Neuro Lecture 7: Visual System
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
What are the functions of CN II? (5)
- Visual acuity
- Binocular vision
- Accomodation
- Pupillary reflex
- Tectospinal reflex
What falls under visual acuity?
- Focal vision
- Ambient vision (peripheral)
How does binocular vision come about?
Due to overlap of visual fields
What is the tectospinal reflex?
A neural pathway that coordinates head and eye movements with visual and auditory stimuli
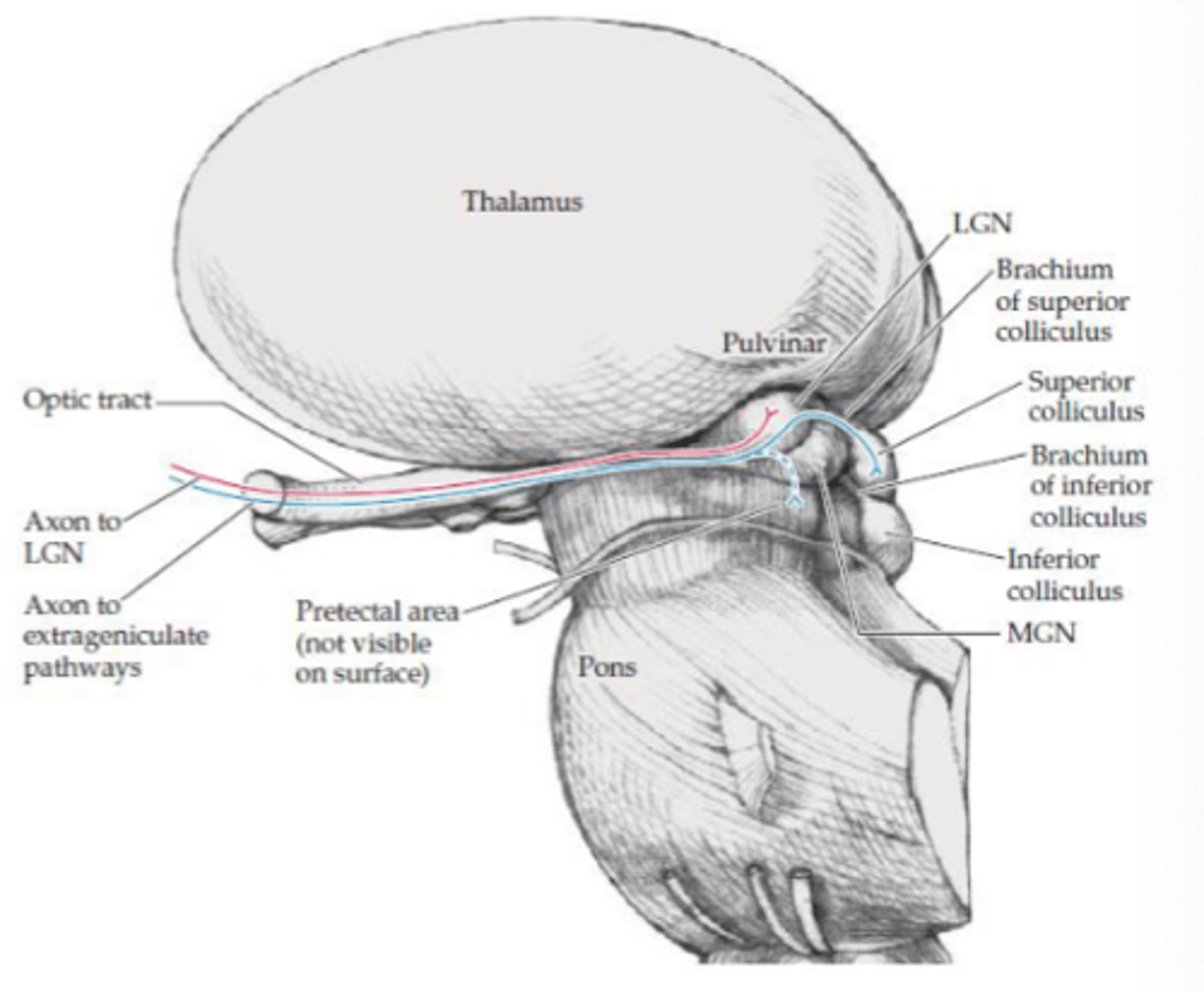
What are the 2 visual pathways?
- Geniculate
- Extra geniculate
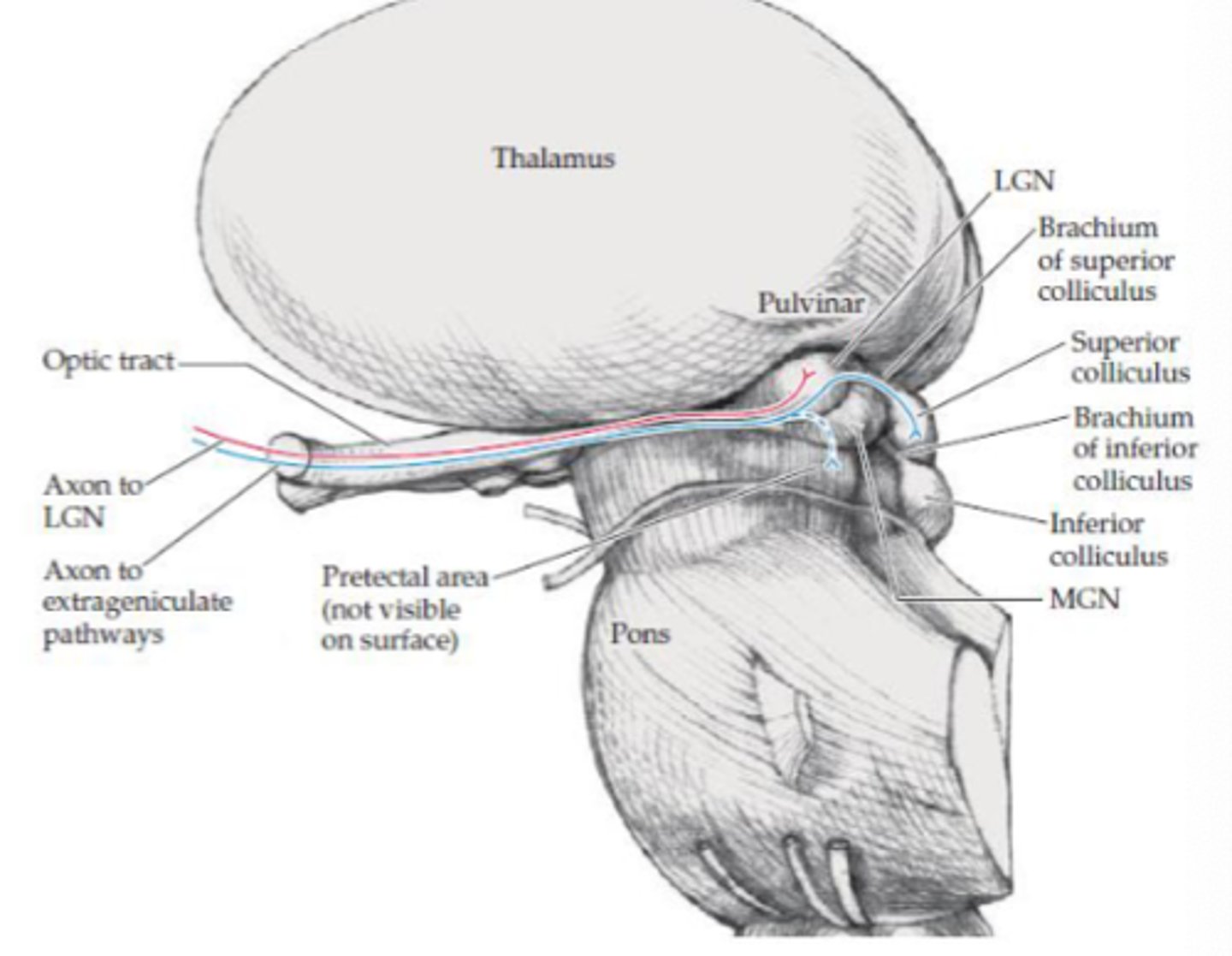
What is the geniculate visual pathway responsible for?
Vision (visual acuity)
Where does the geniculate visual pathway project to?
LGN in thalamus
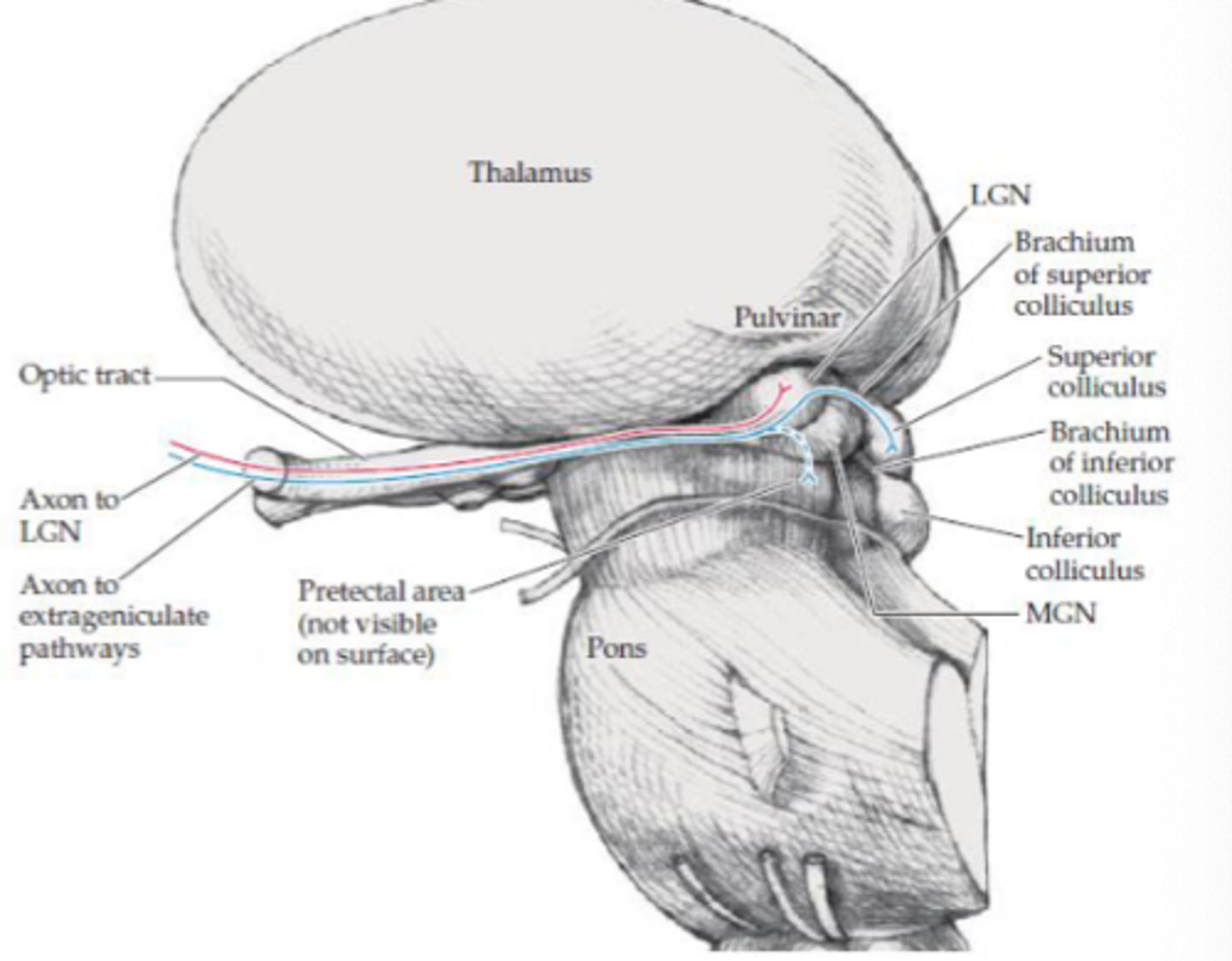
Where does the extra geniculate visual pathway project?
- Pretectal area
- Superior colliculus
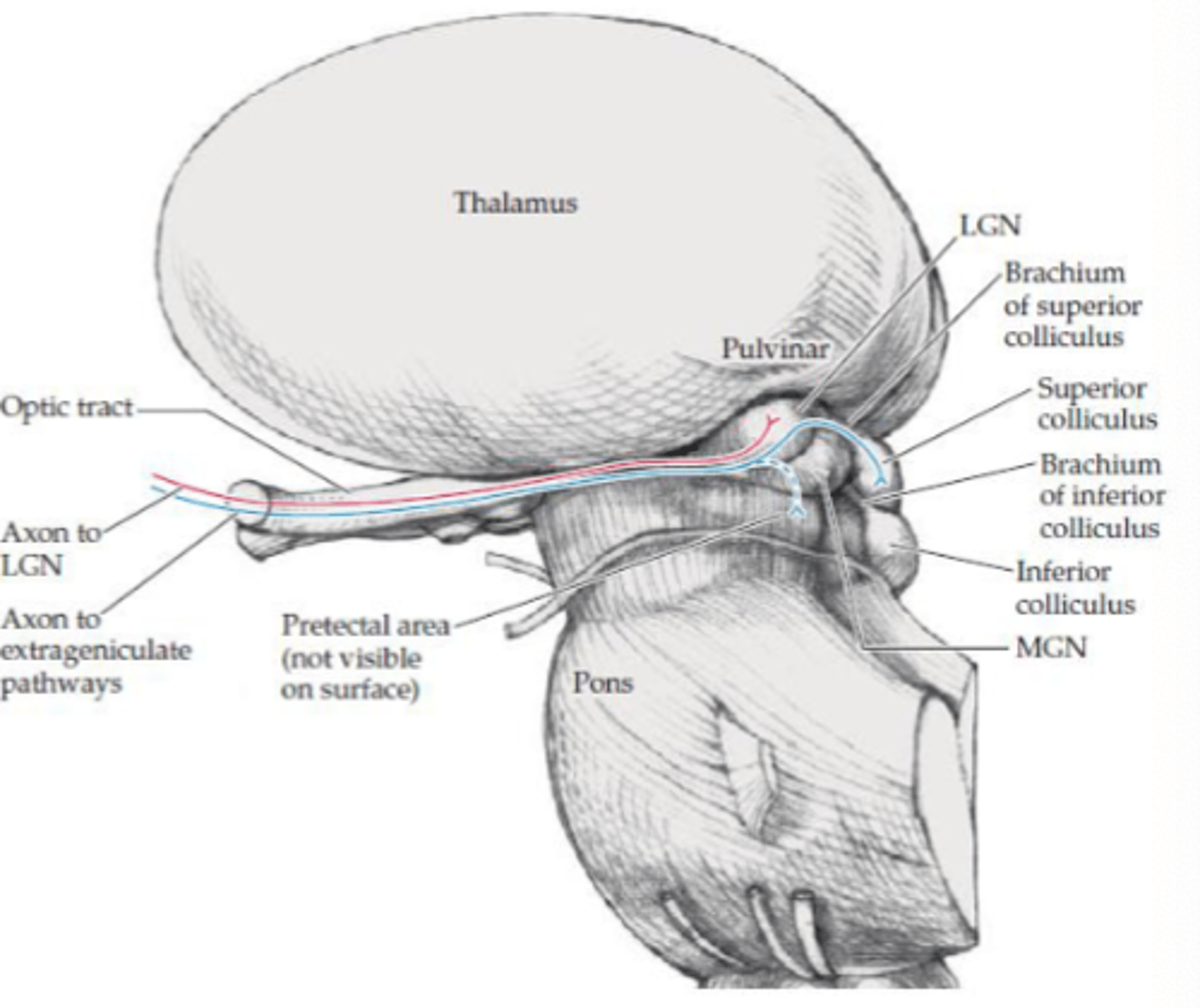
What are the projections to the pretectal area responsible for (extra geniculate)?
Aid with pupillary light reflex
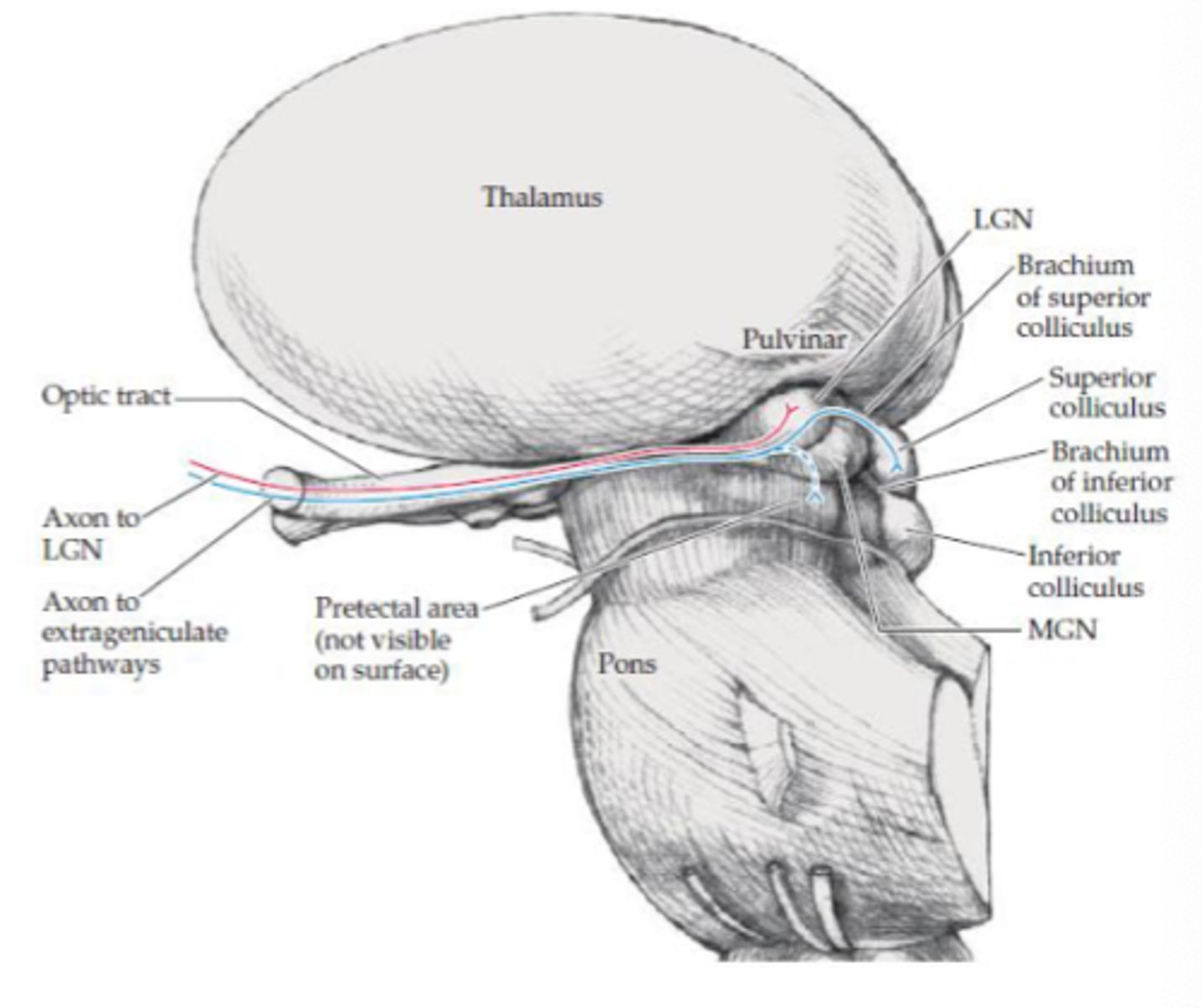
What are the projections to the superior colliculus area responsible for (extra geniculate)?
