MICB Final Exam: Lecture 24 & 25 Bacterial Disease and Uses
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Diptheria (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name, Gram-stain, Spread, Symptoms)
Category: Airborne
Bacteria: Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Structure: Gram-Positive
Spread: Nasal snot (doesn't dry out)
Symptoms: respiratory mucosa, thick mucus, fever, cough
Infection process of Diptheria
1. AB Diphtheria Exotoxin connects to binding site on host
2. Comes into cell in a Coated Vesicle via Endocytosis
3. The pH drops uncoating the vesicle
4. A - B subunits separate
5. B subunit goes to surface cell A subunit leaves vesicle and adds ADP ribose from NAD to elongation factor (EF)-2
-Inhibit translation, no protein syn.
Diptheria Vaccine
DTaP (toxoid vaccine, inactivated toxin)
Tuberculosis (Bacterial Catagory, Bacteria Name)
Category: Airborne
Bacteria: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What important structure of the bacteria that causes TB provides protection?
Mycolic acids in cell wall
Process of TB infection
-Inhaled (infectious dose under 10 cells)
-Lung Phagocyosed by macrophages
-Services Intracellularly, can become latent in tubercles
What is the host response to TB?
Form tubercles
-Bacteria, macrophages, T Cells and Proteins (host and bacterial)
-Bacteria become latent
TB Skin Test
Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)
-Bacterial proteins injected into forearm
-Immune response (induration) measured in mm (48-72 hrs)
-Reaction is delayed hypersensitivity, antigen presenting macrophages attract and activate sensitized memory T cells
TB vaccine
BCG: bacillus calmette-Guerin
-Live avirulent M.bovis
-not standard in US
TB Diagnosis
bloody sputum, chest x-ray, acid-fast staining, culture
TB Therapy
Antimicrobial Therapy
-Rifampin + Isoniazid: inhibits mycolic acid syn
-Daily, 6-9 months
-Antibiotic resistance emerging (MDR, Multidrug-resistant & XDR, extreme drug resistance)
What bacteria causes Streptococcal Diseases?
Category: Airborne
Bacteria: Streptococcus pyogenes (group A Beta Hemolytic) or S. pneumoniae (Gram Postive)
What does Streptococcal Diseases affect? Diagnosis?
Affect: Impetigo, throat, lung, pneumonia, ear (otitis media)
Diagnosis: Culture & Strep Test
How does a strep test work?
Uses labeled antibodies to detect cell wall carbohydrates
Streptococcal Diseases Treatments and Preventions
Treatment: Penicillins (cell wall inhibitor) & Erythromycin (inhibit protein syn.)
Prevention: Prevnar, Pneumococcal Vaccine
