Radioactivity + Fission and Fusion
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
define atomic number
number of protons (bottom number)
define mass number
number of protons + neutrons (top number)
define isotope
atoms with same number of protons but different number of neutrons
what are alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays?
ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process
rank alpha particles, beta particles and gamma rays based on their ionising + penetrating powers
alpha particles = most ionising + weakly penetrating
beta particles = moderately ionising + moderately penetrating
gamma rays = weakly ionising + most penetrating
what stops α, β, γ?
alpha = paper
beta = aluminium
gamma = lead
what is used to detect ionising radiation?
Geiger Muller Tube
how to measure the activity?
place GM tube next to the source + connect it to a counter
measure counts in 10 seconds, repeat 5x, and do an average
remove the source
measure counts in 10 seconds, repeat 5x, and do an average
examples of sources of background radiation
food + drink
cosmic rays
rocks
nuclear accidents
what is activity and what is it measured in?
becquerels (Bq) = measurement for decays per second
define half life
the time taken (on average) for half of the nuclei to decay
finish the sentences :
the half life is different for…
isotopes that decay faster have…
different radioactive isotopes
have shorter half-lives
define irradiation
an object is exposed to ionising radiation
define contamination
the transfer of the source onto/into an object
what are the dangers of ionising radiation?
radiation can cause mutations in living organisms
radiation can damage cells + tissue
problems arising from disposal of radioactive waste
name risks associated with the disposal of radioactive waste
worker/public exposure
theft
future discovery
leaking into environment
how can the risk of worker/public exposure be reduced?
worker → protective clothing, rotate work via shifts, dosimeters - measures dose, tongs, robots
how can the risk of theft be reduced?
secrecy, security (people/lock)
how can the risk of future discovery be reduced?
hide well, pictograms representing injury/death
how can the risk of leaking into environment be reduces?
store waste in lead, check for leaks before disposal
uses of radioactivity when sterilising food + medical equipment
gamma rays
gamma rays kills organisms on food/equipment
gamma = best because its the most penetrating, but is weakly ionising so you need lots
uses of radioactivity in smoke detectors
alpha ionises air causing electrical current smoke disrupts that, lower current
alpha is the best ioniser
uses of radioactivity in leak detection
put gamma emitter in pipes, use GM tube to detect leaks
gamma = best because its the most penetrating
nuclear reactions (including fission + fusion + radioactive decay) is a source of what?
source of energy
how does 235U go through the process of fission?
235U nucleus absorbs slow neutron forming unstable 235U
236U fissions, forming 2 lighter daughter nuclei + releases a 2-3 fast neutrons
what does the process of fission (235U) produce?
2 lighter daughter nuclei
small number of neutrons
how is a chain reaction set up?
slow neutron is absorbed by 235U nucleus
this forms unstable 236U nucleus
236U nucleus fissions
this releases more neutrons
those neutrons are absorbed by other 235U nuclei
what is the purpose of control rods and what are they made of?
made of boron
absorbs neutrons, allowing us to control the rate of fission
what is the purpose of a moderator and what are they made of?
made of graphite or water
slows down fast neutrons so they can cause fission
what is the purpose of shielding and what are they made of?
made of steel or concrete
stops neutron radiation from escaping the nuclear reactor
define fission
the split of an unstable nuclei
define fusion
2 lighter nuclei joined together to make a heavy nucleus, a small amount of mass is lost and converted into energy
fill in the blanks!
fusion is the ____ source for ____.
energy
stars
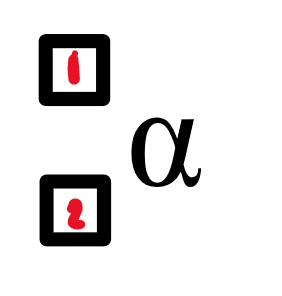
what is in the nucleus of an alpha particle?
2 protons + 2 neutrons
4
2
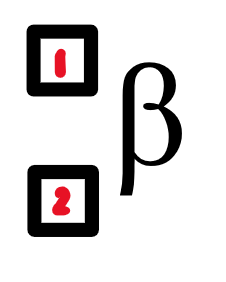
what is in the nucleus of a beta particle?
an electron
0
-1
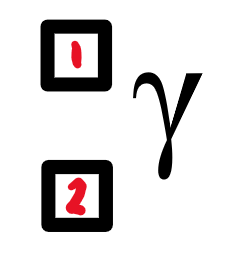
what is a gamma ray?
high electromagnetic wave
0
0