Sphenoid & Ethmoid Bones
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the sphenoid bone?
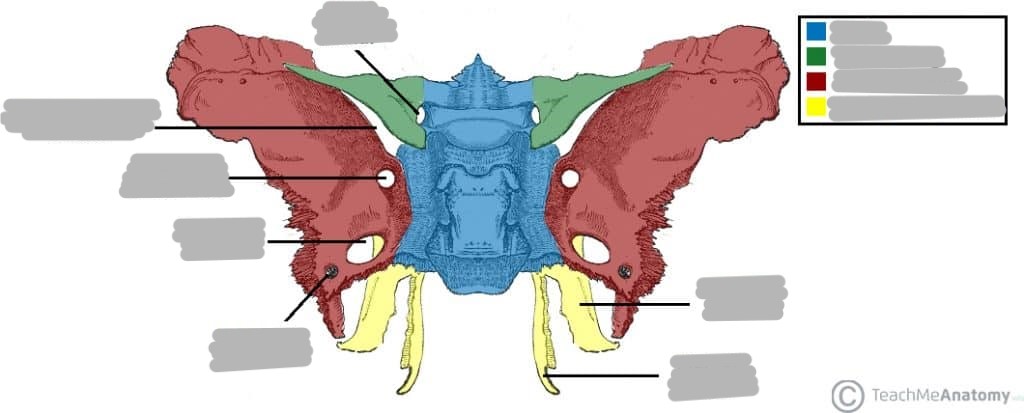
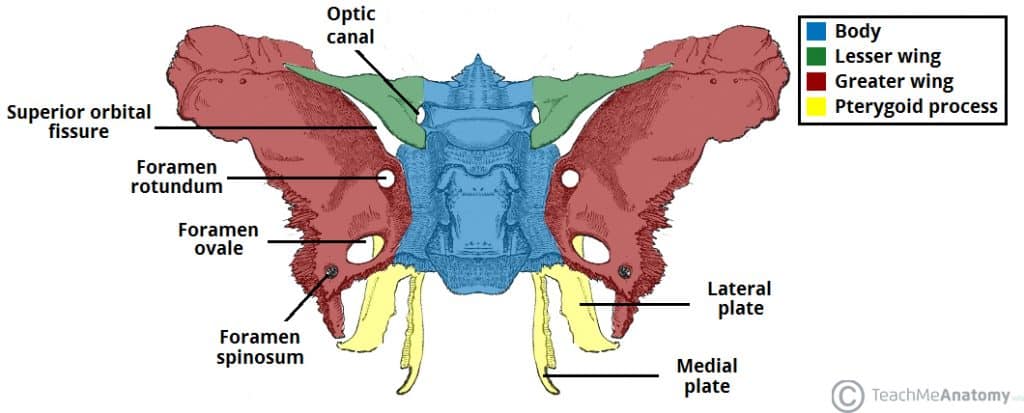
irregular, wedge-shaped (or bat shaped) bone on the floor of the skull (middle cranial fossa)
What makes up the sphenoid bone?
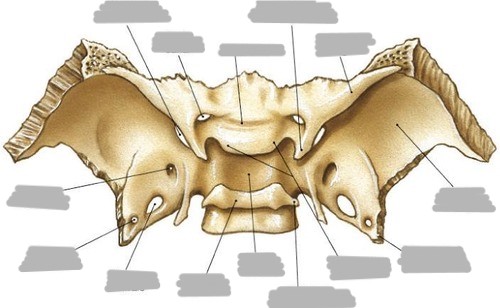
body
2 lesser wings
2 greater wings
2 pterygoid processes
What is the “keystone of the cranial floor?”
