Chapter 9: L-Spine, Sacrum, Coccyx
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
AP Lumbar Spine Leg Position
Knees and hips flexed
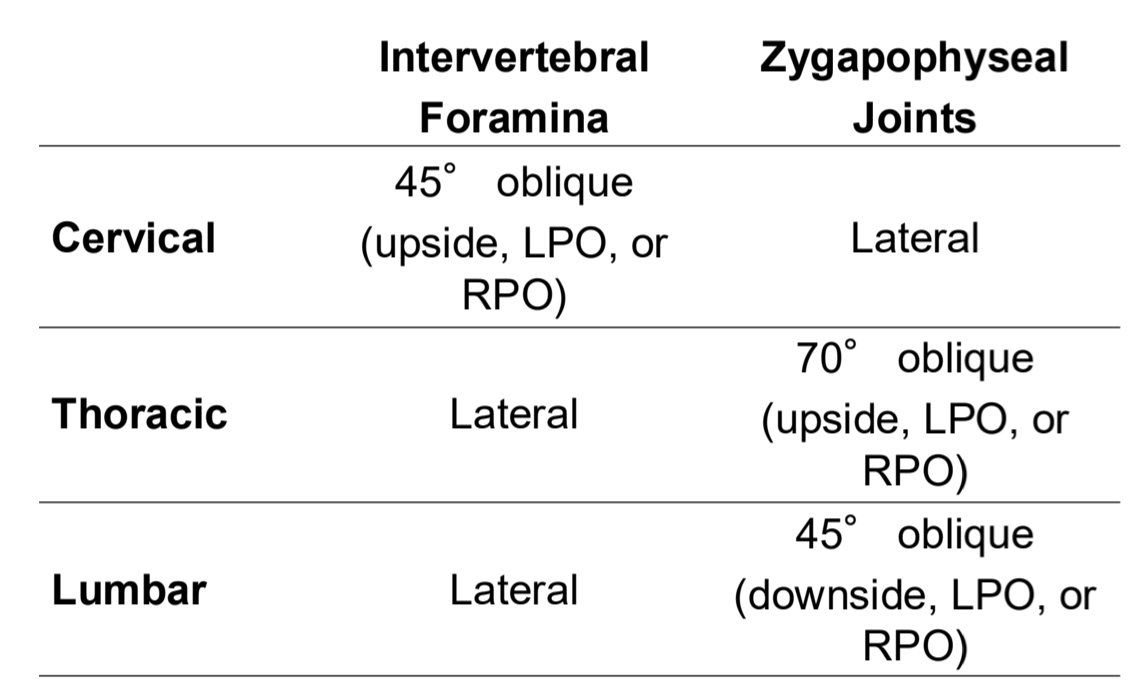
Lead Mat Usage
lateral L spine
absorbs scatter
Ankylosing spondylitis
pain and stiffness of SI joints, intervertebral joints, and costovertebral joints
bamboo spine
ankylosis: union of bones
complete rigidity of spine and thorax
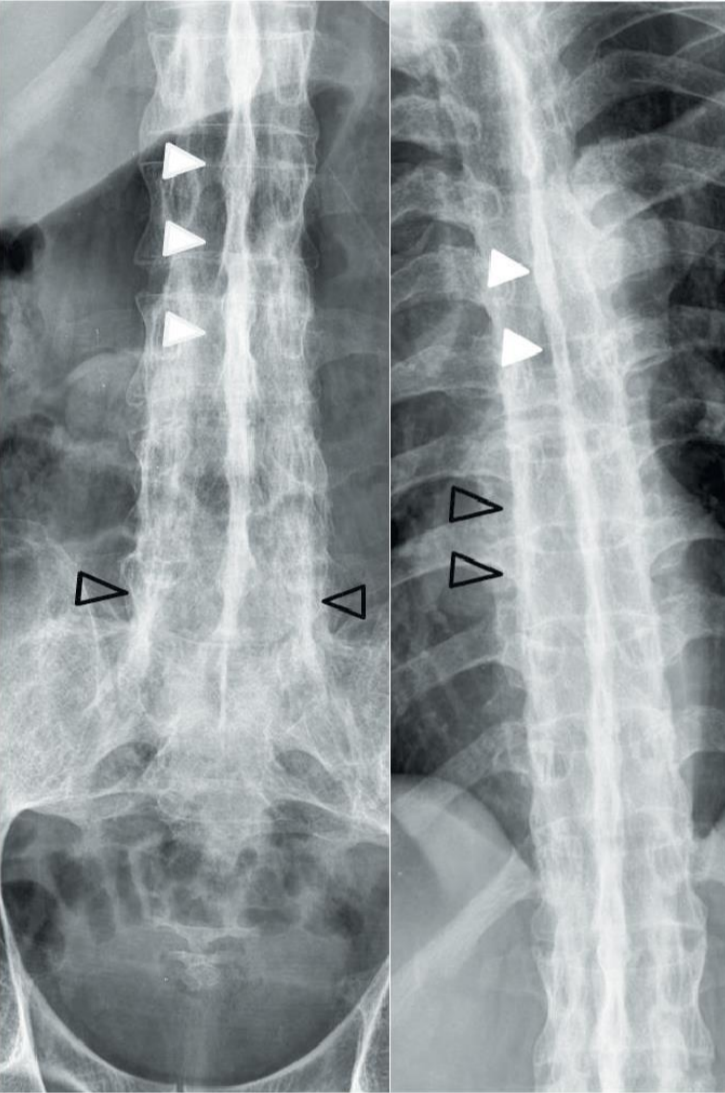
Compression fracture
superior and inferior surfaces of vertebral body are driven together, producing a wedge shape
rarely causes a neurological deficit
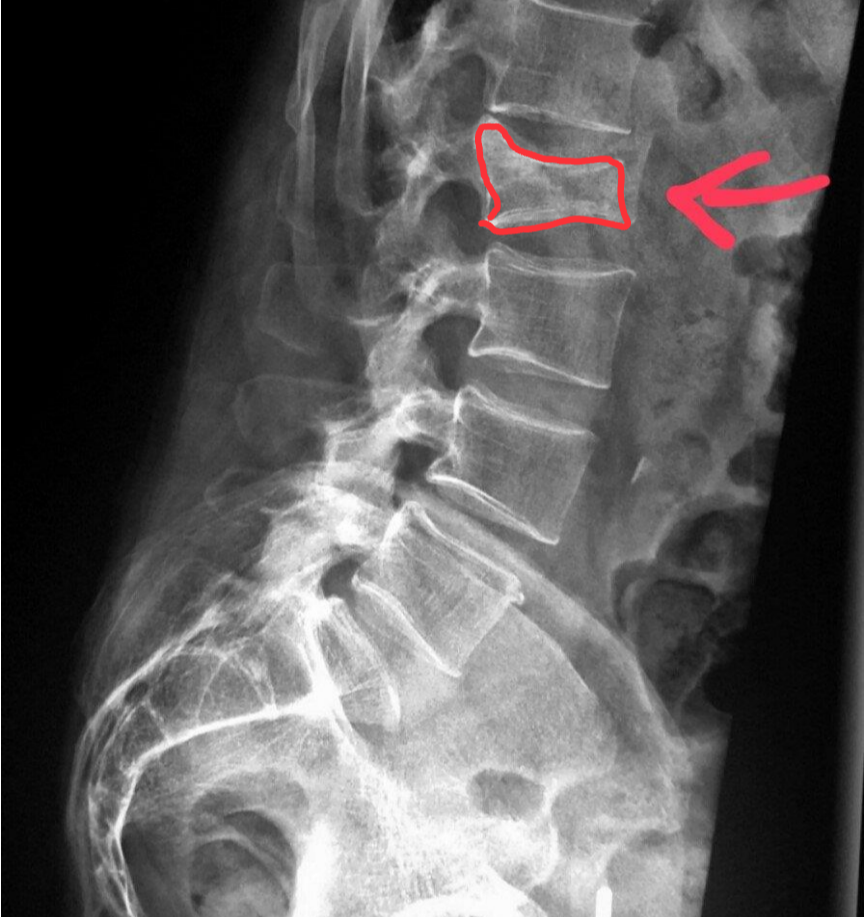
Chance fracture
results from hyperflexion force that causes fracture through vertebral body and posterior elements
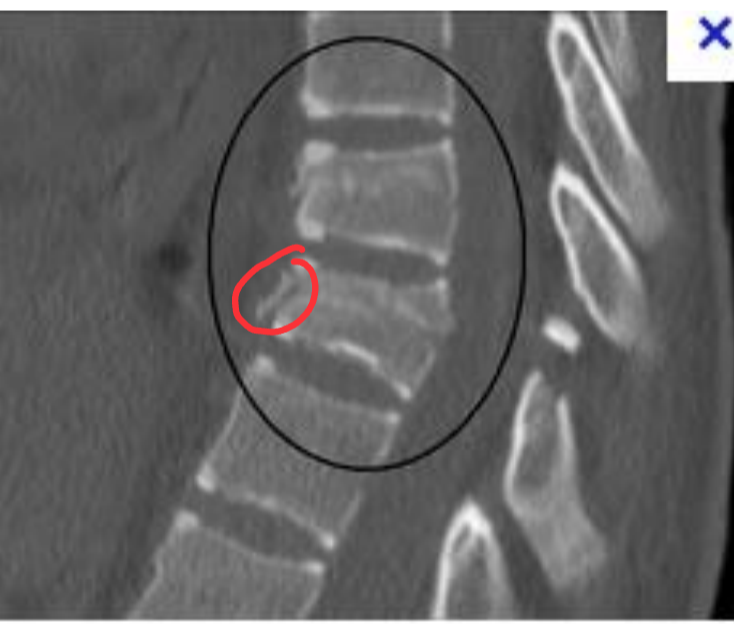
Herniated Nucleus Pulposus