-Polysaccarhirde based
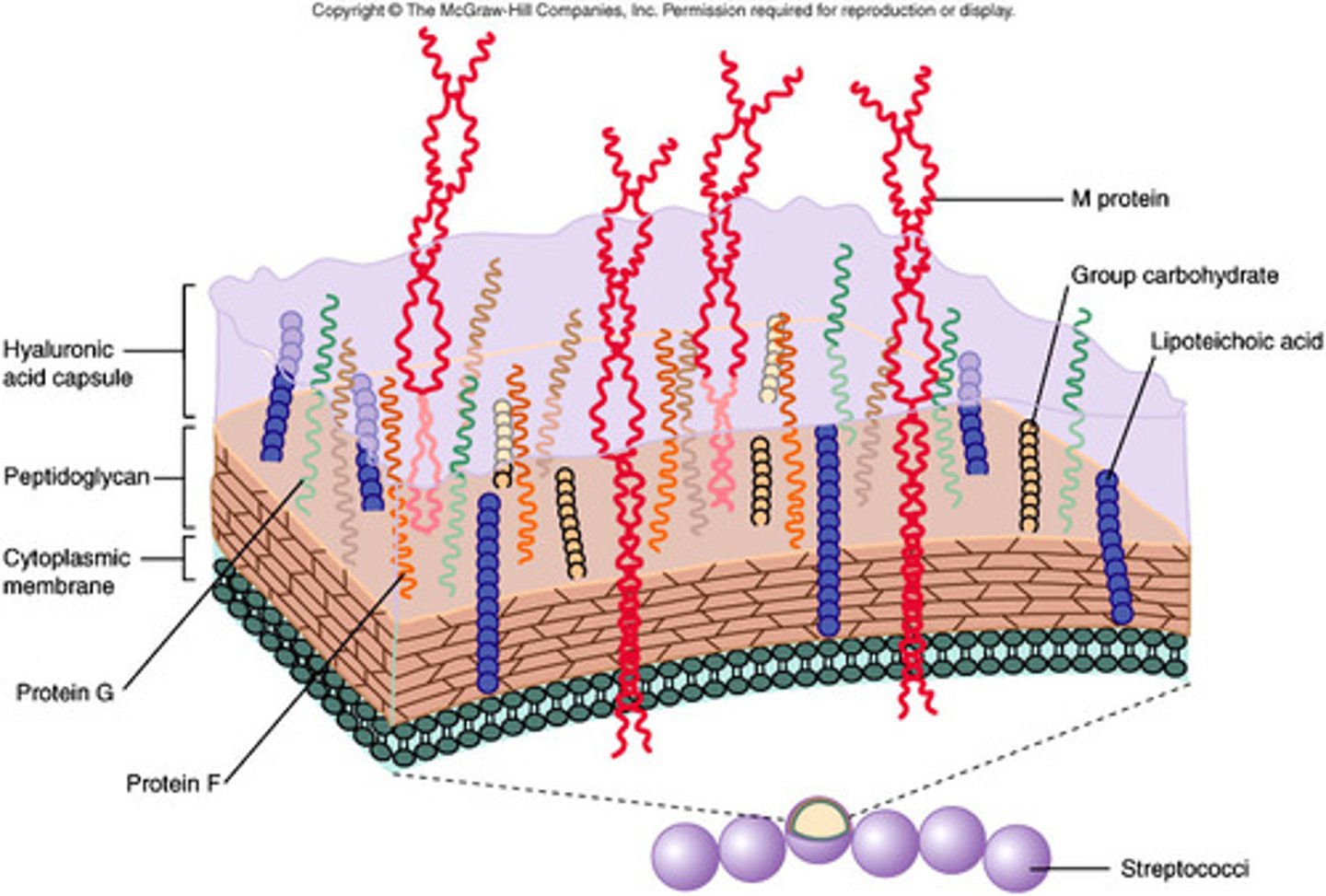
Streptococcal virulence factors
- Capsule and M protein -> promote adherence
- Antibody to M protein can x-react with heart tissue
- Causing Rheumatic Fever, an autoimmune disease
What kind of bacteria is the major "Flesh eating bacteria"? What does it cause?
Group A Streptococci
-Makes tissue destroying protease
-Lead to Necrotizing fasciitis
What bacteria is associated with too decay? Why?
Streptococcus mutans
-Part of dental plaque biofilm
-Fermentation --> acid --> enamel decay
Pertussis
Category: Airborne
Bacteria: Bordetella pertussis (Gram Negative)
What is the process of infection of whooping cough? What does it cause?
Colonize ciliated cells if the respiratory tract
Stage 1: Cold-like symptoms
Stage 2: Prolonged Cough (with inspiratory gasp or whoop)
What are the virulence factors of Pertussis?
-Pili: adherence
-Siderophores: acquire iron
-Pertussis toxin: AB exotoxin
Pertussis vaccine
Previous Vaccine DTP
DT-toxoids
P-killed bacteria
Current Vaccine DTaP
DT-toxoids
aP-acellular, toxoid, and other protein antigens
Tdap booster
Pertussis treatment
tetracycline
erythromycin
What is meningitis? What causes it?
-Inflammation brain, spinal cord meninges (membranes)
-Bacteria, Viruses Fungi
Bacteria:
-Haemophilus influenzae
-Streptococcus pneumoniae
-Neisseria meningitides (Gram-negative)
Neisseria meningitides bacterial virulence catagory and infection process
Category: Air Borne
Cause: Meningococcal Disease
Spread: Person-to-person, respiratory or throat secretion
Infection: Cross mucosal barrier into blood
Neisseria meningitides virulence factors and structure
Factors: Pili, capsules, lipopolysaccardide (LPS)
Structure: Gram Negative, Diplococcus
Serogroups
groups of strains with common surface antigens (A, B, C, Y, W)
-Based on capsular polysaccarides
Meningitis Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms: Flu like, Initial sore throat, vomiting, confusion, stiffness in neck, rash
Diagnosis: Gram stain spinal fluid, culture
Meningitis Treatment and Prevention
Treatment: Antibiotics (cell wall, protein syn. etc)
Prevention:
MCV4 Vaccine: Based on capsular polysaccharide (doesn't protect against B strain)
Bexsero: Based on group B outer membrane protein (not capsular material)
What bacteria causes the Plague?
Yersinia pestis (gram -)
What are the forms of the plague?
Arthropod-Borne
Bubonic: Flea vector
Pneumonic: Person to Person
What form of the plague has flu like symptoms and is more dangerous?