the sphenoid, because it articulates with all of the other cranial bones
The central part of the sphenoid is the ___
body
Explain the location and makeup of the body of the sphenoid
location
anterior surface forms the posterior wall of the nasal cavity
½” anterior and ½” superior to EAM
made up of:
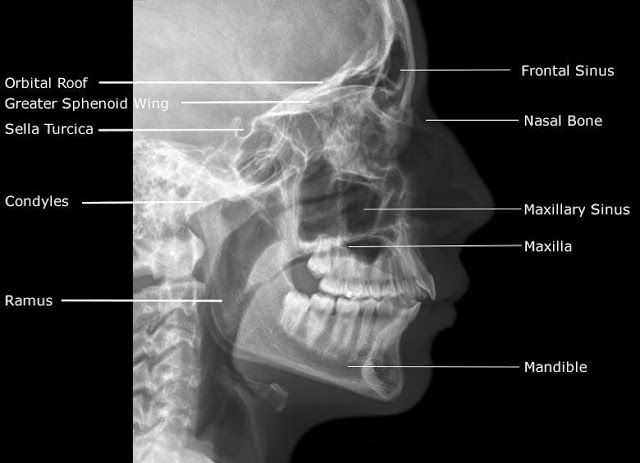
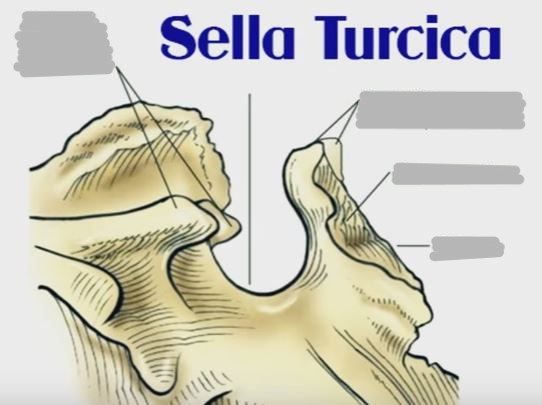
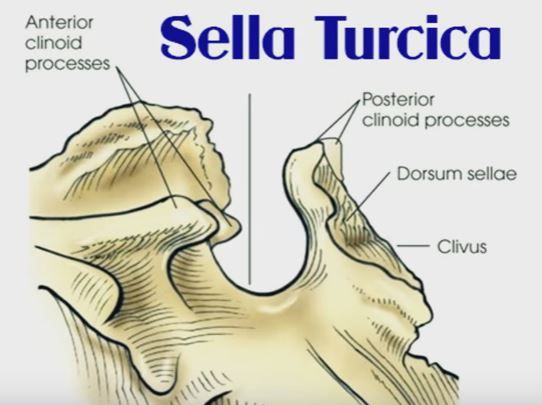
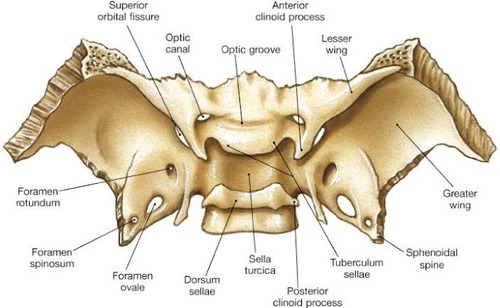
sella turcica (turkish saddle)
tuberculum sellae
dorsum sellae - posterior clinoid process
pituitary fossa
optic foramen/canal
The optic foramen/canal contains the ___
optic nerve and optic groove
(optic groove/chiasmatic groove extends across the anterior portion of the superior surface of the body
What are the greater wings of the sphenoid?
2 wing-like plates that originate from each lateral surface of the body
List the 3 foramen of the greater wings of the sphenoid
foramen rotundum
transmits the maxillary nerve out of the cranium
anterior, perfectly round
foramen ovale
transmits mandibular nerve out of the cranium
posterior to rotundum, oval shaped
foramen spinosum