- Linked with tectospinal tract (medial tract)
- Reflexive eye movements to visual stimuli
- Directs visual attention and eye movements to visual stimuli
Where is the human eye located?
Orbit
What does the orbit consist of?
- Sclera
- Choroid
- Retina
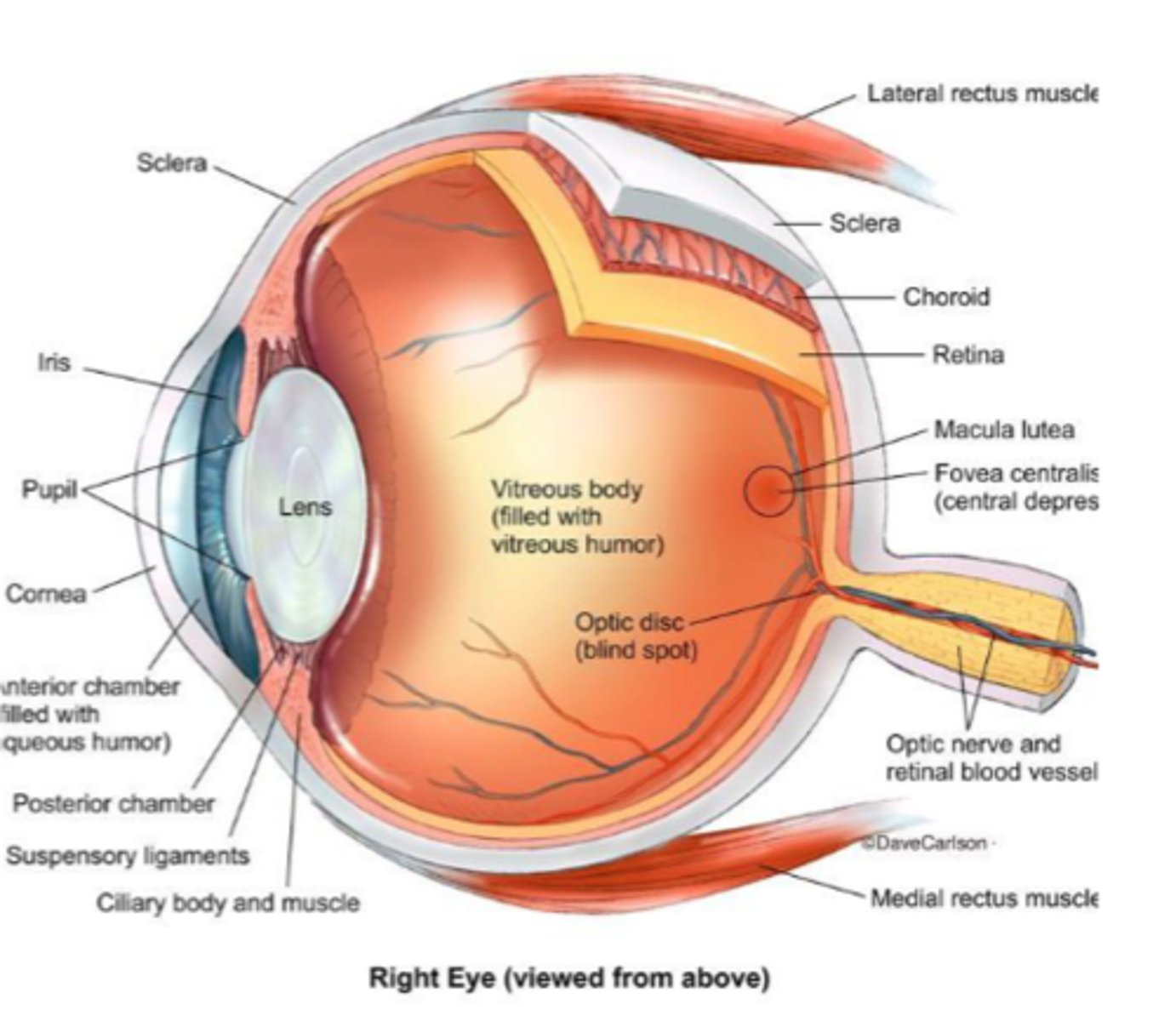
What structures form the outer layers of the eye? (9)
- Sclera
- Cornea
- Ciliary body (posterior chamber)
- Ciliary muscles
- Anterior chamber
- Iris
- Pupil
- Lens
- Zonular ligaments
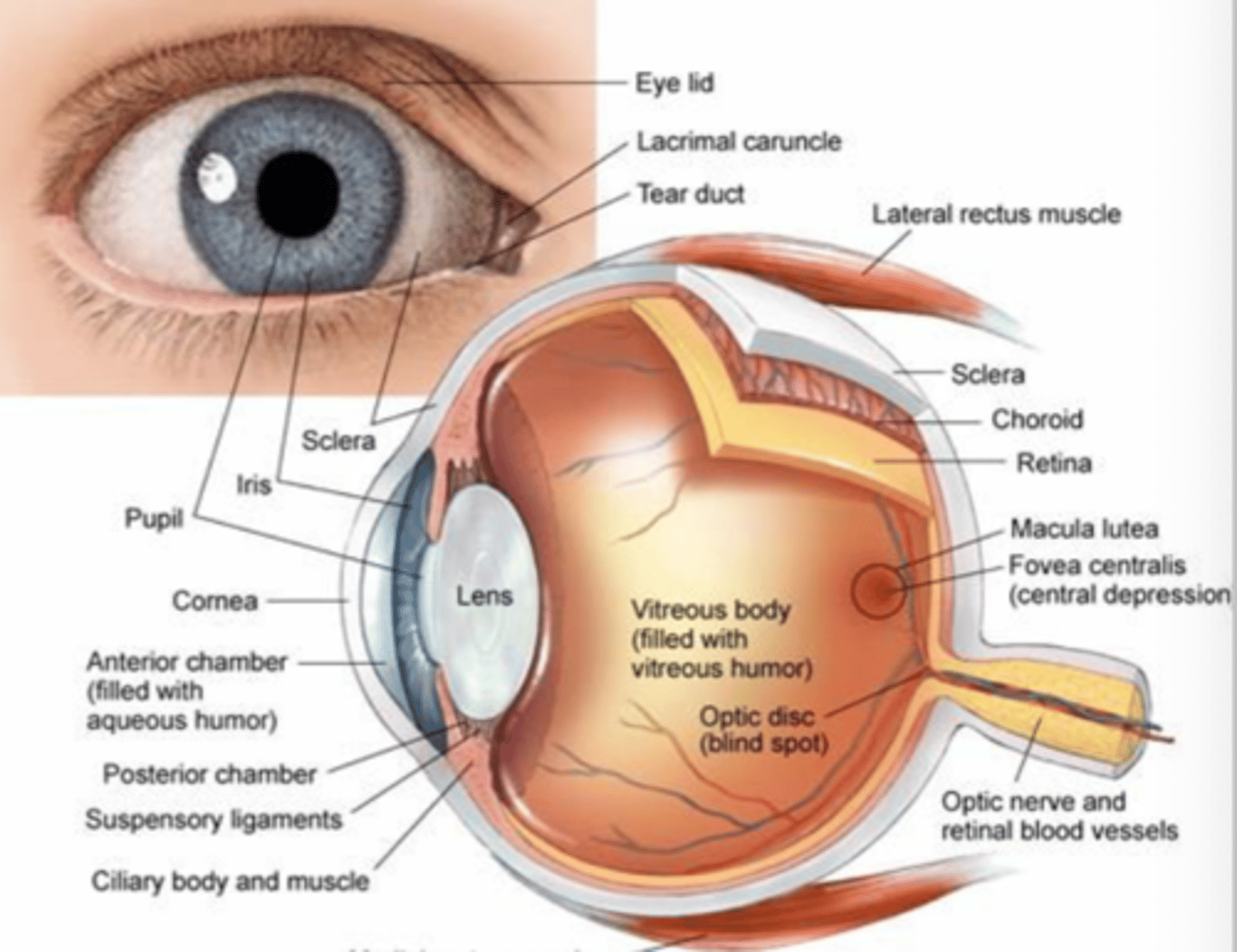
What color is the sclera?
White
What color is the cornea?
Transparent
What is the function of the ciliary body (posterior chamber)?
Produces aqueous humor
What does the anterior chamber of the eye contain?
Aqueous humor
What does aqueous humor do?
Nourishes and maintains pressure in the eye
What is the function of trabeculae in the eye?
Drains the aqueous humor
What happens if drainage is blocked in the eye?
- Glaucoma
- Affects vision (primarily peripheral vision)
What is the iris responsible for?
Muscles that regulate light into the eye by controlling pupil size
What is the pupil also known as?
Aperture
What is the function of the lens?
Refracts light
What is the function of the zonular ligaments?
Connects the ciliary body to the lens
What are the inner components of the eye (4)?
- Vitreous body
- Retina
- Macula
- Fovea
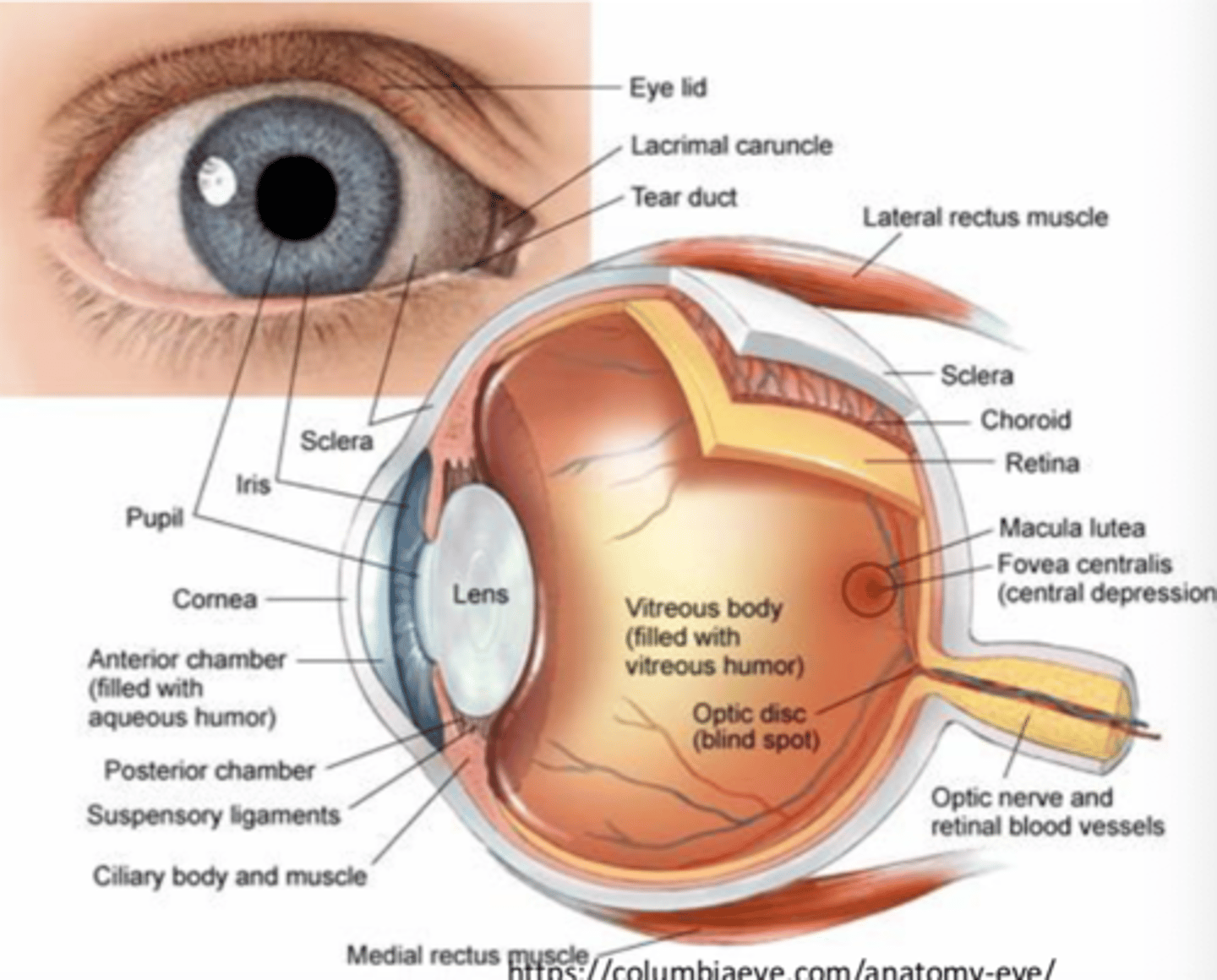
What is contained in the vitreous body?
Vitreous humor
What is the retina?
Neural tissue with photoreceptors
What is the retina made up of?
- 6 layers
- Ganglion cells
- Photoreceptors (rods/cones)
What is the function of the retina?
Senses light and converts image to electrical impulses
What is the function of rods?
- Sensitive to low light
- Low spatial acuity
- Provide peripheral vision
Where are rods located?
On the retina, outside the macula
How many rods do we have in our eyes?
More numerous (120 million)
What is the function of cones?
- Sensitive to high light
- Find detail and color
- High spatial acuity
Where are cones located?
Primarily at the center of the retina (macula)
How many cones do we have in our eyes?
Fewer in number (6-12 million)
Where is the macula located?
On the retina
What is the function of the macula? (4)
- Pigmented
- Central vision
- Clearly see sharp, fine detail, color perception
- Has photoreceptors (cones)
Where is the fovea centralis located?
Depression in the center of the macula
What is the function of the fovea?
- Sharpest/Maximal visual acuity (central vision)
- Enables reading, recognizing faces, driving
What is a disorder of the macula called?
Macular degeneration
What area has the highest concentration of cones?
Macula/fovea
Where is the blind spot of the eye? (4)
- Optic disc
- Exit of ganglion cell axons on retina
- Photoreceptors are absent
- ~15º off center in temporal field
What does the exit of ganglion cell axons in the blind spot (optic disc) form?