Pneumonic plague is almost 100% fatal if not treated early
-Category A bioweapons agent
Buboe
enlarged lymph node
How does Yersina inject toxic proteins into human cells?
Type 3 secretion system - injectosome
What is the structure of the Type 3 secretion system?
-Hallow basal body
-Hallow Needle
-Form Pore in Membrane of human cells
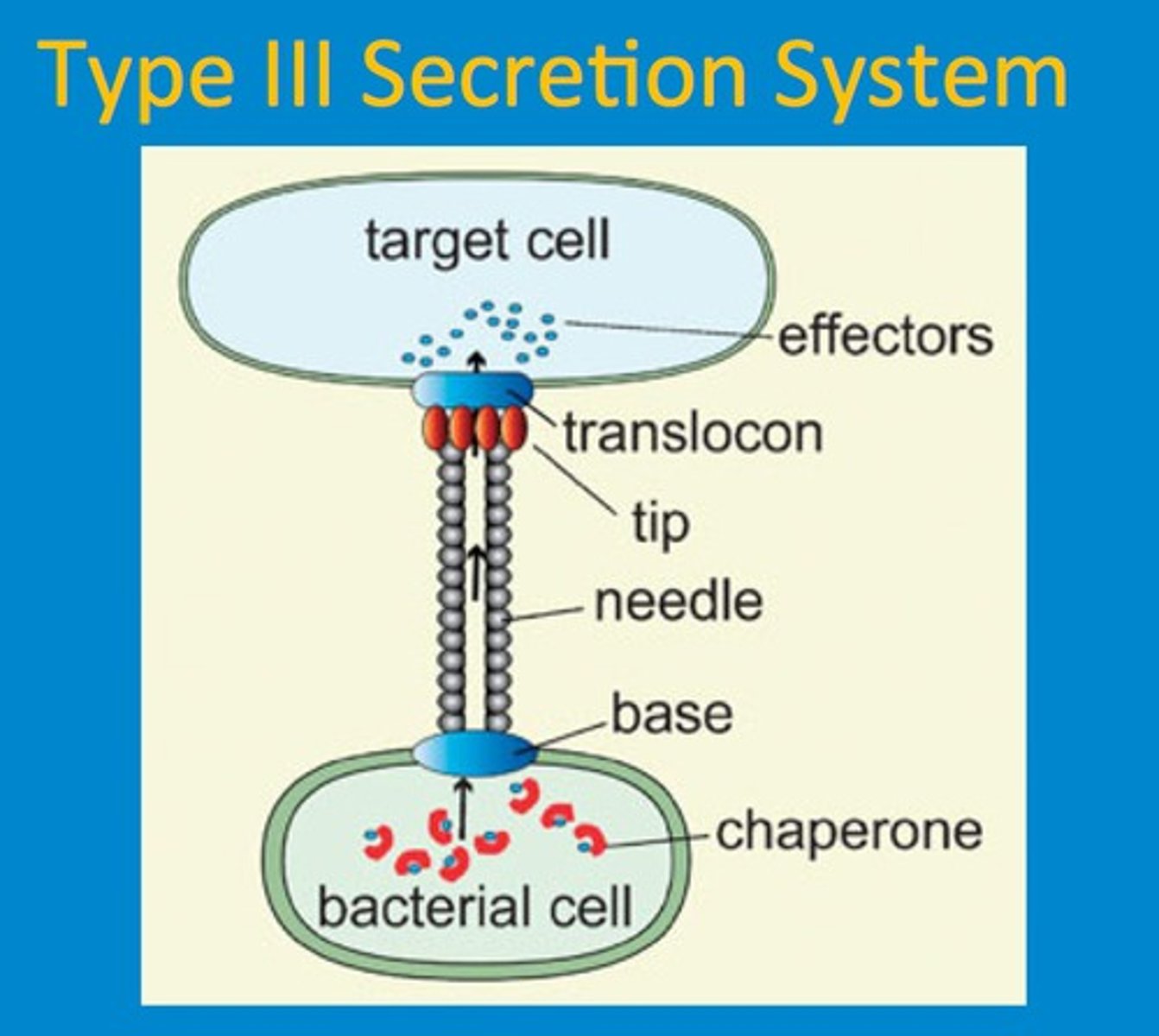
What does Yersina inject into human cells? What do they do?