transmits the middle meningeal artery
posterior to ovale, tiny
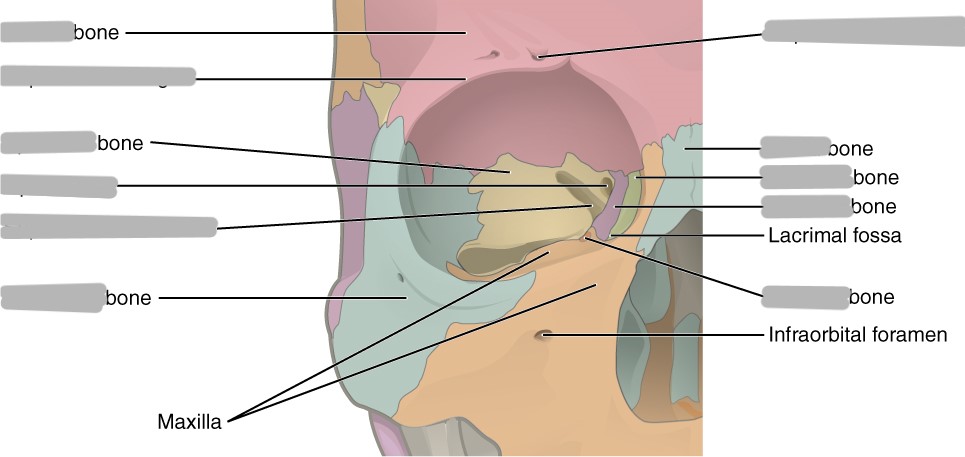
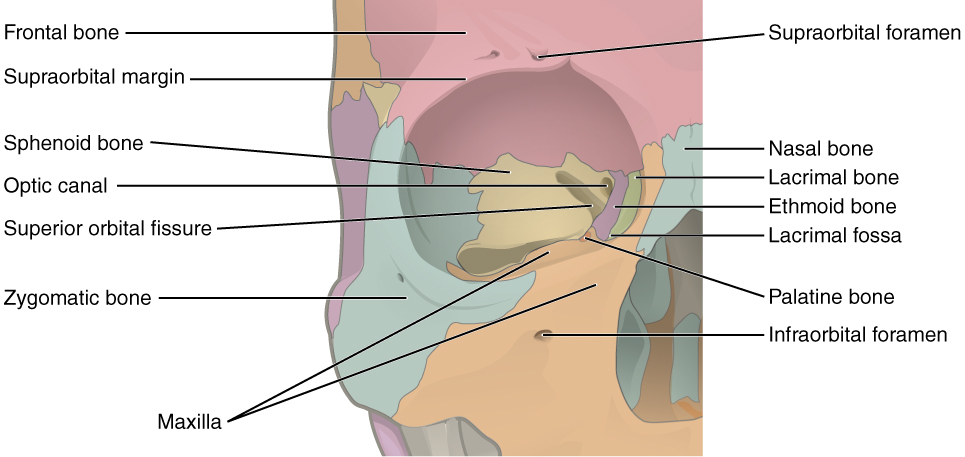
Explain the location, shape, and function of the superior orbital fissure
on the medial margin of the greater wing of the sphenoid
“slit” shaped
transmits 3rd, 4th, and 5th cranial nerves
Explain the location and function of the inferior orbital fissure
between maxilla, zygoma, and greater wing of the sphenoid
transmits maxillary branch of the 5th cranial nerve
What are the 2 points of the lesser wing?
What are the 2 points on the dorsum sellae?
wing: anterior clinoid processes
dorsum sellae: posterior clinoid processes
What are the pterygoid processes?
inferior projections at the junction of the body and greater wing
What are the names of the pterygoid processes?
lateral pterygoids
medial pterygoids (longer, thinner, and has hook/hamulus)
What is the function of the pterygoid processes?
attachment for pterygoid muscle (help move and protrude the mandible)
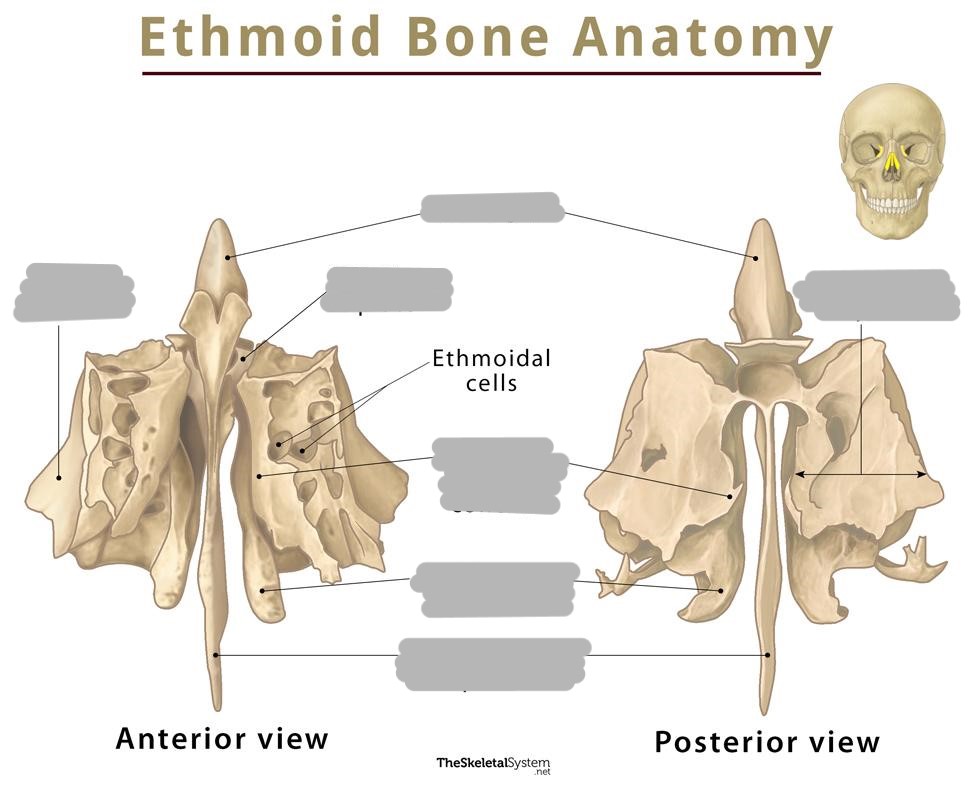
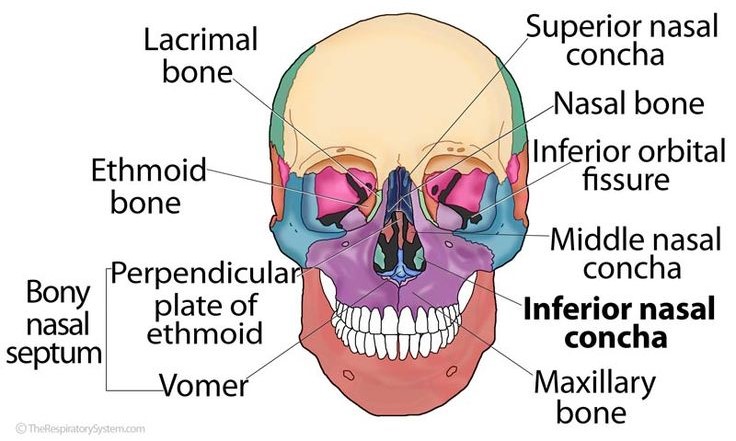
Where is the ethmoid bone located?
