MesoAmerican Architecture
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Mayan
Centered in Teotihuacan and their capital city Tikal (1500 BCE - 1548 BCE).
Aztec
Settled in Lake Texcoco and found the town Tenochtitlan. Tenochtitlan is considered as the Venice of the Americas. (1400 BCE - 1520 BCE).
Inca
Centered in the City of Cusco (1200 BCE - 1535 BCE).
Thatched Roof
Made from local materials such as palm leaves and to protect them from rain and the sun.
Wattle and Daub Walls
Often constructed from wooden poles or logs used as basic structure to support walls and roof.
Central Hearth
A fire pit was common for a Mayan house, it served as a source of light, warmth and also a place for cooking.
Storage
For food tools and other belongings.
House Orientation
The orientation of the house might have been influenced by astronomical and religious considerations.

Chichen Itza
It is a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period the most diverse population in the Maya world, a factor that could have contributed to the variety of architectural styles at the site.

Tikal Temple
Is the designation given to one of the major structures at Tikal, one of the largest cities and archaeological sites of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in Mesoamerica. It also is known as the Temple of the Great Jaguar because of a lintel that represents a king sitting upon a jaguar throne.
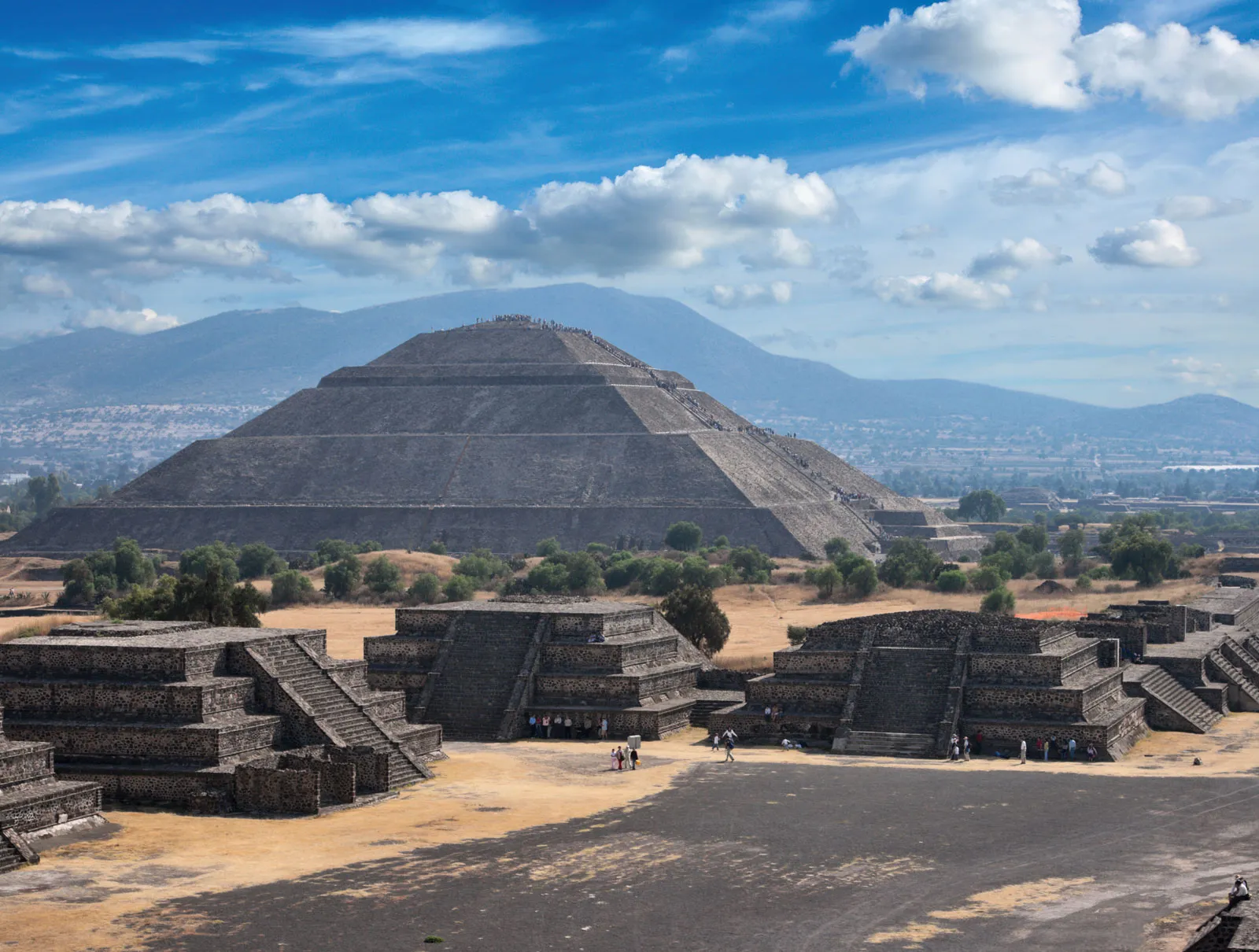

Pyramid of the Sun
is situated in Teotihuacan, Mexico, and is the largest pyramid in the city. Constructed around 200 AD, it stands approximately 65.5 meters tall. Believed to be of great religious significance, it played a central role in the ancient Mesoamerican cities rituals and ceremonies.

Pyramid of the Moon
Located at the northern end of the Avenue of the Dead in Teotihuacan, Mexico. It is dedicated to the Great Goddess. Built around the same time as the Pyramid of the Sun, it is smaller but holds cultural and religious importance.

Avenue of the Dead
The main monuments of the city of Teotihuacan are connected to each other by a central road of 45 meters wide and a length of 2.4 kilometers. It is believed to have been paved with tombs.

