Exercise #2: The Microscope
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
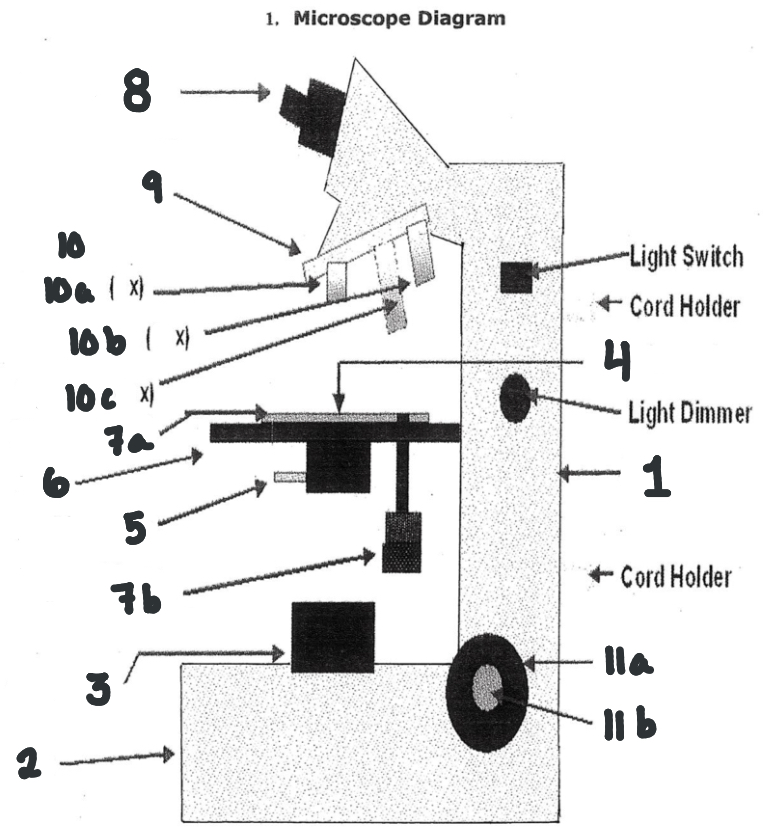
Label the microscope
1) Arm
2) Base
3) In base illuminator (light source)
4) Condenser
5) Iris diaphragm and lever
6) Mechanical stage
7a) Slide positioner
7b) Adjustment knobs
8) Ocular lens/es (10x)
9) Rotating nosepiece
10) Objective lenses
10a) low power objective (4x)
10b) medium power objective (10x)
10c) high power objective (40x)
11a) Coarse focus adjustment knobs
11b) Fine focus adjustment knobs
What is the function of the in-base illuminator (light source)
provides even, high intensity light, that travels through the condenser to the specimen
What is the function of the condenser?
concentrates light from the illuminator onto the specimen
What is the function of the iris diaphragm and lever
The iris diaphragm regulates how much light is on the specimen
What is the function of the mechanical stage
allows for precise and controlled movement of the specimen slide
What is the function of the slide positioner and adjustment knobs?
holds the slide in place
moves the slide vertically or horizontally
What is the function of the ocular lenses?
How much does it magnify?
magnifies 10x the image produced by the objective lens and produces a virtual image
What is the function of the rotating nose piece?
holds objectives, rotates to change amount of magnification
What are the objective lens/es and their function?
How much do they magnify?
gathers light from a specimen, magnifies it, and forms an inverted image, further magnified by the ocular lens
low power objective (4x)
medium power objective (10x)
high power objective (40x)
How do you calculate the total magnification?
objective lens magnification x ocular lens magnification
What are the functions of the coarse and fine focus adjustment knobs?
A rapid control which allows for quick focusing
initial focusing
A slow but precise control used to fine focus
viewing at higher magnifications
What is field of view?
the illuminated area that you can see when you look into the microscope
As magnification decreases FOV gets?
smaller
FOV - inverse relationship
Low Power
Medium Power
High Power
Large FOV
Medium FOV
Small FOV
What is depth of field?
How much of a specimen is in focus
DOF- inverse relationship
Low Power
Medium Power
High Power
Large DOF
Medium DOF
Small DOF
The iris diaphragm can have an effect on?
The depth of field
What is the total magnification
ocular lenses x objectives
LO = 40x
MO = 100x
HO = 400x