Electric Circuits
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Principle of charge conservation
states that the total electric charge in a closed system does not change
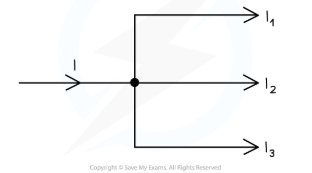
Kirchoff’’s 1st law
States the sum of the currents entering a junction is always equal to the sum of the currents leaving the same junction.
I.e..
In a series circuit current is the same at all points
in a parallel circuit the current divides at the junctions and each branch has a different value
Kirchhoff’s 2nd law
states the sum all voltages in a series circuit is equal to zero
So Voltage in a series circuit is shared across all components and equals the total V
but Voltage in a parallel circuit is equal across each branch
Deriving R total (series circuit)
Using (K1) and ohms law each resistor has the equation
V1 = IR1, V2=IR2 V3=IR3
Using (K2) Vt= V1+V2+V3
Vt = I(R1+R2+R3)
This then simplifies to
Rt = R1+R2+R3
Deriving R total (parallel circuit)
Using (K2) and ohms law each resistor has the equation
Vt/R1 = I1, Vt/R2 = I2, Vt/R3 = I3
Using (K1) Sum of currents entering a junction is equal to that leaving
It = I1 + I2 + I3
It = V/R1 It = V/R2 + V/R3
It = Vt (1/R1 +1/R2 + 1/R3)
1/Rt = 1/R1 +1/R2 + 1/R3