Peds Ex 2 Child Injuries/Poisoning/Toxicology (1/5) Sandy
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Mother comes into emergency room with child's urine (see image). Dipstick shows negative for blood. What should you ask the mother?
What the child has recently consumed (beets, berry cereal, magic marker)
Majority of poisonings occur in ______ and are _______ substance
1. home
2. single
What non drug substance is very bad for children to ingest? Why?
Button batteries it can cause necrosis in esophagus and nares
1. If a child ingest button batteries, they must be removed within ____ hours or risk of vocal cord paralysis or esophagotracheal fistula increases tremendously.
2. When is the worse time for ingestion of these button batteries?
3 Hours
Christmas
Can ulcerate glottis, esophagus, and retina (chemical eye burns). Rising in adolescents due to an internet challenge.
Detergent pods
These types of magnets are small, rounded bead like and if ingested ONLY 2 are needed to shred the intestines. These agents are 10x stronger than an ordinary magnet so the risk of injury is greater than coins or batteries.
Rare earth magnets
Kraton is an herbal supplement that ingestion in kids can causes?
1. HTN
2. tachycardia
3. coma
4. seizures
Problem with kraton if mom takes it to ween off heroin while prego?
kid gets withdrawals
What is the most dangerous time for poisoning ?
Christmas (tree and mistletoe is poisonous)
True/False
Melatonin ingested in excess doses it could lead to GI, CNS and cardiovascular issues
True
Poisoning in children <1 year of age is caused by?
1. Iatrogenic (by physician)
2. Parental Error
Age that most kids ingest chemical products
5
Poisoning in children > 6 years is assumed to be ____ until proven otherwise ? Why?
attempted suicide because they should know better to not take meds at this age
Poisoning most commonly occurs in the _______ or ______ under circumstances of decreased supervision - i.e. illness, moving or chaotic house hold environment
kitchen or bathroom
This was created to help reduce the rate of accidental poisonings
Poisoning prevention Act of 1970
How did the Poisoning Prevention Act help to reduce the rate of accidental poisoning ?
1. Establishing poison control centers (familiar with all substance ingredients and risk)
2. Enforce manufacturer labeling of products
3. Increased patient and physician awareness about dangers of poisoning
4. Child resistant packaging
5. Reduce size of package
True/False
There is no such thing as child proof packaging
True (child resistant packaging)
Once a child has swallowed a poison, there is a _____ chance they will do it again this year
50%
A. Keep inedible objects separate from ______ and out of reach
B. Keep products in original ________
C. Read _______ before using product
D. Never refer to medicine as _______
E. Never give medication in the _______
F. Do not allow children to take medications (even vitamins) without _______
G. Keep _________ out of medicine cabinet (should not even know whats inside)
H. Keep all products in ________ containers (grandparents)
A.food
B. containers
C. label
D. candy
E. dark
F. supervision
G. toothpaste
H. childproof
What is the purpose of differentiating between a toxic and non-toxic ingestion?
avoid over treatment
Consumption of inedible product which usually does not produce symptoms --no product is entirely safe
NON TOXIC INGESTIONS
What is the criteria for nontoxic ingestion?
1. Absolute identification of the product
2. Single product ingestion (not a polypharmacy)
3. Assurance of no signal word on container (danger, poison, caution)
4. Estimation of amount ingested and time of ingestion
5. Availability for parents to call back if sxs develop
With liquids, the volume of swallow in an child between 18 months to 3 years is ?
About 1 teaspoon ( 4.5mL)
With liquids, the volume swallow in an adult ?
about 1 tablespoon (15 mL)
What is the rule of thumb for drug toxic dose?
5x therapeutic dose or single tablet except narcotics or digitalis
True/False
A single table of narcotics or digitalis is considered TOXIC
TRUE
If the amount ingested is under 5x the therapeutic dose its not considered toxic unless its?
1. Opiate narcotic
2. Digitalis
If you're unsure if the ingested product is toxic to child what should you do?
always call poison control
What questions should you ask parents to help identify the unknown poison?
Have parents ....
1. Bring container in
2. Name/spell our product (SCOPE: mouthwash or an insecticide)
3. Read ingredients
What questions can ask that will help give you clues to the unknown poisoning?
1. Who: Age (> 6 = alarm)
2. What: What was child doing prior to onset of sxs (playing doctor), what was available at the time
3. Where: Where was he playing (garage, bedroom)
4. How much: Quantity available
If a child presents with burns on the lips, tongue or mouth what type of poisoning should you be suspicious for?
Corrosives
If a child presents with gasoline odor on the breath what type of poisoning should you be suspicious for?
Petroleum distillates
If a child presents flushed, mydriasis, hyperthermia and delirium what type of poisoning should you be suspicious for?
Anticholinergics
What are some ways children can get their hands on anticholinergics?
Pills, Belladonna plant, Jimsonweed
If a child presents CNS depression, hypothermia, hypotension and miosis what type of poisoning should you be suspicious for?
