Time of Death and Postmortem Changes Overview
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Death
Cessation of circulation and irreversible cessation today.
Anoxia
Absence of oxygen in tissues.
Ischemia
Restriction of blood supply to tissues.
Cerebral Anoxia
Brain damage from 4-6 minutes without oxygen.
Hypothermic Resistance
Children can resist cerebral hypoxia for 30 minutes.
Brain Death
Incapable of sustaining respiration and circulation.
Brain Criteria
Legal determination of death using brain function.
Postmortem Changes
Physiochemical changes leading to tissue liquification.
Postmortem Clock
Estimation of time of death based on changes.
Environmental Factors
Temperature, ventilation, and humidity affect postmortem changes.
Body Characteristics
Build and health state influence postmortem phenomena.
Injury Analysis
Survival time and injury details assist in time estimation.
Time of Death Estimation
Cannot be pinpointed; ranges are provided instead.
Window of Death
Interval indicating individual was alive before death.
Reliable Testimony
Witness accounts and documents refine time of death.
Postmortem Cooling
Body temperature declines until reaching ambient temperature.
Normal Body Temperature
Average human body temperature is 98.6°F.
Cooling Rate
Cools 2.0°F to 2.5°F in first few hours.
Slower Cooling
Cools 1°F over next 12 to 18 hours.
Core Temperature Measurement
Preferred for accuracy over skin temperature.
Bernard Knight's Review
Accuracy of body temperature measurements remains low.
Algor Mortis
Postmortem cooling of the body temperature.
Cooling Mechanisms
Three ways body loses heat postmortem.
Clothing Impact
Clothing decreases heat loss rate.
Body Fat Impact
Increased fat reduces cooling speed.
Water Immersion Effect
Cool water increases cooling times.
Children's Cooling Rate
Children cool faster due to body mass ratio.
Hyperthermia
Higher body temperature affecting cooling rate.
Corneal Clouding
Thin film on eyes postmortem; 2-3 hours if open.
Tache Noir
Blackish discoloration in eyes partly open.
Pupil Dilation
Pupils dilate due to muscle relaxation.
Myosis
Pinpoint pupils, may persist in opiate deaths.
Postmortem Lividity
Purplish-blue discoloration from blood settling.
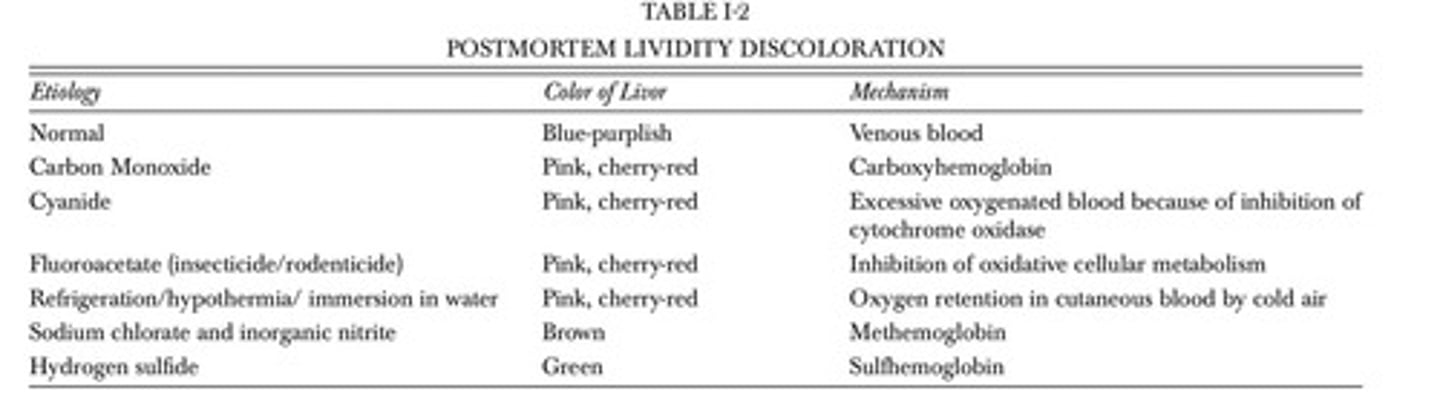
Lividity Timing
Evident as early as 20 minutes postmortem.
