Cell Junctions w/ ECMs
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the primary components of gap junctions?
connexins!
Plasmodesmata
allow plant cells to transfer RNA and proteins
much larger than gap junctions
cell membranes between two cells are continuous
allows plant cells to communicate despite cell wall
What is the singular form of Plasmodesmata?
Plasmodesma
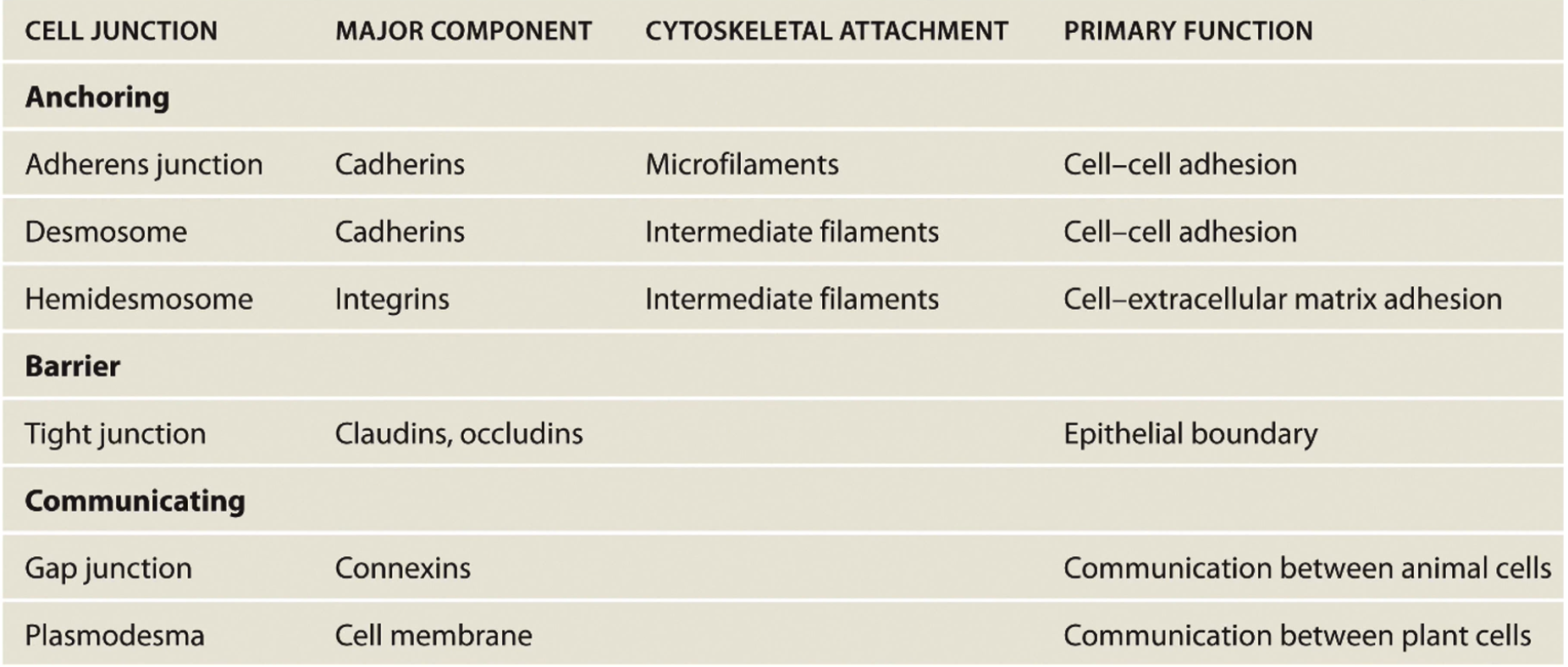
Summary: What are the Anchoring Cell Junctions?
Adherens junctions
Desmosome
Hemidesmosome
What are the major components of the Anchoring Cell Junctions?