Narcotics
Any time a patient shows up with an abrupt onset of symptoms between the ages of 1-5 y/o with multiple organ system involvement and no other disease fits the pattern. What are you thinking ?
THIS is POISONING!!
This was a drug that was once used as a cough syrup and to induce vomiting that was used in the past but is no longer in favor because of delay in onset of emesis and poor yield (only 1/3 of gastric contents). It was contraindicated with caustics and hydrocarbons.
IPECAC (emesis)
What age does gastric lavage work?
only older children and not smaller children bc of the small bore of tube they would have to use (not big enough to get the chunks out)
This works very well at absorbing large amounts of toxins but is not effective in the absorption of heavy metals, iron, hydrocarbons, cyanide, or low molecular weights alcohol.
Activated charcoal
What is the only problem with activated charcoal?
Taste terrible, very hard to get down
Used in conjunction with activated charcoal because it increased transit time. But there is no clinical evidence that this is of value.
cathartics (lax)
A Whole Bowel Irrigation works well due to the instillation of large amount of ____________, which is a large molecule to draw water from gut wall into lumen.
polyethylene glycol (Miralax)
If you use whole bowel irrigation approach in small children, what must you start the patient on as well because they're at an increased risk of.....
IV FLUIDS!!! to prevent dehydration
This can be used to excrete the product via urination but it cannot be administer alone. Must acidify or alkalize urine.
Diuresis
For diuresis, what pH do we need the urine in salicylates? what can we give to make this happen?
alkaline
bicarb
Just to clarify which methods of tx of poisoning have been proven to work? ***
1. Activate charcoal
2. Whole Bowel irrigation
3. Dialysis
Ingestion of acetaminophen in children ______ years of age - accidental - rarely in toxic amounts
< 6
Ingestion of acetaminophen in children ____ years - attempted suicide - toxic amounts common
> 6
1. Under normal circumstance, acetaminophen absorption takes?
2. In overdose circumstance, acetaminophen absorption takes?
1. 1 – 2 hours
2. Delayed up to 4 hours (important to know when they ingested it)
The toxicity of acetaminophen ingestion is secondary to?
hepatocellular necrosis
What is the toxic dose for acetaminophen ingestion in children?
> 200mg/kg (6 extra strength tablets)
What is the toxic dose for acetaminophen ingestion in teens/adults?
7.5 g (15 extra strength tablets)
This stage of acetaminophen poisoning is within 12 to 24 hours where the pt will experience GI symptoms such as N/V, diaphoresis, lethargy, pallor and anemia.
Stage 1
What stage must tx begin in acetaminophen poisoning?
Stage 1 between 12-24 hours
This stage of acetaminophen poisoning that start 24-48h and the patient appear better but they may feel some RUQ pain and have elevated bilirubin, abnormal LFT's and oliguria
Stage 2: 24-48 hours
What stage does heptocellular necrosis occur?
second (24-48hrs)
How do you dx acetaminophen poisoning?
1. Suspicious
2. Acetaminophen lvl > 4 hr post ingestion (takes this long to absorb)
This stage of acetominophen poisoning is bw 72-96 hours when marked liver function abnormalities, vomiting, nausea, malaise may reappear
Third
How do you tx acetaminophen poisoning?
1. Activated charcoal: Within 1-2 hours of ingestion
2. N-acetyecysteine: if plasma level is high or >16
3. Baseline liver chemistry and Repeat q 4 hr
True/False
Aspirin must be considered in therapeutic situations as well as in acute overdoses
_______ is another source to be considered
True
methyl salicylates (oil or wintergreen)
What does Bengay have in it to cause 2nd degree burns in children?
salicylate (aspirin)
Aspirin is rapidly absorbed in therapeutic doses, what's the absorption in overdoses?
slowed up to 24 hours because of saturation
of metabolic pathways
Why is salicylate posiosing called the great masquerade?
1. Block Kreb cycle
2. stops oxidative phos.
3. blocks AA syn
4. decrease platelets adhesiveness
5. increase pulm capillary permeability
6. stimulates resp center
Which of the following are symptoms associated with salicylate poisoning ?
A. N/V (GI irritation)
B. Hyperpnea & hyperventilation (Kussmaul)
C. hyper or hypoglycemic
D. Alkalosis with alkaluria which progresses to aciduria (after K+ loss)
E. Cardiovascular collapse and pulmonary edema
F. Bleeding, agitation, restlessness, confusion
G. All of the above
G. All of the above
What type of breathing can be present is salicylate poisoning?
What 3 things can salycilate poisoning present like?
Kussmals
(Hyperventilation and hyperpnea)
1. PNA
2. DKA
3. Encephalitis
What tests are diagnostic for salicylate poisoning ?
