Data Structures - Labs
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
connected_components(Graph<V> G, Map<V, V> representative)
for (V v: G.vertices()){
representative.put(v, null);
visited.put(v, ____ );
}
for (V v : G.vertices()) {
if (!visited.get(v)) {
DFS(_, G, representative, visited, _);
}
}
false, v, v
public static <V> void DFS
if (!visited.get(current)) {
visited.put(current, ____);
representative.put(current, _____);
}
for( V v: G.adjacent(current)){
if (!visited.get(v)){
representative.put(__, current);
DFS(_, G, representative, visited, __);
}
true
repVertex
v
v
repVertex
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
int index = hash(key);
LinkedList<Entry> entries = table.get(index);
boolean hasKey = false;
for (int i = 0; i != entries.size(); ++i) {
if (entries.___(i).___.equals(key)) {
hasKey = true;
break;
}
}
return hasKey;
}
get
key
public V get(K key) throws Exception {
int index = hash(key);
LinkedList<Entry> entries = table.get(index);
for (int i = 0; i != entries.size(); ++i) {
if (entries.get(i).key.equals(key)){
return entries.get(i).____;
}
}
throw new Exception("Value not found.");
}
value
public void put(K key, V value) {
int index = hash(key);
LinkedList<Entry> entries = table.get(index);
for (int i = 0; i != entries.size(); ++i) {
if (entries.get(i).key.equals(___)){
entries.get(i).___ = value;
return;
}
}
entries.add(___ Entry(___, ____));
}
key
value
new
key
value
public void remove(K key) {
int index = hash(key);
LinkedList<Entry> entries = table.get(index);
for (int i = 0; i != entries.size(); ++i) {
if (entries.get(i).key.equals(key)) {
entries._____(i);
return;
}
}
remove
public E peek() {
if (keys.isEmpty()){
throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty.");
}
return keys.get(__);
}
0
public void push(E key) {
keys.add(key);
int index = keys.size() - 1;
while (index > 0) {
int parent = getParent(index);
if(comparator.compare(keys.get(____), keys.get(____)) >=__ ) {
break;
}
____(index, parent);
_____ = _____;
}
}
index
parent
0
swap
index , parent
public E pop() {
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty");
}
if (keys.size() == 1) {
return keys.____;
}
E ___ = keys.get(0);
keys.set(__, _________);
minHeapify(0);
return min;
}
remove(0)
min
0, keys.remove(keys.size() - 1)
private void minHeapify(int i) {
int left = getLeft(i);
int right = getRight(i);
int smallest = i;
if (___ < keys.size() && comparator.compare(keys.get(___), keys.get(smallest)) < 0) {
smallest = ___;
}
if (____ < keys.size() && comparator.compare(keys.get(___), keys.get(smallest)) < 0) {
smallest = ____;
}
if (smallest != ) {
swap(i, smallest);
minHeapify(______);
}
left
left
left
right
right
right
i
smallest
A __________________ is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is filled
complete binary tree
A ____________ is a complete binary tree in which for every node n, its key is less or equal to its parent’s key (except for the root)
max heap
__16__
/ \
14 10
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
8 7 9 3
/ \ /
2 4 1What tree is this an example of?
This is a max heap
left(i)2*i + 1
right(i)
2*(i + 1)parent(i)
floor( (i-1) / 2 )What is the time complexity of max_heapify?
O(log(n))
So the time complexity of build_max_heap is _____.
O(n)
What is the time complexity of extract_max?
Time complexity: O(log n)
What is the time complexity of sortInPlace()?
O(n log(n))
What is the time complexity of the insert method?
O(log(n))
What is the time complexity of maximum()?