Adherens junctions = Cadherines
Desmosome = Cadherines
Hemidesmosome = Integrins
What are the Cytoskeletal Attachments of the Anchoring Cell Junctions?
Adherens junctions = Microfilaments
Desmosome = Intermediate Filaments
Hemidesmosome = Intermediate Filaments
What are the Primary Function of the Anchoring Cell Junctions?
Adherens Junctions = Cell-cell Adhesion
Desmosome = Cell-cell Adhesion
Hemidesmosome = Cell-extracellular matrix adhesion
Summary: What are the Barrier Cell Junctions?
Tight Junctions
Summary: What are the Barrier Cell Junctions’ major component(s)?
claudins
occludins
Summary: What are the Barrier Cell Junctions’ primary function(s)?
Epithelial boundary
Summary: What are the Communication Cell Junctions?
Gap Junction
Plasmodesma
Summary: What are the Communication Cell Junctions’ major component(s)?
Gap Junction = Connexins
Plasmodesma = Cell Membrane
Summary: What are the Communication Cell Junctions’ primary function(s)?
Gap Junction = Animal cell comms
Plasmodesma = Plant cell comms
Summary Table
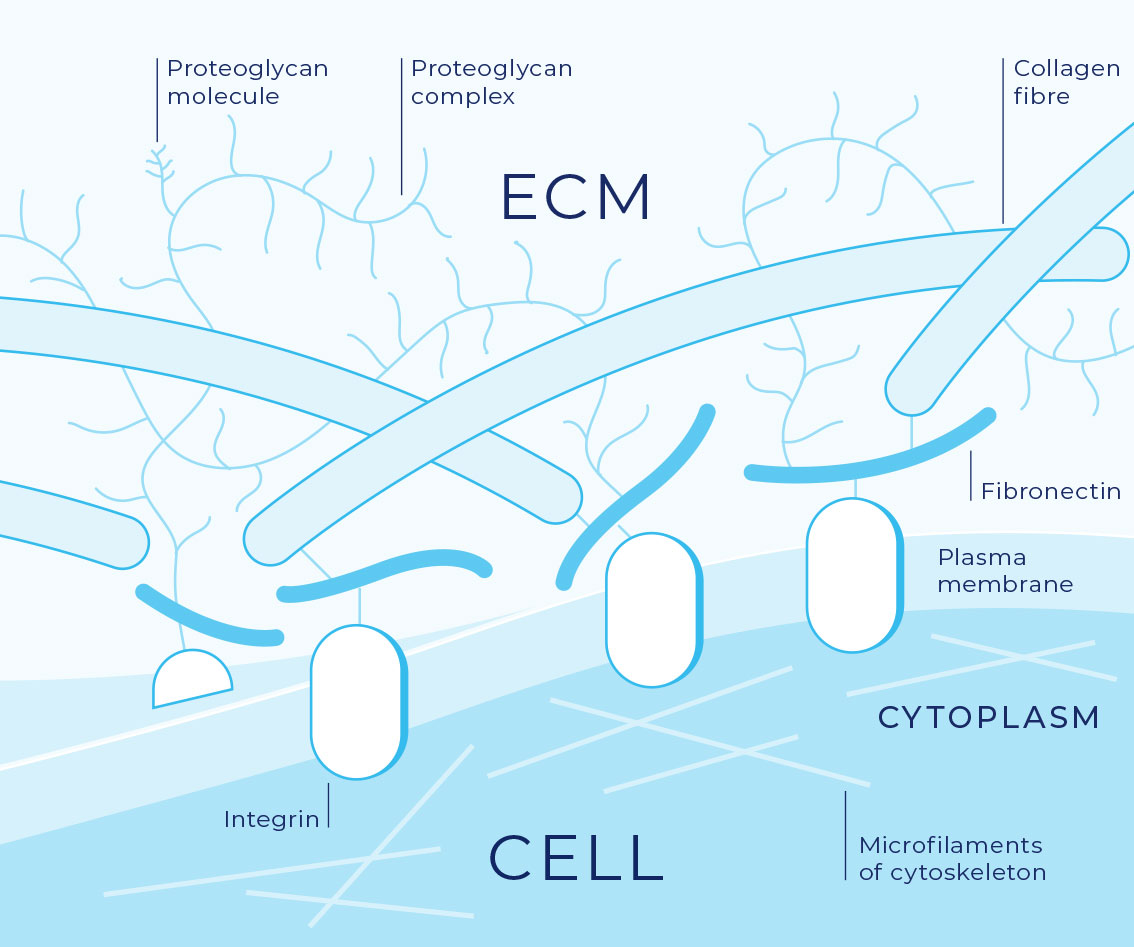
What is the ECM? Tell me about it.