herniated lumbar disk
The soft inner part of the intervertebral
disk (nucleus pulposus) protrudes through the fibrous outer layer, pressing on the spinal cord or nerves. It occurs most frequently at the L4–L5 levels, causing sciatica
CT and MR work best to detect
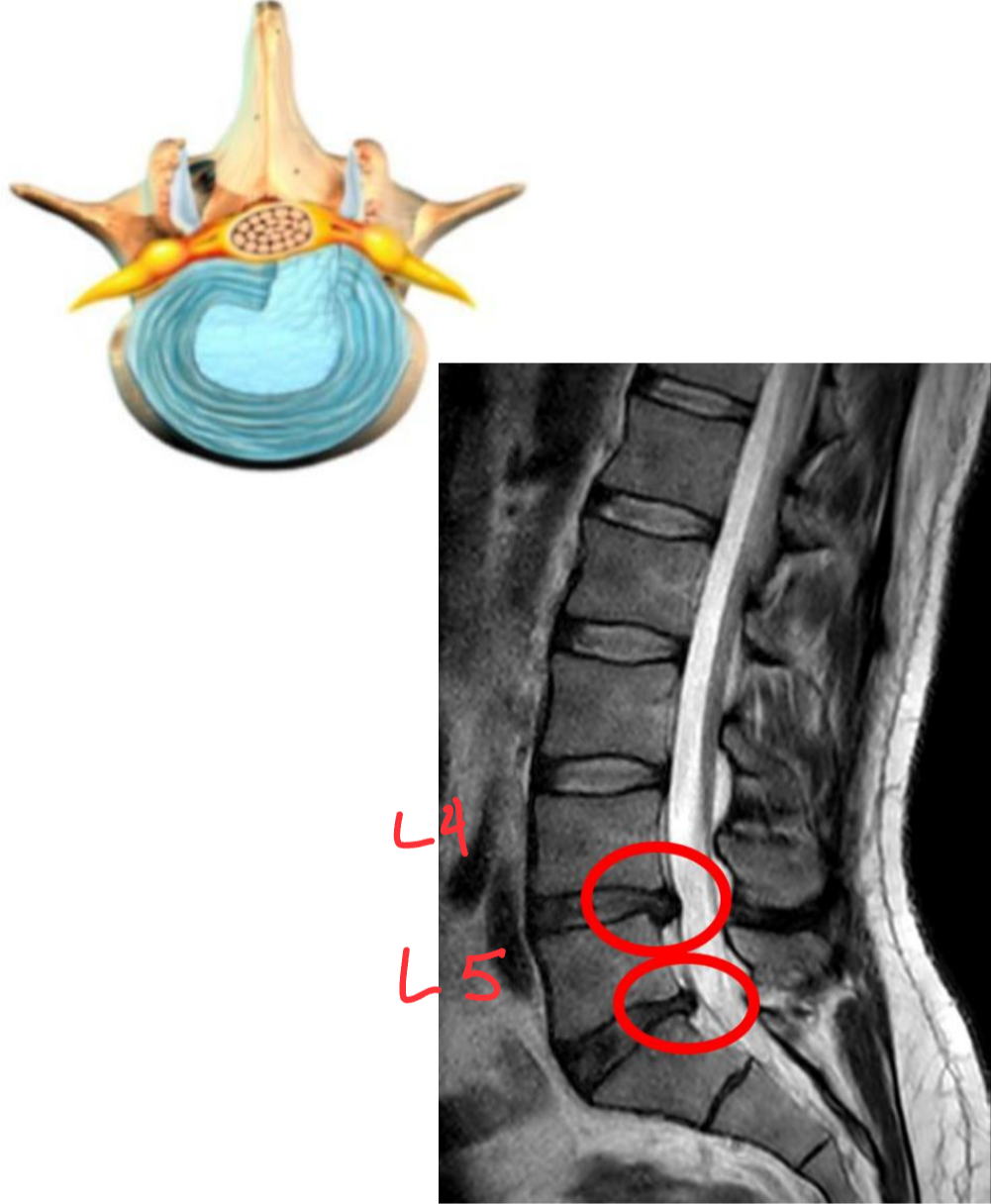
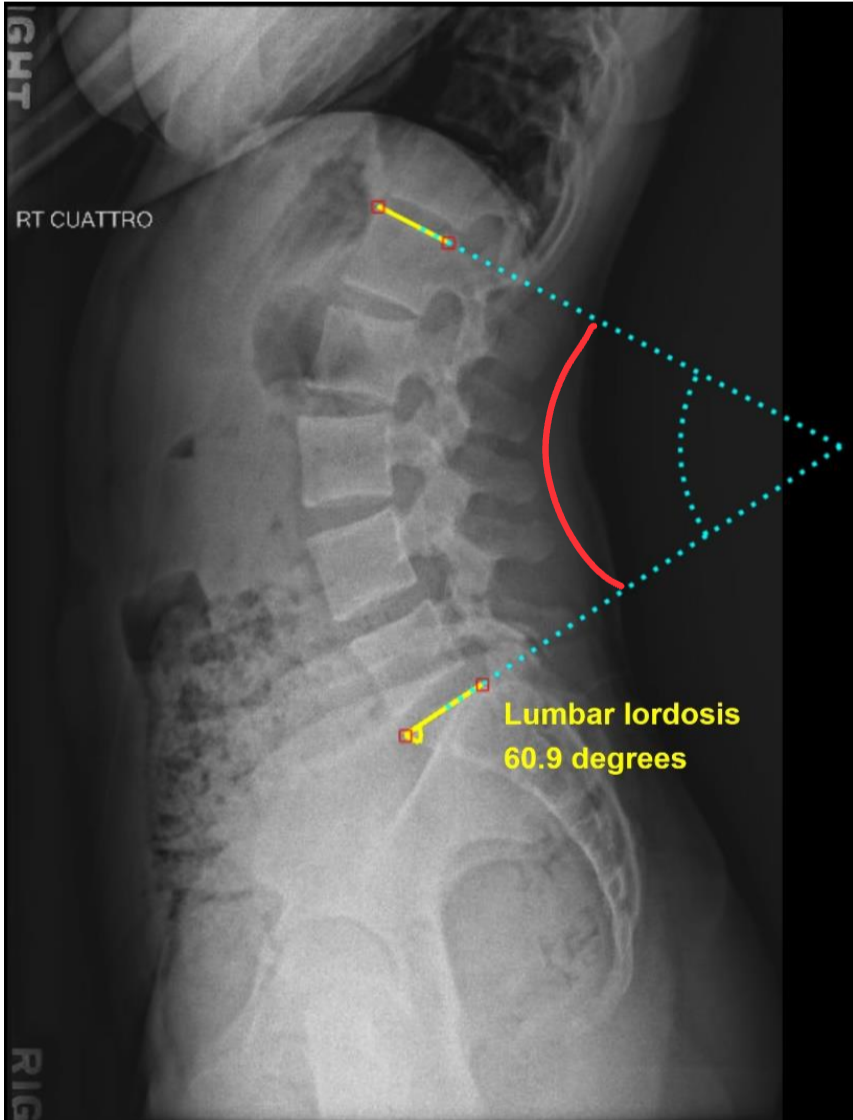
Lordosis
abnormal or exaggerated concave lumbar curvature
Types of metastases
osteolytic: destructive lesions with irregular margins
osteoblastic: proliferative bony lesions of increased density
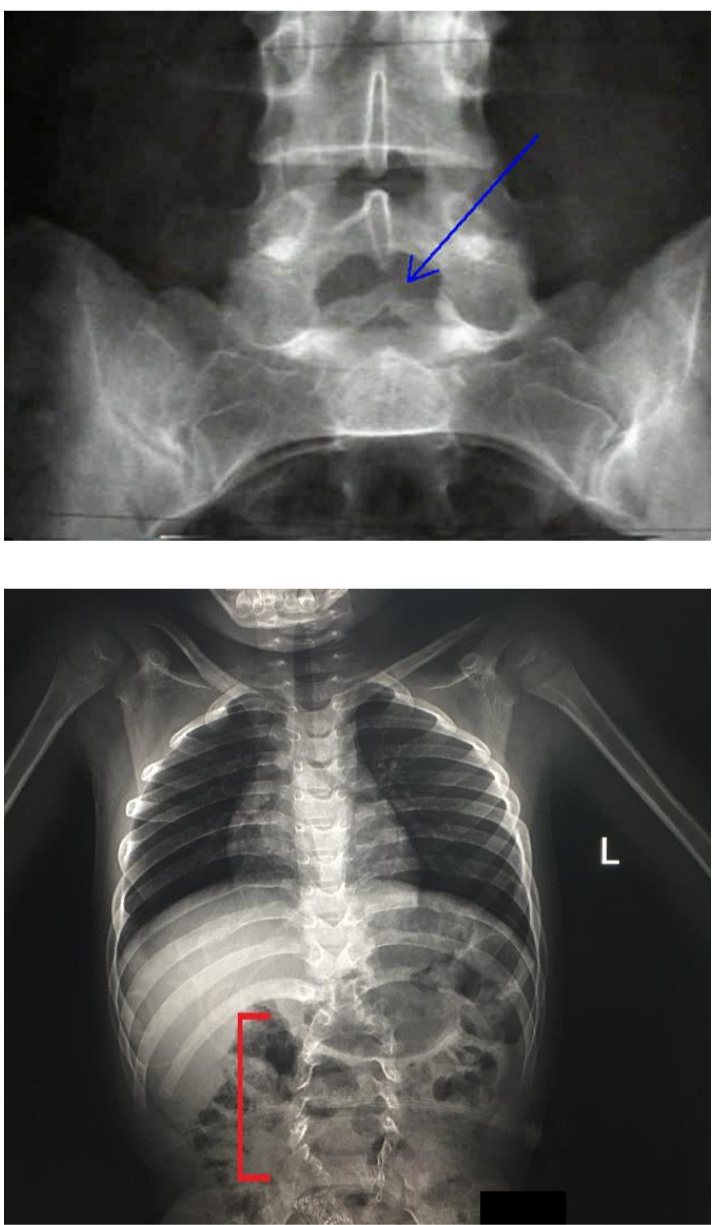
Spina Bifida
Congenital condition in which the posterior aspects of the vertebrae fail to develop, thus exposing part of the spinal cord
usually at L5
ultrasound detects best
Spondylolisthesis
Involves the forward movement of one vertebra in relation to another.