Optic nerve
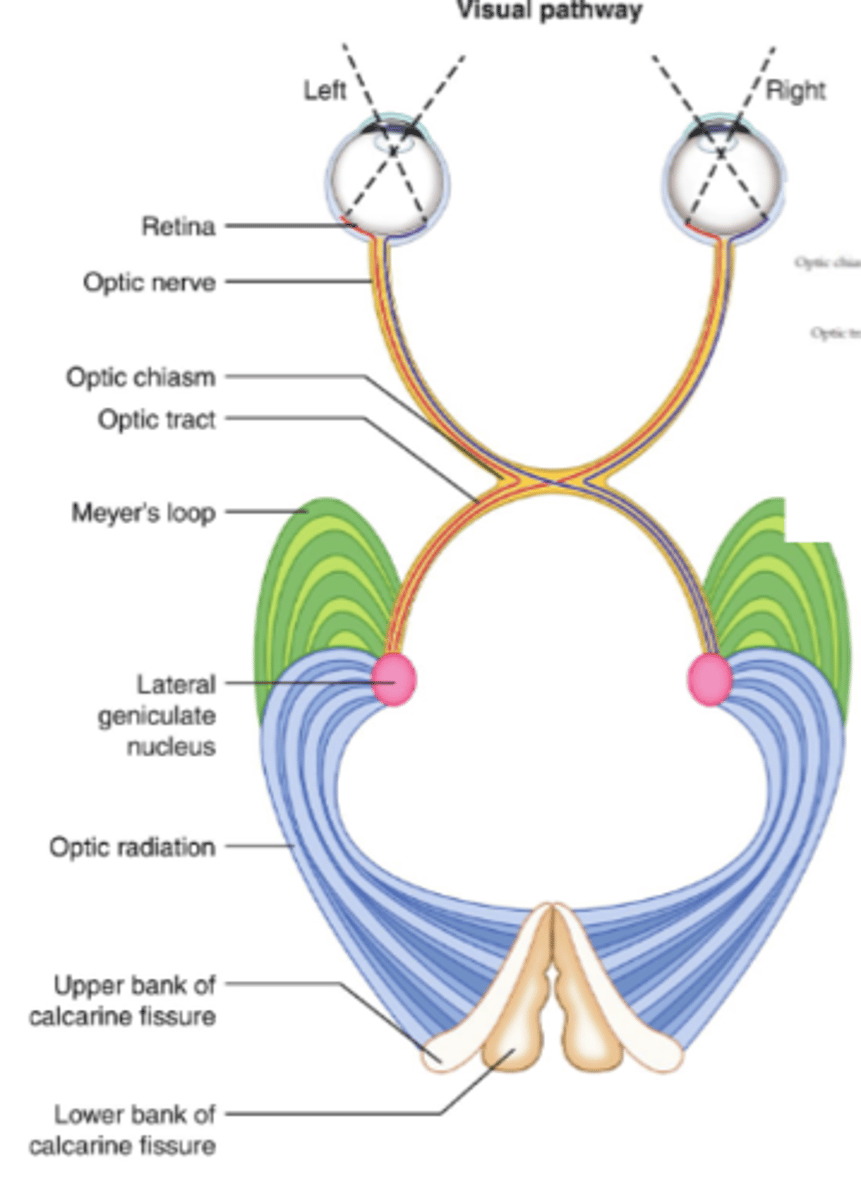
What is the first step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Retina
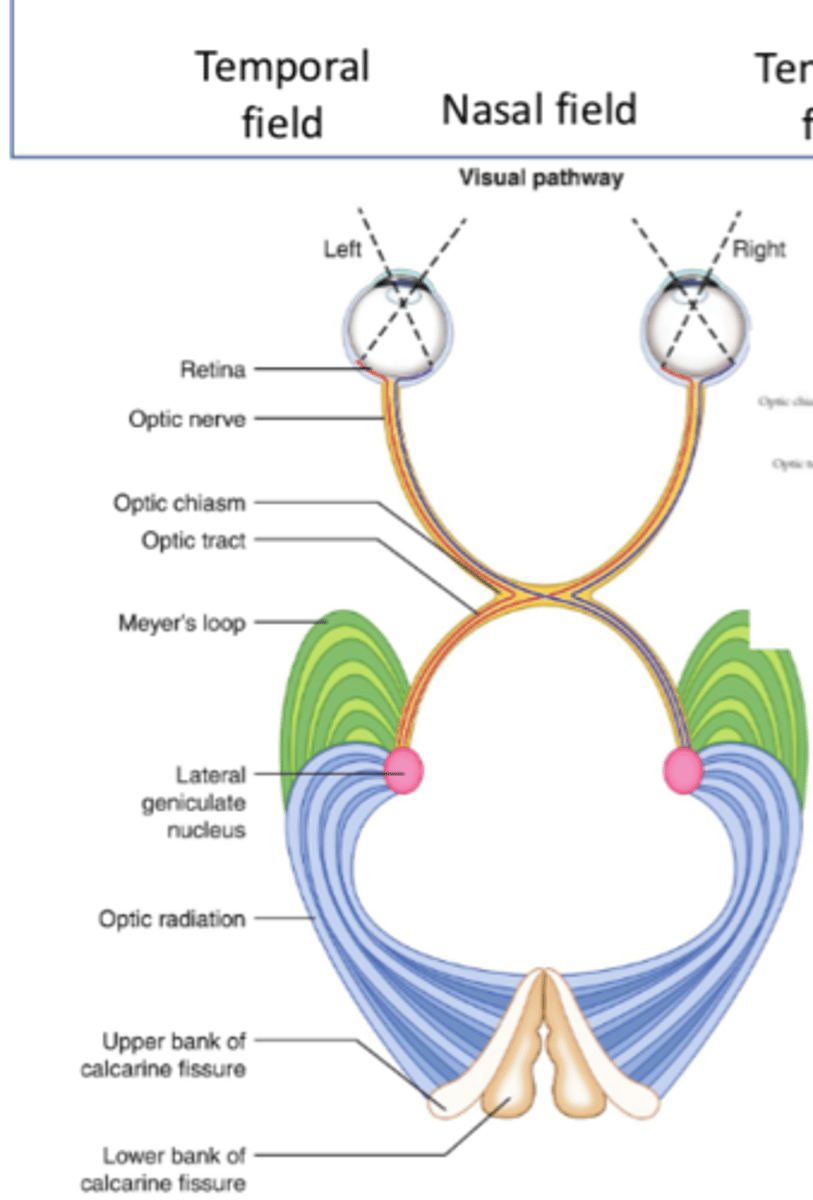
What is the second step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Optic nerve (via ganglion cell axons)
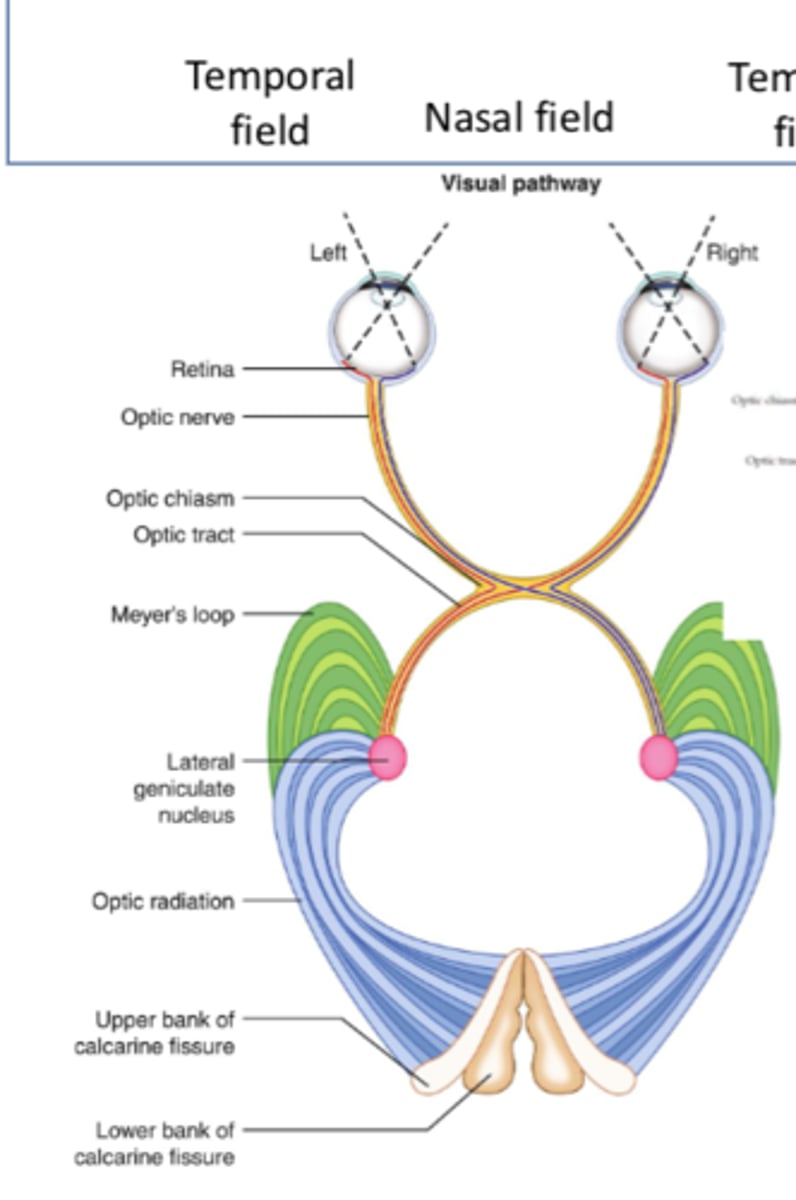
What is the third step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Optic chiasm
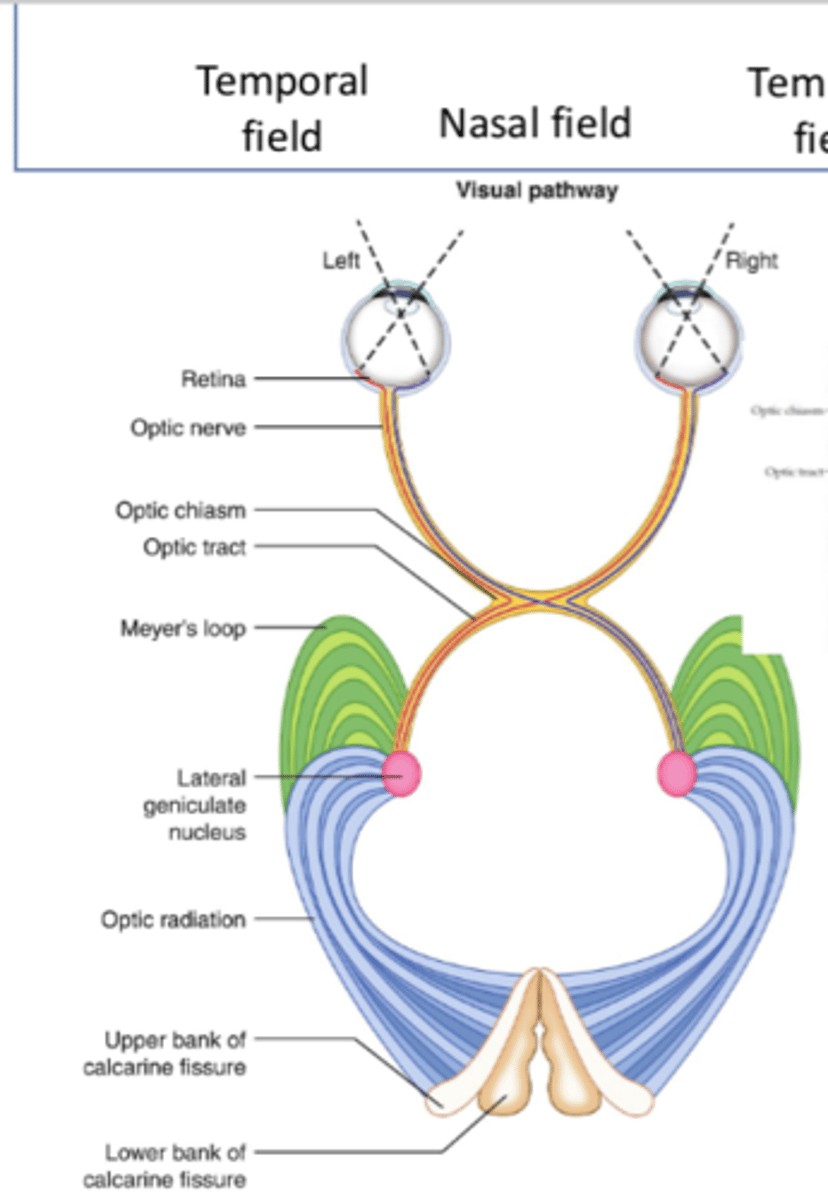
What is the fourth step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Optic tract (posteriorly)
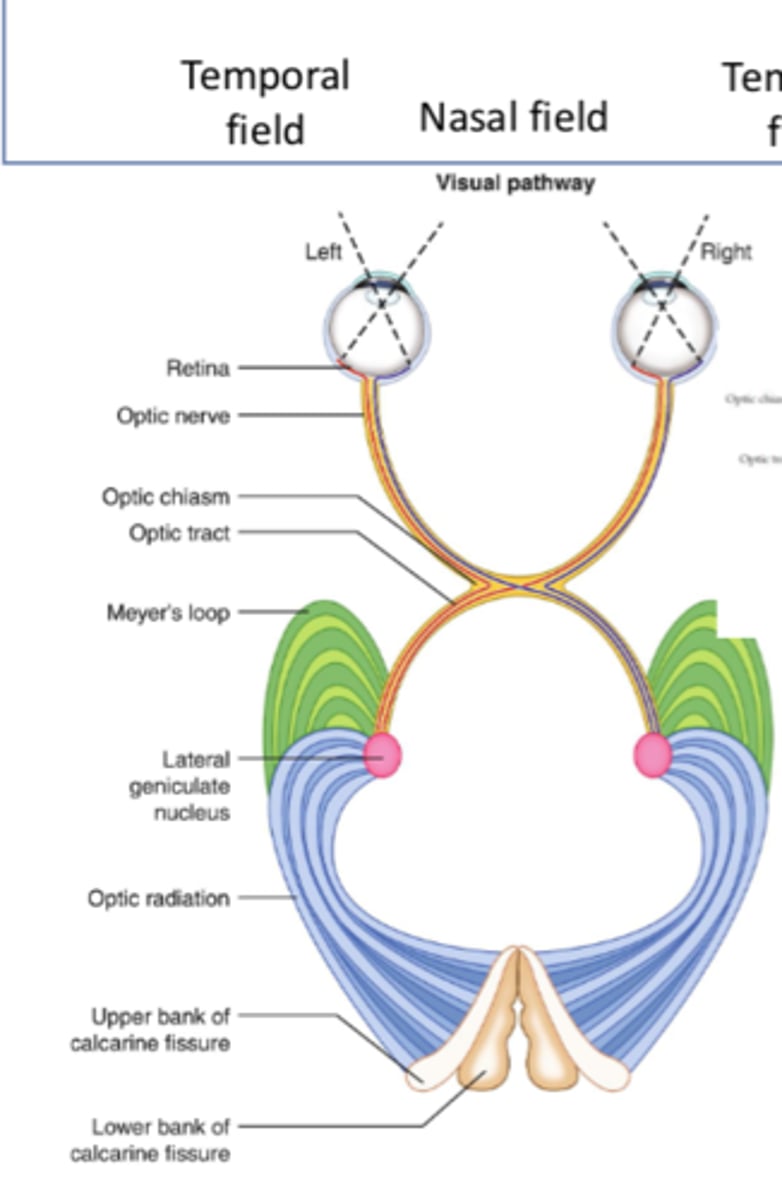
What is the fifth step of the geniculostriate pathway?
- LGN of thalamus
- First synapse, most of the fibers
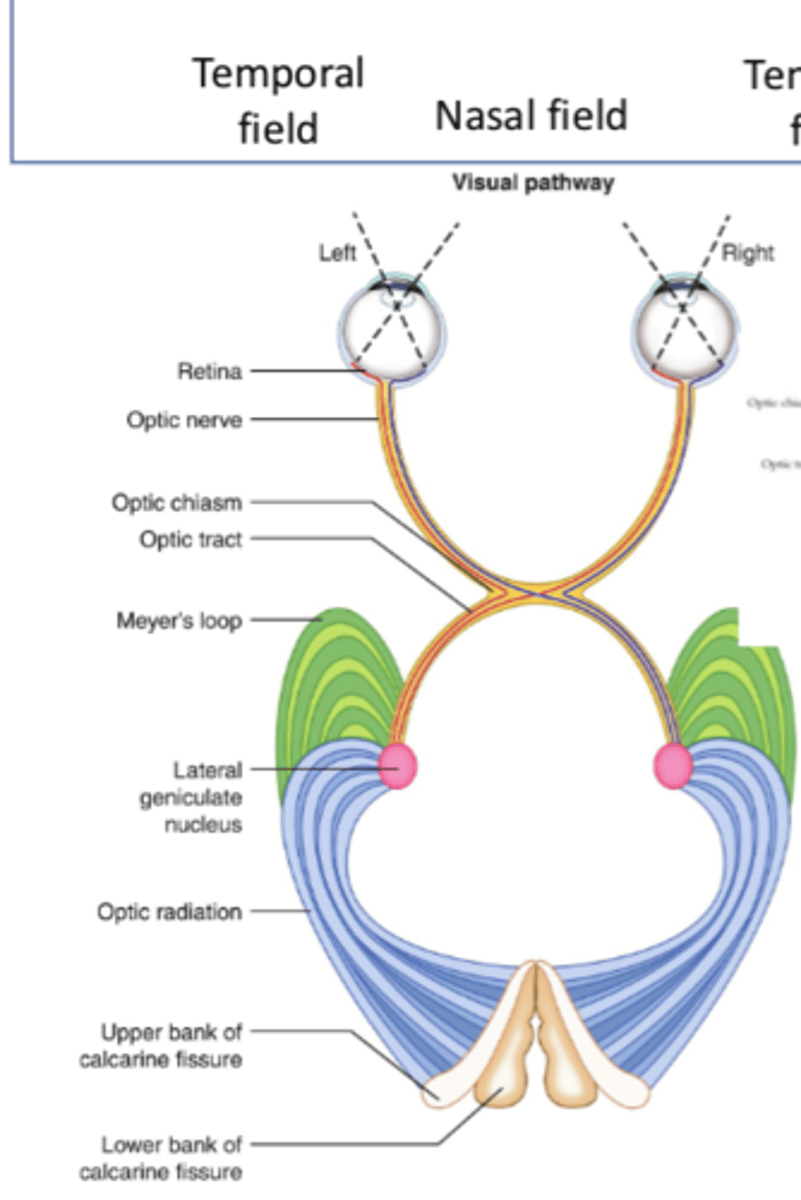
What is the sixth step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Optic radiations
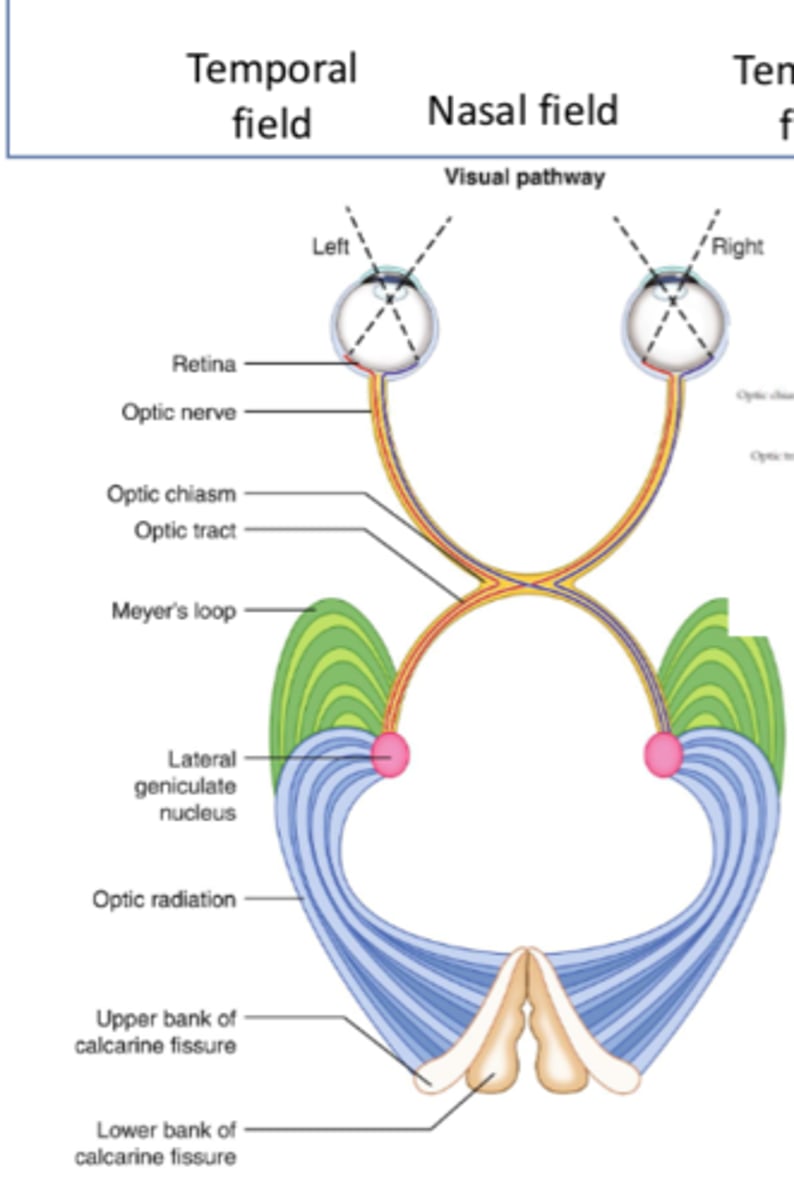
Where do superior optic radiations travel to?
Upper bank of calcarine fissure (primary visual cortex)
Where do inferior optic radiations travel to?
Lower bank of calcarine fissure (primary visual cortex)
What is the seventh step of the geniculostriate pathway?
Superior/inferior banks of calcarine fissure
Where is the temporal field of vision projected to?
