C3.2 Defence against disease
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
What do pathogens cause?
Infectious diseases
Pathogens
Infectious disease-causing organism
Infectious disease
Can be passed from 1 organism to another
Types of pathogens
Viruses
Bacteria
Fungi
Protists
Do archae cause disease in humans?
No
What does careful observation lead to?
Improtant progress
Example of careful observation leading to important progress
CO during 19th-century epidemics of childbed fever (due to an infection after childbirth) in Vienna + cholera in London led to breakthroughs in the control of infectious disease
CO led to break thrus in disease control
Primary defence system
Non specific
Skin
Mucous membranes
How does the skin defend against pathogens?
Acts as a physical AND chemical barrier to pathogens
How does the skin act as a physical barrier to pathogens?
Outer layer covered in dead cells = tough → difficult for pathogens to penetrate
Forms scabs → prevents pathogens from entering when the skin is damaged
Natural MO on the skin compete w harmful pathogens for nutrients
How does the skin act as a chemical barrier to pathogens?
Sebaceous glands produce antimicrobial secretions (sebum) → kills bacteria
How does sebum defend against pathogens?
Maintains skin moisture + lowers the pH
Low pH inhibits growth of bacteria + fungi
Where are mucous membranes found?
Skin openings
Eg nose, reproductive organs, airways
How do mucous membranes defend against pathogens?
Secrete mucus → traps pathogens
Cilia on lining of MM waft them
What happens to the trapped pathogens by mucus / cilia?
Swallowed → destroyed by HCl
Or expelled by coughing
What does mucus contain that helps it destroy pathogens?
Lysozyme = anti-bacterial enzymes
Break down bacterial CW (chatgpt)
Why can antibiotics be used to treat bacterial infections but not viral infections?
Bacteria have peptidoglycan cell walls
Viruses don’t
Purpose of blood clotting
Seal cuts in skin to:
Prevent excess bleeding
Prevent pathogen entry
Clotting factors
Proteins in the blood
Control bleeding
Released by platelets
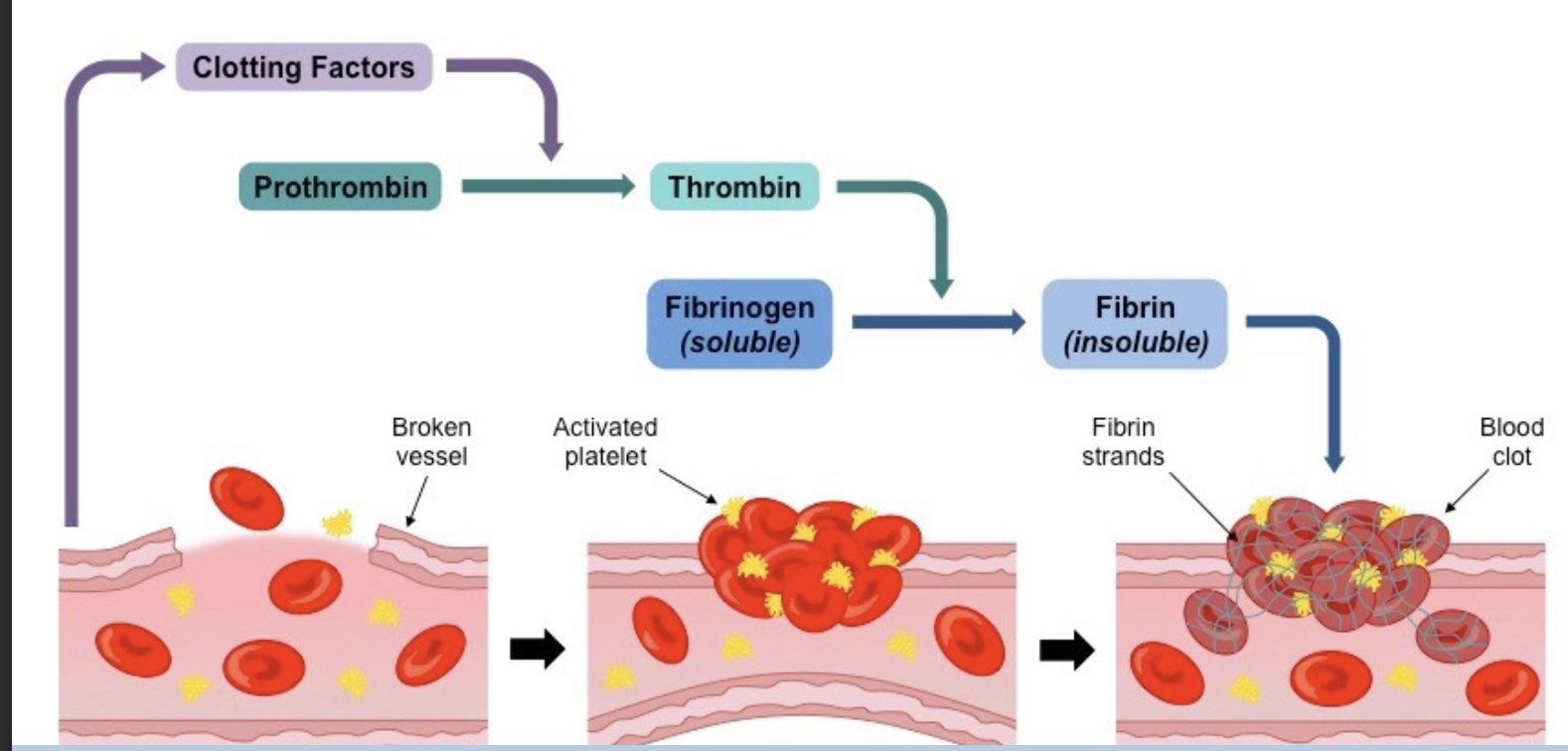
How is a clot formed?