Usually at L5-S1 or L4-L5
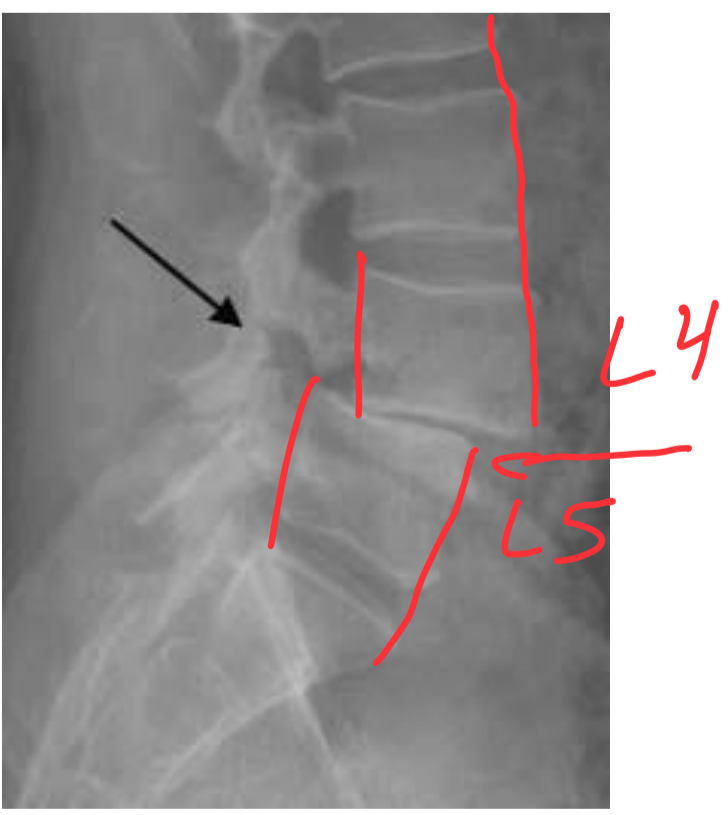
Spondylolysis
The dissolution of a vertebra, such as from aplasia (lack of development) of the vertebral arch and separation of the pars interarticularis of the vertebra.
Scottie dog neck appears broken
most common at L4 or L5
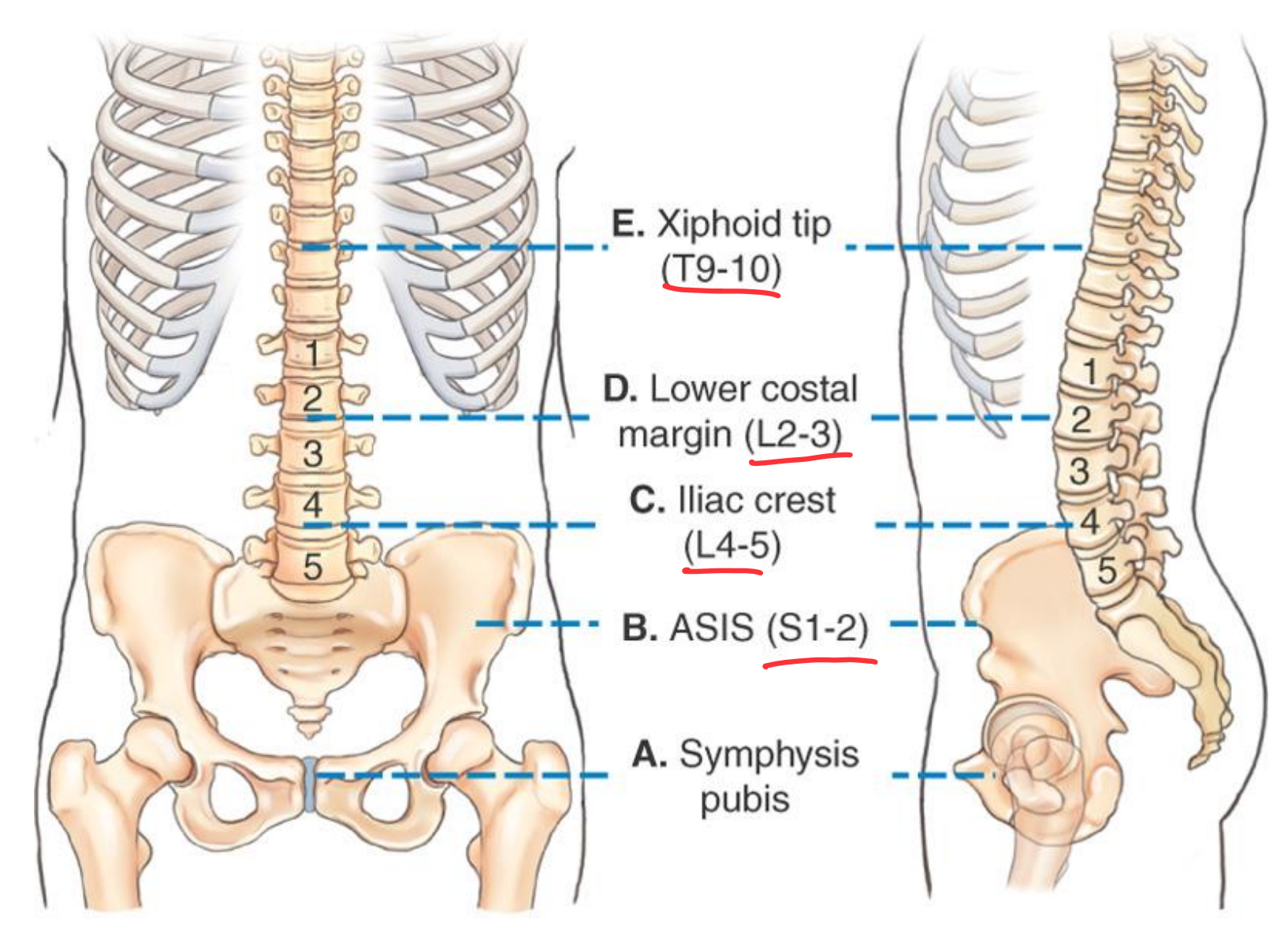
Lumbar Spine Topographical landmarks
AP Lumbar Spine Clinical Indications
Pathology of the lumbar vertebrae, including fractures, scoliosis, and neoplastic processes
AP Lumbar Spine
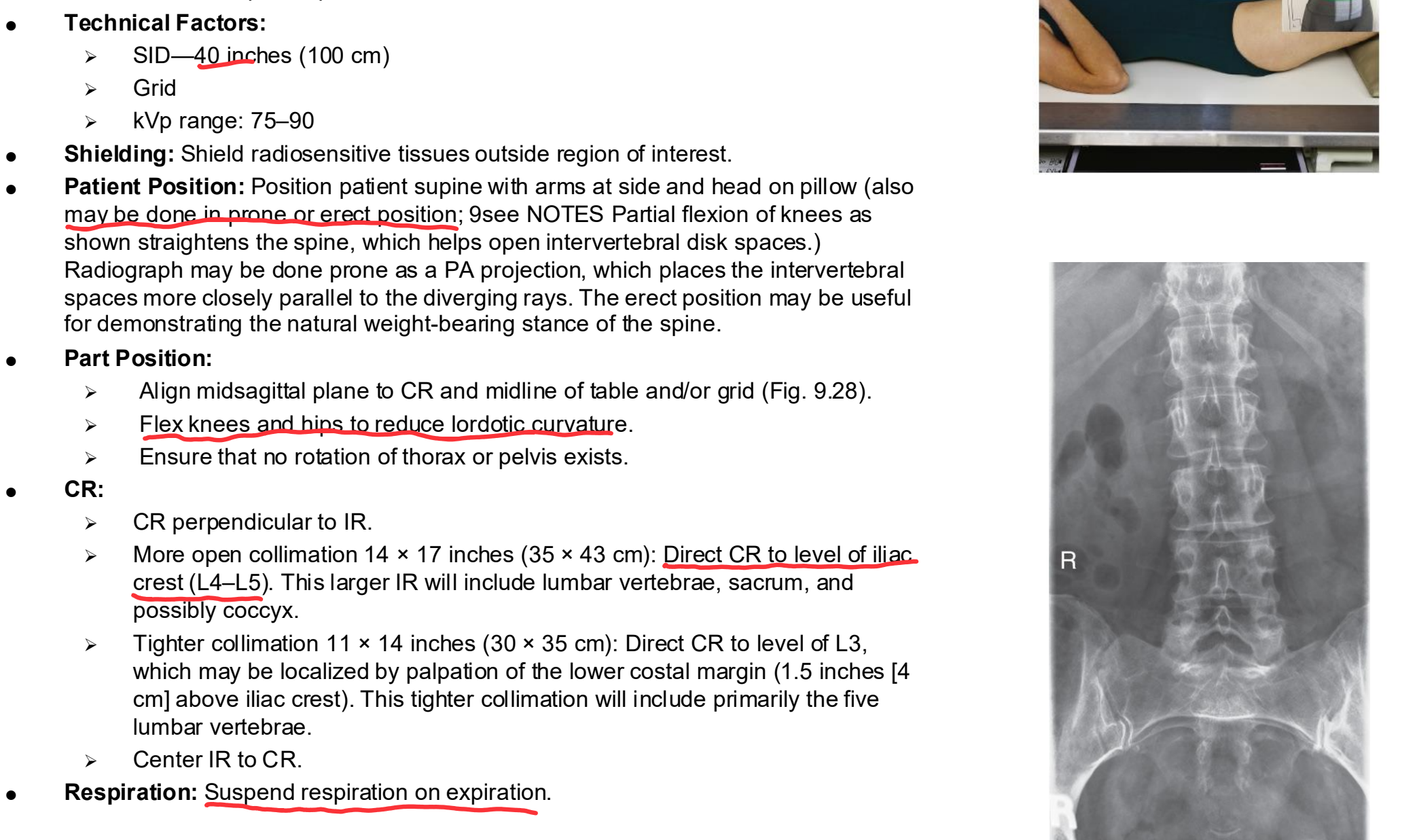
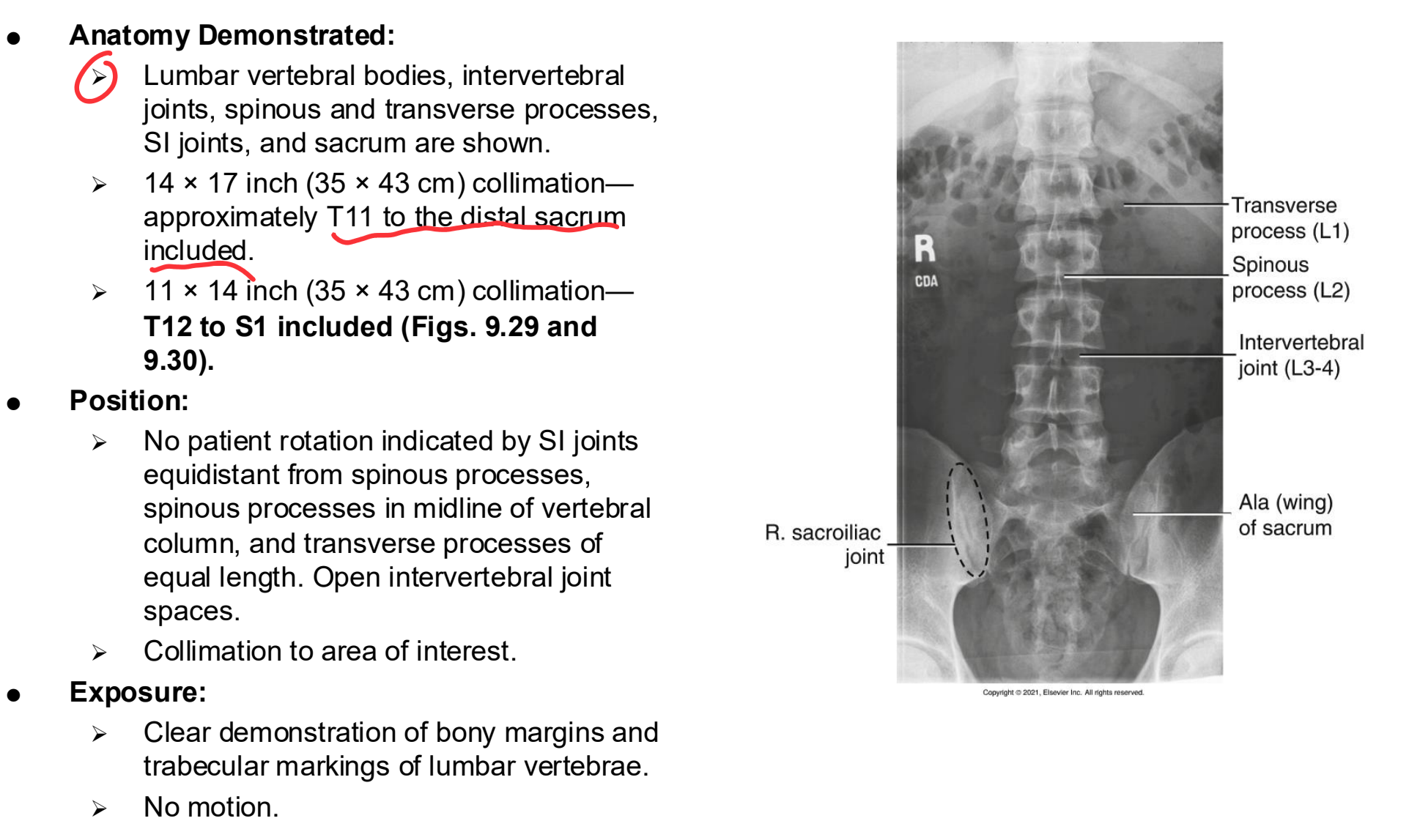
AP/PA Lumbar Spine Eval Criteria
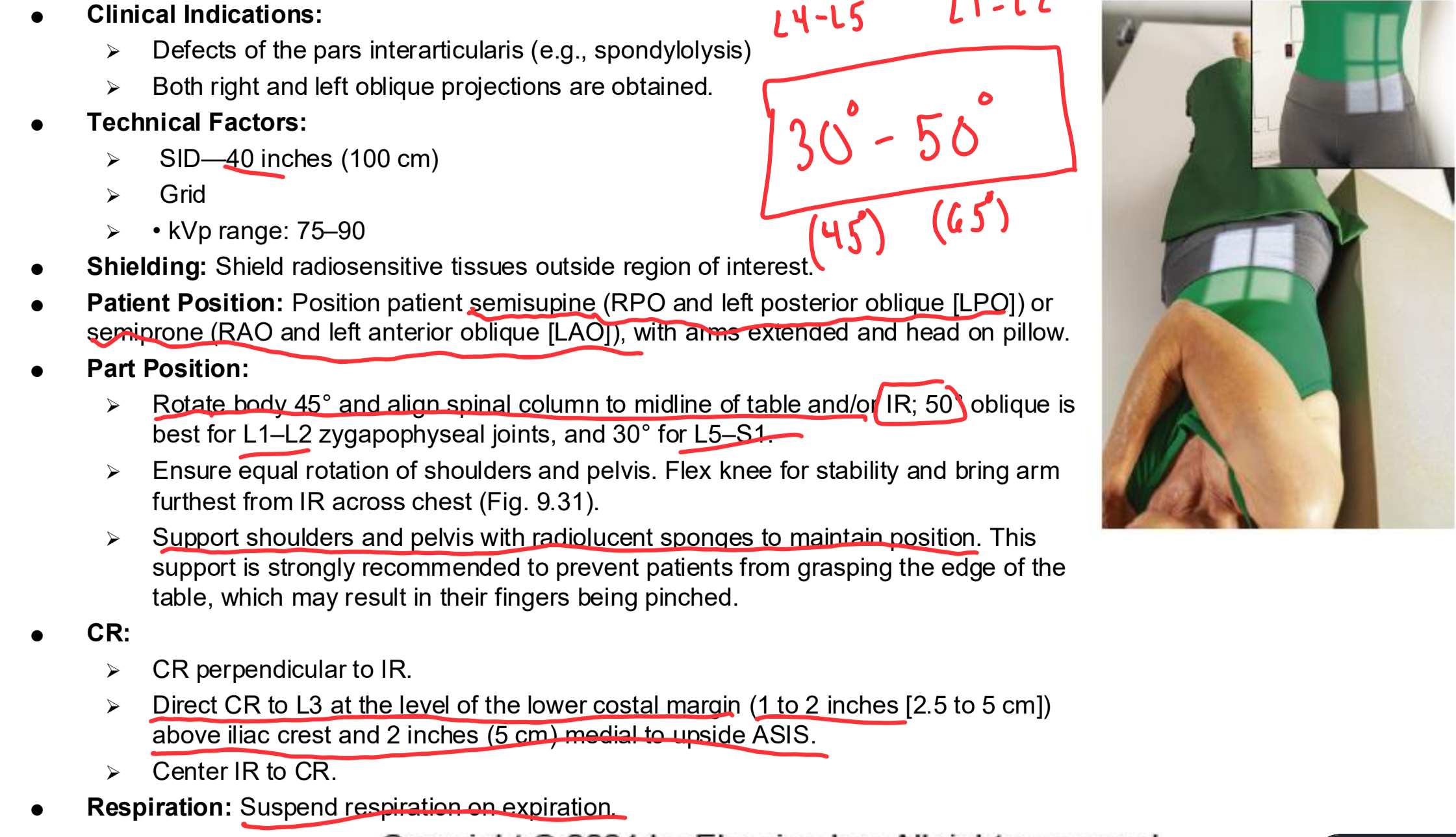
Oblique Lumbar Spine Clinical Indications
Defects of the pars interarticularis (e.g., spondylolysis)
Both right and left oblique projections are obtained.
