HD 1.1a Cognitive Development - Piaget
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Cognitive development includes transformations in a child’s
thought, language, and intelligence
Piaget’s theory proposes that cognitive development begins with, and that development is a result of a child’s innate ability
to adapt to the environment
Piaget’s theory proposes that cognitive development is a result of the child’s interface with
the physical world, social experiences, and physical maturation.
4 stages of Piaget’s cognitive development
Sensorimotor
Preoperational
Concrete operations
Formal Operations
Conservation is a conceptual tool that allows a child to recognize that
when altering the appearance of an object, the basic properties do not change.
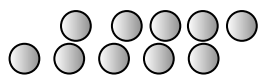
When the child’s response is
“The row on top has more buttons”
This is an example of
Lack of conservation skills in concept of numbers

When the child’s response is
“The one on the bottom is longer.”
This is an example of
Lack of conservation skills in concept of length
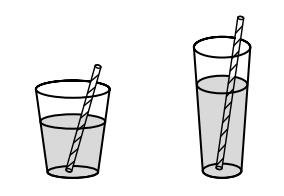
(the same amounts of juice are poured into two
different glasses)
When the child’s response is
“The taller glass has more juice.”
This is an example of
Lack of conservation skills in concept of liquid
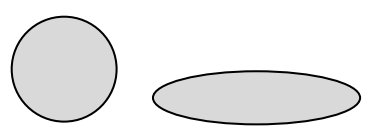
(rolling one ball of clay into a log)
When the child’s response is
“The log has more clay.”
This is an example of
Lack of conservation skills in concept of matter
Two fundamental cognitive concepts of adaptations in Piaget’s stages of development are
Assimilation, accommodation
Assimilation
When children fit new knowledge into template of existing schemes
Preschool calls a lion “doggie” because child only knows one type of four-legged animals
Example of assimilation
Accommodation
When children take existing schemes and adjust them to fit their experience
A preschool child plays the keys on piano to hear different sounds of musical notes. On electric keyboard, learned that keyboard must be turned on before it can be played. Child learned to accommodate this new info to fit the experience.
Example of accommodation
Stage 1 of Piaget’s Cognitive Development is called
Sensorimotor period: infancy
Stage 1 Age
Birth through 2 years
Piaget Stage 1 Characteristics
Egocentric: Thinking only of oneself.
Starting to understand symbolic thought.
Organizes thoughts by schemas.
Experiences the world through their senses and actions (grabbing, looking, touching, hearing, putting things in their mouth).
Achieves object permanence by 18-24 months.
Sensorimotor
As a baby, you experience the world through touch (sensory) and physical actions (motor)
Object exists even when not visible
Object permanence
Stage 2 of Piaget’s Cognitive Development is called
Preoperational period: Early childhood
During stage 2 of Piaget’s Cognitive Development, children’s logic is based on
Their own personal knowledge of the world so far
Piaget Stage 2 Age
2 - 7 yo
Piaget Stage 2 Characteristics for 2-4 years old (Logic and Reasoning)
Causal reasoning - own thoughts cause action
Transductive reasoning - reason from specific to specific
Struggles with centration - can only focus on one piece of info / time
Egocentric
not to be able to take the perspective of others, and instead the child thinks that everyone sees, thinks, and feels just as they do
Ten year-old Keiko’s birthday is coming up, so her mom takes 3 year-old Kenny to the toy store to choose a present for his sister. He selects an Iron Man action figure for her, thinking that if he likes the toy, his sister will too.
Example of egocentrism in preoperational
Centration
preoperational, can only focus on one piece of info at a time
Causal reasoning
preoperational, child believes his thoughts can cause an action
Symbolic thought
preoperational, think in images and symbols
Stage 2 Characteristics for 5-7 years old
Personal and social perception
Thinking (2)
Language (2)
No longer egocentric, intuitive and representational thought, fast-mapping, drastic language development
5-7 year-olds are more curious, creative and cognitively developed through their _____ and _____ thought
Intuitive, representational thought
Intuitive thought
Preoperational, learn about the world by asking lots of why questions
Representational thought
Preoperational, make their own representations of objects (ex: using hands as phones)
Fast mapping
Concrete operation, using context to determine meaning of words
Stage 3 of Piaget’s Cognitive Development is called
Concrete operations Period: Middle childhood
Stage 3 Age
7 - 11 yo
Stage 3 Characteristics (Logic and Reasoning)
Concrete - use logic to solve problems in physical world
Metacognition
Stage 3 Characteristics (Thinking about Objects)
Mastered conservation
Can categorize (classification) and arrange objs (seriation)
Understand reversibility, transitivity
Classification
concrete operational, classify and divide objects in sets
Seriation
concrete operational, arrange objects in logical progression
A child arranges sticks in order from smallest to largest.
Example of seriation
Transitivity
concrete operational, drawing conclusions about 2 objects, knowing the third obj
Stage 4 of Piaget’s Cognitive Development is called
Formal operations period: Adolescence
Stage 4 Age
12 yo - adult
Stage 4 Characteristics (Types of Reasoning)
Abstract, hypothetical-deductive, logical, moral
A state of balance; Development is motivated by the search for a stable balance toward effective adaptations.
Equilibrium
Children make errors in their thinking because they cannot understand that an operation moves in more than one direction and original state can be recovered
Irreversibility
If Emma plays with a ball of clay, she believes that the clay must always be in this same form to remain the same amount. When a classmate plays with the clay and gives it back as a long, narrow piece, Emma thinks she’s getting back less.
Example of irreversibility
the ability to form ideas about “what might be.”
Hypothetical-deductive reasoning
Tommy makes a general observation that short students are not selected for the school basketball team. Since Tommy is short, he deduces that he will not be selected.
Example of hypothetical-deductive reasoning
Drawing conclusions from specific examples to make a general conclusion, even when the conclusion is not accurate (concrete operations).
Inductive reasoning
All of the balls on the school playground are round. By developing a mental schema, a child may reason that all balls are round. This would be an inaccurate conclusion since a football is not round.
Example of inductive reasoning (concrete operation)
When a child fails to understand the true relationships between cause and effect
Transductive reasoning
Bill was mean to his little sister. His sister got sick. Bill reasoned that he made his sister sick.
Example of transductive reasoning
The child uses words and images (symbols) to form mental representations to remember objects without the objects being physically present.
Symbolic Function Substage
A child’s dog is lost, so the child scribbles a picture of the dog; or the child pretends that a stuffed animal is the missing dog.
Example of symbolic function substage
Educational Implications of Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development (Children as learners)
Children are NOT passive learners, they actively move through operational stages
Educational Implications of Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development (Testing)
He quantified the conceptual learning process → children’s cognitive milestones are predictable and orderly and can be tested
Educational Implications of Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development (Children’s mind seeks)
State of equilibrium, each stage they form new ways to operate and adapt
Educational Implications of Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development (Teaching)
Teachers can avoid presenting materials that is beyond the child’s cognitive ability