BIO 106: EXAM 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
DNA
nucleic acid composed of nucleotides
2
New cards
what are the parts of nucleotides
sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogen base
3
New cards
what kind of sugar is in a DNA nucleotide?
deoxyribose
4
New cards
What are the nitrogen base groups made of?
two purines and two pyrimidines
5
New cards
DNA purines
adenine and guanine
6
New cards
DNA pyrimidines
cytosine and thymine
7
New cards
What kind of pyrimidine can only be found in DNA?
thymine
8
New cards
Is DNA double or single stranded?
double
9
New cards
do DNA strands run in opposite or the same direction?
opposites
10
New cards
DNA strands are _____ to each other; not exactly alike.
complimentary
11
New cards
DNA
A = _____
A = _____
T
12
New cards
DNA
T = ____
T = ____
A
13
New cards
DNA
C = _____
C = _____
G
14
New cards
DNA
G = _____
G = _____
C
15
New cards
DNA strands are held together by _____ bonds.
hydrogen
16
New cards
What makes up the backbone of DNA strands?
sugar/phosphate group
17
New cards
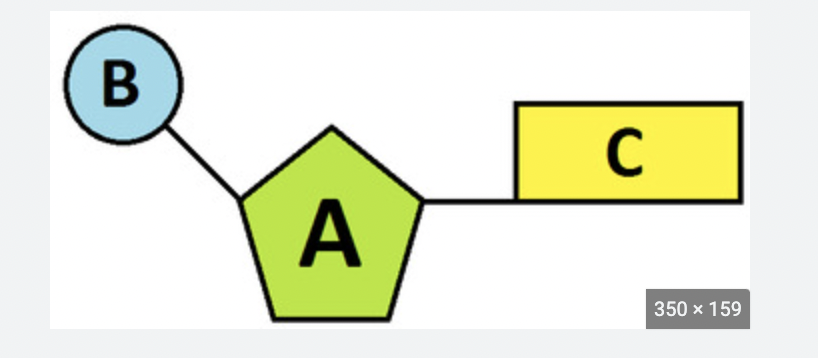
Identify the nucleotide parts.
B: phosphate
A: Sugar
C: nitrogen base
A: Sugar
C: nitrogen base
18
New cards
Where is DNA located?
in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
19
New cards
____ is the storage of genetic info.
DNA
20
New cards
Replication
DNA makes an exact copy of itself before new cells are made
21
New cards
T/F: DNA can replicate
true
22
New cards
T/F: DNA cannot mutate
false
23
New cards
Mutation:
a change in the original lineup or order of DNA
24
New cards
T/F: DNA does not undergo transformation
false
25
New cards
Transformation:
the introduction of new DNA into a bacteria cell
26
New cards
transfection:
introduction of new DNA in eukaryotic cells
27
New cards
Who discovered DNA transformation, but he did not know it was DNA that was transforming?
Griffith
28
New cards
Who concluded that DNA is the transforming principle in Griffith's experiments?
Avery and McCarthy
29
New cards
Who concluded that DNA, not protein, is responsible for storing genetic info?
Hershey and Chase
30
New cards
Who discovered DNA's complimentary pattern?
Chargaff
31
New cards
Who discovered that DNA is in the shape of a double helix?
Watson and Crick
32
New cards
Who discovered the semi-conservative replication of DNA?
Stahl
33
New cards
Semi-conservative replication of DNA:
each DNA double helix is composed of an old strand and new strand
34
New cards
DNA replication:
makes an exact copy of itself
35
New cards
When does DNA replication occur?
before cellular reproduction
36
New cards
Where does DNA replication occur?
inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
37
New cards
how many phases can DNA replication go through?
3
38
New cards
put the phases of DNA replication in order.
1. DNA helicase
2. DNA polymerase
3. DNA ligase
2. DNA polymerase
3. DNA ligase
39
New cards
DNA helicase
unravels DNA in double helix
40
New cards
DNA polymerase
adds free complementary nucleotides to each DNA
41
New cards
DNA ligase
seals DNA fragments on one DNA strand
42
New cards
RNA:
nucleic acid that is composed of nucleotides
43
New cards
What are the parts of RNA
sugar
phosphate group
nitrogen base
phosphate group
nitrogen base
44
New cards
What kind of sugar does RNA have?
ribose
45
New cards
RNA purines
adenine and guanine
46
New cards
RNA pyrimidines
cytosine and uracil
47
New cards
What kind of pyrimidine can only be found in RNA?
uracil
48
New cards
RNA
A = ____
A = ____
U
49
New cards
RNA
G = ____
G = ____
C
50
New cards
RNA
C = _____
C = _____
G
51
New cards
RNA
U = ____
U = ____
A
52
New cards
transcription
DNA makes RNA
53
New cards
Translation
RNA makes proteins
54
New cards
every gene will have ____ alleles- Mendel
2
55
New cards
law of segregation:
alleles will separate during meiosis
56
New cards
law of independent assortment:
allele separation is completely random
57
New cards
One allele is _____ (mask/hides the expression of another allele), and one allele is _______ ( masked/hidden in the presence of another allele).
dominant
recessive
recessive
58
New cards
individuals are ________ (having same alleles for a gene) or ______ (having different alleles for a gene)
homozygous
heterozygous
heterozygous
59
New cards
multiple alleles
many genes will have this because of mutations
60
New cards
co-dominance
2 dominant alleles being expressed equally
61
New cards
what is an example co dominance?
ABO blood type
62
New cards
incomplete dominance
dominant allele does not completely hide the recessive allele
63
New cards
What is an example of incomplete dominance?
pink flowers
64
New cards
polygenetic inheritance
many genes control one physical characteristics
65
New cards
What is an example of polygenetic inheritance?
eye color
66
New cards
pleiotropy
one piece of DNA controlling many physical characteristics
67
New cards
Dominant
capital; always shows up
68
New cards
recessive
lowercase; only shows up by itself
69
New cards
homozygous
use same letters; same uppercase or lowercase
70
New cards
heterozygous
uses different letters; uppercase first and lowercase after