Oblique Lumbar Spine
Oblique Lumbar Spine Eval Criteria
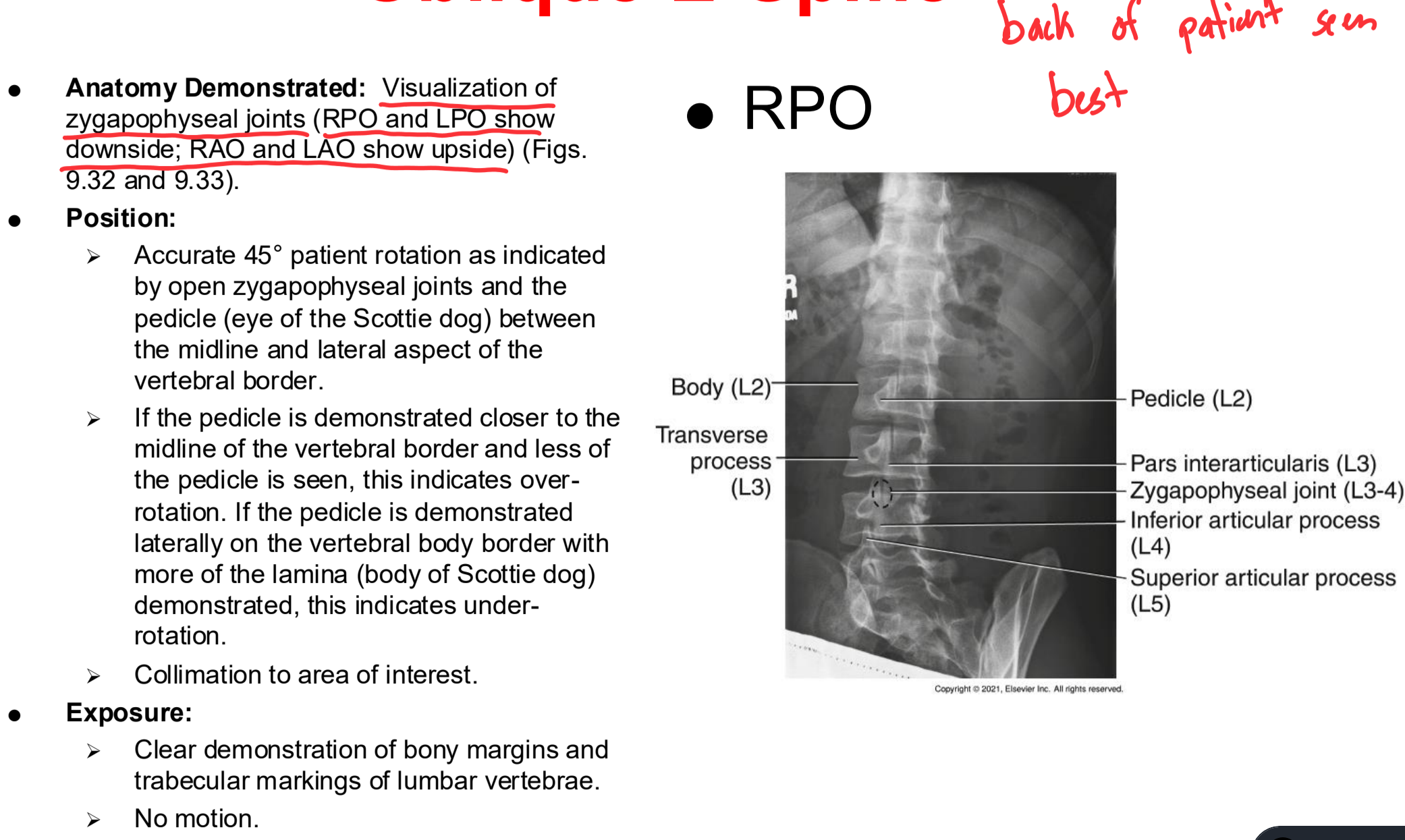
Lateral Lumbar Spine Clinical Indications
Pathology of the lumbar vertebrae including fractures, spondylolisthesis, neoplastic processes, and osteoporosis
Lateral Lumbar Spine

Lateral Lumbar Spine Eval Criteria
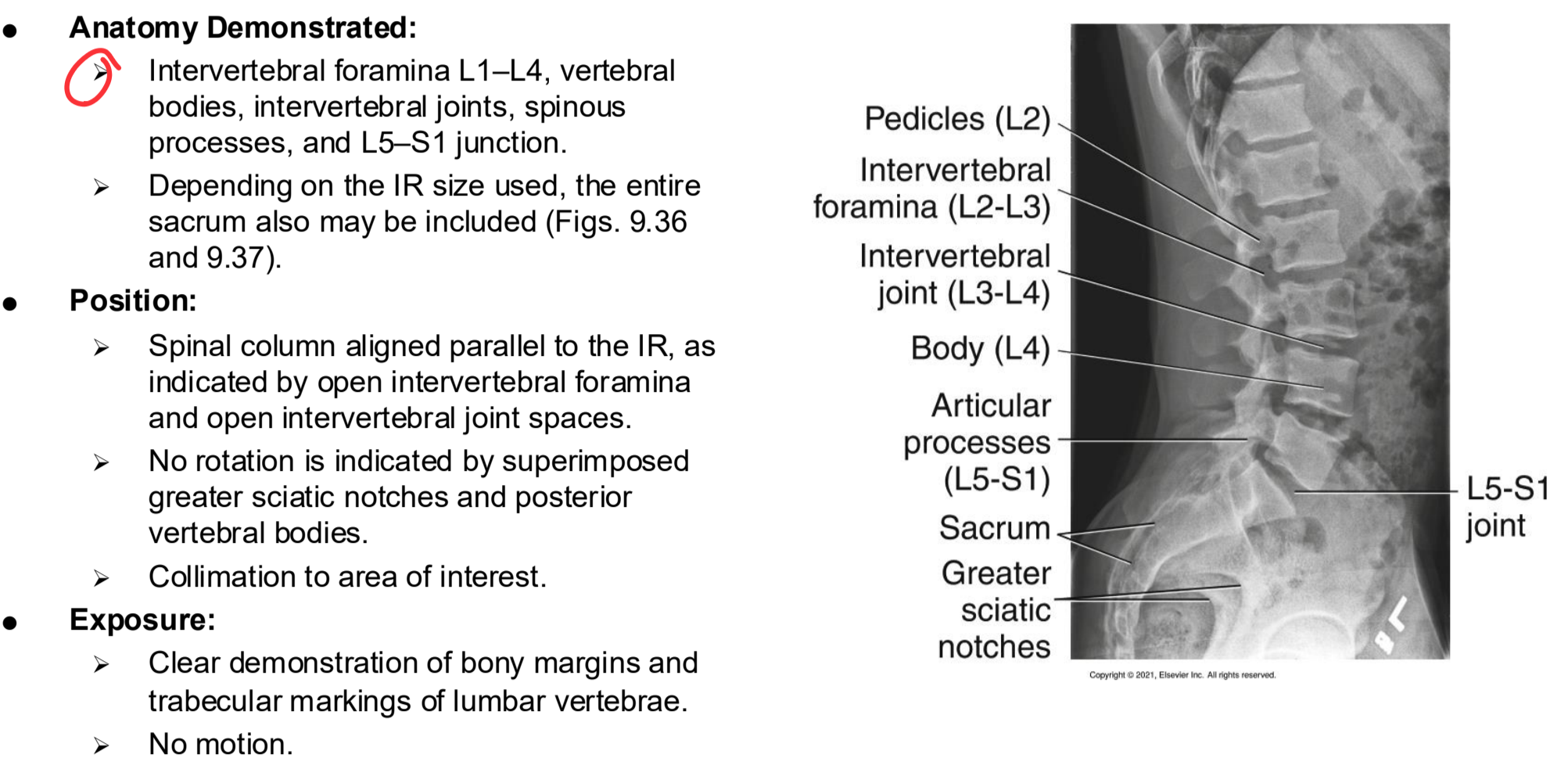
Lateral L5-S1 Clinical Indications
Spondylolisthesis involving L4–L5 or L5–S1 and other L5–S1 pathologies
Lateral L5-S1

Lateral L5-S1 Eval Criteria
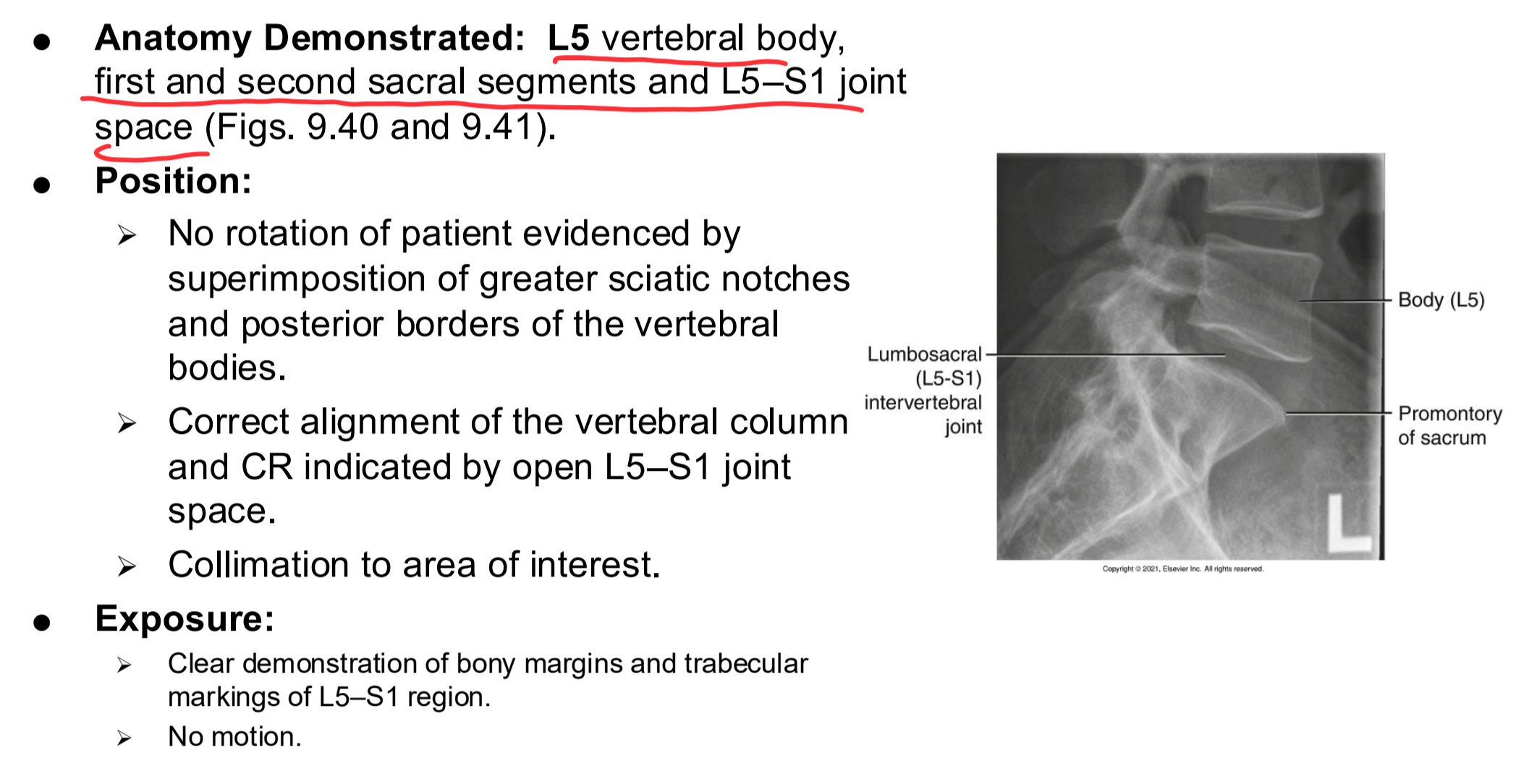
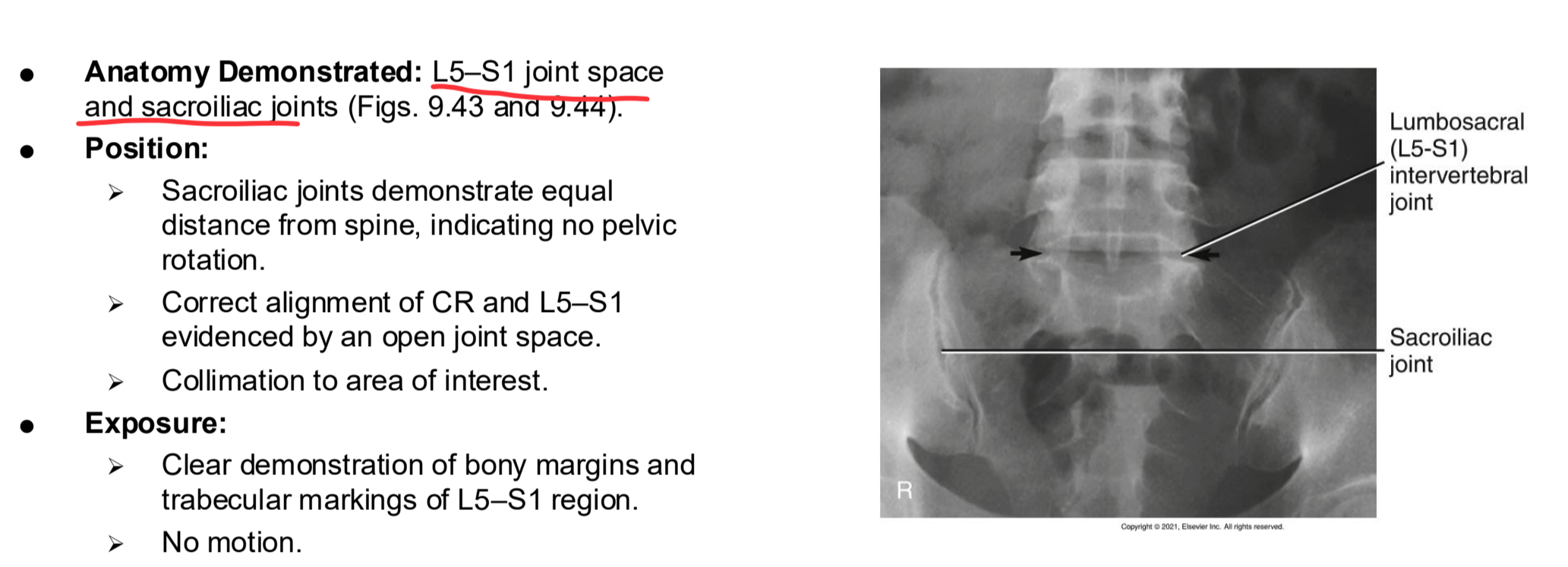
AP Axial L5-S1 Clinical Indications
Pathology of L5–S1 and the sacroiliac joints
AP Axial L5-S1
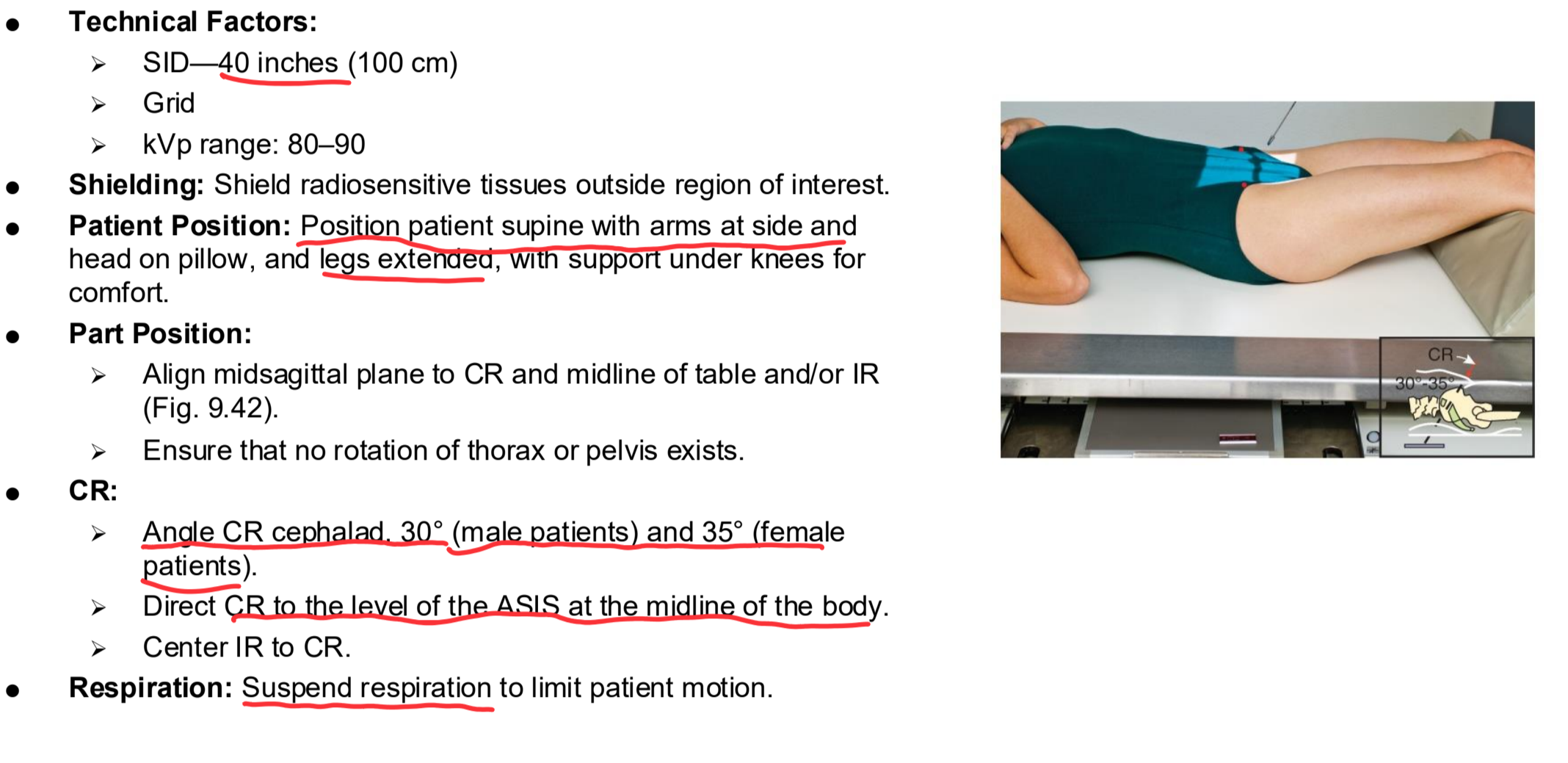
AP Axial L5-S1 Eval Criteria
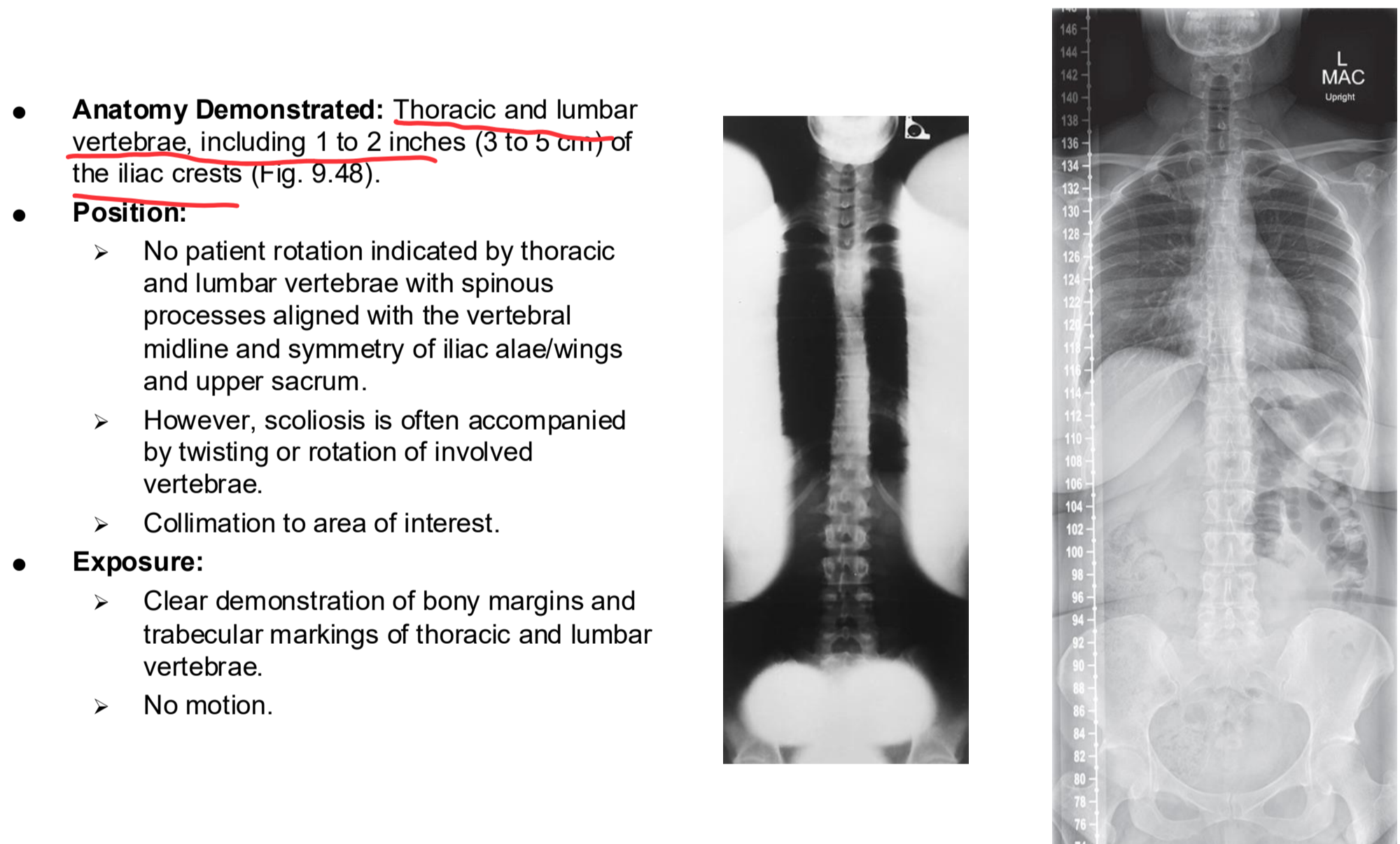
PA/AP Scoliosis Series Clinical Indications
