Acct351 Ch7: Financial Assets
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Def fincl instrument ?
Fincl instrument: °any contract that gives rise to a fincl asset of one entity and a fincl liability or equity instrument of another entity.
(fincl asset : in this course, fincl liability : in IFA 2)
What are the 3 main groups of fincl instruments (fincl assets) ?
Equity instrument: °a contract that gives the holder the residual interest in an entity after deducting its liabilities.
expl : CS
either strategic or non-strategic instrument
Debt instrument: °any fincl instrument that is not an equity intrument or a derivative.
expl : a bond
typically a non-strategic investment
Derivative: °an instrument that has all of the following characteristics:
» its value changes according to a specified variable (i.e. interest rate or stock price)
» it requires no initial net investment or a small investment relative to non-derivative contracts with similar exposure
» it is settled at a future date
expl : stock option
typically non-strategic
« Strategic Equity Investments »
What is a strategic investment ?
°gen a long term investment, where an enterprise invests in another company in order to:
Access resources
Extend market reach
Increase operational efficiency
This is done by influencing mgmt decisions of the investee company in a variety of ways.
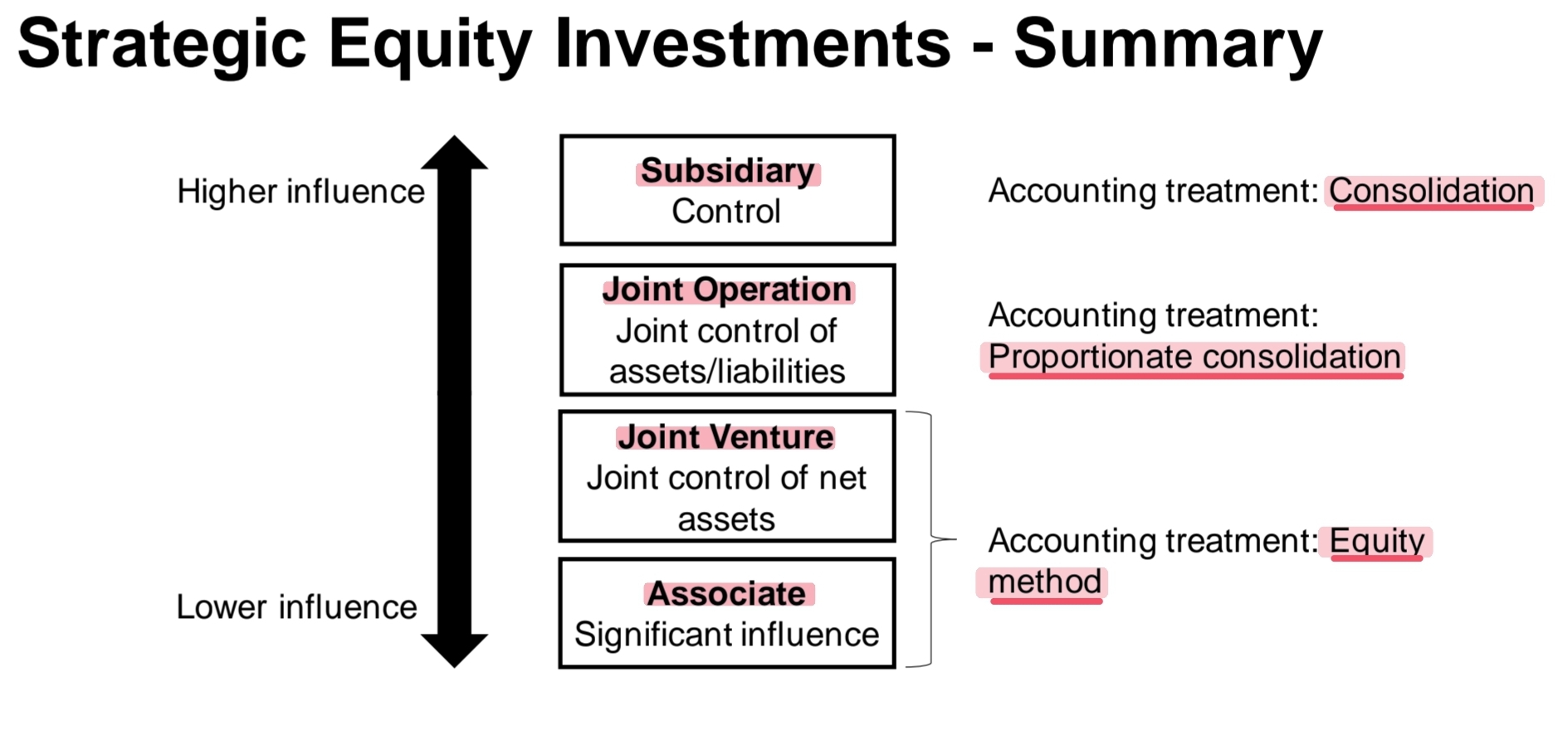
What are the 4 types of strategic investments ?