Extracellular Matrix
layer of material secreted y region of cell membrane in extracellular matrix
formed from insoluble mix of proteins and polysaccharides
Two general functions:
act as a supportive & protective material
allow for expression of different cell functions
What in plants is a type of ECM?Tell me more.
cell wall
composed of 3 layers
What are the 3 layers of Plant ECMs?
Middle Lamella
Primary Cell Wall
Secondary Cell Wall
Tell me about the Middle Lamella
made of carbs
main mechanism by which plant cells adhere to one another
Tell me about the Primary Cell Wall
thin+flexible
made of cellulose fibres, pectin, and several other proteins
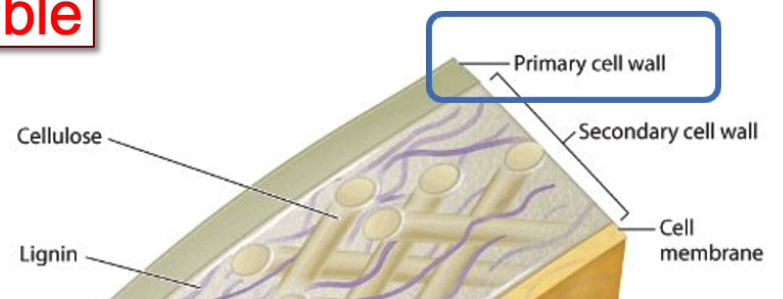
Tell me about the Secondary Cell Wall
rigid
made of cellulose and lignin
hardens cell wall and makes it water resistant
What about Animal ECM? Tell me about that
connective tissue is extensive in ECM
mixture of proteins and polysaccharides secreted by cells