To determine the degree and severity of scoliosis
A scoliosis series may include two PA projections taken for comparison, one erect and one recumbent
A PA rather than an AP projection is highly recommended because of the significantly reduced dose to radiation-sensitive areas, such as the female breasts and thyroid gland. Studies have shown that this projection results in approximately 90% reduction in dosage to the breasts. 4
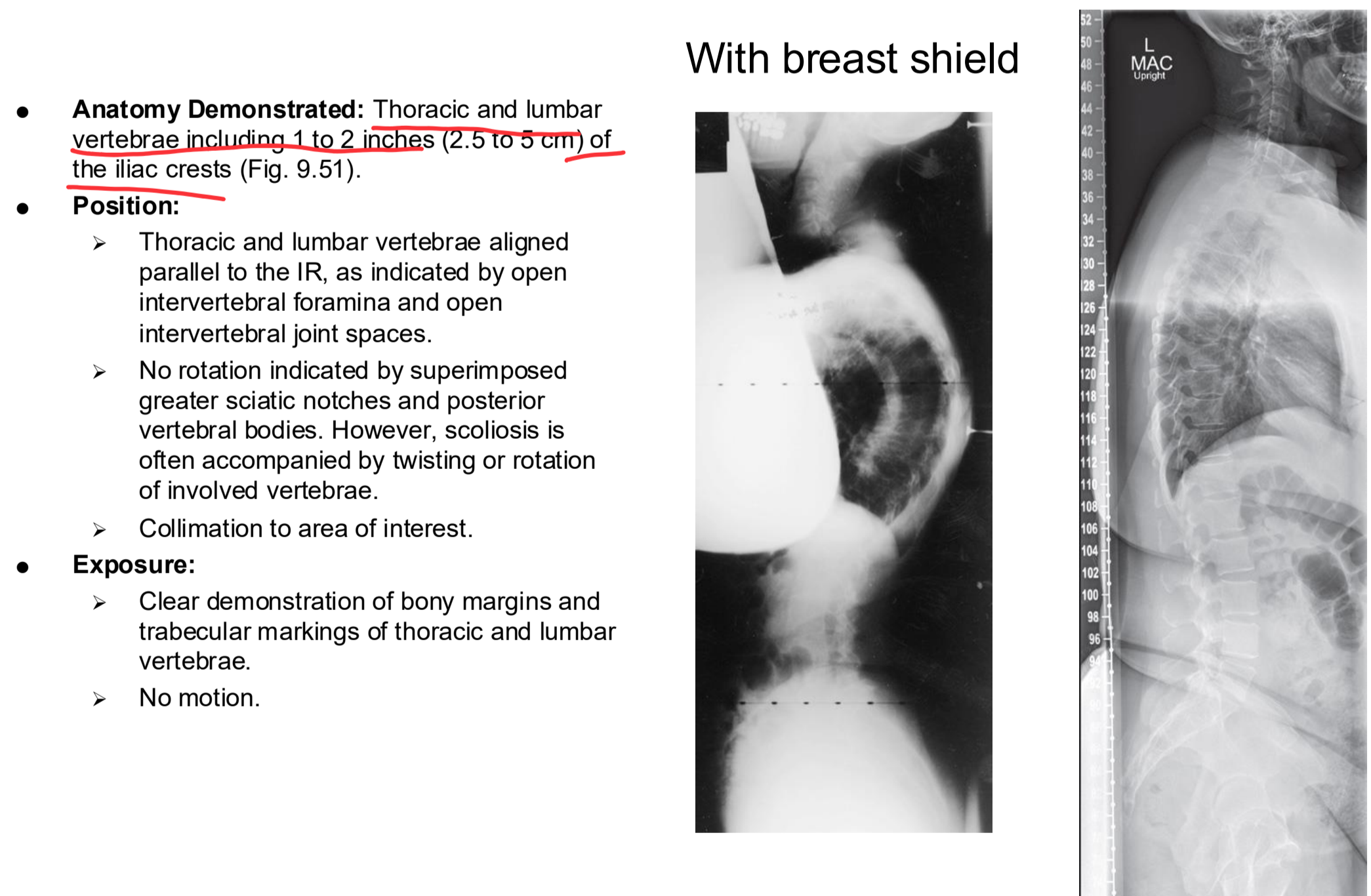
Scoliosis generally requires repeat examinations over several years, especially for pediatric patients. Measures should be taken to provide careful shielding. Fig. 9.46 demonstrates an example of shielding that can be used during a scoliosis series. Fig. 9.47 demonstrates the radiographic appearance with the use of shielding.