O(1)
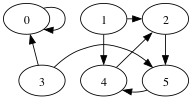
Represent graph as an adjacency list:
|0| ->
|1| ->
|2| ->
|3| ->
|4| ->
|5| -> |0| -> 0
|1| -> 2 -> 4
|2| -> 5
|3| -> 0 -> 5
|4| -> 2
|5| -> 4
Represent graph as an adjacency list:
|0| ->
|1| ->
|2| ->
|3| ->
|4| -> |0| -> 1 -> 2 -> 4
|1| -> 0 -> 2
|2| -> 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4
|3| -> 2 -> 4
|4| -> 0 -> 2The _______________ representation of a graph is an array of linked lists.
Adjacency List
Adjacency lists are good for storing ________.
sparse graphs
The _______________ representation of a graph is a Boolean matrix.
Adjacency Matrix
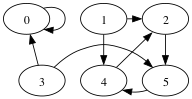
0 1 2 3 4 5
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 0 0Fill matrix above.
0 1 2 3 4 5
0 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 1 0
2 0 0 0 0 0 1
3 1 0 0 0 0 1
4 0 0 1 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 0 0
2 1 1 0 1 1
3 0 0 1 0 1
4 1 0 1 1 0 Adjacency matrices are good for __________
dense graphs
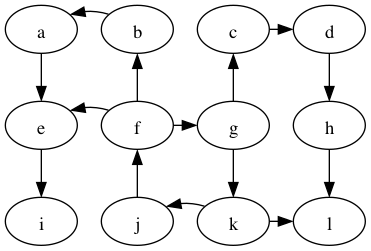
What is a shortest path from g to f?
g → k → j → f
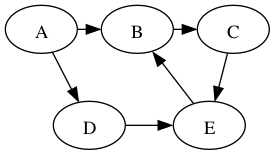
parents
P[A]
P[B]
P[C]
P[D]
P[E]
parents
P[A] = A
P[B] = A
P[C] = B
P[D] = A
P[E] = D
What is the time complexity of BFS?
O(V + E)
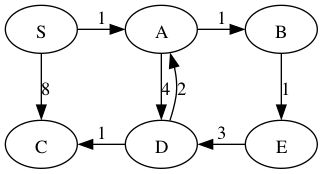
Dijstra’s algorithm
W = 0
W = 1
W = 2
W = 3
W = 5
W = 6
W=0 S
W=1 S->A
W=2 S->A->B
W=3 S->A->B->E
W=5 S->A->D
S->A->B-E
W=6 S->A->D->C
S->A->B-EDijkstra’s approach to growing the tree is to store all the potential next ______ (those that are adjacent to the tree) in a ____________ ordered by the path weight within the current tree plus the weight of the lightest edge to that vertex.
vertices
priority queue
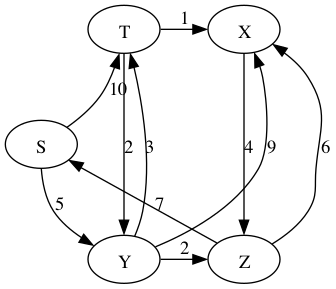
Use Dijkstra’s to compute the distances from S to all the other vertices in the following graph.
S:
T:
X:
Y:
Z:
Answers:
S: 0
T: 8
X: 9
Y: 5
Z: 7
Time complexity of Dijkstra’s algorithm
O((n+m) log(n))
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: n pushes to queue
O(n log(n))
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: n pops to queue
O(n log(n))
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: m decrease_key on the queue
O(m log(n))
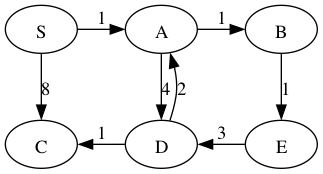
Use Dijkstra’s to compute the distances from S to all the other vertices in the following graph.
