M3: Observational Research, Cohort and Case-Control Studies
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
basic research
-is conducted to increase knowledge and fundamental understanding of the physical, chemical and functional mechanisms of life processes and disease
-is not directed to solving any particular problems in humans or animals
applied research
involves the application of existing knowledge, much of which is obtained through basic research, to solve a practical problem
clinical research
patient or end user-oriented research with human subjects
translational research
part of a unidirectional continuum in which research findings are moved from the researcher’s bench to the patient’s bedsite and to the community
descriptive
-describes an outcome in a population
-a characterizes who, where, or when in relation to the what
analytical
examine the relationship between an intervention/exposure and an outcome in a population
qualitative
-subjective/interpretive observations
-identifies themes in observations
-forms narrative/story/essay
-does not test a hypothesis, but may lead to hypothesis development
quantitative
-objective/measurable data that is typically analyzed statistically
-test a hypothesis
quantitative research designs
-observational
-experimental
-quasi-experimental
observational research
-non-manipulated study
-researchers do not attempt to influence/manipulate participants or the surroundings
experimental research
-manipulated study
-participants are randomized to receive intervention or control
quasi-experimental
one or more aspects/elements of experimental research is absent or missing
utility of observational research
-studying the otherwise unstudy-able
-prioritizing external validity
-generating research questions
cross sectional research
-participants are observed at one point in time
-data/measurements are collected once
-outcomes: single measure, prevalence of disease/events
cross sectional advantages
-attrition is not a concern
-less costs/expenses
-controls for period effects
-data on ALL variables are collected at one time
cross sectional disadvantages
-do not know temporal aspects
-associations identified between variables may be difficult to interpret
-‘snapshot’ timing not guaranteed to be reflective of real-world settings
longitudinal research
-participants are observed over time
-data/measurements are collected multiple times
-outcome: change over time provides indication of incidence of disease
longitudinal advantages
-you may observe a pattern in the outcome over time
-establishes an order of events
-reduces recall bias of participants
-may provide insight into casual bias mechanisms
longitudinal disadvantages
-time consuming and expensive
-usually requires a large sample size
-affected by ‘cohort effects’
-cannot be used to suggest causation, only associations
-despite temporal aspects, may not know if exposure preceeds outcome
prevalence
-the total number of individuals in a population who have a disease of health condition at a specific period of time
incidence
-the number of individuals who develop a specific disease of experience a health-related event during a particular time period
incidence
-the number of individuals who develop a specific disease of experience a health-related event during a particular time period
case control study
participants are recruited based on an outcome of interes
cohort study
-participants are recruited from a population of interest
-longitudinal study
-example: Framingham heart study
cohort
a collection or sampling or individuals who share common experiences and/or characteristics such as sex, age, activity level, location, education, ect.
prospective cohort studies
-participants are recruited and followed forward in time
-outcome is evaluated in the future
retrospective cohort studies
-participants are recruited and they identify past exposures
-outcome is evaluated at time of recruitment
advantages of cohort studies
-longitudinal
-best external validity
-representative
multiple exposure outcomes
disadvantages of cohort studies
-large sample is required
-expensive
-attrition bias
-measurement bias
-poor internal validity
attrition bias
occurs when participants drop out of a long-term experiment or study
measurement bias
a form of inaccurate measurement in which the data consistently overestimate or underestimate the true value of an event
case
those with outcome/disease of interest
control
those without outcome/disease of interest
advantages of case control studies
-smaller # of people needed
-because disease is already prevalent, no need for longitudinal
recruiting for case control studies
-population based
-hospital based
population based recruitment strengths
-cases are representative of population
-results are generalizable to population
population based recruitment weaknesses
more difficult to recruit
hospital based recruitment strengths
-easy to identify
-typically have access to medical history
Hospital based recruitment weaknesses
-may be more sick than general population or population cases
-may be different in other ways compared to general population
control group recruitment
-want to control for potential confounding variables
-often recruit from family or friends
selection bias
occurs when the subjects studied are not representative of the target population about which conclusions are to be drawn
recall bias
type of information bias common in case-control studies where the cases (or their families) are more likely to recall a prior exposure than the controls
non-differential misclassification
-cases and controls are misclassified equally
-will make detection of a true effect less likely
differential misclassificiation
-only one group are misclassified
-can alter the magnitude and/or direction of the effect
case control study design
-cross sectional or longitudinal
-longitudinal are always retrospective
absolute risk
-the actual risk of some event happening given the current exposure
-no comparison between groups
relative risk
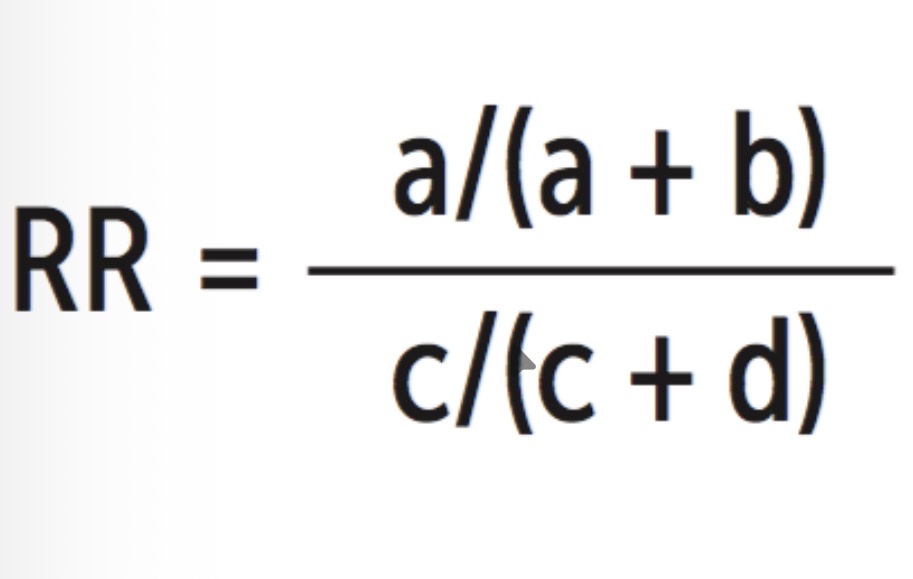
odds ratios
-measure of how strongly an even is associated with exposure
-the odds of the even occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a non-exposed group