CHEM 6410 RXNs
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
great LGs
weak bases
OTs, OMs, I-, BR-, Cl-, (COO- and NH3 are ok LGs)
sulfonates are better than halides
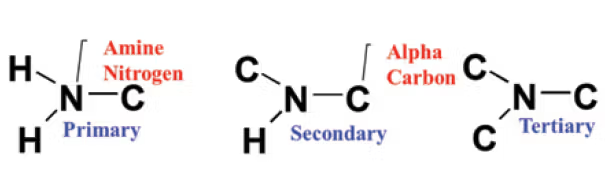
what makes a good nucleophile
strong base
left on PT, up on PT (in polar aprotic solvent), and down on PT (in polar protic solvents)
not bulky base
high electron density but not steric hindrance
Gabriel Synthesis: SM
alkyl halide
Gabriel Synthesis: key reagents
pthalamide and base
Gabriel Synthesis: purpose
to create a primary amine
Williamson Ether: SM
alkyl halide and alkoxide
Williamson Ether: key reagents
alkyl halide and base
Williamson Ether: purpose
create ethers (or C-O bonds) using alkoxide (deprotonate OH) or tosylates
Finkelstein: purpose
synthesize alkyl iodides from alkyl chlorides or bromides through a halogen exchange reaction driven by the insolubility of the resulting metal halide (like NaCl or NaBr) in acetone
Finkelstein: SM
alkyl halids like R-Cl and R-Br
Finkelstein: key reagent
NaI in acetone, or R-Cl, R-Br, OMs, OTs, MsCl
Heine: purpose
ring expansion via double inversion
N-acylaziridines into 2-oxazolines
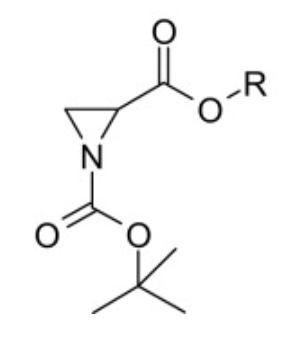
Heine: key reagents
NaI or KSCN
TMS-I
Heine: SM
N-acylaxiridine
Appel: purpose
converts alcohols into alkyl halides with an inversion of bond
Appel: key reagents
PPh3 and CCl4/ CBr4
Appel: SM
alcohols
Mitsunobu: purpose
converts primary or secondary alcohols into antoher functional groups (such as esters, ethers, and amines)
Mitsunobu: key reagents
PPh3 and DEAD/DIAD and H-Nuc
Mitsunobu: SM
alcohol
SN2 electrophiles
primary then secondary are best
common polar protic solvents
H2O, MeOH, EtOH,
common polar aprotic solvents
acetone, DMSO, and DMF; ethers like diethyl ether and THF; halogenated solvents such as dichloromethane and chloroform; and hydrocarbons including hexane, toluene, and benzene
example of strong base
NaH, LDA, LHMDS
example of strong acid
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO₃, H₂SO₄, HClO₃, HClO₄