1. Serum salicylates
2. Ferric Chloride
What if the serum salicylate is
A. > 20 mg/dL
B. > 70 mg/dL
A. Observe
B. Treat
what color does the ferric chloride test comes back for Salicylate poisoning
purple
If you catch salicylate poisoning early what can you tx with?
Activate charcoal
What are the goals for tx for salicylate poisoning ?
1. Rehydrate pt
2. Correct electrolyte imbalance
3. Alkalinization of the urine with IV bicarbonate to increase excretion
4. Ventilation
True/False
Serious complications from Ibuprofen are rare
True
What is the toxic dose of ibuprofen?
>400mg/kg
In children, Ibuprofen doses of ______ mg/kg do not cause toxicity (this is why toxcitiy is RARE)
100
Ibuprophen toxicity symptoms begin within _____- of ingestion & resolve after_____
4 hours
24 hours
What are the sxs of ibuprofen toxicity?
1. GI irritation
2. platelet dysfunction
3. nystagmus, tinnitus, deafness
4. serious: coma and seizure(rare)
What is the tx for ibuprofen toxicity?
- no specific antidoe
- can give charcoal
Lead poisoning is considered acute or chronic poisoning?
Chronic
What molecules in the body does chronic lead ingestion mess with?
replaces iron in heme
competes with Ca
implants in bone
True/False
Lead poisoning can be due to old paints (households), batteries, cable sheathing (computers), Folk remedies such as Kohl, Kajal, Kaumkam, Subma.
True
What is the MC route of lead poisoning?
Oral (hand to mouth)
Lead disturbs cellular metabolism of every organ because its a heavy metal.
1. What does lead replace in hemoglobin resulting in anemia?
2. What does lead compete with ?
1. Replaces IRON
2. Competes with Ca2++
Since lead replaces calcium in bone, what can be seen on Xray at the epiphyseal plate ?
lead lines (hyper dense)
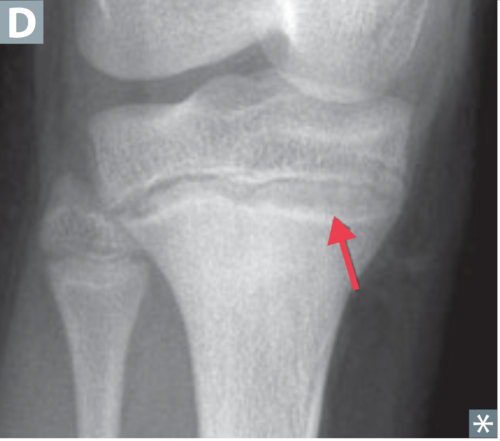
What are the sxs of lead poisoning?
1. lethargy, irritable, vomitting and ataxia
2. CNS issues
3. ANEMIA
Patient experiencing abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation and PICA. What do you suspect ?
lead poisoning
T or F: PICA is a sign of lead poisoning
T
How do you dx lead poisoning?
Auto Screen 1-2 y/o
What questions need to be asked for screening in lead poisoning ?
1. Was your home built before 1970 (lead paint)?
2. Is there any peeling paint or plaster in the home?
3. Does the child visit any homes in which an individual is being treated for lead poisoning?
4. Any recent construction done in your home?
5. Have any of the child's friends had an elevated lead level?
What is the lead level we have to be below to be considered normal?
<3
Any lead level above _____ is reported
> 5
Lead level between...... what do we have to do?
A. <3
B. <9
C. 10-15
D. 15-19
E. 20-24
F. >45
A. Normal
B. Kids can have learning disabilities
C. Significant poisoning, repeat 3 months
D. Repeat 2 months, increase calcium and iron in diet, Lab reports to board of health (goes to house for remediation)
E. Repeat 1 month
F. Hospitalized and chelation therapy
Lead level above >70 means?
lead encephalitis and needs to be hospitilized for two drug chelation
Will drug treatment remove all the lead from the body?
no! its everywhere
Why does the summer increase lead levels in body?
Vit D makes more Ca and displaces lead in bones
What is the #1 cause of poisoning death in children <6 y.o?
Iron poisoning
What's the MC source of Iron poisoning? Why?
Iron tablets because they look like candy; enteric coating
True/False
Iron is classified as a food product therefore it is not a drug and they do NOT regulate it
True
Iron exposure severity is based on the amount of
elemental iron
How much elemental iron is considered a lethal dose?
> 60mg/kg
What is the hallmark sign of iron ingestion toxicity ?
GI symptoms such as N/V, abdominal pain, bleeding 2/2 irritation of gastric mucosa
What occurs in each stage of iron posoining?
A. Stage 1: 30 min to 6 hours
B. Stage 2: 6-12 hours
C. Stage 3: 12-24 hours
D: Stage 4
E: Stage 5: 2-4 weeks
A. n/v/d (GI)
B. cellular damage and no GI symptoms
C. hypotension and drowsiness --> die in this stage
D. hepatotoxicity,
E. plyoric stenosis and scarring