S:
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
S: 0
A: 1
B: 2
C: 6
D: 5
E: 3
Definition. A __________ is a subset of edges of a graph that form a tree and that connect all the vertices in the graph.
spanning tree
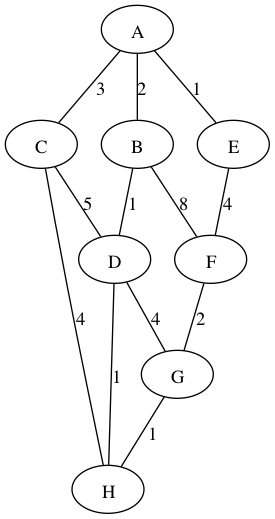
Apply MST to this tree, list the edges within the tree
A→E
B→ D
D→H
H→G
A→B
G→F
A→C
Time complexity of sort with Kruskal’s Algorithm
sort: O(m log m)
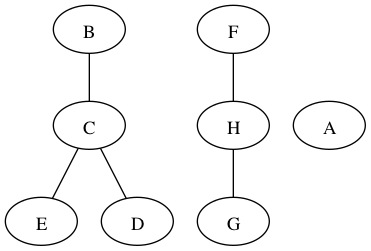
Identify the connected components in the following graph. For each connected component, choose the node that is lowest alphabetically (A before Z) to be the representative.
A: A
B: B
C: B
D: B
E: B
F: F
G: F
H: F
Apply breadth-first search to the following graph starting at vertex a, marking the edges in the breadth-first tree. When choosing the order in which to process and visit nodes, give priority to nodes that are earlier in the alphabet (a before b). Select the option with the breadth-first tree marked with green edges.
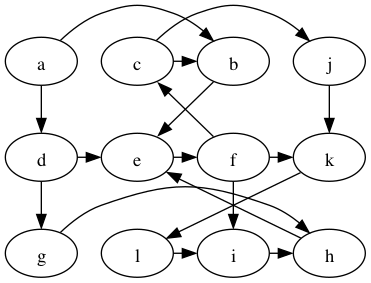
Edges:
A → B
A → D
B → E
C → J
D → G
E → F
F → C
F → I
F → K
G → H
K → L
Apply Dijkstra's shortest paths algorithm to the following edge-weighted directed graph with node d as the source.
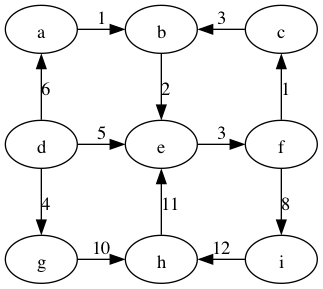
Give the distance of the shortest path from node d to every node in the graph:
A: 6
B: 7
C: 9
D: 0
E: 5
F: 8
G: 4
H: 14
I: 16
What is the time complexity of Dijkstra's single-source shortest-paths algorithm when implemented using a binary heap? Let n be the number of vertices and m be the number of edges in the graph.
O((n+m) log(n))
public class HashTable<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
class Entry {
Entry(K k, V v) { key = k; value = v; }
K key; V value;
};
protected ArrayList<LinkedList<Entry>> table;
public void put(K key, V value) {
Entry found = null;
for (Entry e : table.get( ______)){
if (e.key.equals(________){
found = e;
}
if (found == null) {
table.get(hash(key)).add(____)
}
else {
________ = value;
}
}
...
}
hash(key)
key
new Entry(key, value)
found.value
static void heapify(int A[], int heap_length, int current_node) {
int left = _____________;
int right = ____________;
int largest = current_node;
if (left < heap_length && A[ left ] > A[ largest ]){
largest = left;
}
if (right < heap_length && A[ right ] > A[ largest ]){
largest = right;
}
if (largest != current_node) {
swap(A, _____, largest)
heapify(A, heap_length, _______);
}
}
2 * current_node + 1
2 * current_node + 2
current_node
largest
What is the big(O) for hashing the key?
O(1)
What is the division method for hashing?
Good to choose a prime number for m, not close to a power of 2 or 10.h(k) = k mod m
What is the Multiple Add and Divide Method for Hashing?
where:
p is a prime number larger than m
a,b are randomly chosen integers between 1 and p-1.
h(k) = ((a * k + b) mod p) mod mUsing the division method and chaining, insert the keys 4, 1, 3, 2, 0 into a hash table with table size 3 (m=3).
