine
quetiapine
cariprazine
risperidone (not FDA approved)
Monitoring for thiiothyronine?
thyroid—> may lead to hyperthyroidism
an adequate trial of antidepressants is ___-___ weeks at max dose.
4-8
Preferred drugs for acute tx phase?
monotherapy with:
SSRI
SNRI
mirtazapine
buproprion
What did the STAR*D trial results suggest?
less than 1/3 of pts. achieve remission with initial SSRI monotherapy
switching or augmentation are good strategies
changing may be a good option for pts. that can’t tolerate or do not respond
augmentation may be a good option for partial responders
What are the 1st and 2nd line tx for depression in the elderly?
1st line: SSRIs
2nd line: Mirtazapine, Buproprion
For moderate to severe depression in children/adolescents, what drugs have age considerations?
idk how imp
fluoxetine 8-18yrs old
escitalopram >12 yrs old
sertraline not FDA approved but used
Desipramine—> has several cases of sudden death in children
How is depression during pregnancy and lactation managed?
weight the risks (suicide, preeclampsia, low birth weight) and benefits
tx should include psychotherapy (maybe even ECT)—> pharm therapy recommended for those with mod/severe depression
medications in preg
SSRIs associated with pulmonary HTN especially in 3rd trimester
paroxetine is Cat D and associated iwht septal wall defects
SSRIs associated with withdrawal syndrome in babies
buproprion, mirtazapine—> cat C
lactation—> paroxetine or sertraline preferred