Injects effector proteins, Yops
Target:
-Block actin polymerization of cytoskeleton (inhibit phagocytosis of macrophage to engolf pathogen)
-Signaling, disrupting transcription factor NFkB
Lyme Disease
Arthropod-Borne
Bacteria: spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi
Vector: Blacklegged (deer) tick
Stages (and symptoms) of Lyme disease
1. Localized Stage: 7-10 Days
-Bulls eye rash (erythema migrans)
-Flu like Symptoms
2. Disseminated: Weeks or Months
-Muscle pain, arthritis
3. Late: Years
-Affect nervous system
What stage is the most treatable for lymes disease? Treatments?
Localized stage
-Doxycycline: Target Protein Syn. (from tetracycline)
-Penicillin: Target Cell Wall
In the Disseminated stage of lyme disease, what happens to the antibody?
Antibody to Borrelia proteins may cross react with human MHC
Anthrax (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name)
Direct Contact
Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax Virulence Factors
Capsule
Toxin: 3 part AB toxin targeting macrophages and cell death
-Toxin and Capsule encoded on seperate plasmids
Forms of Anthrax
Cutaneous--cut, abrasion
Pulmonary--spores inhaled
Process of infection in pulmonary anthrax
-Spores enter macrophages in lungs
-Spores undergo germination and produce toxins
-toxin kills macrophages and other cells
-bacteria spread and fatal if reach bloodstream
Treatment for pulmonary anthrax
Early Ciprofloxacin
Staphylococcal Disease (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name)
Direct Contact
S. aureus: invasive, virulent
S. epidermidis: less invasive, less virulent
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Staphylococcal Disease
Diagnosis: Coagulase test can be used to differentiate strains
Symptoms: Boils, carbuncles, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning
Virulence factors of the more invasive bacteria causing Staphylococcal Disease
S. aureus
-Superantigens (TSST-1)
-Capsules
-IgA protease
-Coagnulase
-DNases
-Biofilm
How are virulence genes of Staphylococcal Disease controlled?
Quorum sensing
Two componet system
How are food and water borne bacterial diseases prevented?
Sanitation measures, antitoxins, and antibiotic therapy
Botulism (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name, Found In, Infection Process)
Category: Food and Water Borne
Bacteria: Clostridium botulinum
Found: Honey, canned foods
Process: AB toxin blocks acetylcholine release at neuromuscular junction
Listeriosis (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name)
Category: Food and Water Borne
Bacteria: Listeria monocytogenes
Cholera (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name, Infection Process, Treatment)
Category: Food and Water Borne
Bacteria: Vibrio cholerae
Process: Toxin causes hypersecretion
Treatment: Rehydration therapy, doxycycline
Salmonella (Bacterial Disease Category, Bacteria Name)
Category: Food and Water Borne
Bacteria: Salmonella typhimurium
What is the infectious strain (and name) of E.coli? What is its infectious dose?
E. coli 0157:H7
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)
Dose under 100 (other strains 1,000s to millions)
Carriers of E. coli
Cattle, Swine
What is the E. coli toxin, and what does it do?
Shiga Toxin - AB Toxin
-Binds to glycoprotein receptors on kidney & intestinal cells
-Cleaves human rRNA, stop translation to make proteins
Where are the toxin genes for the E. coli
Prophage (integrated form of viral genome)
What is the name for kidney failure caused by E. coli?
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
What microbe is used to make Kimchi and Sauerkraut?
Leuconostoc
What is Natto?
soybeans fermented with Bacillus natto
Why is Natto stringy?
From bacterial capsular polysaccaride
What are the major fermentation products used in the food industry?