Nasal retina
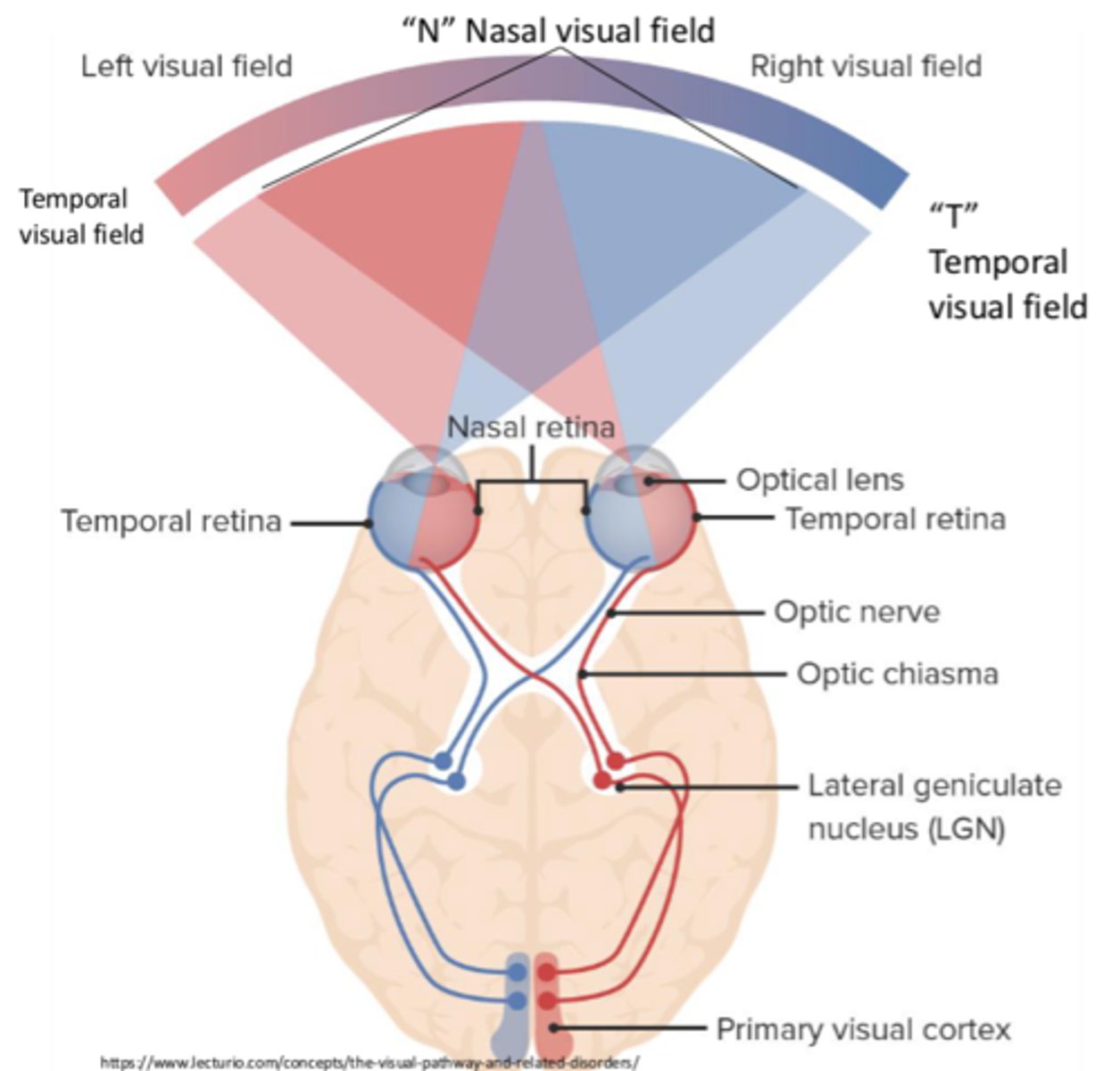
Where is the nasal field of vision projected to?
Temporal retina
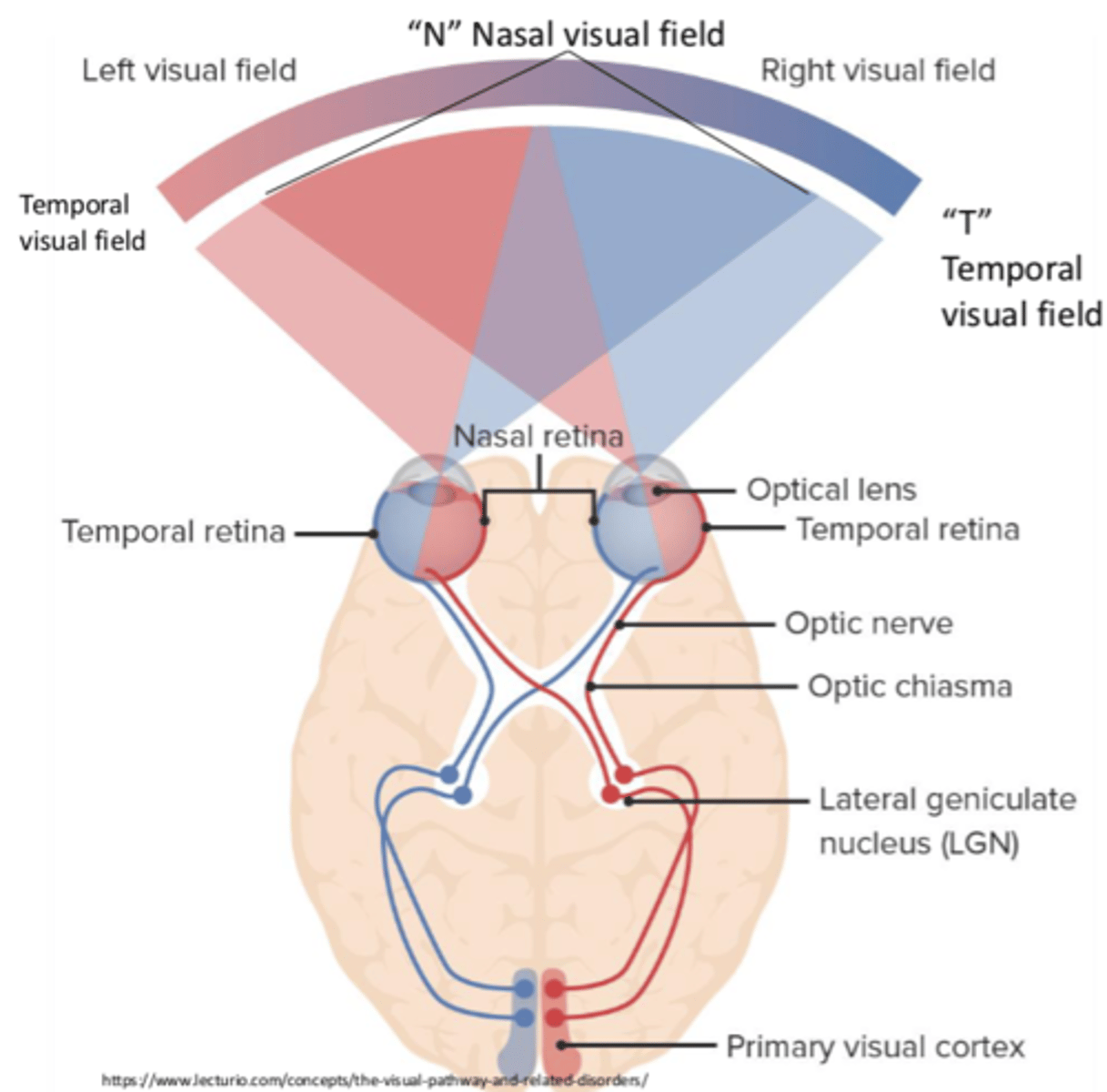
Does the information that enters the temporal retina cross over?
No
Does the information that enters the nasal retina cross over?
Yes
What does the processing of the temporal/nasal fields of vision lead to?
Binocular vision
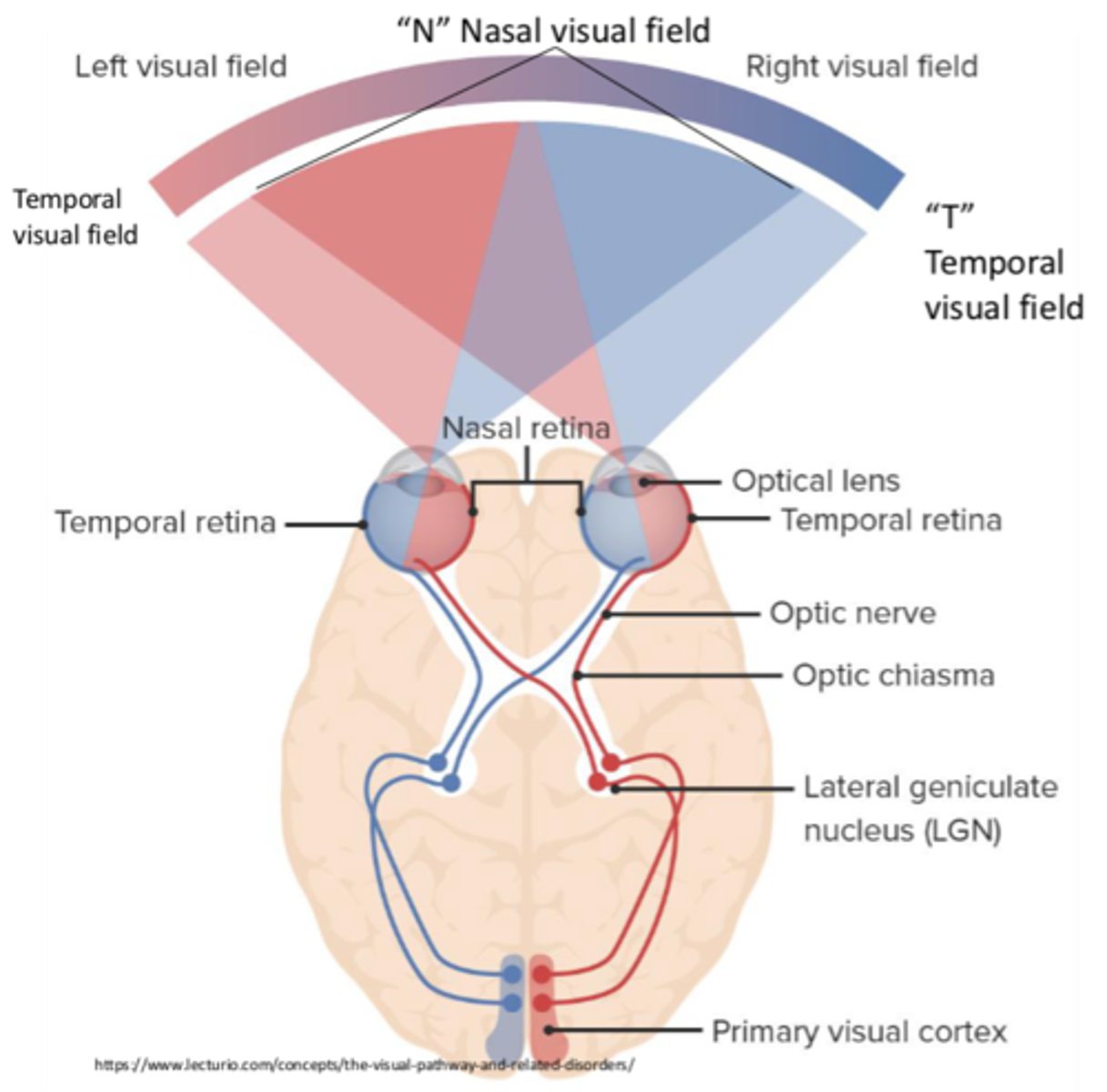
Where is the right visual field represented?
Left visual cortex
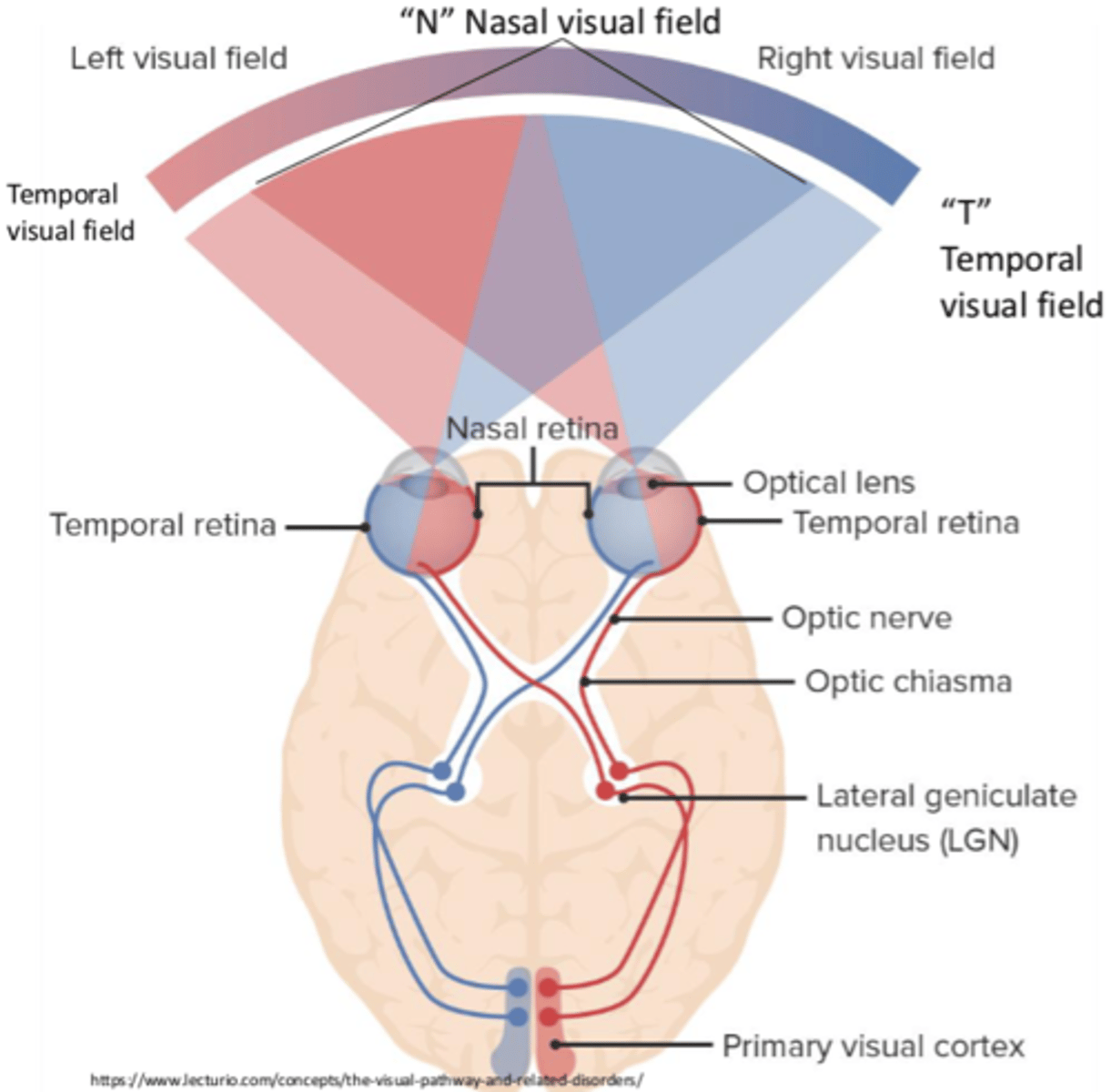
Where is the left visual field represented?
Right visual cortex
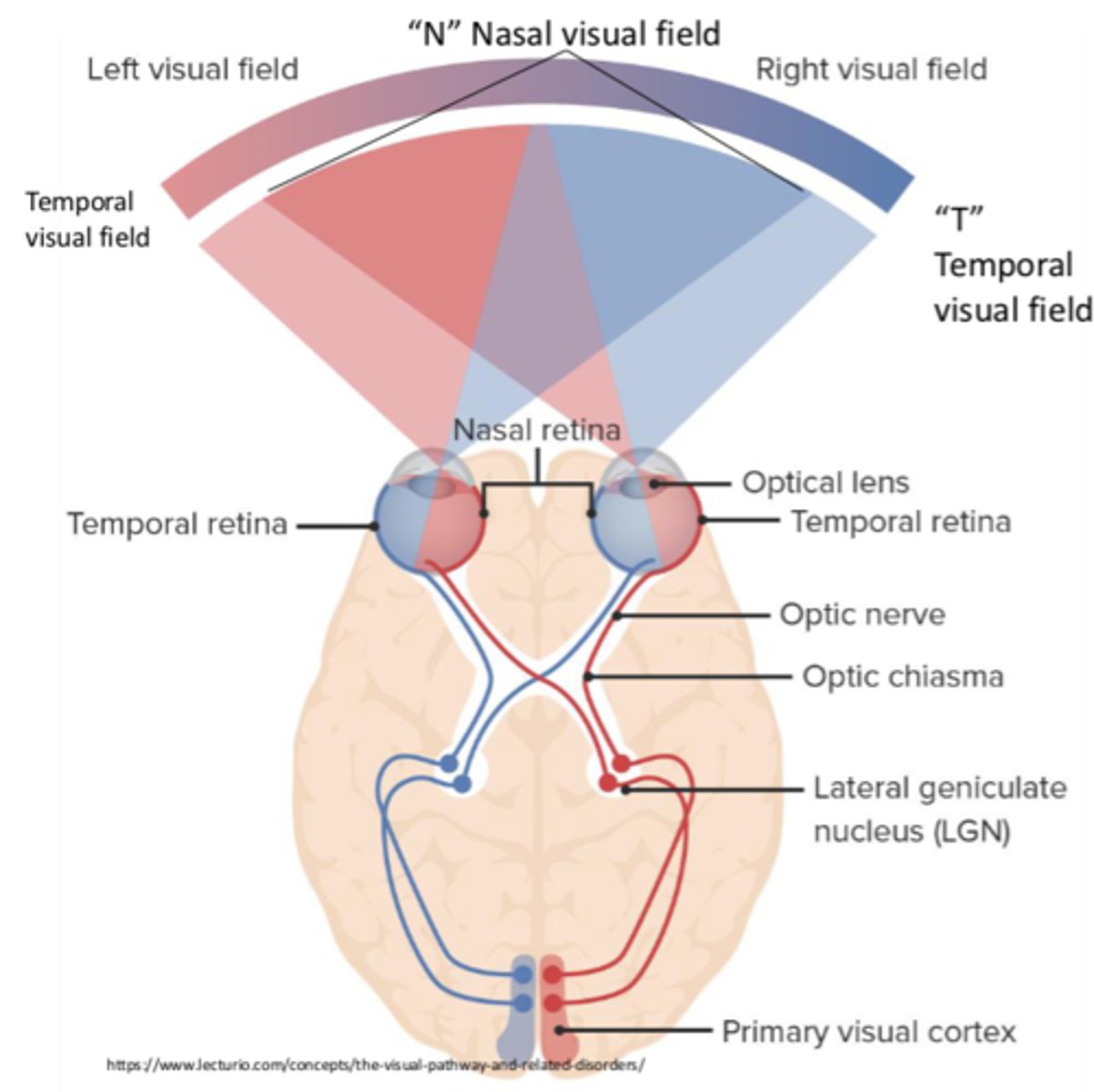
Where is the primary visual cortex located?