Platelets release clotting factors
Cascade pathway →
Rapid conversion of fibrinogen (soluble) to fibrin (insoluble) by thrombin
Erythrocytes (RBC) trapped
Blood clot hardens → forms scab
More detailed explanation of the clotting cascade
Platelets attach to injury site + release clotting factors
Cause prothrombin → thrombin (enzyme)
Thrombin converts fibrinogen (soluble) → fibrin (insoluble)
Fibrin forms a mesh → traps platelets + RBC → clot
Thrombin
Catalyses clotting process
Fibrinogen
Soluble protein
Circulates in blood plasma
Fibrin
Insoluble protein
Forms scabs
2 types of immune system
Innate
Adaptive
Innate immune system
Responds to broad categories of pathogen
Doesn’t change during an organism’s life
Adaptive immune system
Responds in a specific way to particular pathogens
Builds up a memory of pathogens encountered, so the immune response becomes more effective
How does the adaptive IS make the immune response more effective?
Builds up a memory of pathogens encountered
Defence against pathogens levels
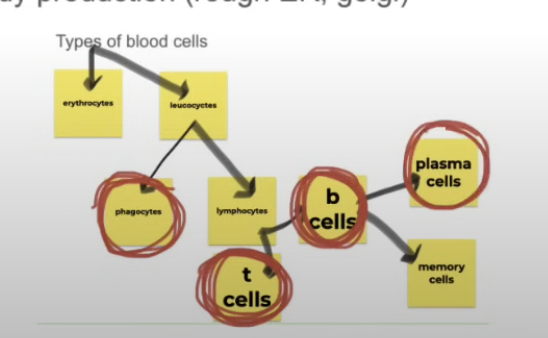
2 types of blood cells
RBC (erythrocytes)
WBC (leucocytes)
Phagocytes (engulf)
Lymphocytes (produce antibodies)
2 types of lymphocytes
B cells
T cells
Which type of WBC does the innate vs adaptive IS use?
Innate- phagocytes (engulf)
Adaptive- lymphocytes (build memory)
Compare innate vs adaptive immune systems
INNATE
Phagocytes
Constant thru out organism's life
Not specific (attack any foreign body)
ADAPTIVE
Lymphocytes
Builds memory / immunity thr out organism’s life
Specific (diff response for each pathogen(
Phagocytes (or macrophage)
WBC part of innate immune system
Non specific
Infection control by phagocytes
Move from blood to inflection site via amoeboid movement
Phagocytes recognize pathogens
Phagocytes engulf pathogens by endocytosis
Phagocytes digest them using enzymes from lysosomes
When a phagocyte responds to the presence of a pathogen, the following events happen:
Enzymatic digestion
Exocytosis
Phagocytosis
Vacuole formation
Endocytosis
Which of the following would be the correct order of events?
Endocytosis / phagocytosis
Vesicle formation
Enzymatic digestion
L release digestive E
Exocytosis
Waste
Vesicle forms around pathogen
Lysosome fuses with vesicle
Digestive enzymes destroy pathogens
Lymphocytes
WBC
In adaptive immune system
Produce antibodies
Where are lymphocytes found?