Lactic, propionic, ethanolic
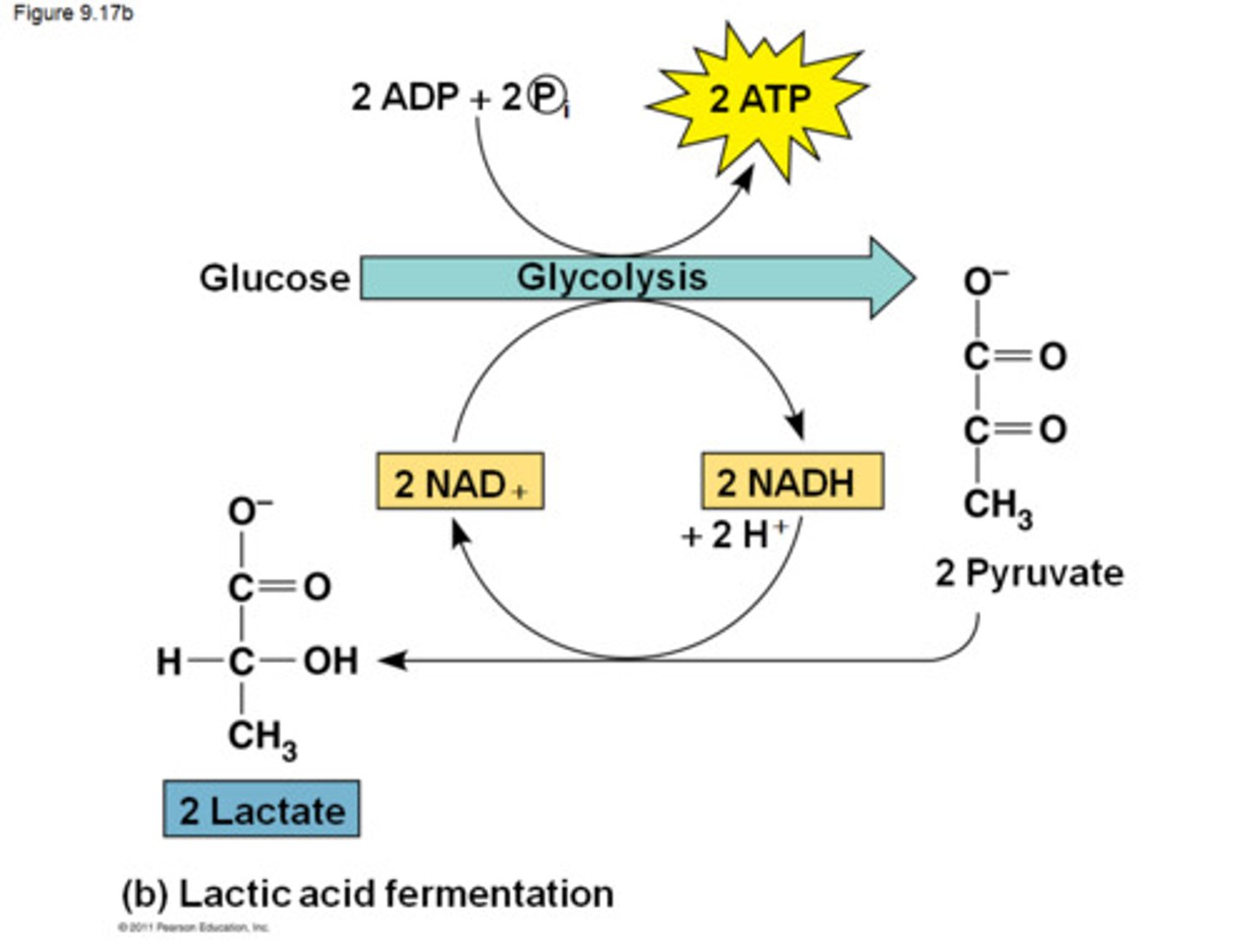
Process of Fermentation
Glycolysis
1. Glucose
2. ADP to ATP via substrate-level phosphorylation;
NAD+ oxidized to NADH
3. 2 Pyruvate
4. NADH reduced to NAD+
When O2 low, pyruvate accepts e- that otherwise would have been on NADH
5. Waste products: Latic acid, ethanol, propionic acid
Starter Culture Bacteria used in Yogurt Production
Lactobacillus and Streptococcus
What fermentation product is used to make yogurt?
Lactose (in milk) hydrolyzed to glucose, fermented to lactic acid
Contamination with what microbe is a major concern in yogurt production?
One phage could disrupt whole process
Process of Cheese Production
Milk -1-> Coagulation, Curd -2-> Cheese
1. Add Lactococcus starter and renin enzyme
2. Ripening - more microbes added for specific cheeses
Microbe added for Swiss Cheese? Blue and Brie?
Swiss: Propionibacterium
Blue/Brie: Penicillium (fungus)
Probiotics (what are they? Benefits? Examples of foods that have them)
Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, etc.
Microbes added to diet to improve health
Benefits: Vitamin prod., Improved digestion, Pathogen inhibition
Foods: Kombucha, Activia
Prebiotics
compounds (fiber) that promote growth of beneficial microbes
Microbes in Komuncha Tea
Fermented tea using Bacteria (Bacillus) and Yeast (Saccharomyces)
SCOBY
symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast
The starter culture
Beer-spoilage bacteria
Gram-Positive of the Bacteria Domain
What are the ingredients to beer?
barley: Breakdown of complex starches and proteins
hops: Antibacterial for flavor
water
yeast: Saccharomyces
How is beer made?
-Malting & mashing
-plant enzymes breakdown complex starches & proteins
What microbes are used in Ginger Beer? Fermentation products?
Fermentation of Ginger Spice and Sugar with
Saccharomyces and Lactobacillus