Banks of the calcarine fissure (occipital lobe)
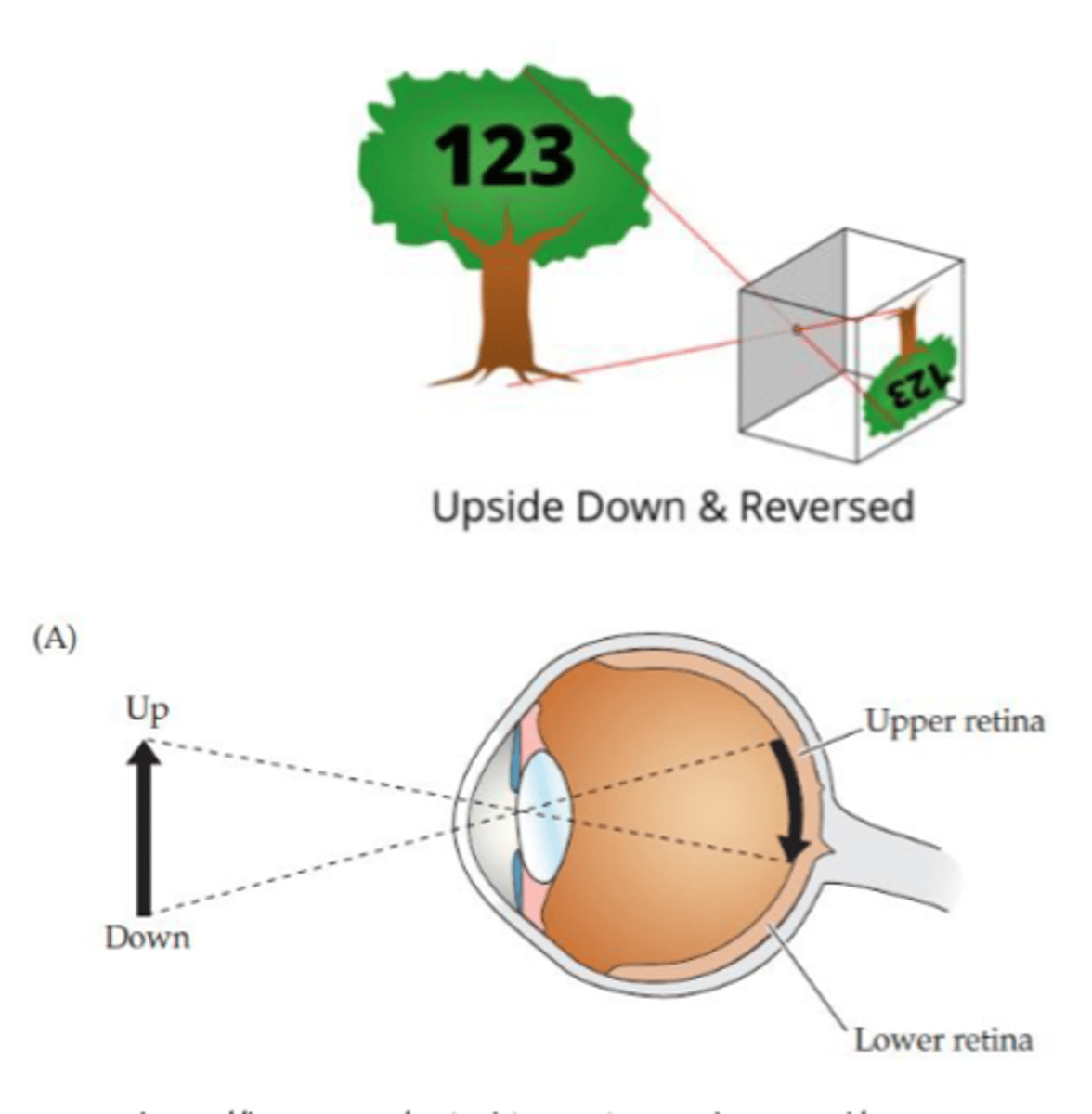
Visual images on the retina are...
- Reversed (flipped laterally)
- Inverted (upside down)
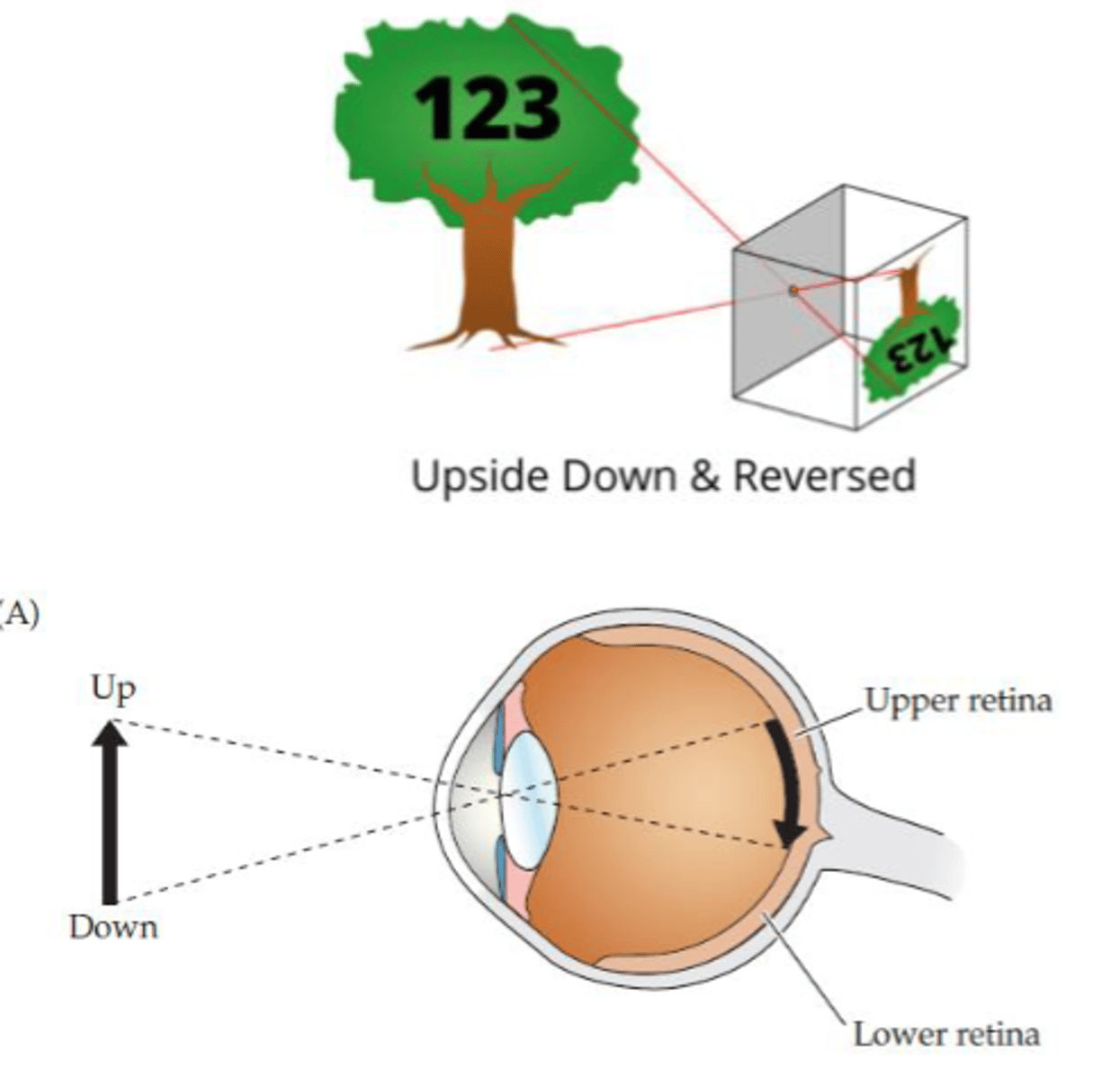
How are images reversed on the retina?
- Temporal field projected to nasal retina
- Nasal field projected to temporal retina
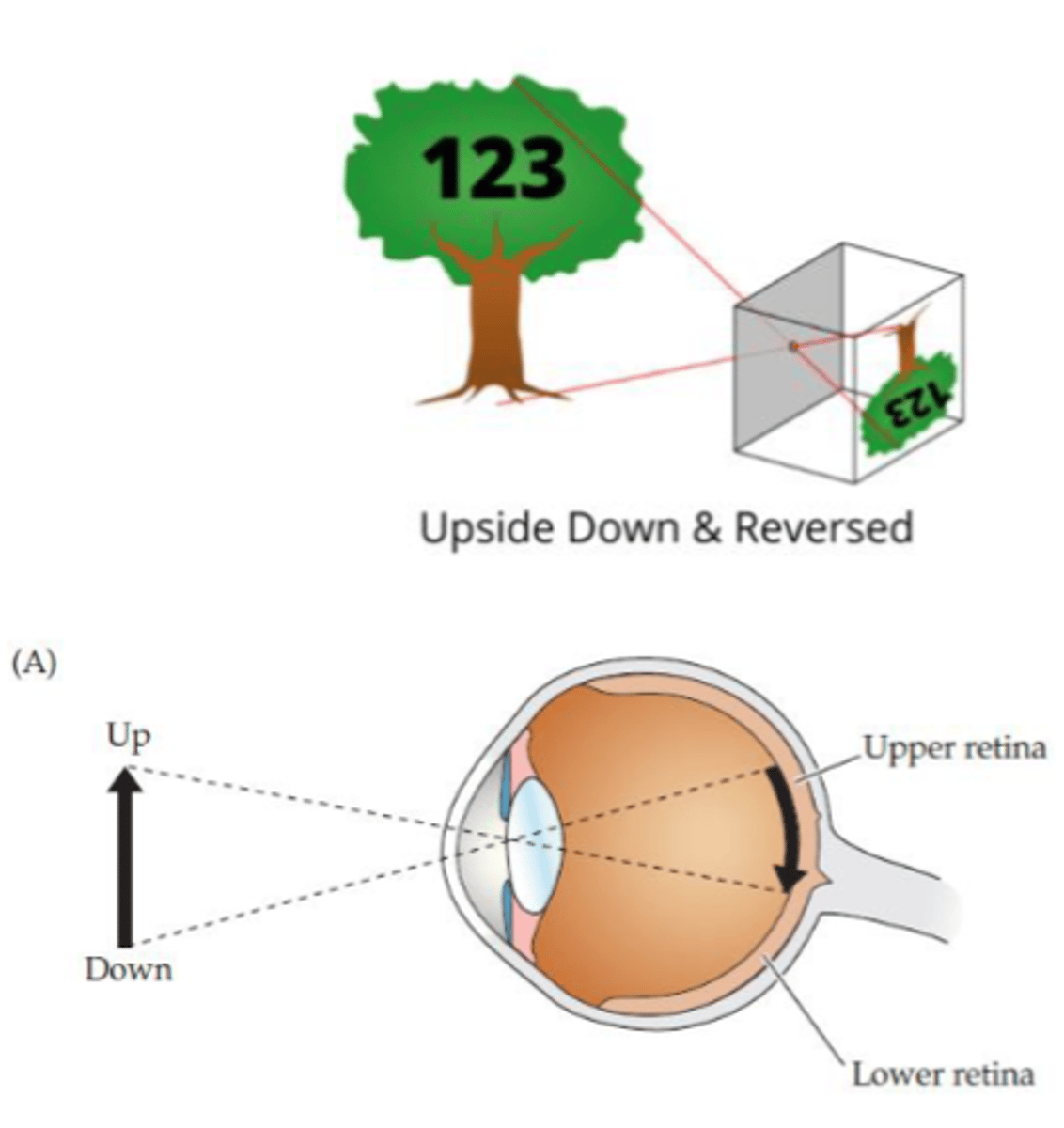
How are images inverted on the retina?
- Upper visual space projected onto lower retina
- Lower visual space projected onto upper retina
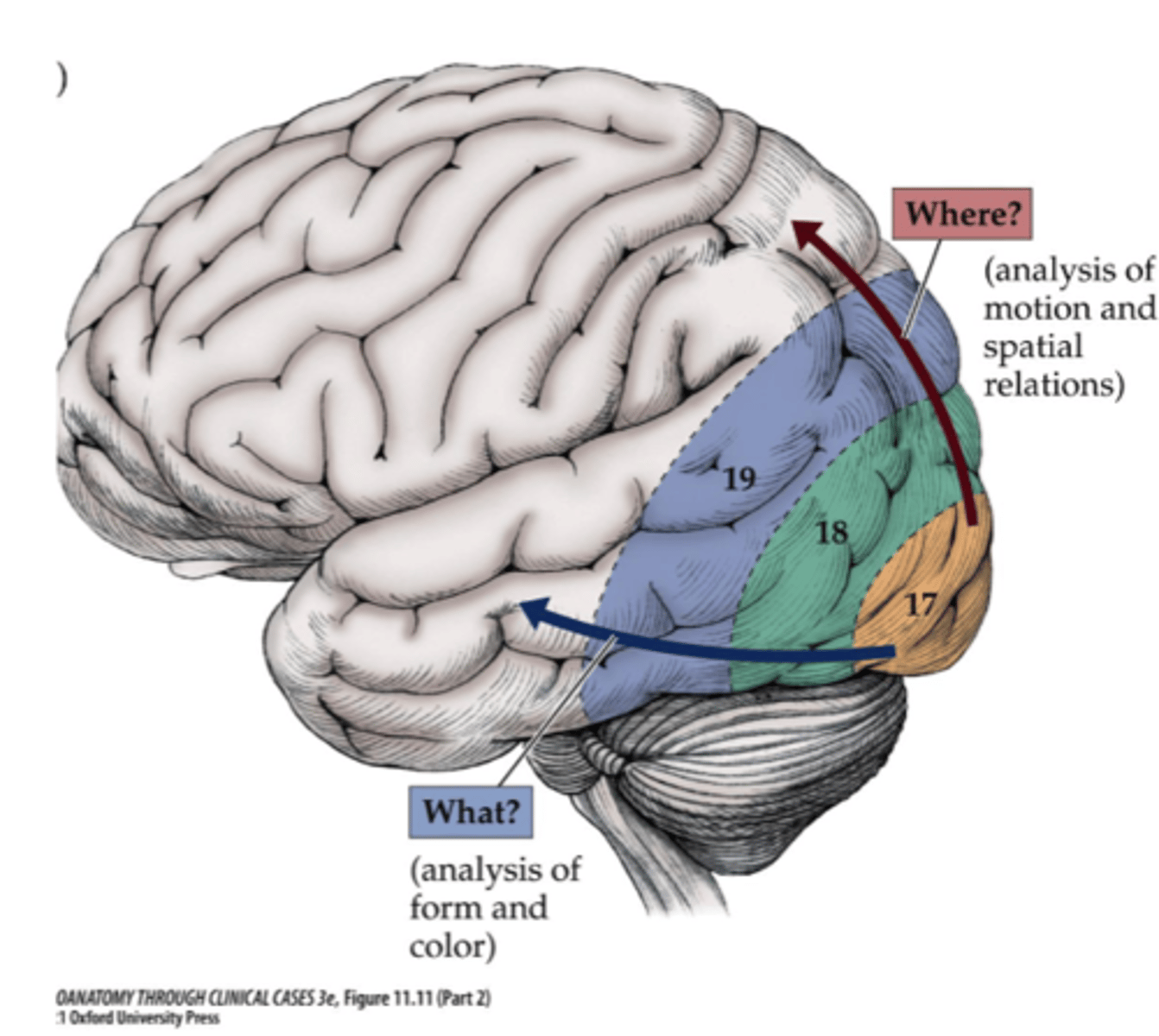
Where is the motion spatial analysis processed for the visual processing pathways?
Dorsolateral parieto-occipital cortex
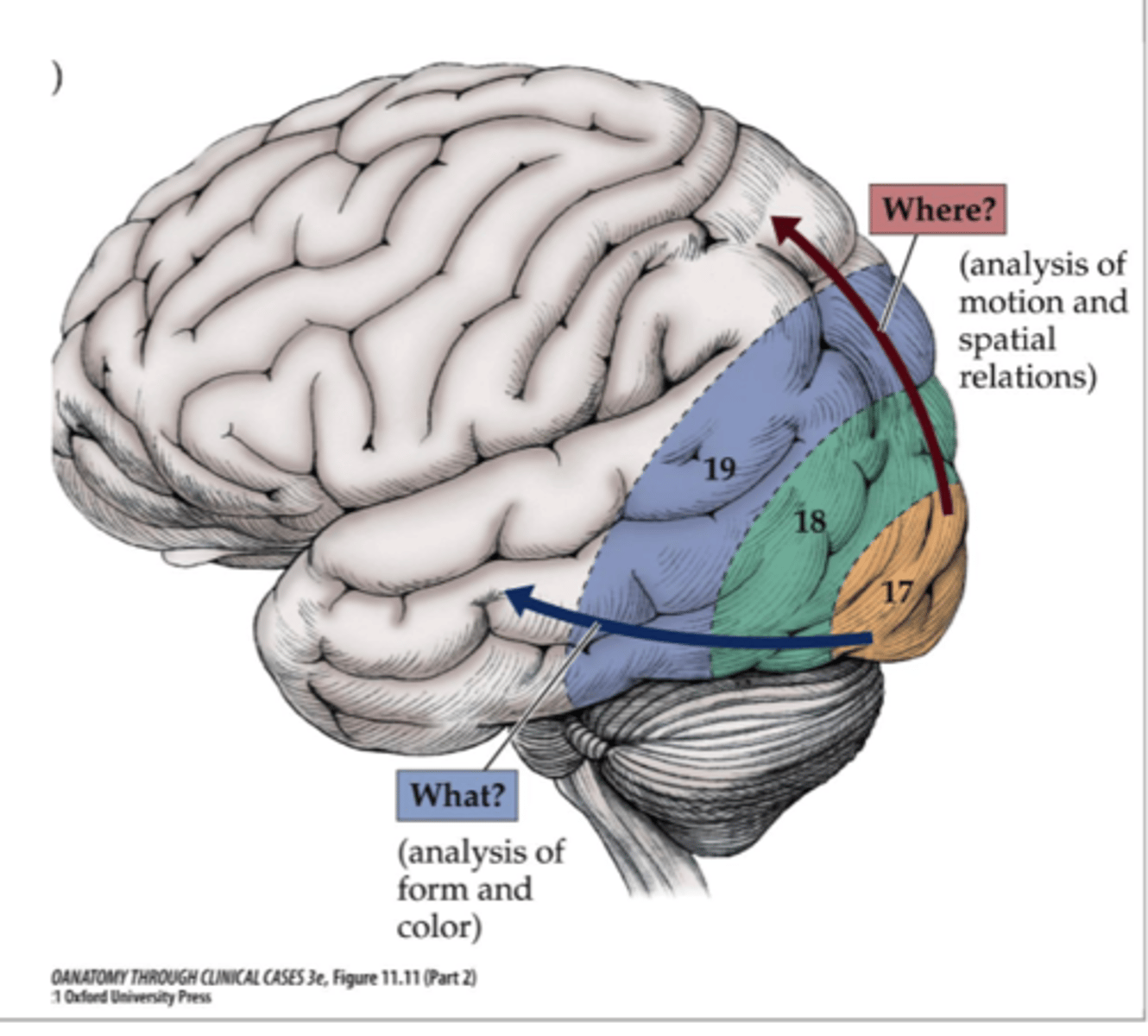
Where are form/color, faces, and letters processed for the visual processing pathways?
Inferior occipito-temporal cortex
What is the blood supply of the retina/eye?
Central ophthalmic artery
What is the blood supply of the optic chaism?
Circle of Willis
What is the blood supply of the optic radiations?
Deep branches of MCA and PCA
What is the blood supply of the primary visual cortex?