Blanching of Lividity
Early lividity can be blanched by compression.
Tardieu Spots
Pinpoint hemorrhages from burst capillaries.
Diagnostic Clue
Unusual lividity discoloration indicates cause of death.
Rigor Mortis
Postmortem muscle stiffness following flaccidity.
Rigor Onset
Becomes apparent within 30-60 minutes postmortem.
Rigor Duration
Maximum stiffness within 12 hours, then subsides.
Muscle Rigidity Order
Smaller muscles stiffen before larger ones.
Rigor Reversibility
Once established, rigor cannot reappear.
Factors Affecting Rigor
Exercise, heat, drugs accelerate or slow rigor.
ATP Hydrolysis
ATP breaks down to ADP, producing lactic acid.
Rigor mortis
Postmortem muscle stiffness due to ATP depletion.
Cadaveric spasm
Clenched fist seen in deaths from tension.
Decomposition
Disintegration of body tissues after death.
Autolysis
Self-dissolution by body enzymes postmortem.
Putrefaction
Decay caused by bacteria and microorganisms.
Putrefactive changes
Dependent on temperature and individual's health.
Green discoloration
Early sign of decomposition on abdominal skin.
Gaseous bloating
Swelling due to gas production in decomposition.
Mummification
Drying of tissues in low humidity environments.
Brownish discoloration
Appearance of mummified skin after drying.
Adipocere
Waxy fat saponification in high humidity.
Subcutaneous fat
Fat layer affected by adipocere formation.
Environmental conditions
Factors influencing decomposition rate and severity.
Skeletonization
Process of bones breaking down over time.
Weathering changes
Slow degradation of bones lasting decades.
Pupillary disparity
Unequal pupil size due to rigor mortis.
Misleading artifacts
Postmortem changes that mimic antemortem injuries.
Destructive environmental factors
Conditions altering appearance of postmortem artifacts.
Sepsis
Infection influencing decomposition speed.
Cocaine ingestion
Substance affecting postmortem changes.
Time of death
Estimation based on decomposition stages.
Anthropophagy
Preying animals/scavengers assaulting human remains.
Postmortem Vegetal Growth
Fungi development on decomposing bodies.
Forensic Entomology (FE)
Study of insects in legal investigations.
Postmortem Interval (PMI)
Time elapsed since death occurred.
Insect Growth Factors
Temperature and environment influence insect development.
Bow Fly Life Cycle
Stages from egg to adult fly.
Egg Stage
Initial stage of bow fly life cycle.
Larval Stages
Development stages before metamorphosis into adults.
Puparial Stage
Transition from larva to adult fly.
Exhumation
Disinterment of buried human remains.
Legal Exhumation Reasons
Autopsy, identity verification, cause of death.
Body Condition Post-Exhumation
Unpredictable variables affect preservation quality.
Preservation Structures
Skeleton, arteries, and teeth aid identification.
Exhumation Disadvantages
Time and embalming affect forensic findings.
Exhumation Process
Legal procedures vary by jurisdiction.
Next of Kin Authority
Family has primary control over exhumation.
Soil Sample Collection
Analyzing soil for chemicals like arsenic.
Embalming Artifacts
Misinterpretation risks from embalming processes.
Civil Litigation Exhumation
Evaluates medical negligence or treatment issues.
Unlawful Burials
Illegal disposal leads to rapid tissue decay.
Animal Activity Evidence
Signs of scavenging near surface burials.
Forensic Team Roles
Includes toxicologists, serologists, and forensic dentists.