Both:
Circulate in the blood
Contained in lymph nodes
An invdividual has a v large no of what type of lymphocyte?
B-lymphocytes
What does each B-lymphocyte make?
A specific type of antibody
Antibody
Protein produced by lymphocytes in response to an antigen
It recognizes a specific antigen + binds to it as part of an immune response
What happens when antibodies bind to antigens on pathogens?
Tag it for destruction by other immune cells
Or prevent it from binding with other host cells
What are antibodies specific to?
Antigens
So need diff lymphocyte types to make lots of diff antibodies
Antigens
Recognition molecules that trigger antibody production
Glycoproteins or other proteins
Usually located on the outer surfaces of pathogens
Where are antigens usually located?
Outer surfaces of pathogens
What do antigens that are recognised as non-self stimulate?
An immune response
Specifically antibody production by B-lymphocytes
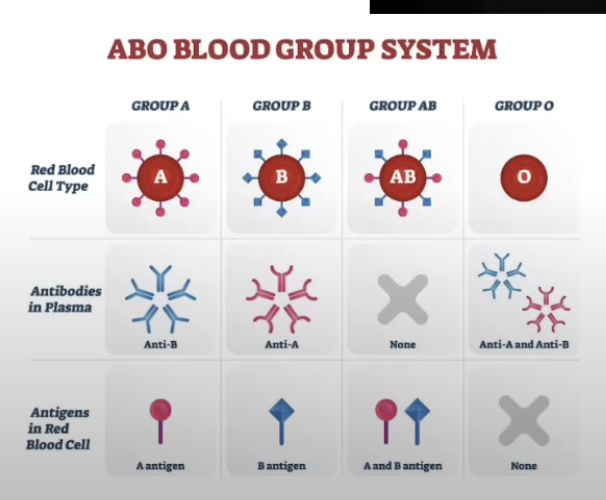
Example of antigens stimulating an immune response (erythrocytes)
Antigens on the surface of RBC may stimulate antibody production if transfused into a person with a diff blood group
ABO blood types, antigens, antibodies
B lymphocytes = B cells
Helper T-lymphocytes = T helper cells
2 roles of the (antigen specific) B cells
Produce antibodies
Become memory cells
B cells can only produce AB + become memory cells only when…
They have been activated
What does the activation of B cells require
Both:
Direct interaction with the specific antigen
Contact with a helper T-cell that has also become activated by the same type of antigen (Contact w activated T cell)
Process of activating B cells by T cells
Pathogen engulfed by phagocyte (say entire phagocytosis process)
Antigen (from destroyed pathogen) presents itself outside the phagocyte
T helper cell binds to antigen → becomes activated
Activated T cell binds to specific B cell
B cell activated
What happens after B lymphocytes are activated?
Activated B cells multiply to form clones of antibody-secreting plasma B cells
Plasma B cells
Activated B-cells first divide by mitosis to produce large no of plasma B-cells
Capable of producing the same type of antibody.
Thru what process to activated B cells divide?
Mitosis
Why do activated B cells need to divide?
Bc relatively small no. of B-cells that respond to a specific antigen
So divide to produce sufficient quantities of antibody
2 types of cells activated B cells divide into?
Plasma B cells (produce AB)
Memory cells (for immunity)
What happens when activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells?
Grow
Produce organelles for AB production (eg rough ER, golgi)
What specific type of cell produces antibodies?
Plasma B cell
Plasma cell produce AB → circulate blood stream
Is the activation of B cells etc part of adaptive or innate immunity?
Adaptive
Cell division pathway
Immunity
The ability to eliminate an infectious disease from the body
What is immunity a consequence of?
Retaining memory cells
How long to memory cells remain in the body?
Years
LT
Memory cells
Lymphocytes that can specific antibodies needed to fight the infection
Survive in the LT
Purpose of memory cells
Produce a rapid response if pathogen is detected again
Faster + stronger response (more ABs, produced more quickly)
HIV full form
Human immunodeficiency virus
How is HIV transmitted?
Via body fluids:
Sexual intercourse (unprotected w infected person)
Blood donation
Sharing of needles w infected person
Breast milk (mother to child) if mother infected
NOT by casual contact (hugging, touching)
Consequence of HIV
AIDS
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
What does HIV do to lymphocytes?
Infect them
Leads to AIDS
How does HIV lead to AIDS?
Only certain types of lymphocyte are infected + killed
Reduction in lymphocytes limits the ability to produce AB + fight opportunistic infections.
What type of lymphocyte does HIV destroy
T cells
Reduced ability to produce AB