0 -> [0,3]
1 -> [1,4]
2 -> [2]what is the worst case big(O) of search in hash tables?
O(n)
What is the big(O) for indexing into the table array slot?
O(1)
What is the big(O) for doing linear search in a chain?
O(λ) or O(n/m)
Suppose we insert these key-value pairs:
(2, "sue"), (3, "larry"), (6, "joe"), (8, "beth")
Into a table of size 4, using mod for the hash function.
hash(key) = key % 4
0| -> (8, "beth")
1|
2| -> (6, "joe") -> (2, "sue")
3| -> (3, "larry")
public E maximum() {
return _______;
}
data.get(0);
E extract_max() {
E max = data.get(0);
data.set(____________);
data.remove(_________);
max_heapify(_______);
return max;
}
0, data.get(data.size()-1)
data.size()-1
0, data.size()
What is the big(O) of this line?
E max = data.get(0);
O(1)
What is the big(O) of this line?
data.set(0, data.get(data.size()-1));
O(1)
What is the big(O) of this line?
data.remove(data.size()-1);
O(1) → because it removes from the end of the array
What is the big(O) of this line?
max_heapify(0, data.size());
O(log(n))
What is the time complexity of this line?
Heap<E> H = new Heap<E>(lessThanOrEqual);
O(1)
What is the time complexity of this line?
H.data = A;
O(1)
What is the time complexity of this line?
H.build_max_heap();
O(n)
What is the time complexity of this line?
for (int i = H.data.size() - 1; i != 0; --i) {
// n iterations * O(log(n)) = O(n log(n))What is the time complexity of this line?
swap(H.data, 0, i);
O(1)
class PriorityQueue<E> {
Heap<E> heap;
PriorityQueue(BiPredicate<E,E> lessThanOrEqual) {
heap = _________;
}
void push(E key) {
_______
}
E pop() {
return __________
}
}
new Heap<>(lessThanOrEqual)
heap.insert(key);
heap.extract_max();
void insert(E k) {
data.add(k);
increase_key(________);
}
data.size() - 1
What is the big(O) of this line?
data.add(k);
O(1)
What is the big(O) of this line?
increase_key(data.size() - 1);
O(log(n))
Adjacency List Big(O) for insert on edges
O(1)
Adjacency List Big(O) for detection on edges
O(1)
Adjacency List Big(O) for removal on edges
O(1)
Adjacency List Big(O) for insert on verticies
O(n) amoritized
static <V> void
bfs(Graph<V> G, V start, Map<V,Boolean> visited, Map<V,V> parent) {
for (V v : G.vertices())
visited.put(_, _____);
Queue<V> Q = ___________
Q.add(____);
parent.put(start, ____);
visited.put(start, _____);
while (! Q.______) {
V u = Q._______;
for (V v : _______)
if (! ______) {
parent.put(___);
Q.____;
visited.put(v, true);
}
}
}
v
false
new LinkedList<V>();
start
start
true
isEmpty()
remove()
G.adjacent(u)
visited.get(v)
v, u
add(v)
DFS(u, G, parent_map, visited) =
visited[u] = ____
for v in G.adjacent(_)
if not ______
_____________
DFS(_, G, parent_map, visited)
true
u
visted[v]
parent_map[v] = u
v
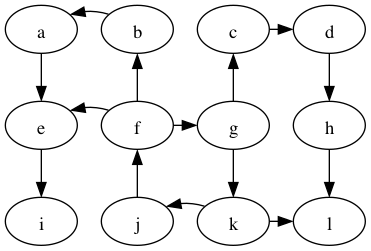
What is the start and end time of the nodes in this graph beginning and ending with g?
A: 13/18
B: 12/19
C: 1/8
D: 2/7
E: 14/17
F: 11/20
G: 0/23
H: 3/6
I: 15/16
J: 10/21
K: 9/22
L: 4/5
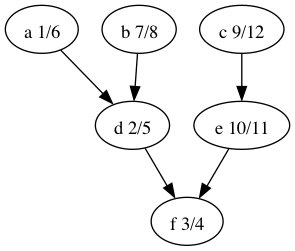
Refering to the image, how would you order the nodes by finish times?
f,d,a,b,e,c.