Chinampas
A tiny man-made island that is immovable and was constructed for farming in a freshwater lake. It relies on small, rectangular plots of fertile arable ground to cultivate crops on the shallow lake beds in the Valley of Mexico. |They are constructed for agricultural use on freshwater swamps or lake wetlands, and their proportions guarantee the best moisture retention.
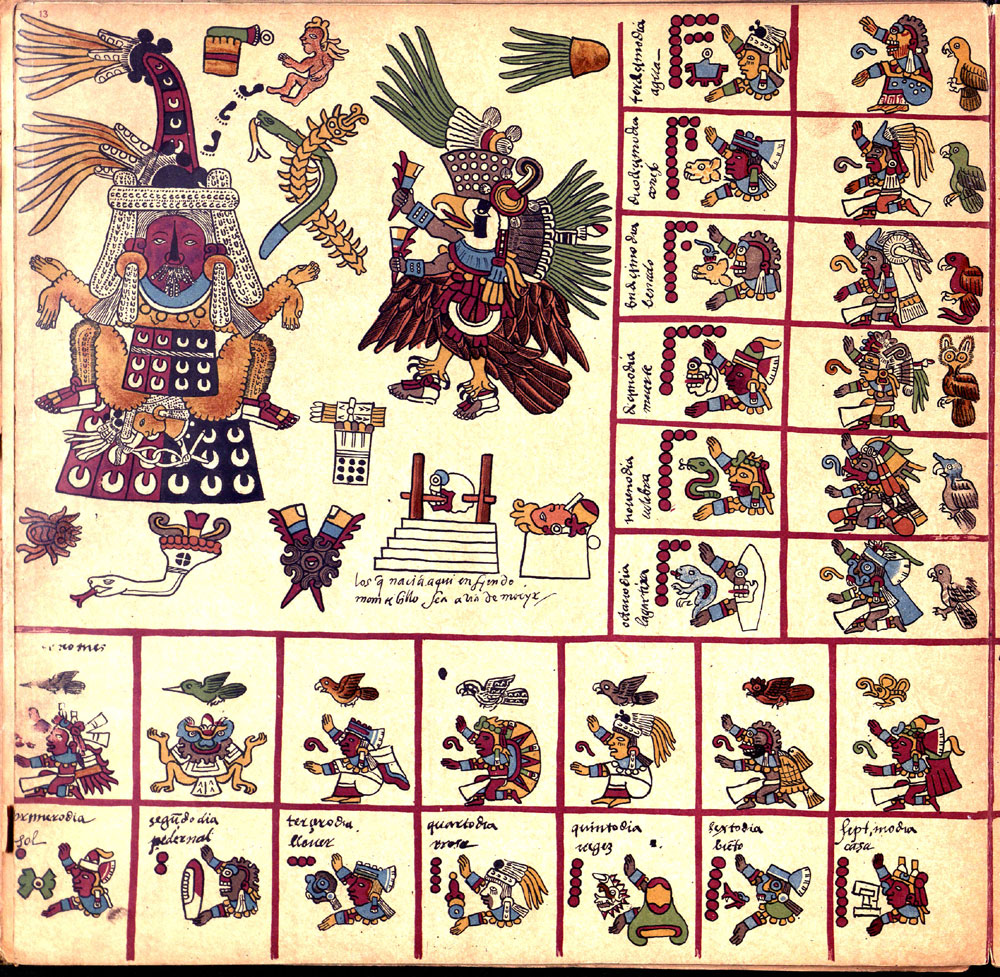

Codex Borbonicus
It is an Aztec codex written by Aztec priests shortly before or after the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire.
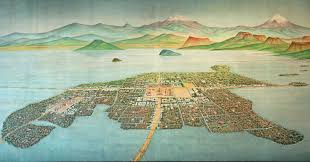
Tenochitlan
Also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican “altepetl” in what is now the historic center of Mexico City.

Templo Mayor
Was the main temple of the Mexica people in their capital city of Tenochtitlan, which is now Mexico City. Its architectural style belongs to the late Postclassic period of Mesoamerica.

Inca Civilization
The Inca Empire existed along the western coast of modern-day South America and their capital city was Cusco in what is now Peru. They ruled for over 100 years until the Spanish invasion in the 1500s.

Machu Pichu
‘The Inca Trail is a network of ancient paths in Peru, primarily known for connecting the city of Cusco to the iconic Machu Picchu
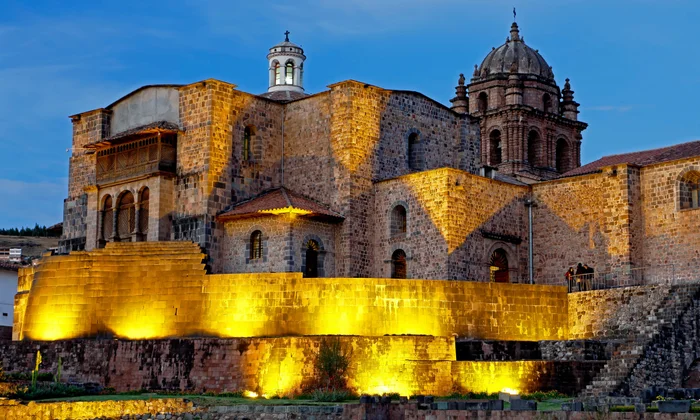

Coricancha
The most important temple in the Inca Empire and was described by early Spanish colonialists. The Inca used ashlar masonry, building from the placement of similarly sized cuboid stones that they hand cut and shaped for this purpose.
Megaron
Single-storey dwelling with a central room and porticoed entrance; columns support roof; thalamus - sleeping area