PA/AP Scoliosis Series

PA/AP Scoliosis Series Eval Criteria
Erect Lateral Scoliosis Series Clinical Indications
Spondylolisthesis, degree of kyphosis, or lordosis
Erect Lateral Scoliosis Series

Erect Lateral Scoliosis Series Eval Criteria
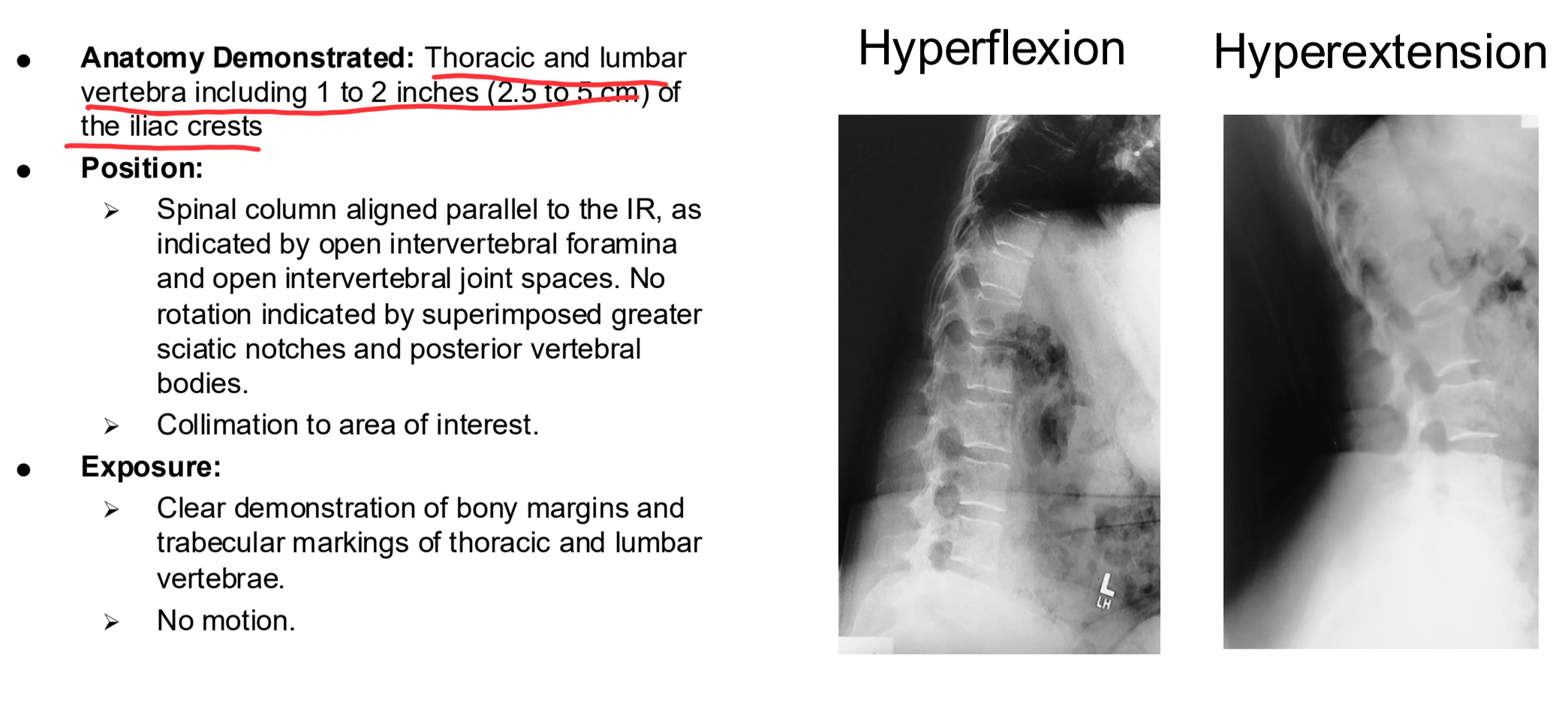
Lateral Spinal Fusions Series: Hyperflex and Hyperextens Clinical Indications
Assessment of mobility at a spinal fusion site
Lateral Spinal Fusions Series: Hyperflex and Hyperextens

Lateral Spinal Fusions Series: Hyperflex and Hyperextens Eval Criteria
AP Axial Sacrum Clinical Indications
Pathology of the sacrum, including fracture
NOTE: The urinary bladder should be emptied before this procedure begins. It is also desirable to have the lower colon free of gas and fecal material, which may require a cleansing enema, as ordered by a physician
AP Axial Sacrum

AP Axial Sacrum Eval Criteria
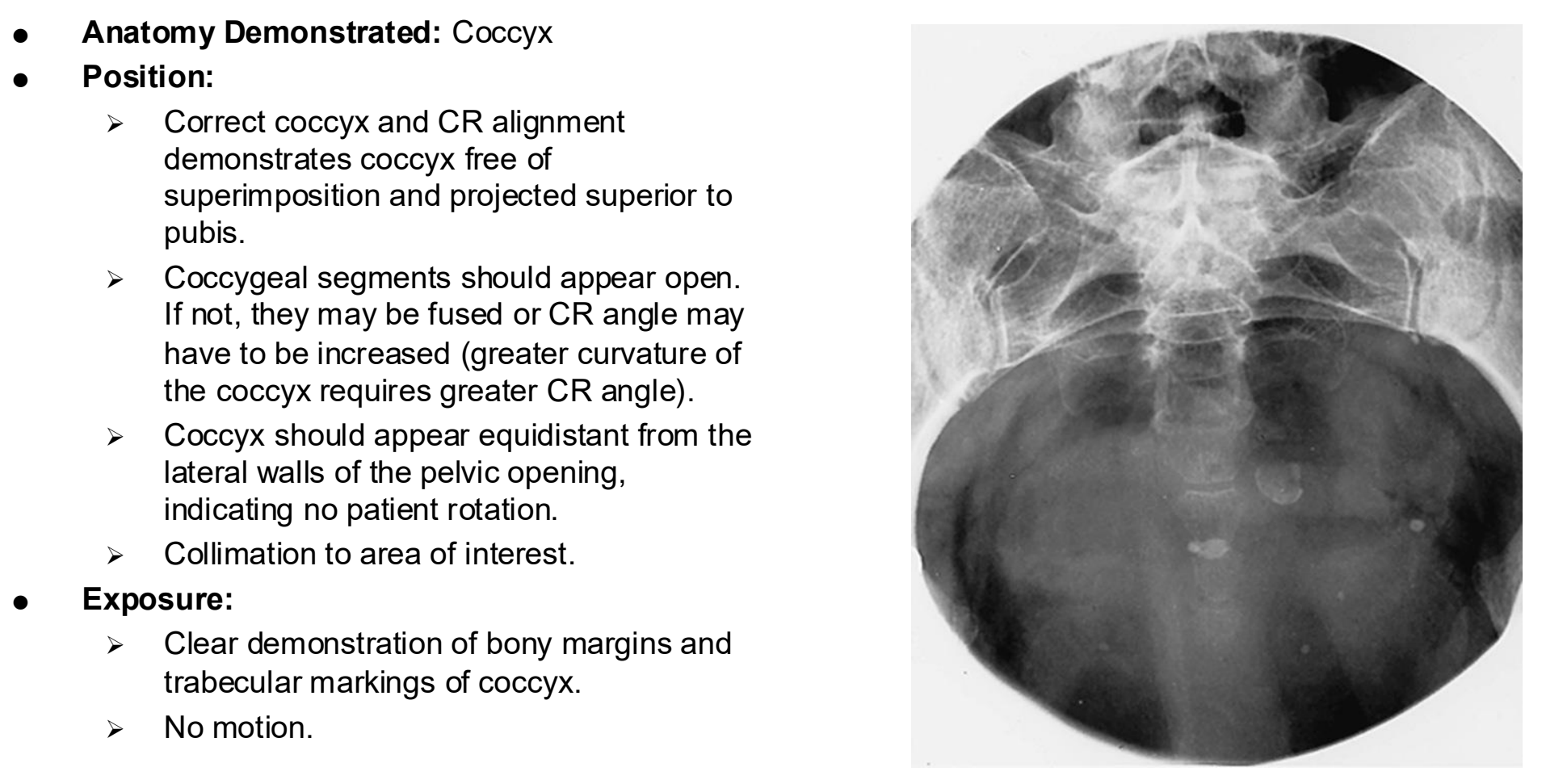
AP Axial Coccyx Clinical Indications
Pathology of the coccyx including fracture
NOTE: The urinary bladder should be emptied before this procedure begins. It is also desirable to have the lower colon free of gas and fecal material, which may require a cleansing enema, as ordered by a physician.
AP Axial Coccyx

AP Axial Coccyx Eval Criteria
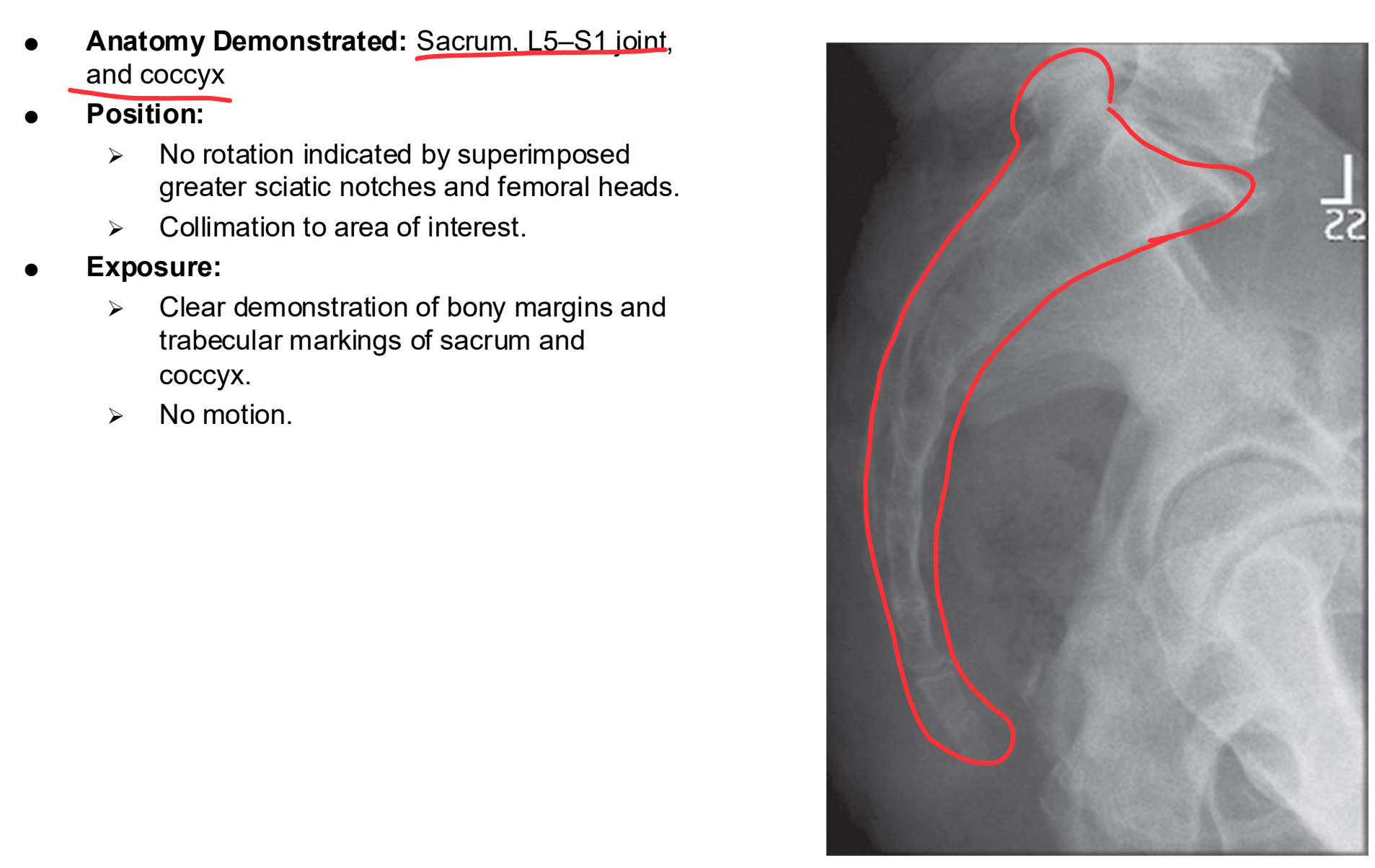
Lateral Sacrum and Coccyx Clinical Indications
Pathology of the sacrum and coccyx, including fracture