Calcarine branch of PCA
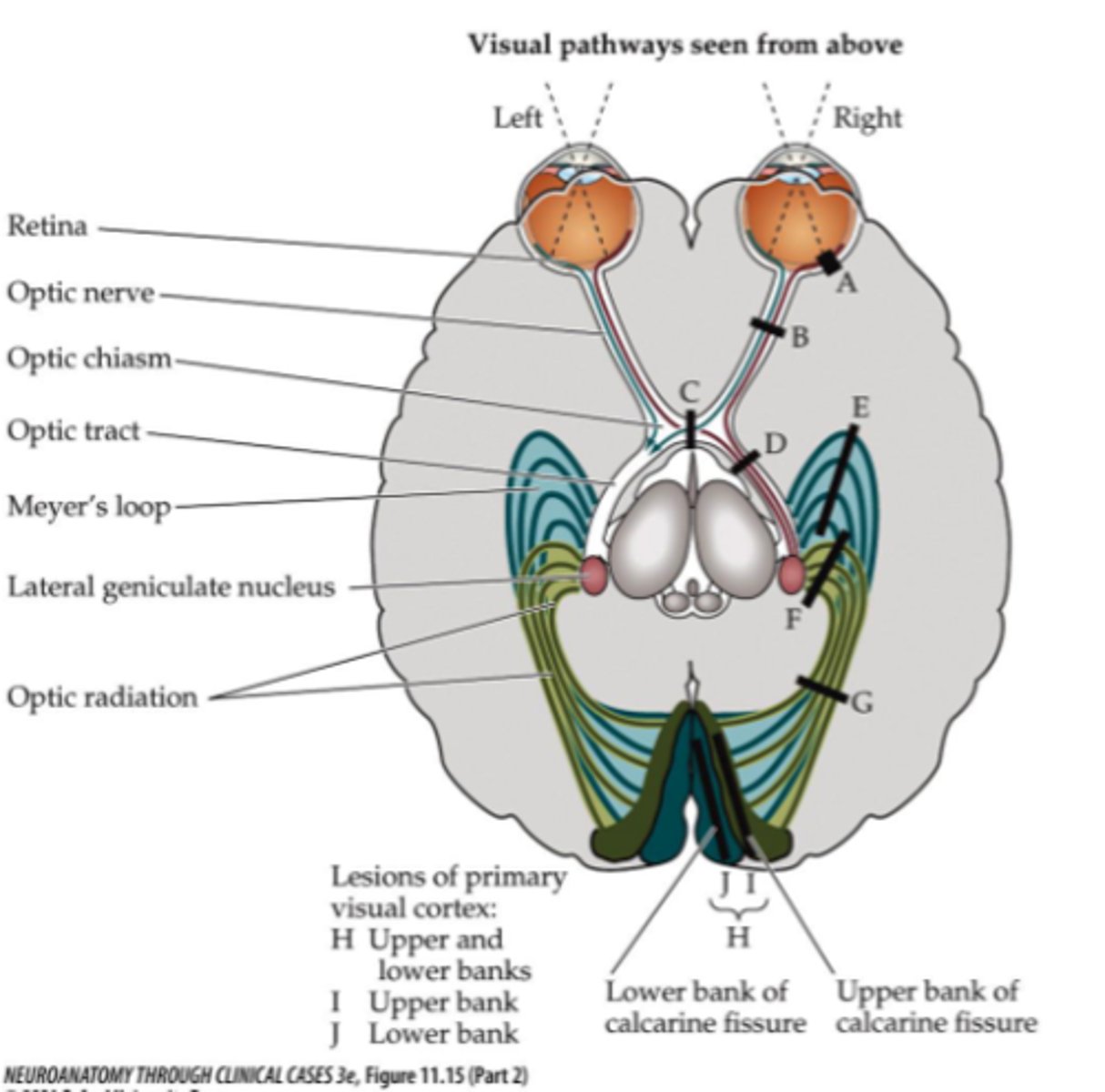
Where is lesion site A?
Retina
What symptom would be present for lesion site A?
Monocular scotoma
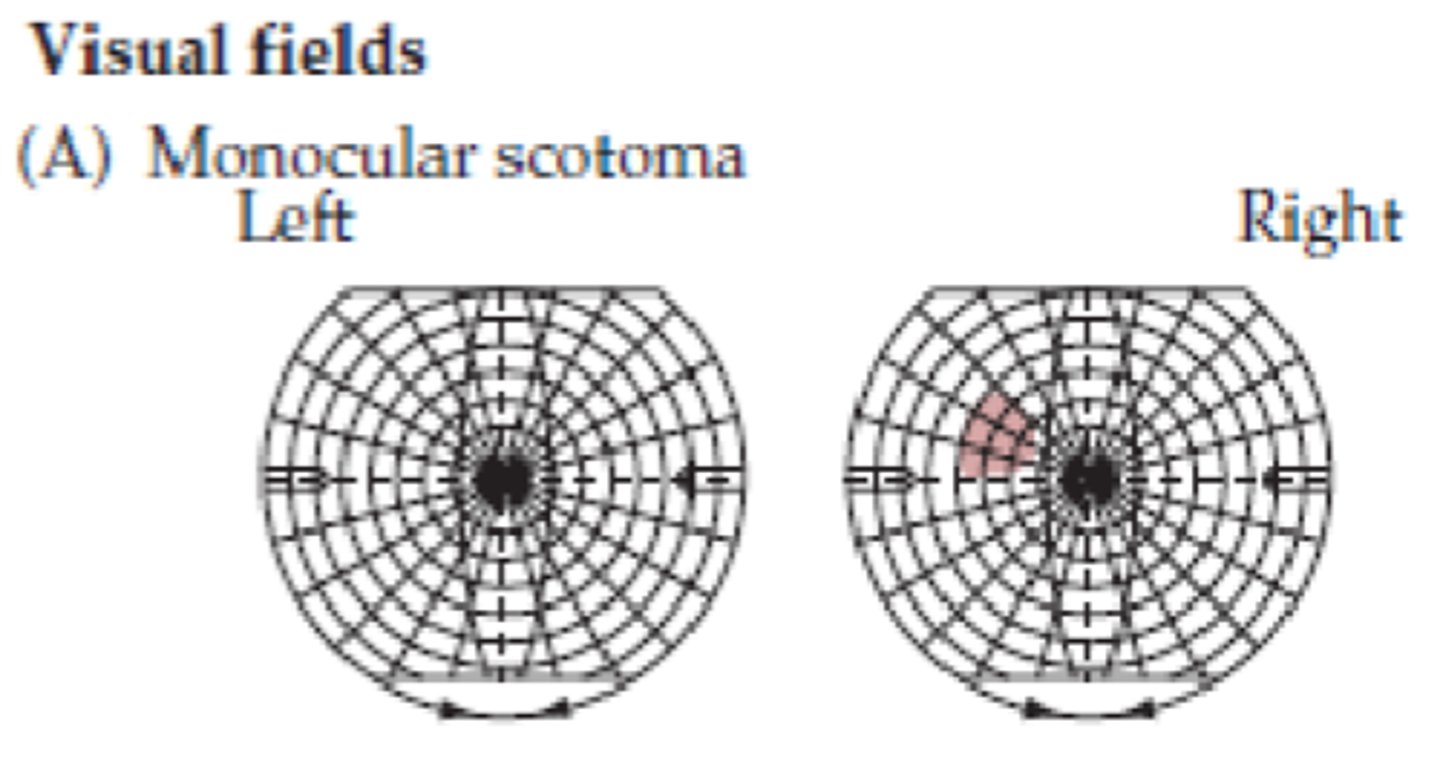
What is a scotoma?
A circumscribed region of visual loss
What type of loss occurs due to a lesion at site A?
Ipsilateral
Where is lesion site B?
Optic nerve
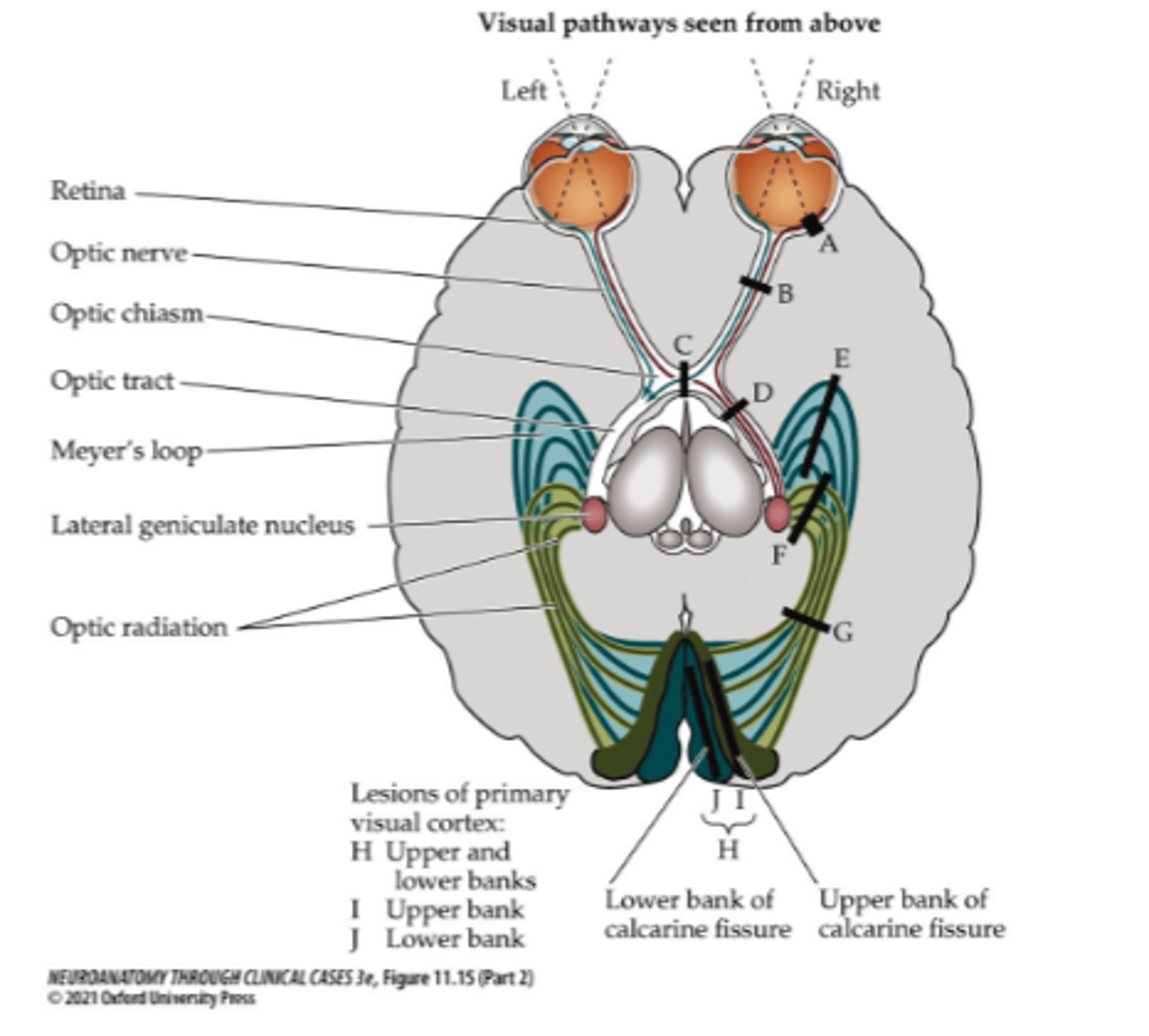
What does a lesion at site B affect (right side)?
- Information from right side
- Right nasal/temporal field of vision
What symptom would be present for lesion site B?
Monocular visual loss
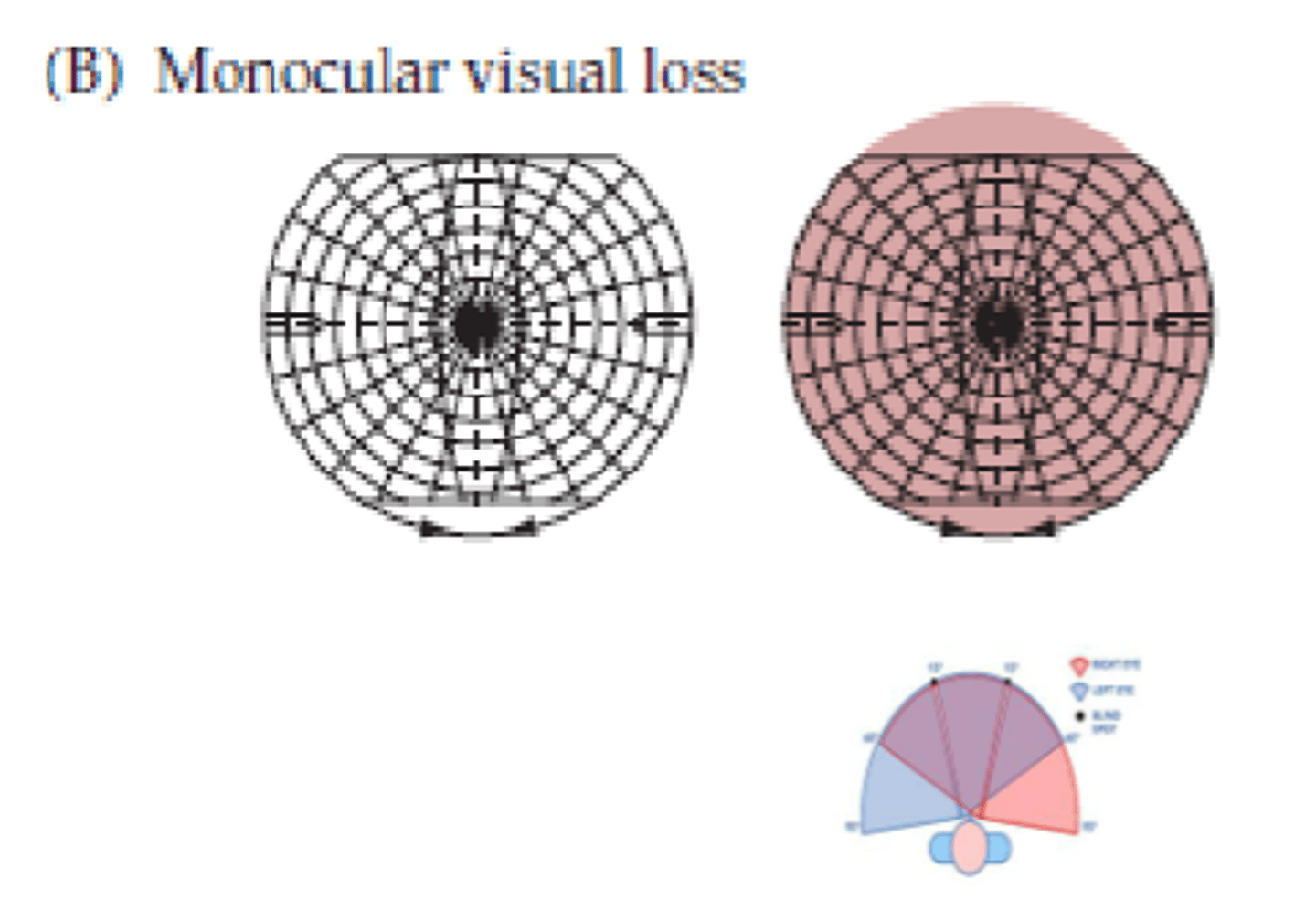
What type of loss occurs due to a lesion at site B?
Ipsilateral
Where is lesion site C?
Optic chiasm (pituitary gland tumor)
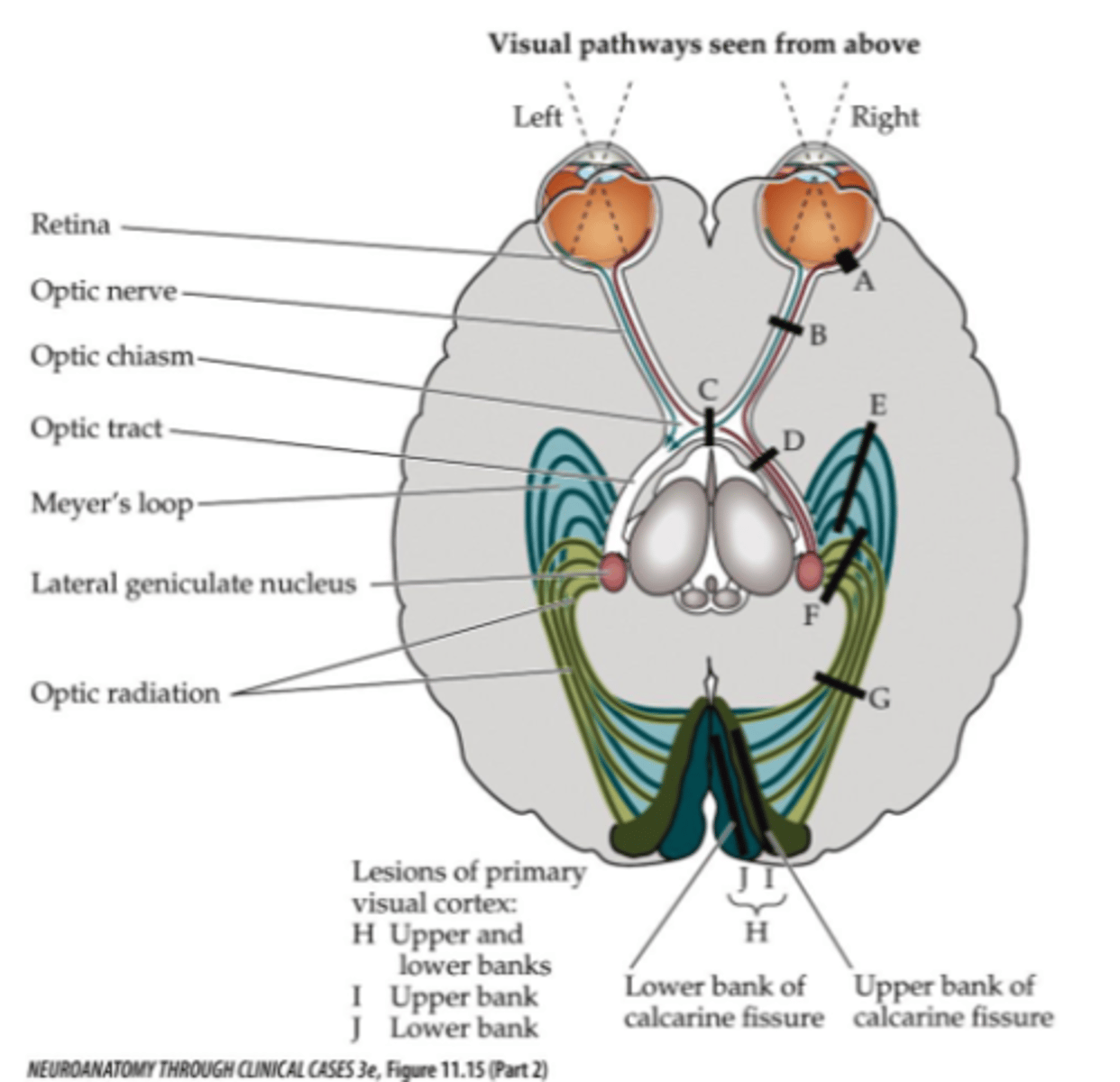
What does a lesion at site C affect?