Backtracking(Board board, Arraylist<Endpoints> goals){
If (________){
return new Arraylist<>();
}
Else{
For (Endpoints: goals){
Wire w = _________;
if (w == _____){
continue;
}
else{
Arraylist<Endpoints> new_goals = new Arraylist<>(________);
new_goals._____(_______);
ArrayList<Wire> result = backtracking(board, _____);
if (_____ == null){
board._____;
_________
}
else{
results.add(_);
return ______;
}
}
}
Return ____;
}
}
goals.size == 0
bfs(board, endpoints);
null
goals
remove
endpoints
new_goals
results
removeWire
continue
w
results
null
static <V> void kruskal_mst(EdgeGraph<V> G,
Map<V,Map<V,Double>> weight,
ArrayList<Edge<V>> T,
DisjointSets<V> sets)
{
for (V v : G._____)
sets._______;
ArrayList<Edge<V>> edges = new ____;
for (Edge<V> e : G.____)
edges.____;
// bucket sort O(n), mergesort O(n log n)
sort(edges, ________);
for (Edge<V> e : edges) {
if (________) {
T.add(e);
sets.union(______);
}
}
}
vertices()
make_set(v)
ArrayList<Edge<V>>
edges()
add(e)
new CompareWeight<V>(weight)
sets.find(e.source()) != sets.find(e.target())
e.source(), e.target()
Make the table for the following DNA sequence:
GAA
GGA T = G G A
j = 0 | 1 | 2 | 3
--------------------------
S i = 0 | |I: |I: |I:
G 1 |D: |M: |M: |I:
A 2 |D: |D: |M: |M:
A 3 |D: |D: |I: |D:
T = G G A
j = 0 | 1 | 2 | 3
--------------------------
S i = 0 | 0 |I:-1 |I:-2 |I:-3
G 1 |D:-1 |M:2 |M:1 |I:0
A 2 |D:-2 |D:1 |M:0 |M:3
A 3 |D:-3 |D:0 |I:-1 |D:2
What is the time complexity of DNA Allignment?
O(mn)
static int match(char c1, char c2) {
if (c1 '_' || c2 '_') {
return __;
} else if (c1 == c2) {
return __;
} else {
return __;
}
}
-1
2
-2
static int score(char[] S, char[] T) {
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != S.length; ++i) {
total += match(___, ___);
}
return total;
}
S[i]
T[i]
What are the 3 steps to developing a dynamic programming solution?
Recursion (top down)
Memorization (arrays and hashtables)
Bottom up formulation using loops
What is the story associated to the 0-1 Knapstack problem?
Suppose you are preparing to hike the Appalachian Trail. Select items from a grocery store that will fit in your backpack while maximizing the number of calories. You have room for 10 ounces of food in your backpack and you are not allowed to split items.