NOTE:The sacrum and coccyx are commonly imaged together. Separate AP projections are required because of different CR angles, but the lateral projection can be obtained with one exposure centering to include both the sacrum and coccyx. This projection is recommended to decrease gonadal doses.
Lateral Sacrum and Coccyx

Lateral Sacrum and Coccyx Eval Criteria
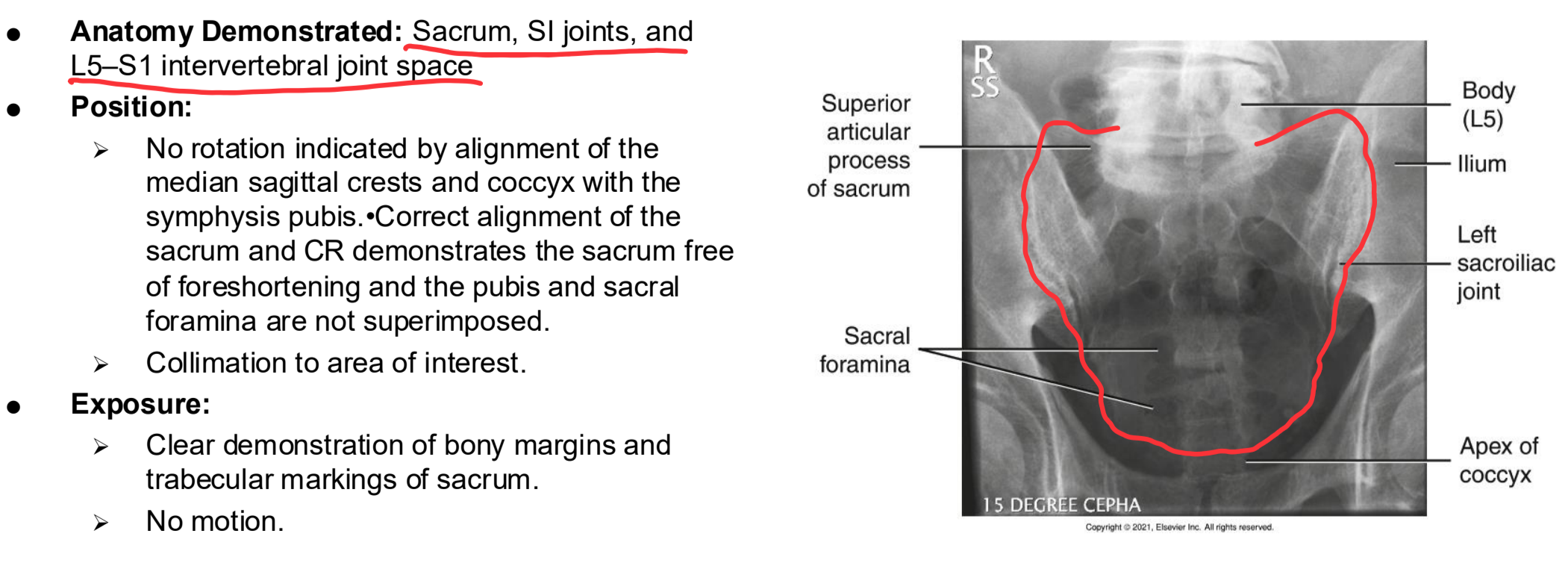
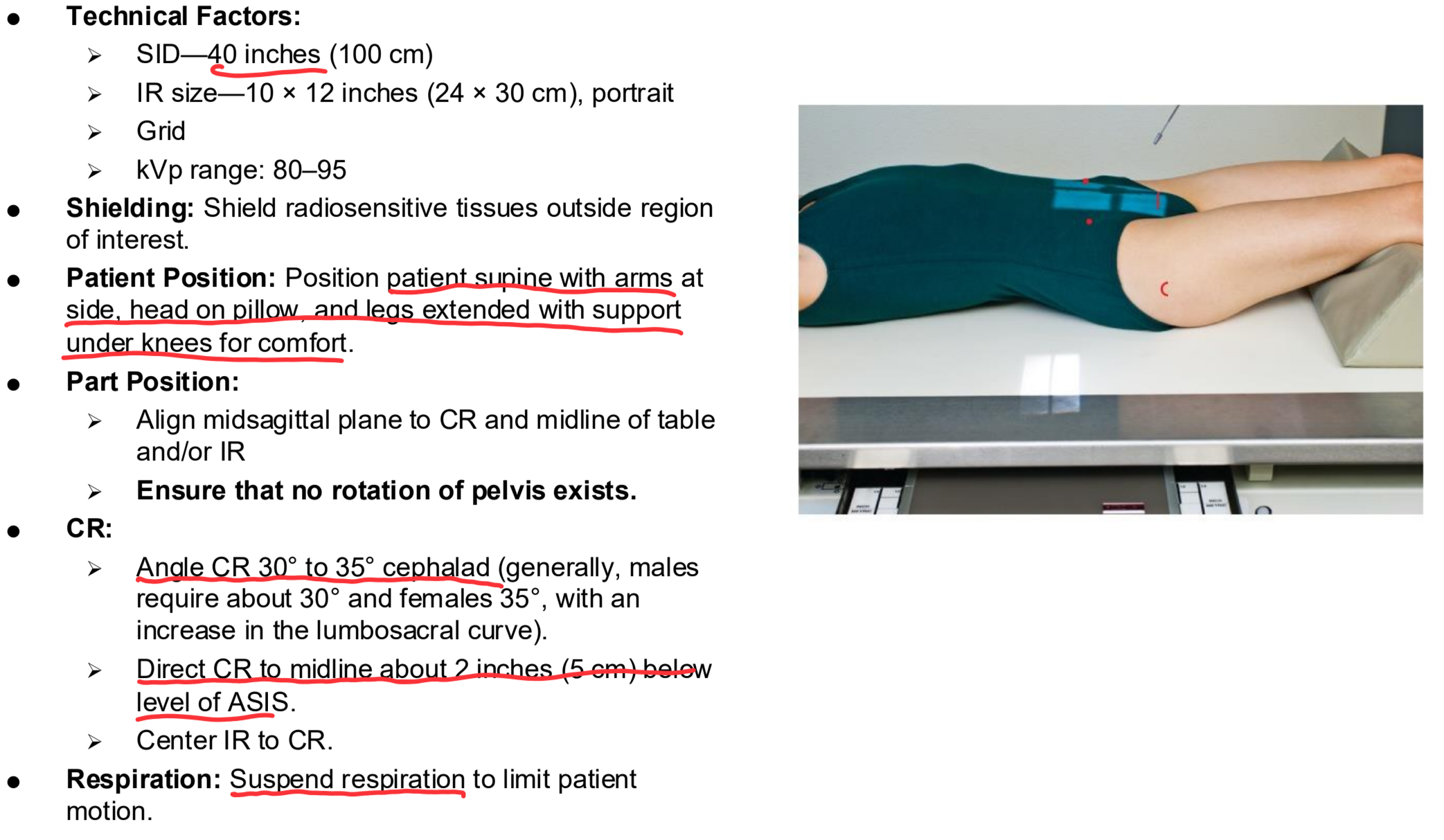
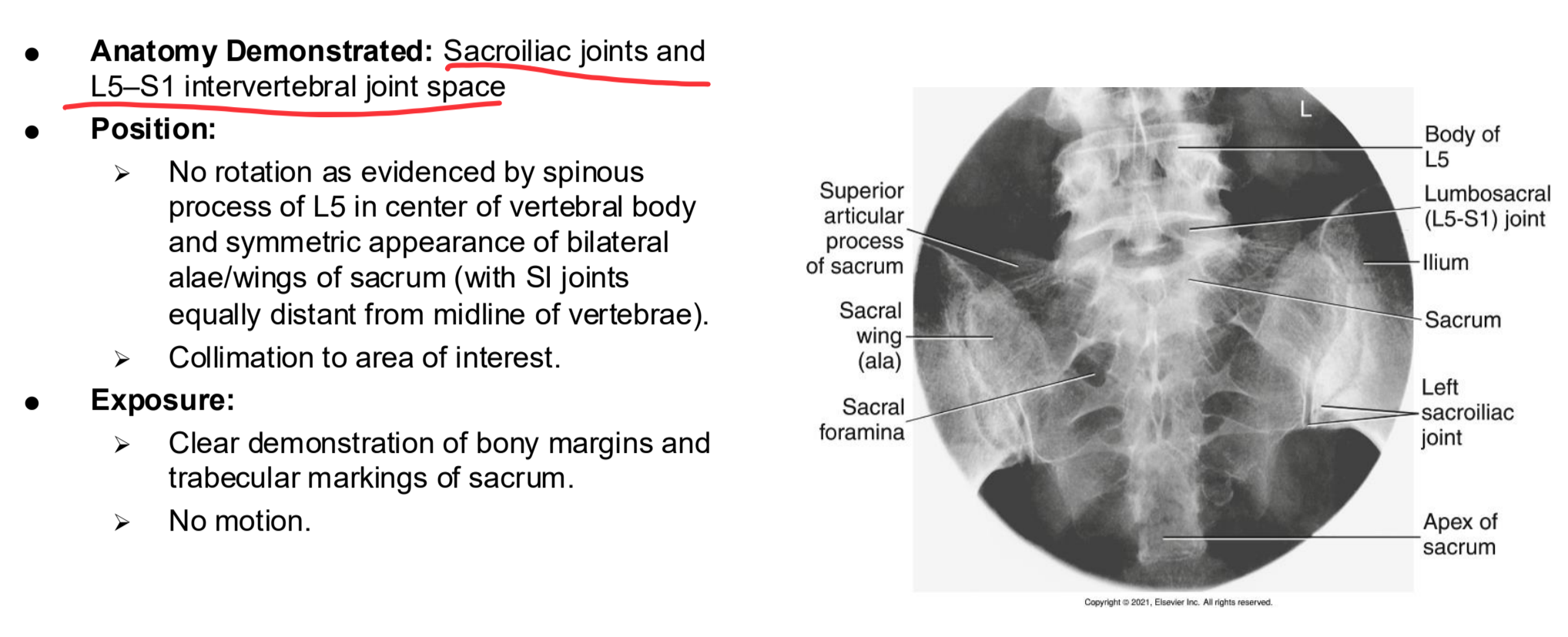
AP Axial SI Joints Clinical Indications
Pathology of the SI joint, including fracture and joint dislocation or subluxation
AP Axial SI Joints
AP Axial SI joints Eval Criteria
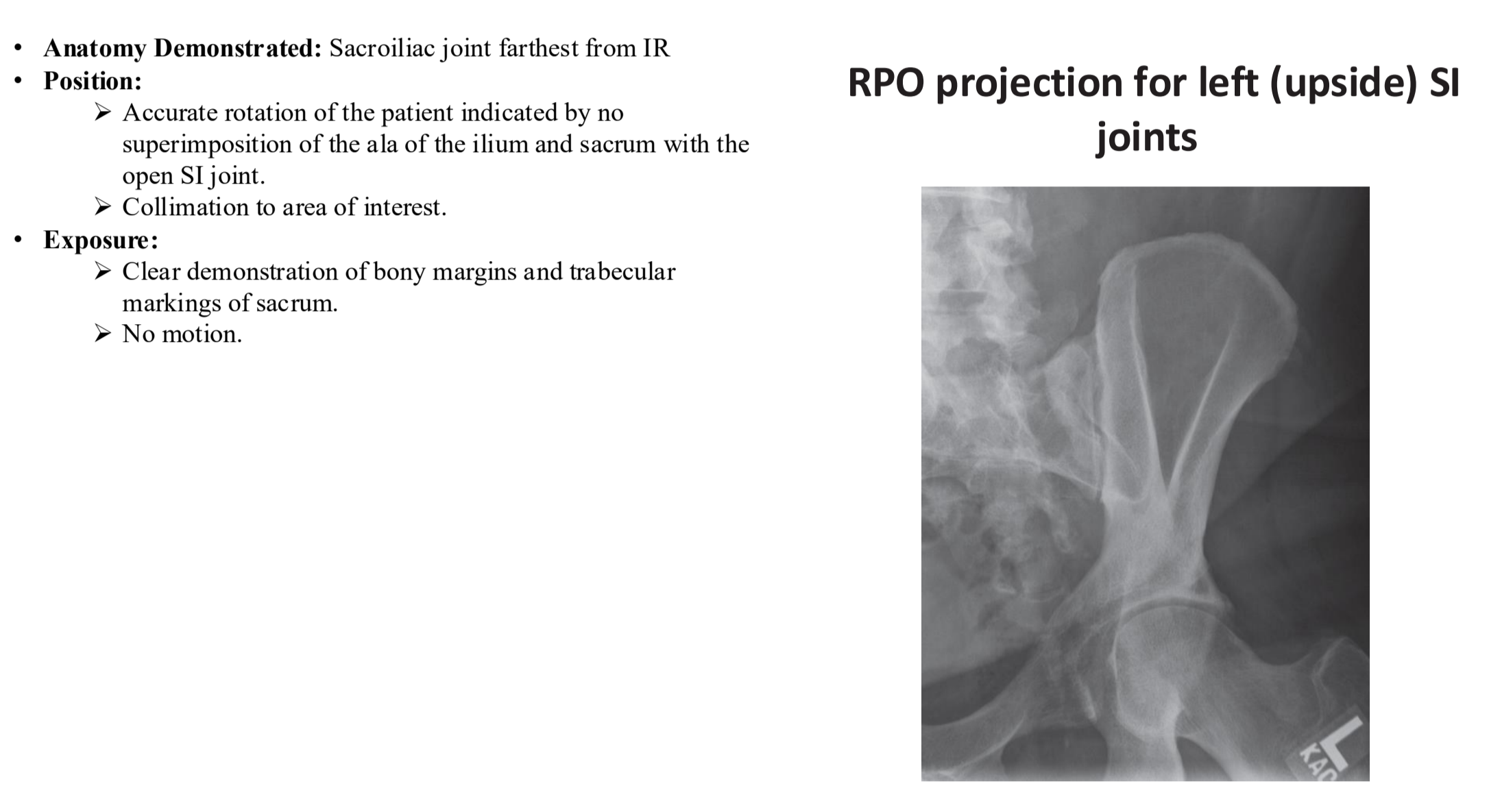
Posterior Oblique SI Joint Clinical Indications
Pathology of the SI joint, including dislocation or subluxation
Bilateral study for comparison
Posterior Oblique SI Joint

Posterior Oblique SI Joint
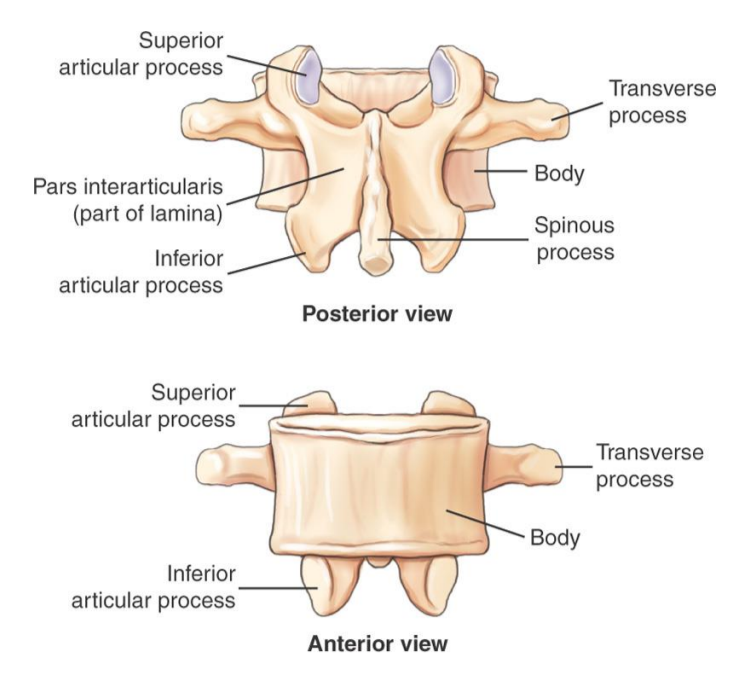
Typical Lumbar Vertebra (Lateral)
Typical lumbar Vertebra (Superior View)
Typical Lumbar View (posterior and Anterior)
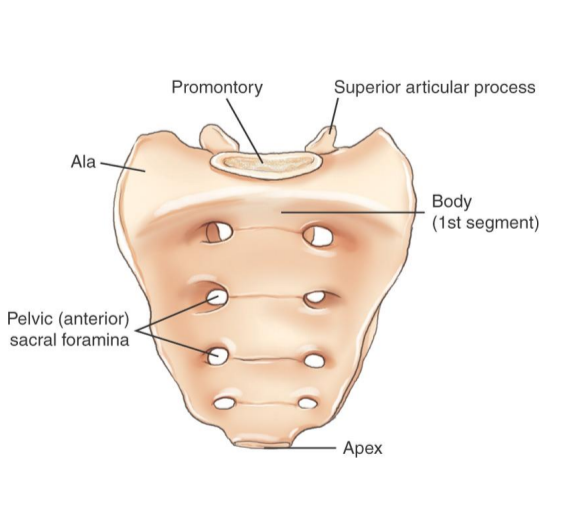
Sacrum (anterior view)
concave from the front
Lateral Sacrum and Coccyx
concave from anterior
convex from posterior
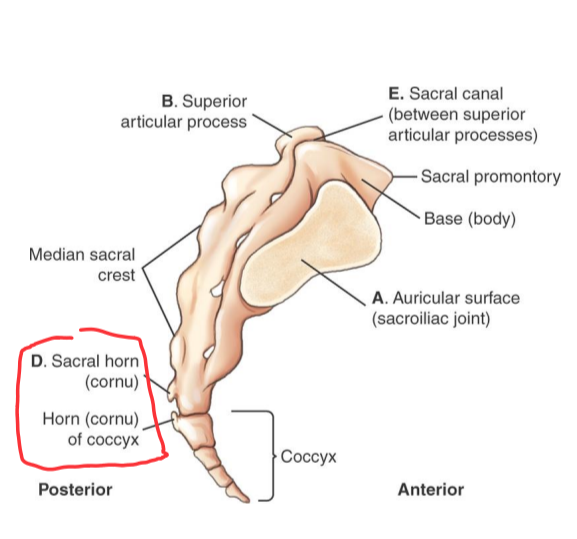
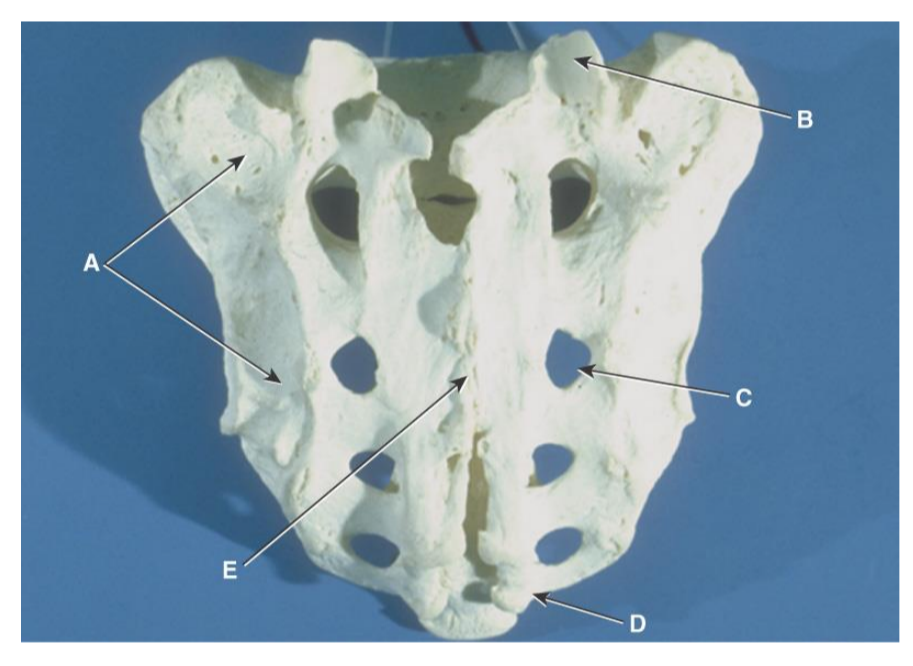
Sacrum Anatomy Review (posterior)
A. Auricular Surface
B. articulating facets of the superior articular processes
C. posterior sacral foramina
D. sacral horns
E. enclosed sacral canal
Coccyx (anterior)
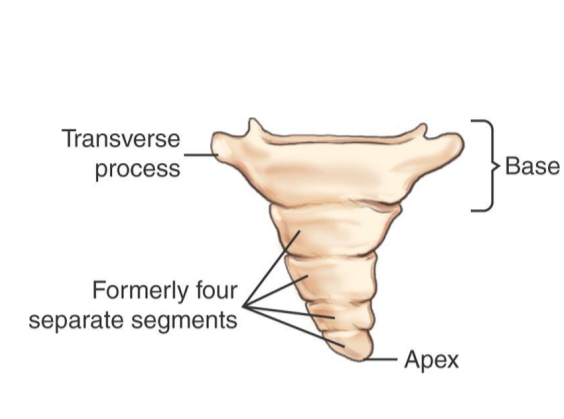
Male vs female Coccyx