- Information from left and right
- Temporal field (nasal retina)
- Peripheral vision
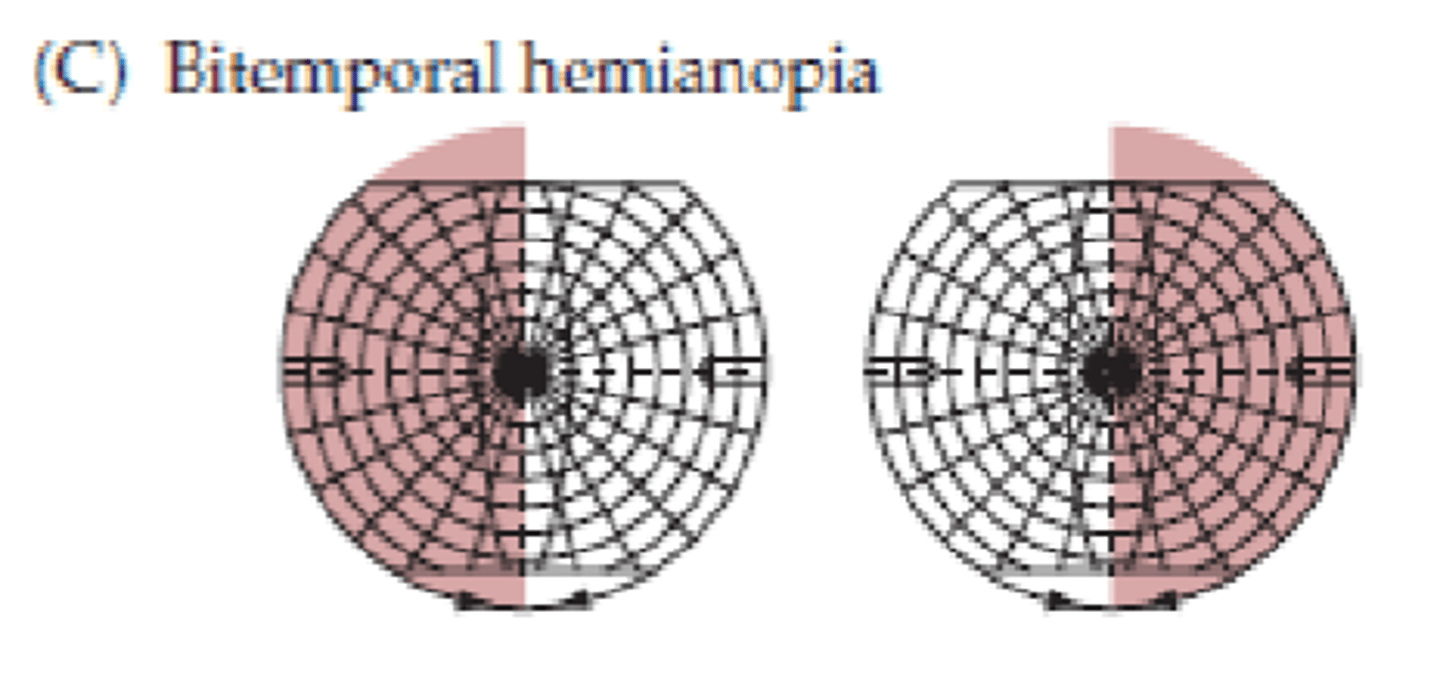
What symptom would be present for lesion site C?
Bitemporal hemianopia
Where is lesion site D (right side)?
Right optic tract
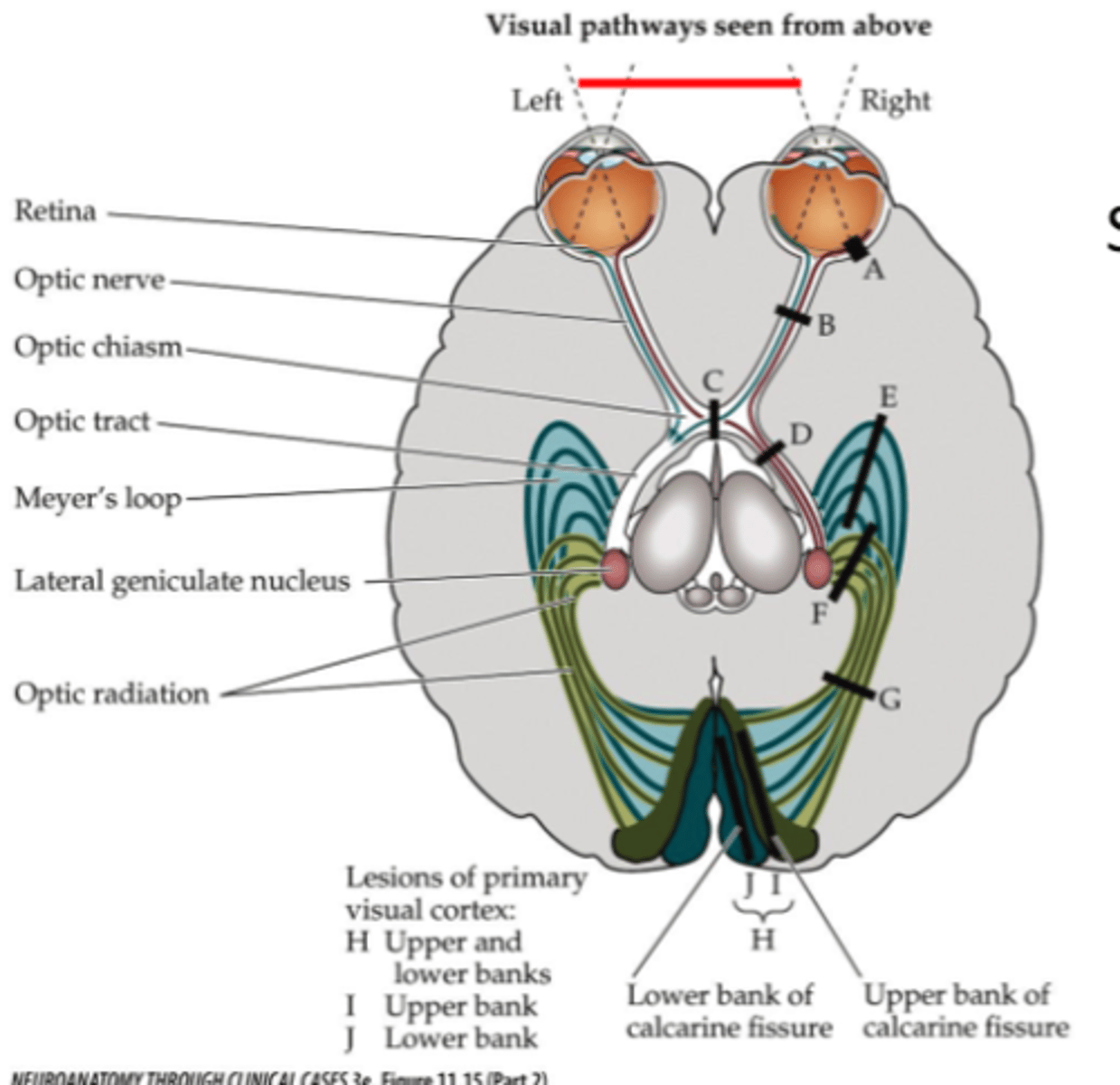
Where is lesion site G (right side)?
Right optic radiation
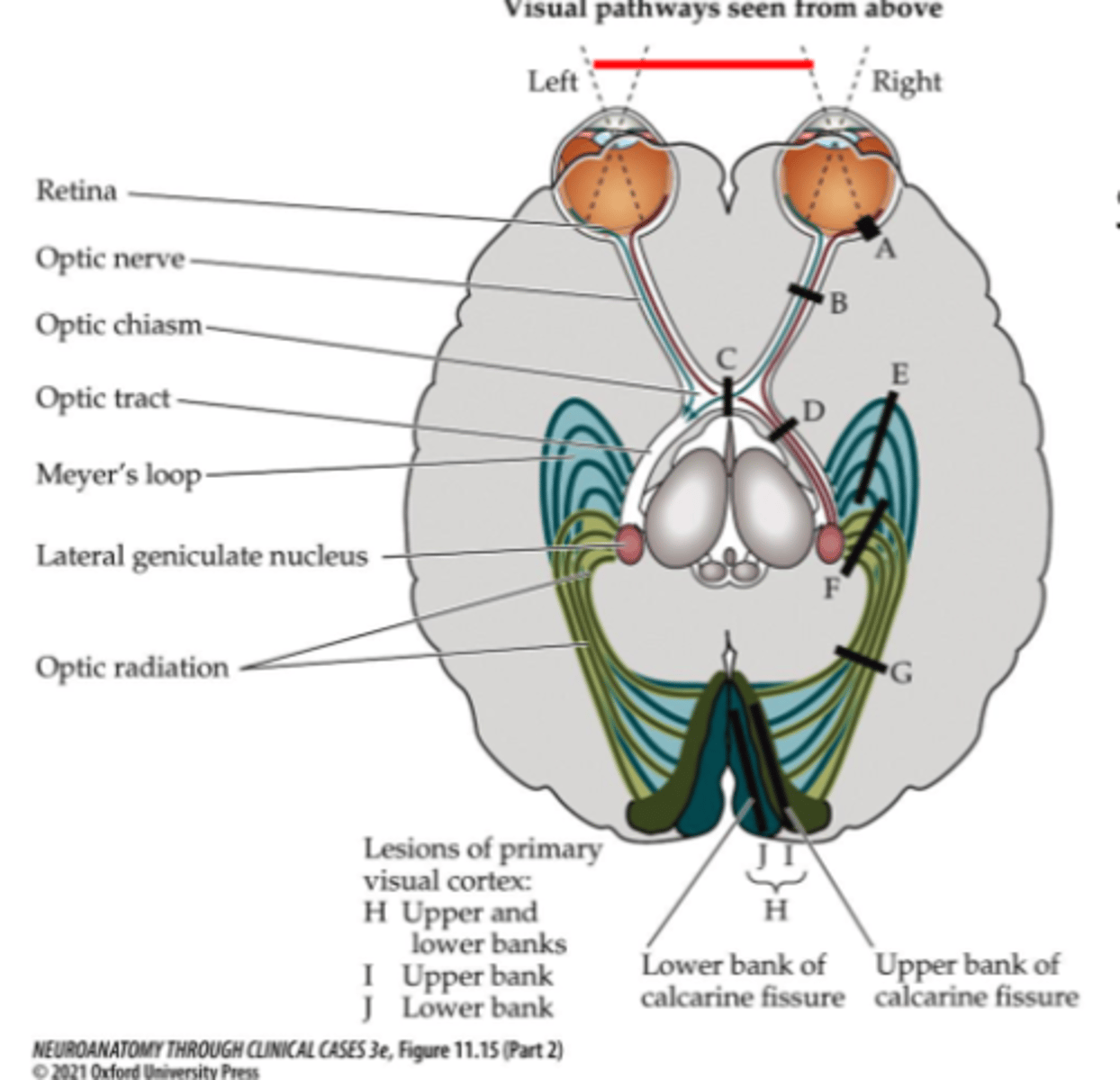
Where is lesion site H (right side)?
Right primary visual cortex
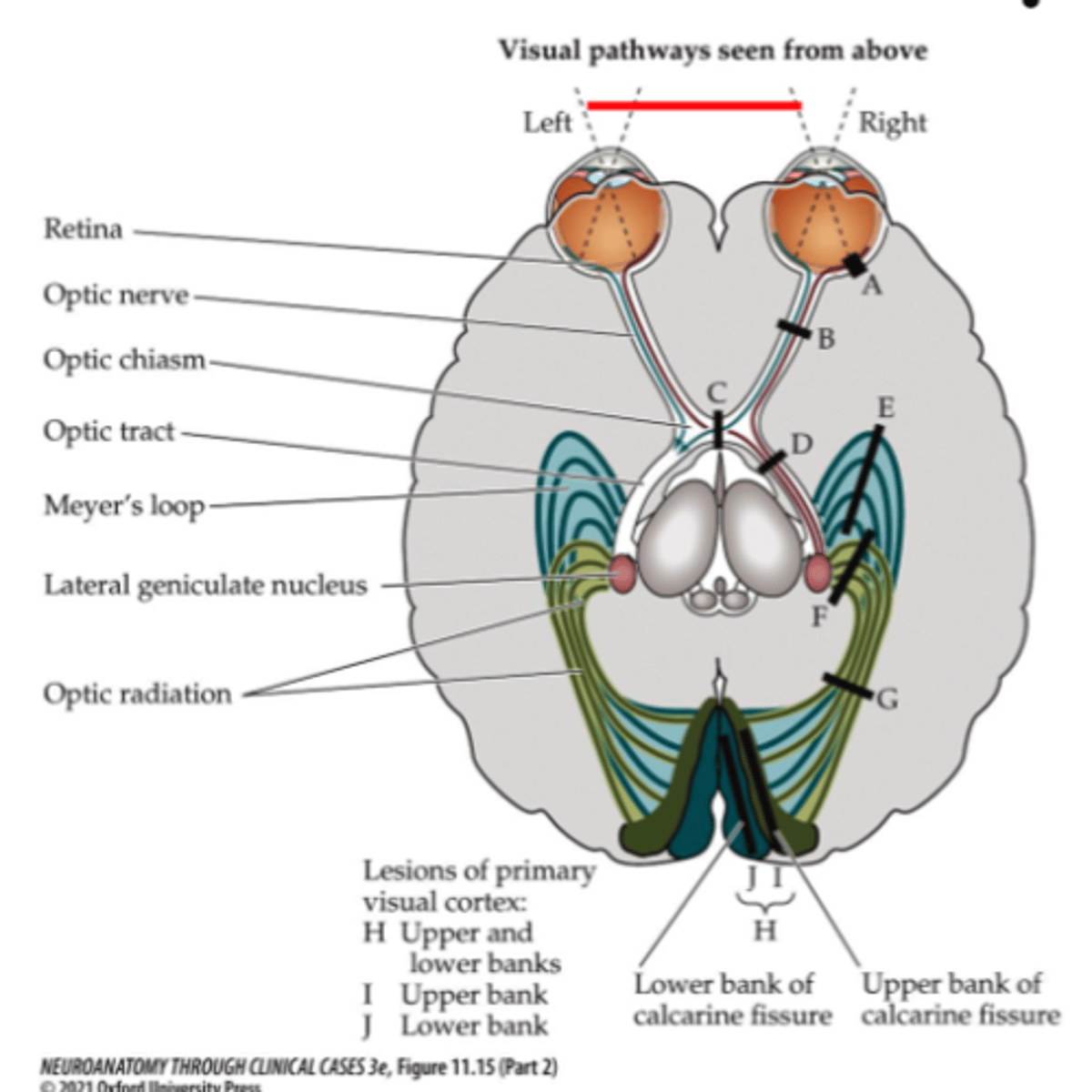
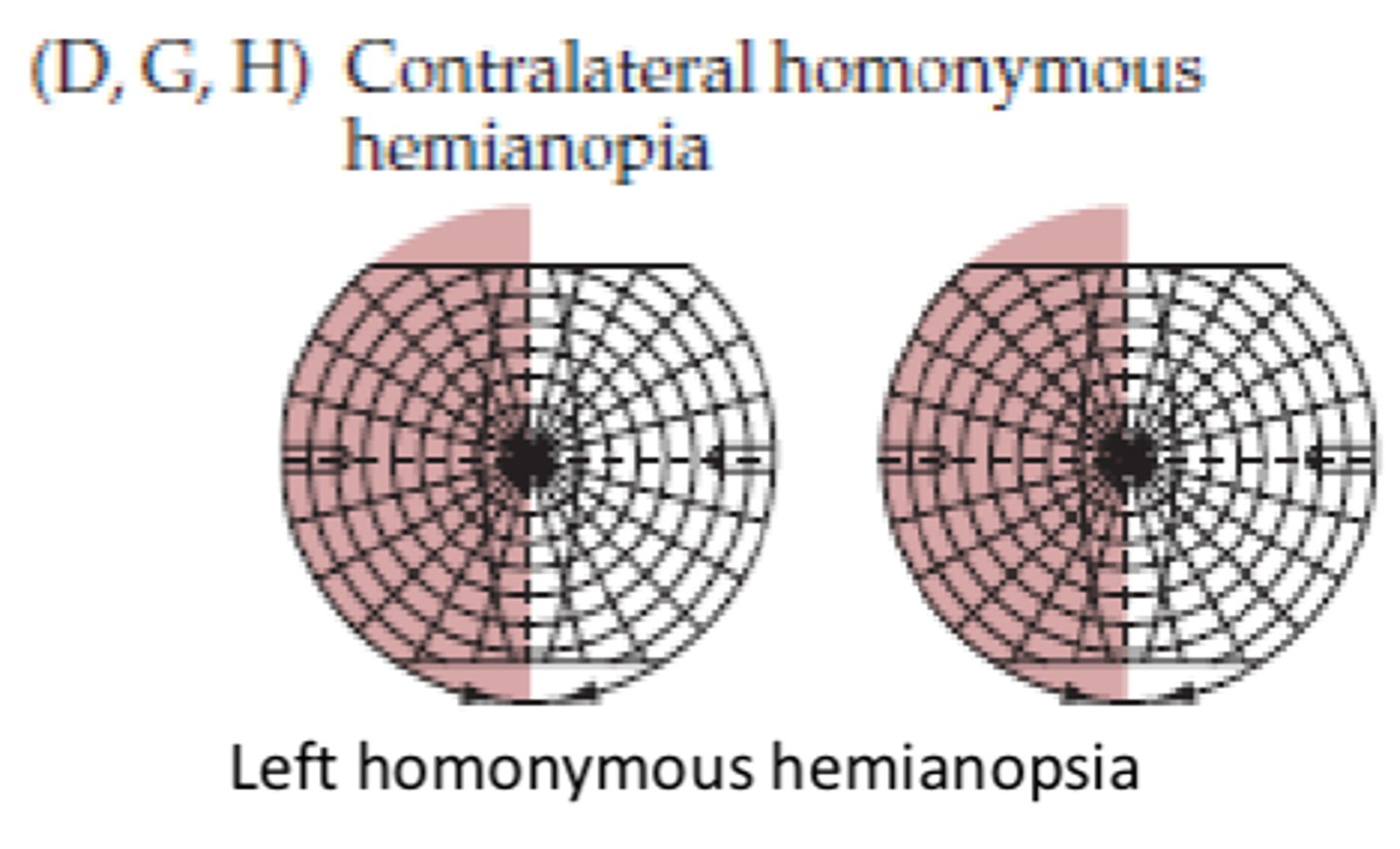
What does a lesion at site D, G, or H affect (right side)?
- Contralateral vision (left visual field)
- Left nasal field of vision
- Right temporal (retinal) field of vision
What symptom would be present for lesion site D, G, or H?
Contralateral homonymous hemianopia
Where is lesion site F (right side)?
