Hydration and Sleep
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Why is water good for our body?
Maintains blood volume, transport nutrients, remove body waste products, regulates body temp by absorbing heat
What do we intake water through?
Food and beverages
How does water loss occur?
Respiratory loss, Insensible perspiration, sweat, urinary loss, gastrointestinal tract water loss, fecal loss
The need for water is influenced by what factors?
Body size, age, physical activity, heat and altitude, health status, medications and supplements
What is the average water intake for women?
2.7L
What is the average water intake for men?
3.7L
Intake sources of water?
81% beverages, 19% food

Water Gain
Food and Bevs 2.2L/day, metabolic fnx 250-350ml/day
Lungs are loosing
-250 to -350ml
Insensible perspiration loosing
-450 to -1900
Urine loosing
-500 to -1000
Feces loosing
-100 to -200
What happens with dehydration during exercise?
A decrease in blood pressure leads to vasoconstriction, which leads to an increase in blood pressure, then increases sodium retention, which then leads to water retention
What are Electrolytes?
Minerals in the body with an electrical charge, (ions)
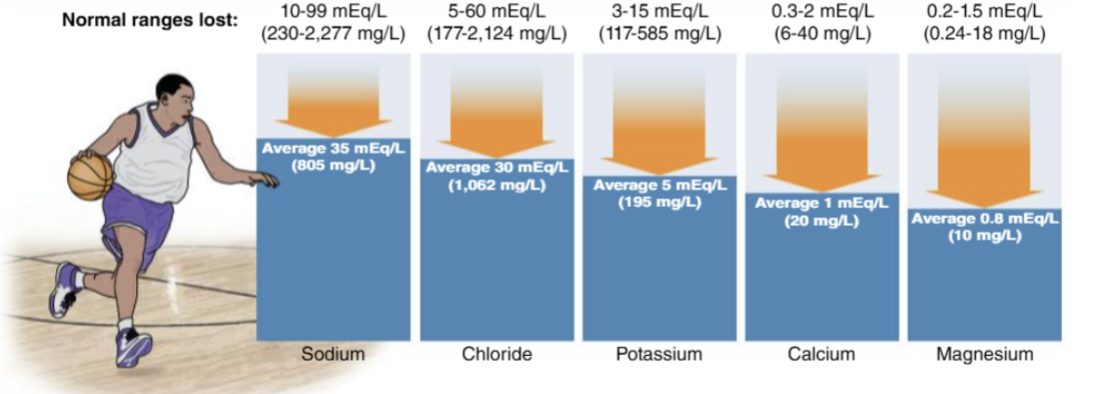
What are the main electrolytes?
Sodium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, calcium
What are the main functions of electrolytes?
Essential for muscle contraction and nerve conduction, maintains fluid levels through concentration gradients, maintains total fluid levels, so when concentration increases, this stimulates thirst!
What happens when dehydration occurs?
Causes a drop in blood volume, stretch receptors in blood vessel signal ADH and thirst
How does the body compensate for dehydration?
Blood vessels constrict, water in the kidneys is reabsorbed, release of antidiuretic hormone
What is the purpose of diuretics?
Increase water/sodium loos through urination, some common types are coffee, tea, alcohol, meds
What are symptoms of dehydration?
Increase body temp, decrease sweat rate, decrease BP, hast heart rate, sunken eyes, dizziness
What happens when you drink alcohol?
Decreases ADH production, going to cause more urine production and increase dehydration
What is Hyper hydration?
Over hydration, rare, cause edema and hyponatremia
Symptoms of hyper hydration
Confusion, inattentiveness, blurred vision, muscle cramps
What percent fluid loss can impair exercise performance?
1-3%
How much should athletes drink to reduce BW loss to?
<2%
What can sweat loss range from?
0.3>4L/hr
What can sodium loss range from?
230 to >2000mg/L
What does dehydration lead too?
Decreased sweat rate, blood volume, BP, memory, conentration
Different assessments for dehydration
Urine, body weight before and after, sweat patches
Recommended water intake before exercise?
4 hours before the activity, drink enough to urinate 5-7ml/kg body weight
During exercise, average intake?
0.4-0.8L/h. 1.2L/Hr for people with extremely high sweat rates
What to do with significant sodium loss?
Replace with a sports drink containing sodium and carbohydrate
less than 30-60g carbohydrate/hour
Beverages should be cool but not cold
less than 8% carbohydrate
Replenishment after exercise?
Replenish 125-150% of fluid loss. 1.5 L / kg body weight loss
20-24oz per pound lost
Practical solutions for athletes to stay hydrated?
Drink from a 24-32oz water bottle each day
Set goals and timeframes to consume liquid throughout the day
Drink 16oz of liquid with every meal
Set phone reminders to drink 4-6oz
Try adding smoothies, juice-based popsicles, and soups to your diet
Factors of sleep that effect recuperative outcomes
Length, quality and phase
Sleep deprivation has been linked to what?
Decrease ANS resources
What factors can influence sleep quality?
Alcahol, caffeine
Dairy protein sources may increase what?
Sleep duration
Can large meals or meals close to sleep negatively impact
sleep quality?
Yes
What are two derivatives of trytophan?
Seratonin and melatonin, carbohydrates help
Increase in what influences tryptophan across the blood brain barrier?
Insulin
How many hours before bed can a high GI meal signifcantly reduce sleep latency by half?
4 hours
High Carb meals can increase what?
REM sleep and decrease light sleep
Melatonin
Displays sedative effects and influences core temperature
Night time milk
Night time milk has a higher percentage (39.42 pg/mL compared
to 4.03 pg/mL)
Antioxidants
Key for recovery and immunity, may postively impact sleep by decreasing inflamation (Tart Cherry)
B vitamins
B-vitamins play critical roles in the sleep hormone
maintance
◦B12 helps melatonin secreation
◦B6 helps synthesize serotonin
◦B3 helps spare tryptophan