Chapter 1.1: Information Systems Today
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Characteristics of the Digital World
The proliferation of mobile devices, changes in technology enables new ways of working and socializing, and boundaries between work and leisure time are blurring.
Knowledge worker
professionals who are relatively well educated and who create, modify, and/or synthesize knowledge as a fundamental part of their jobs.
Knowledge Society
a society in which education is the cornerstone of society and there is an increase in the importance of knowledge workers.
e-business
an organization that uses information technologies or systems to support nearly every part of its business.
Digital Divide
those with access to information systems have great advantages over those without access to information systems.
Globalization
the integration of economies throughout the world, enabled by innovation and technological progress. Brought about by falling transportation nad telecommunication costs.
Outsourcing
the moving of business processes or tasks (such as accounting, manufacturing, or security) to another company or another country. A decrease in communication costs has led to a increase in this.
Demographic changes
changes in the structure of populations related to factors such as age, birth rates, and migration.
Urbanization
the movement of rural populations to urban areas, to a point where 50 percent of the world’s population is now living in cities
Shits in economic power
changes in countries’ purchasing power and control over natural resources
Resource scarcity
limited availability of fossil fuels and other natural resources
Climate change
large-scale and long-term regional and global changes in temperatures and weather patterns.
Sustainable development
development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
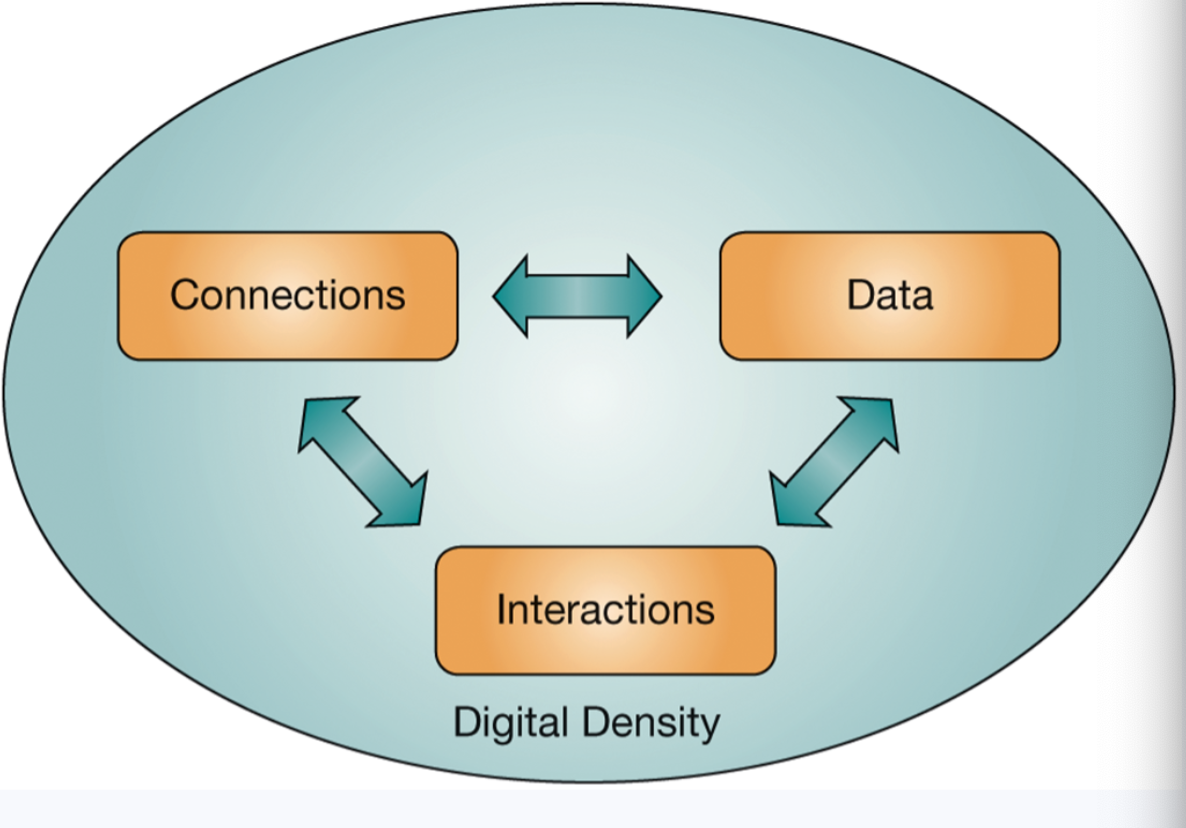
Digital density
the amount of connected data per unit of activity
The Drivers of Digital Density: Connections
The past: only between organizations
Then: between people
Now: connect just about any elements of the physical world to the digital world. Increased mobility using mobile apps. Increased micro-moments (buy something, contact someone, increase productivity)
Apps
software programs designed to perform a particular, well-defined function
Micro-moments
a person almost instinctively picks up a mobile device to accomplish a particular goal—to buy something, know something, do something, or go somewhere.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
people using their own devices for work-related purposes.
Consumerization of IT
technological innovations are first introduced in the consumer marketplace before being used by organizations, and businesses must constantly evaluate how a wide variety of new technologies might influence their ways of doing business.
IoT (Internet of Things)
a network of a broad range of physical objects that can automatically share data over the internet—is a key factor in increasing digital density.
Sensors
devices that can detect, record, and report changes in the physical environment
Smart home technologies
technologies enabling the remote monitoring and controlling of lighting, heating, or home appliances such as the Nest Learning Thermostat
Wearable technologies
clothing or accessories that incorporate electronic technologies, such as the Apple Watch, Samsung’s Galaxy Gear, or the Fitbit
Quantified self
the logging of all aspects of one’s daily life, ranging from monitoring and recording of activities, performance, or intakes to monitoring bodily states (such as moods or physiological data) to improve one’s overall health and performance.
Industrial Internet of Things
enables the convergence of information technology and operations technology, offering the potential for tremendous improvements in efficiency, product quality, agility, and flexibility, allowing companies to mass produce customized products, better monitor supply chains, and so on.
Big Data
extremely large and complex datasets, which are characterized as being of high volume, variety (i.e., many different types of data), and velocity (i.e., the data are being collected and analyzed at ever-increasing rates).
The Drivers of Digital Density: Interactions
increasing connections and data enable new value-added interactions and business models.
Artificial intelligence
using information technologies to simulate human intelligence
Robotics
the use of robots to perform manual tasks
network effect
the notion that the value of a network (or tool or application based on a network) increases with the number of other users
APIs (application programming interfaces)
intermediaries that provide ways for different components of software to interact and exchange data or functionality using common web communication protocols.
Computer literacy
the knowledge of how to operate a computer
Healthcare IS
information systems that support various healthcare processes, ranging from patient diagnosis and treatment to analyzing patient and disease data to running doctors’ offices and hospitals
Computer fluency
the ability to independently learn new technologies as they emerge and assess their impact on one’s work and life—is what will set you apart in the future.