Right superior portion of optic radiation
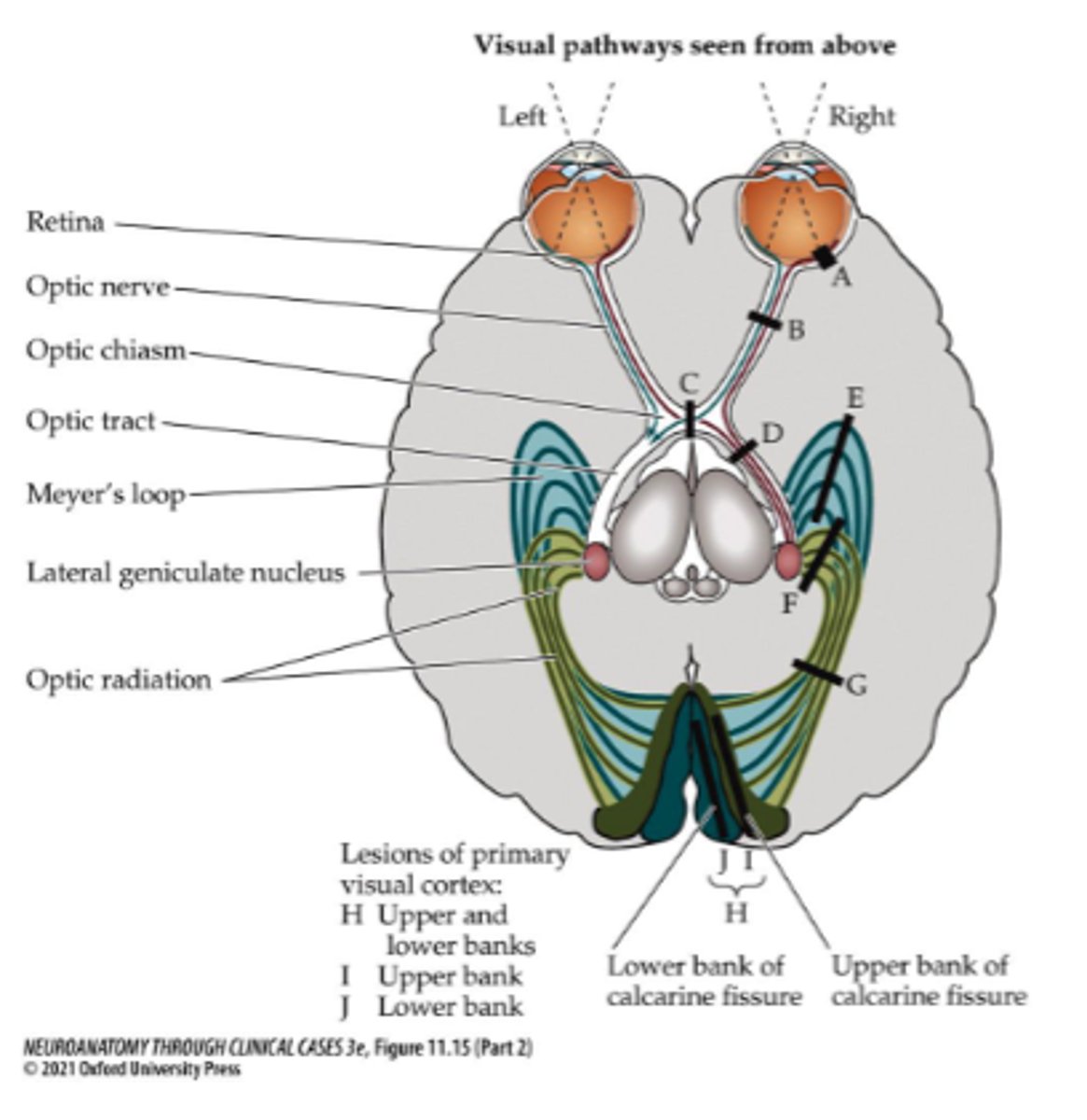
Where is lesion site I (right side)?
Right superior bank of calcarine fissure
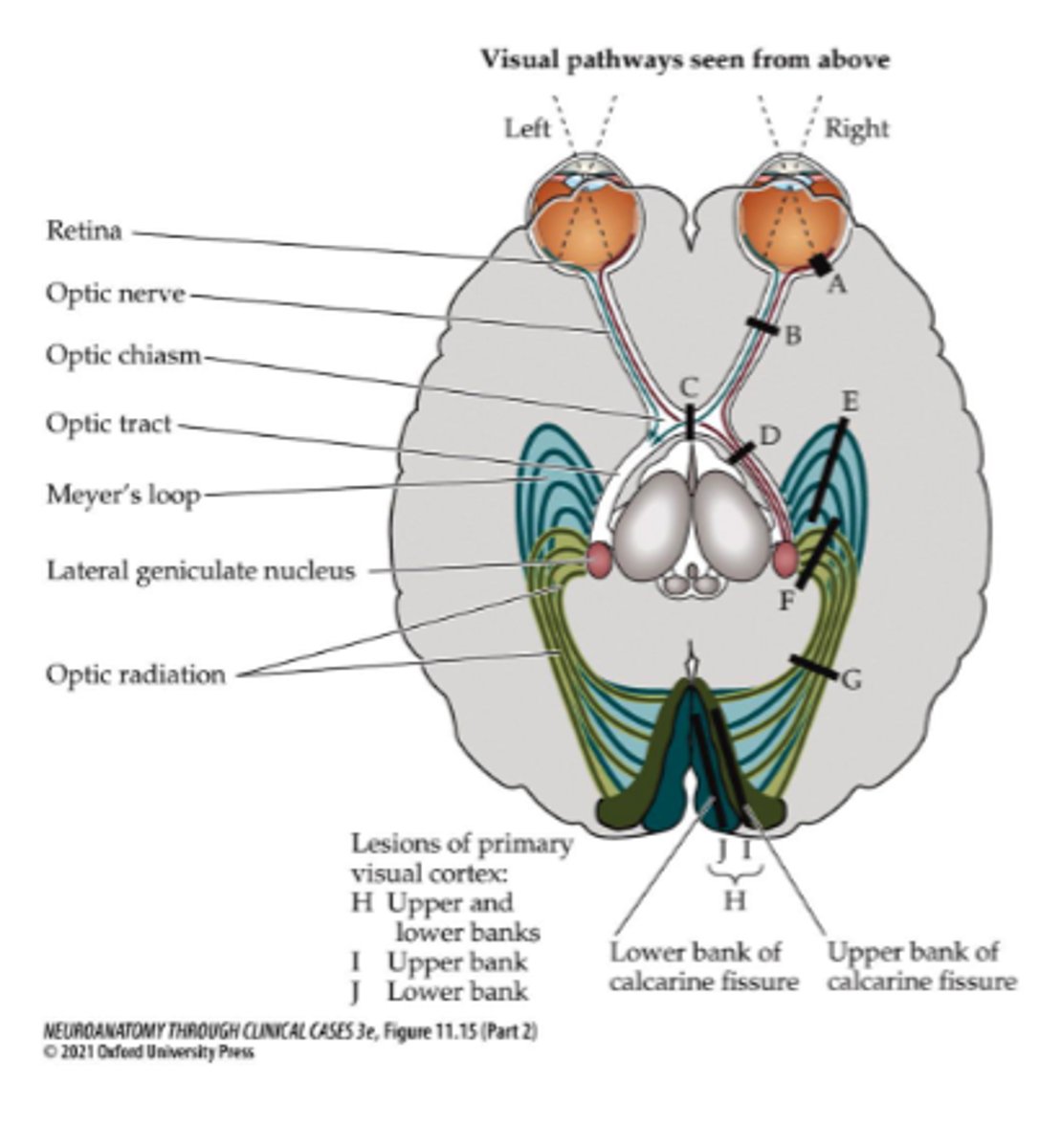
What symptom would be present for lesion site F or I?
Contralateral inferior quadrantanopia
What can cause a lesion at site F or I (5)?
- Lesions involving parietal lobe
- Infarcts in inferior division of MCA
- Tumors
- Demyelination
- Trauma
Where is lesion site E (right side)?
- Right inferior portion of optic radiation
- Meyer's loop
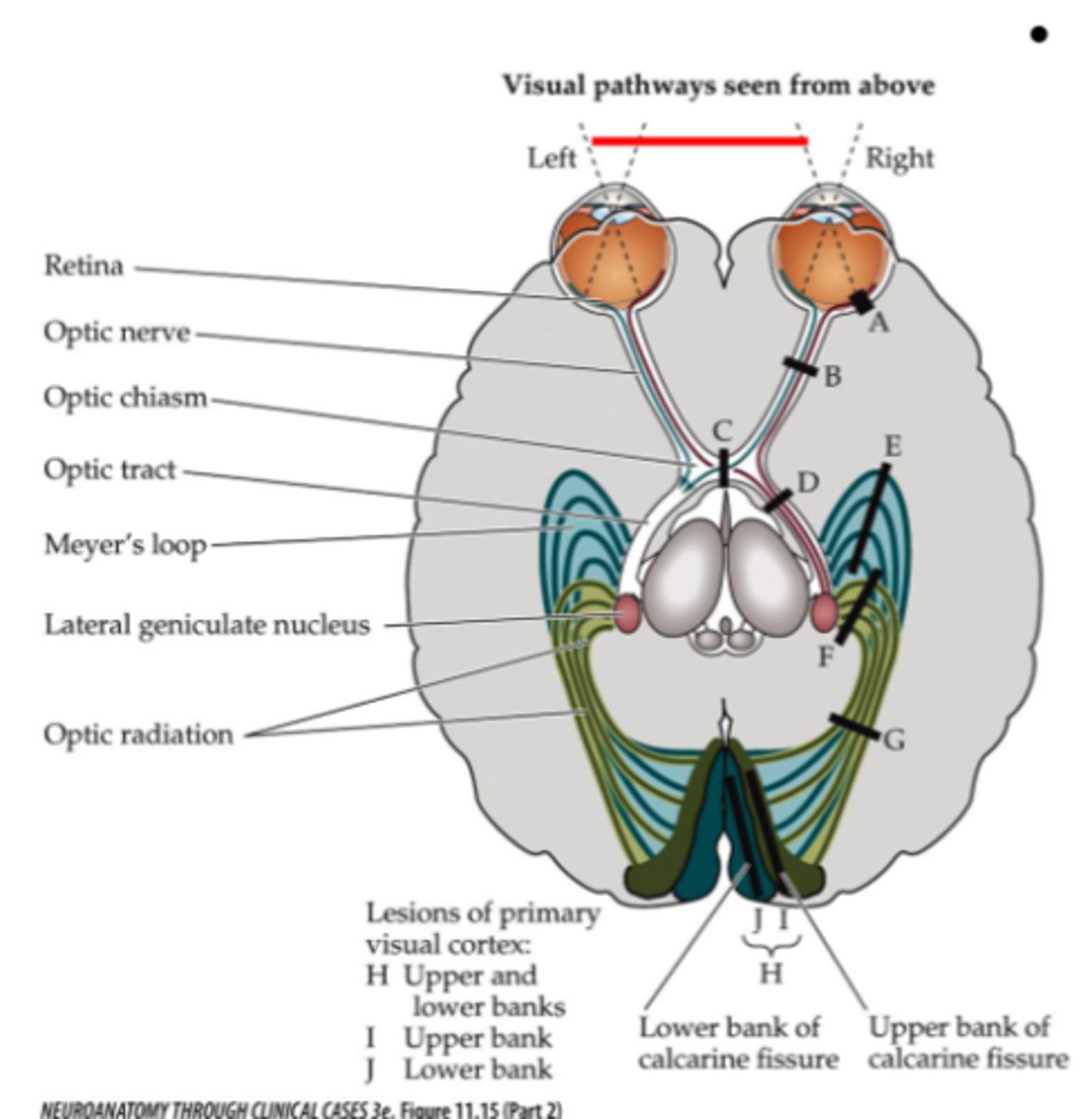
Where is lesion site J (right side)?
Right inferior bank of calcarine fissure
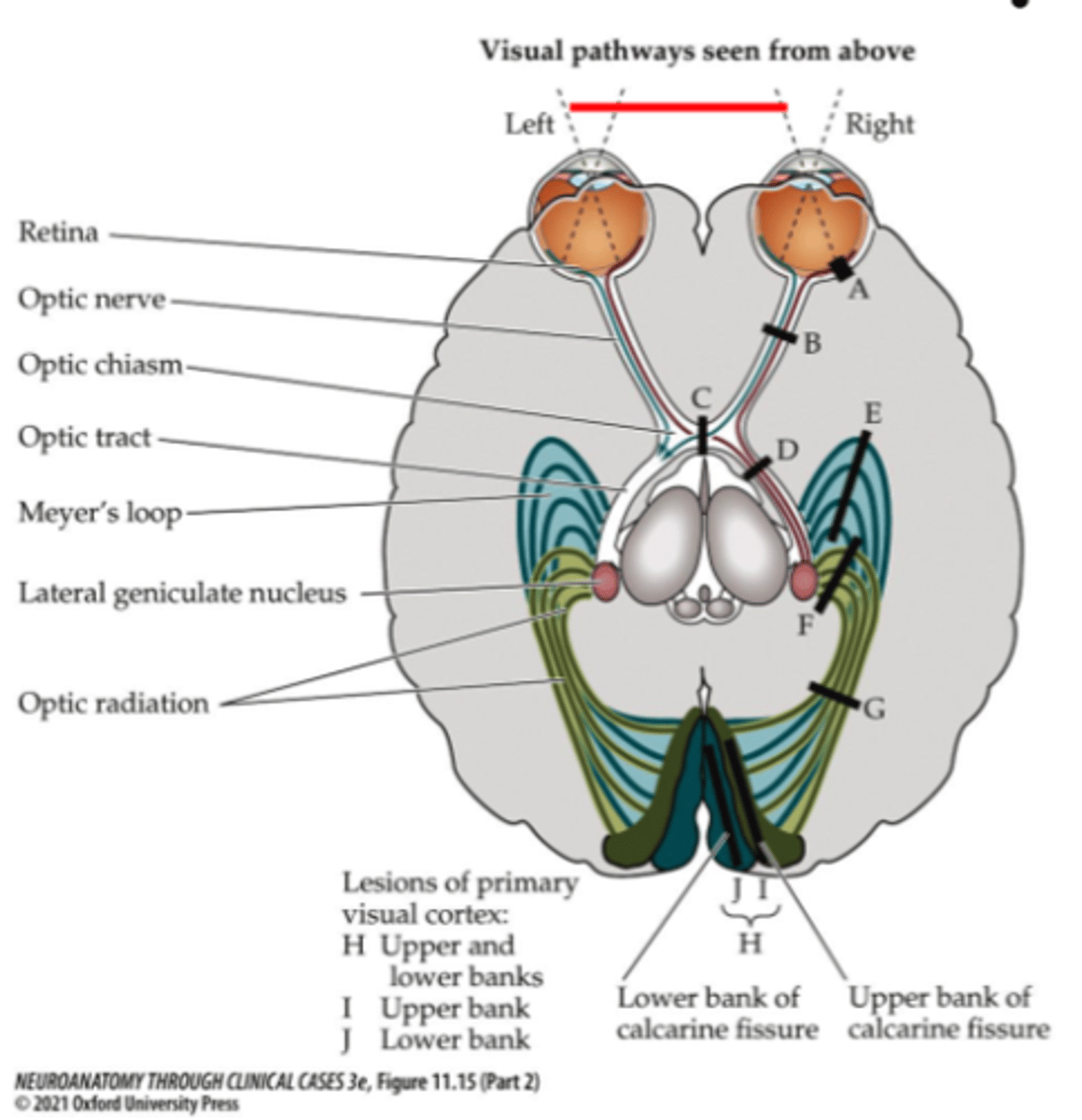
What symptom would be present for lesion site E or J?
Contralateral superior quadrantanopia
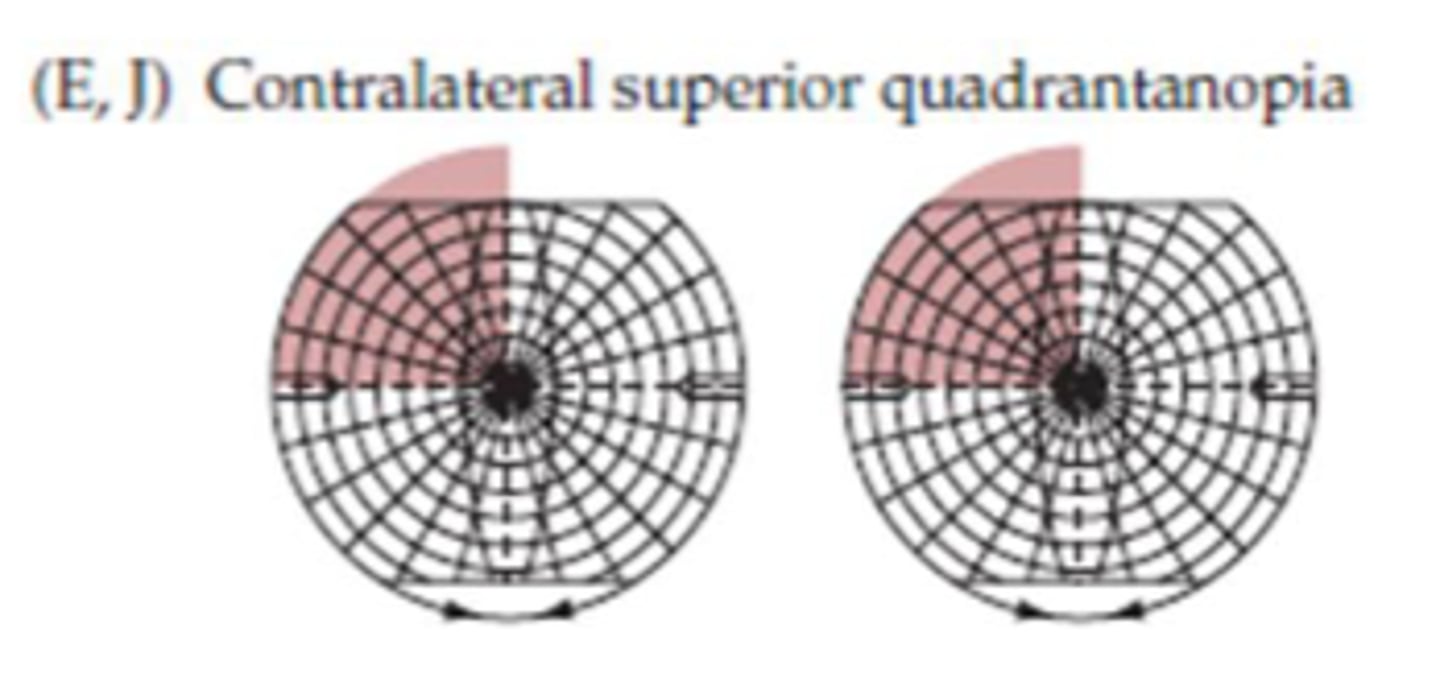
What can cause a lesion at site E or J?
Lesions involving temporal lobe
Where should you test for visual field deficits?
- Both sides
- All 4 quadrants
What are the visual field deficit tests (5)?
- Visual acuity
- Color vision
- Visual fields
- Visual extinction
- Blink to threat
What are the 2 specific tests for visual field testing?
- Confrontation
- Perimetry testing
What is a central scotoma?
A blind spot that occurs in the center of one's vision
What can cause a central scotoma?
Macular degeneration
What can cause monocular vision loss?
Optic neuritis
What can cause bitemporal hemianopia?
Pituitary adenoma