anterior floor between the orbits
The ethmoid bone forms the ___
orbits and nasal septum
The ethmoid bone consists of what?
cribriform plate
perpendicular plate
ethmoidal labyrinths
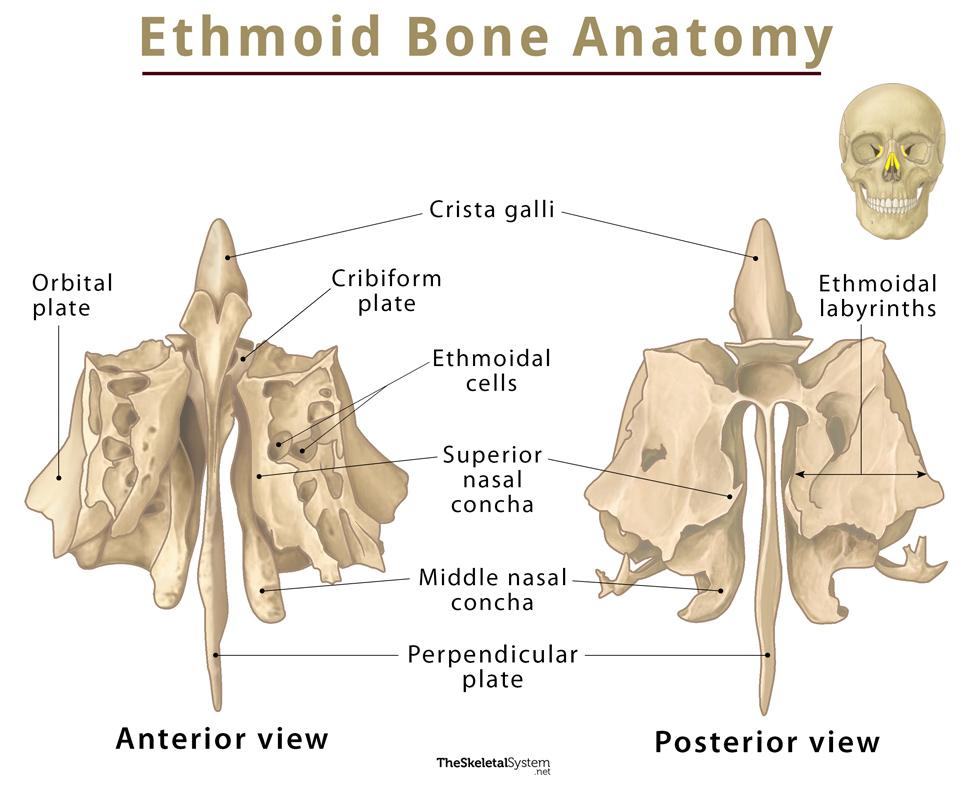
Explain the cribriform/horizontal plate of the ethmoid
received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone
perforated foramina (olfactory foramina) for transmission of the olfactory nerves
Explain the crista galli
projects superiorly off of the cribriform plate and serves as the attachment for the falx cerebri (a fold of dura mater that separates brain hemispheres)
Explain the perpendicular/vertical plate of the ethmoid
makes up the nasal septum (with the vomer)
thin, flat bone the projects inferiorly from the inferior surface of the cribriform plate
Explain the ethmoidal labyrinths/ethmoidal masses
contain air cells divided into anterior, middle, and posterior air cells
medial portion
makes up the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
lateral portion
makes up the medial wall of the orbits
orbital plate
Explain the location and function of the superior and middle nasal conchae/turbinates
project inferiorly form each medial wall are two thin scroll-shaped processes
filter the air that we breathe