To what do they correspond ? Why are they divided that way ?
There are several ways that influence can be exerted, resulting in 4 types of strategic investments:
Subsidiaries
Joint operations
Joint ventures
Associates
The detailed acctg treatment for these investments is covered in advanced acctg courses.
(We will focus on understanding and classifying these types of investments)
Subsidiaries def ?
°When one company invests in the equity of another in order to have control over this company.
(How is control defined here ?)
—> parent company > subsidiary
—> “Control” when holds over ..% (?) of the voting shares
How is control defined here ?
Control is defined as the pwr to govern the fincl and operating policies of an entity
—> “Control” when holds over 50% of the voting shares
What is the acctg treatement for this type of investment ? (subsidiary)
It’s consolidation: it means to prepare the fincl statements as if the 2 companies are one economic unit.
(See expl slides 10-11)
Joint Arrangements def ? and types ?
°Contractual arrangement where 2+ parties undertake an economic activity subject to joint control (when the strategic dec relating to the act requires the unanimous consent of both parties).
For IFRS, 2 types :
Joint operations
Joint ventures
Joint operations ?
°When each investor has the rights to the assets and obligations for liabilities of the arrangement
=When 2 parties formed an unlimited liability partnership to operate the arrangement
Each party owns a proportion of the assets and exposure to liabilities and will jointly control the operations
What is the acctg treatment for Joint Operations ?
Proportionate consolidation : Each party willl include their portion of the assets, liabilities and income on their respective fincl statements.
Joint venture ? (def, expl, acctg treatment)
An operation where each investor has the rights to the net assets of the arrangement. Each parties will not have direct control over the assets or exposure to the liabilities.
expl : sharing control over a separate legal entity (which would have limited liability).
Acctg treatment : equity method (IFRS)
What is the equity method ?
°When an investment is recorded on the balance sheet at its cost.
Each period this investment is adjusted for the investors share of the investees changes in net assets.
Income will be recognized based on their share of the investees net income.
Associates ?
An investment that doesn’t rise to the level of control : we will look for a significant influence.
(What is significant influence ?)
typically when the investor holds 20-50% of the voting power of the investee.
An associate (or affiliate) is an investor with significant power.
How is defined significant influence ?
Significant influence is °the power to participate in the fincl and operating policy decisions of the investee.
What method will be used for associates ?
The equity method
(expl) Do expl 1: Equity Method (Slide 18)
What entries ?
Income Statement pres ?
BS pres ?
Strategic Equity Investments - Summary ?
« Non-Strategic Investments »
Non-strategic investment def ?
°Investment that does not meet the threshold of control or significant influence.
Classifications of non-strategic investment ? (3)
Fair value through profit or loss (FVPL)
Fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI)
Amortized cost
FVPL ?
includes portfolio (equity) inv mgmt intends to trade w the expectation of profit
derivatives and any other fincl assets not included in other cat
How is FVPL accounted ?
BS ?
IS ?
Dividends ?
Once the inv is sold ?