female coccyx more vertical
female coccyx more prone to fracture
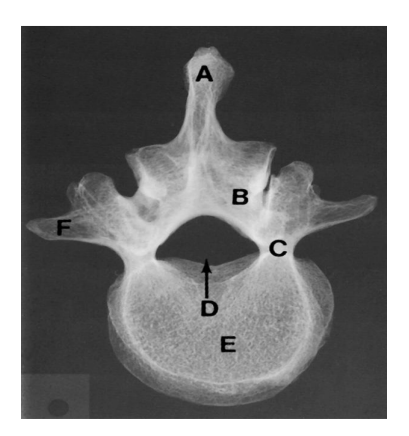
Lumbar Vertebra Anatomy Review (Superoinferior)
A. Spinous process
B. Lamina
C. Pedicle
D. Vertebral foramen
E. Body
F. Transverse process
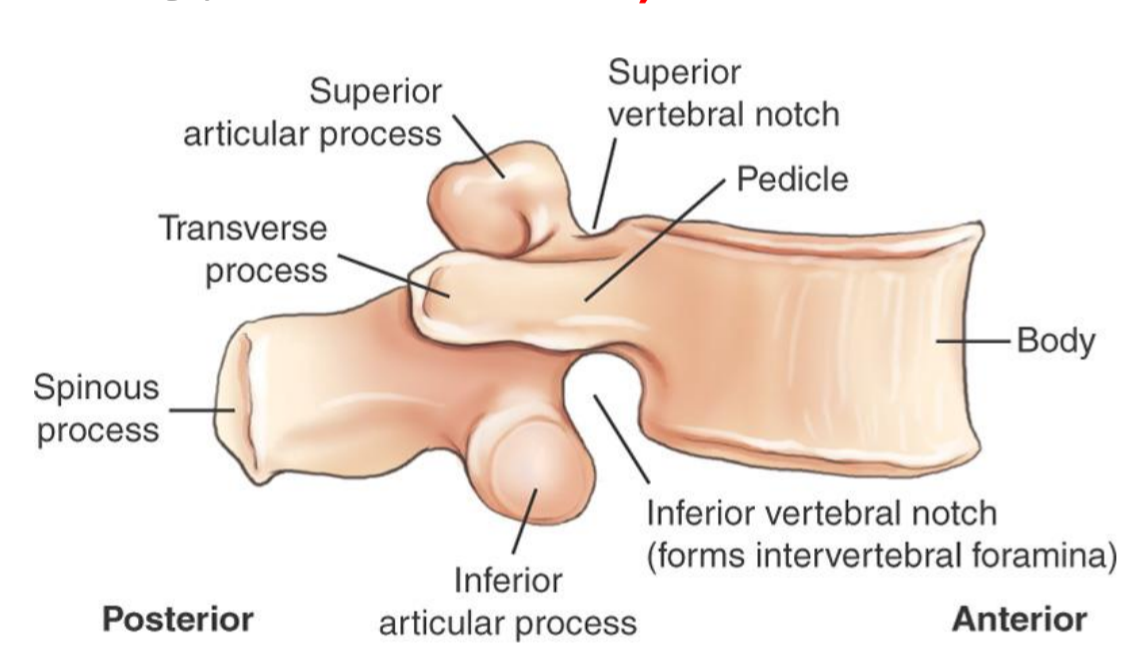
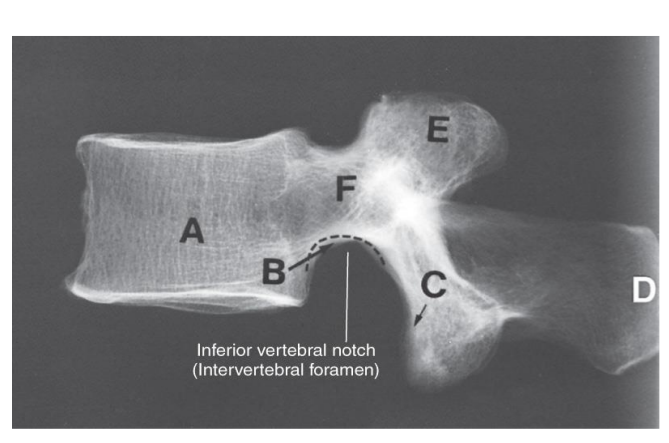
Lumbar Vertebra Anatomy Review (lateral)
A. Body
B. inferior vertebral notch
C. Inferior articular process
D. Spinous process
E. Superior articular process
F. Pedicle
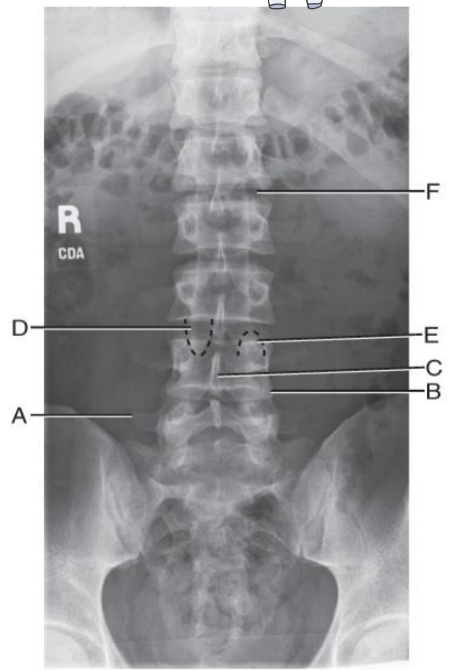
Anatomy Review AP lumbar spine
A. Right transverse process of of L5
B. Lower lateral portion of body of L4
C. Spinous process of L4
D. Right inferior articular process of L3
E. Left superior articular process of L4
F. L1-L2 intervertebral disk space
Anatomy Review Lateral Lumbar Spine
A. Body of L1
B. Body of L3
C. L4-L5 Intervertebral disk space
D. Body of L5
E. L1-L2 intervertebral foramen
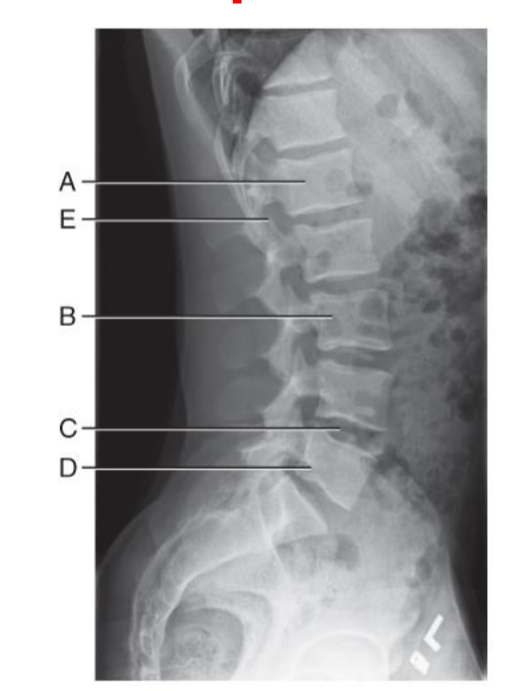
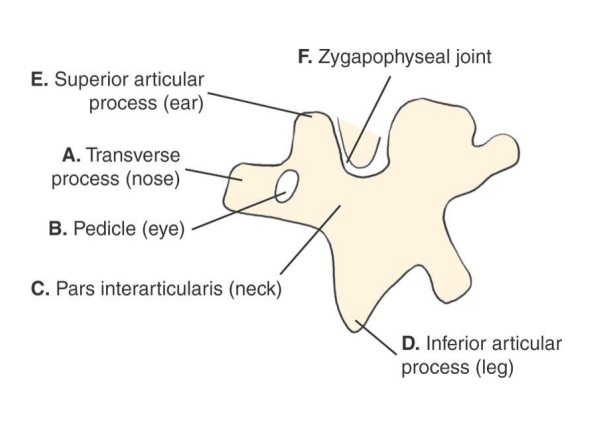
Scottie Dog Anatomy Diagram
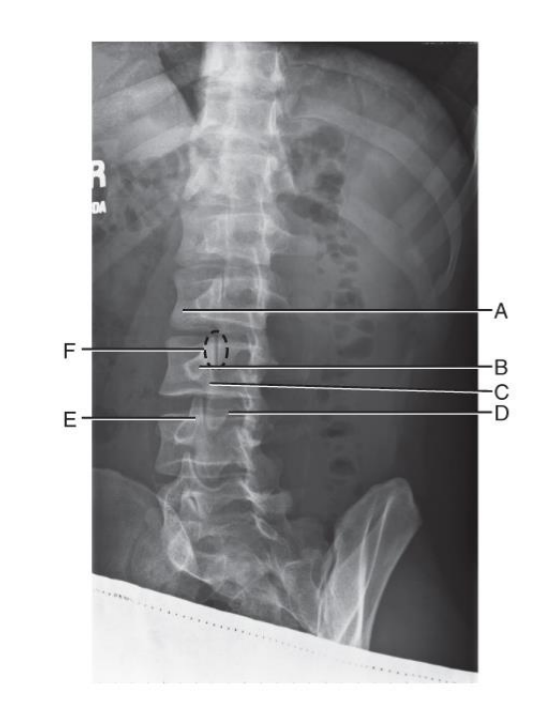
Scottie Dog Radiograph Review
A. transverse process (nose of scottie dog)
B. pedicle (eye of scottie dog)
C. pars interarticularis (neck of scottie dog)
D. inferior articular process (front leg of scottie dog)
E. superior articular process (ear of scottie dog)
F. zygapophyseal joint (union of front leg of above scottie dog with ear of below scottie dog)
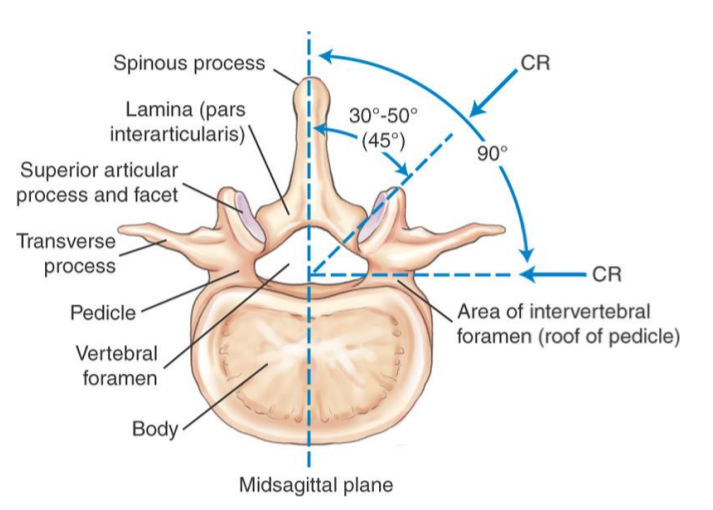
Vertebral Angle Summary