private void fillCache() {
// Top right corner
cache[0][0] = new Result(__,__);
// First row (T)
for (int j = 1; j != m + 1; ++j) {
int score = ________;
cache[0][j] = _______;
}
// First column (S)
for (int i = 1; i != n + 1; ++i) {
int score = _____________;
cache[i][0] = ____________;
}
for (int i = 1; i != n + 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j != m + 1; ++j) {
// Match
int M = ________________
// Insertion
int I = _________________
// Deletion
int D = ________________
int best = Math.max(M, Math.max(I, D));
Direction d;
if (best == M){
d = Direction.DIAGONAL;
}
else if (best == I){
d = Direction.LEFT;
}
else{
d = Direction.UP;
}
cache[i][j] = new Result(best, d);
}
}
}
0, Direction.NONE
cache[0][j - 1].getScore() + judge.getGapCost();
new Result(score, Direction.LEFT)
cache[i - 1][0].getScore() + judge.getGapCost()
new Result(score, Direction.UP)
cache[i - 1][j - 1].getScore() + judge.score(S.charAt(i - 1), T.charAt(j - 1));
cache[i][j - 1].getScore() + judge.getGapCost();
cache[i - 1][j].getScore() + judge.getGapCost();
private void traceback() {
StringBuilder alignedSBuilder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder alignedTBuilder = new StringBuilder();
int i = n;
int j = m;
if (n == 0 && m == 0){
if (cache[0][0] != ___){
______________;
}
________
________
return;
}
while (______) {
Result current = cache[i][j];
current.markPath();
Direction dir = __________;
if (dir _________) {
alignedSBuilder.append(_____);
alignedTBuilder.append(_____);
i--;
j--;
} else if (dir == ________) {
alignedSBuilder.append(_____);
alignedTBuilder.append(_____);
i--;
} else if (dir == _______) {
alignedSBuilder.append(______);
alignedTBuilder.append(______);
j--;
} else {
break;
}
if (cache[0][0] != ____){
cache[0][0].______;
}
}
alignedS = _____________:
alignedT = ___________;
}
null
cache[0][0].markPath()
alignedS = "";
alignedT = "";
i != 0 || j != 0
current.getParent()
Direction.DIAGONAL
S.charAt(i - 1)
T.charAt(j - 1)
Direction.UP
S.charAt(i - 1)
Constants.GAP_CHAR
Direction.LEFT
Constants.GAP_CHAR
T.charAt(j - 1)
null
markPath()
alignedSBuilder.reverse().toString();
alignedTBuilder.reverse().toString()
class Result {
Result(String i, int cal, Result r) {
___ = i;
_____ = cal;
_____ = r;
}
String item;
int calories;
Result rest;
}
item
calories
rest
public static HashSet<String>
knapsack4(int availableWeight,
HashSet<String> items,
HashMap<String, Integer> weight,
HashMap<String, Integer> calories) {
ArrayList<String> items_array = ______;
Result[][] R = __________;
for (int i = 0; i != availableWeight + 1; ++i) {
R[i] = ________;
}
for (int i = 0; i != availableWeight + 1; ++i) {
R[i][0] = ________:
}
for (int numItemsRemaining = 1; numItemsRemaining != items.size() + 1; ++numItemsRemaining) {
for (int availWeight = 0; availWeight != availableWeight + 1; ++availWeight) {
knapsack_one(availWeight, numItemsRemaining, items_array, weight, calories, R);
}
}
Result r = _________;
HashSet<String> choices = new HashSet<>();
while (r != null) {
if (r.item != "None")
choices.add(_____);
________;
}
return choices;
}
new ArrayList<>(items)
new Result[availableWeight + 1][]
new Result[items.size() + 1]
new Result("None", 0, null)
R[availableWeight][items.size()]
r.item
r = r.rest
static void knapsack_one(int availableWeight,
int numItemsRemaining,
ArrayList<String> items,
HashMap<String, Integer> weight,
HashMap<String, Integer> calories, Result[][] R) {
String item = __________;
// Don't purchase the item
Result rest1 = ________;
Result best_result = rest1;
// Purchase the item
if (_________ <= availableWeight) {
Result rest2 = ____________;
int new_calories = _________;
if (new_calories > _________) {
best_result = ___________;
}
}
___________ = best_result;
}
items.get(numItemsRemaining - 1)
R[availableWeight][numItemsRemaining - 1]
weight.get(item)
R[availableWeight - weight.get(item)][numItemsRemaining - 1]
rest2.calories + calories.get(item)
best_result.calories
new Result(item, new_calories, rest2)
R[availableWeight][numItemsRemaining]
What does make_set do?
creates a list with 1 element
What does find do (in union-find)?
follow the element’s pointer to the whole list then take the head element
What does union do (union-find)?
append one list to the other, then update the pointer in the elements of one of the lists
What is the time complexity of find()?
O(1)
What is the time complexity of make_set()?
O(n)