BS : recorded as FVPL Investment.
IS : any unrealized gains at the end of the year will be recorded based on the fair market value at that date.
Dividends : recorded as revenues.
Once sold : any subsequent gain or loss will also be recorded on the IS and be included in net income.
(expl) Do expl 2: FVPL Investment (Slide 23)
FVOCI ?
includes debt securities that companies intend to profit from changes in value and to collect cash flows to which they are entitled.
How is FVOCI accounted ?
BS ?
IS ?
Dividends / Interest ?
Once the inv is sold ?
BS : recorded as FVOCI Inv.
IS : any unrealized gains at the end of the year will be recorded in the OCI section based on the fair market value at that date.
Dividends/Interest : recorded as revenues.
Once sold : the realized gain or loss will be recorded on the IS and included in net income.
(globally same as FVPL)
(expl) Do expl 3: FVOCI Investment (Slide 25)
Exception for Equity Investments with Irrevocable Election:
What are the conditions ?
If
The election is made when entity initially acquires the inv
The inv must be an equity inv
The election is irrevocable, a company cannot change the classficiation later
What is the main difference btwn OCI election & FVOCI section inv ?
What is the main difference btwn OCI election & FVOCI section inv ?
Here, the realized gains/losses will also be included in OCI.
The ttl gains and losses recorded in OCI will then be transferred to R/E as a closing entry in the yr they’re sold.
(expl) Do expl 4: Irrevocable Election (Slide 27)
Amortized cost ?
includes debt investments with fixed/determinable payments representing prcpl and interest that mgmt typically intends to hold until maturity.
°When debt mgmt intents to hold them until maturity.
Over time the company will collect interest payments on these investments.
The effective interest method must be used, that requires the use of discounted cash flow analysis.
Basis of bonds ?
What is a Bond ?
°an inv where an investor loans money to an entity that borrows the funds for a defined period of time at a fixed interest rate.
Some important terminology :
Maturity date
Maturity value / Face value
Coupon pmts
Market yield / effective interest rate
(expl) Take a look at the expl Slide 30
(expl) Do expl 5: Bonds (Slide 31)
Effective Interest Method ?
°requires calculating the amortized cost of the fincl asset at each reporting date.
This means calculating the PV of the asset’s cash flows discounted at the effective interest at each reporting date.
This method works as follows :
Using the bond characterisitics, the PV (price) of the bond will be determined.
If not already provided, the effective itnerest rate shuold be determined and the company prepares an amortization table.
The amortization table can then be used to prepare the jrnl at the time of purchase, each yr end and the maturity date.
Note : the effective interest method will be used for all debt instruments, both those classified as FVOCI and amortized cost.
(expl) Do expl 6: Effective Interest Method (Slide 33)
Summary ?
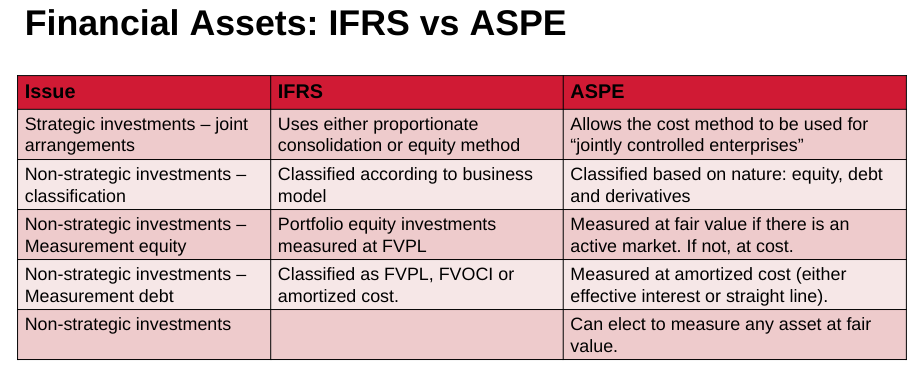
Fincl asset issue & IFRS vs ASPE responses ?