composed of large fibrous proteins
including collagen, elastin and laminin
these proteins are found in gel-like polysaccharide matrix
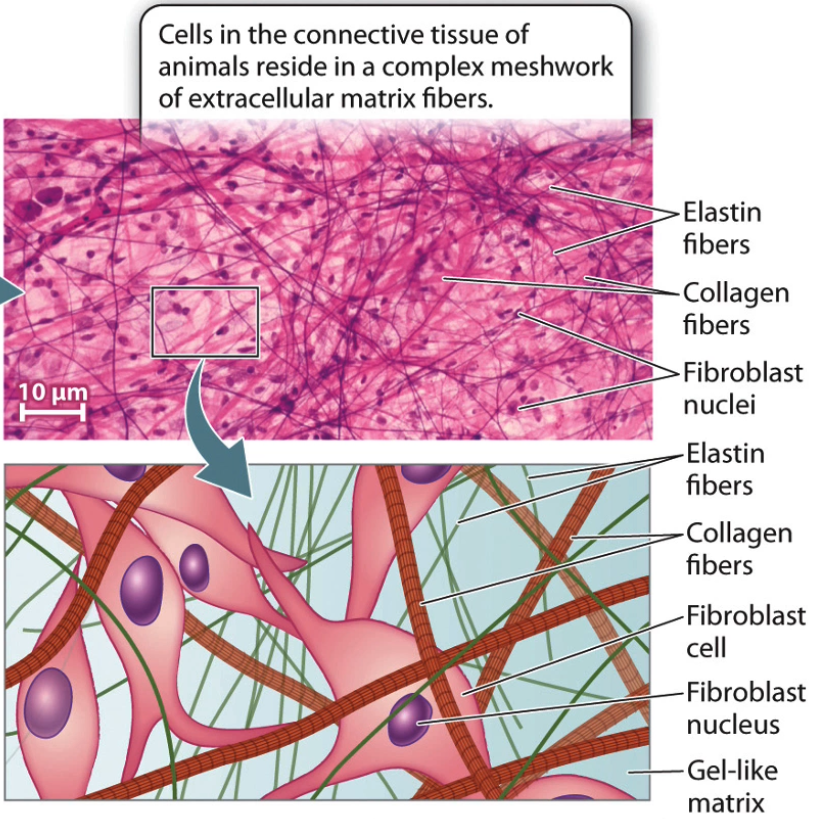
Tell me about Collagen
most abundant protein in animal ECM
most abundant animal protein
type 1 collagen is most abundant
found in dermis of human skin
composed of intertwined fibres that make it stronger
triple helix
bundle of collagen → fibrils → fibres
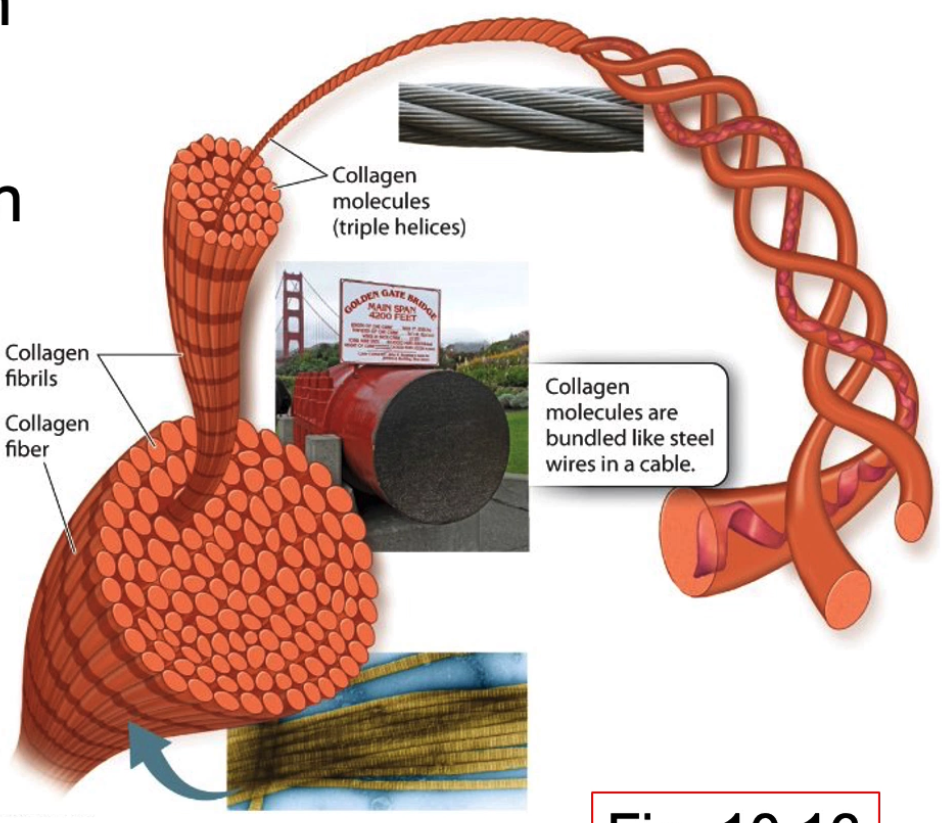
What is the importance of collagen being in the dermis of human skin?
provides support for skin structure
Tell me about Basal Lamina
specialized layer of extracellular matrix that is present beneath all epithilial tissue
provides a structural foundation for epithelial tissues
consists of several proteins
What proteins make up Basal Lamina? What do they do?
Collagen!
provides flexible support
acts as a scaffold
other proteins to assemble on to