2.1 Principles and Indications of Local Anaesthesia
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are contraindications for local anaesthesia?
Fracture confirmation, septic inflammation (periarticular cellulitis, hoof abscesses)
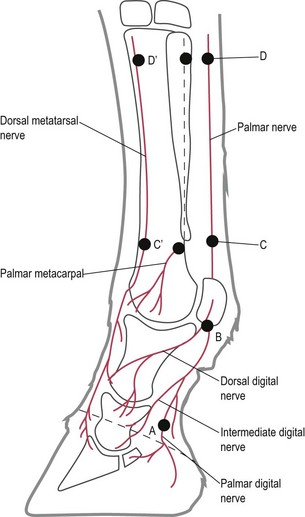
What are the common nerve blocks for the forelimb?
Palmar digital nerve (foot cartilages), midpastern semi-ring block, PDN (proximal sesamoid bones), low palmar nerve block, high palmar nerve block, lateral palmar nerve block, median nerve, ulnar nerve, medial cutaneous antebrachial nerve.
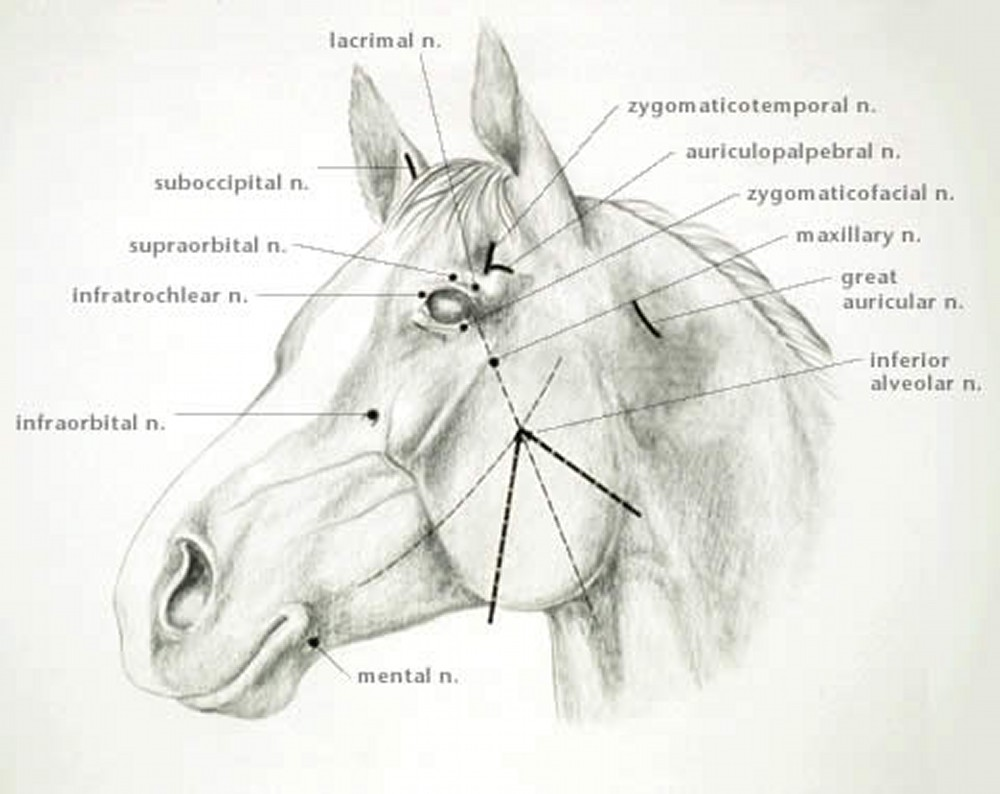
What are the nerve blocks of the head?
Auriculopalpebral nerve block
Diamond block (Supraorbital, lacrimal, zygomatic, infratrochlear)
Retrobulbar nerve block
Maxillary nerve block
Infraorbital nerve block
Mandibular nerve block (inferior alveolar nerve block)
Mental nerve block
What is the typical dosage of mepivacaine for castration off full-sized adult horses?
10ml per testicle.
What is epidural anesthesia?
Injection of an anesthetic into the subarachnoid space. Used on a standing horse.
What are the indications for epidural anesthesia in horses?
Anaesthesia of the perineum
rectovestibular laceration repair
miscellaneous surgeries involving rectum, anus, perineum, tail, urethra, bladder, vulva, vestibule, or vagina.
Relaxation of abdominal contractions during dystocia.
Analgesia of the perineal area and hind limbs of adult horses.
Analgesia or anaesthesia of the perineal area, hind limbs, and abdomen of neonates.
What drugs are commonly used for epidural anesthesia?
Local anesthetics (lidocaine, mepivacaine, ropivacaine)
alpha2 agonists (xylazine, detomidine)
opioids (morphine, methadone, hydromorphone)
tramadol
ketamine.
Where are the injection sites for epidural anaesthesia?
Between 1st and 2nd coccygeal vertebrae, OR
Lumbosacral space
DO NOT USE PROXIMAL EPIDURAL SPACE!!! (withers)
Which drugs for mydriasis of the eye?
Atropine, adrenaline
Which nerves are injected for dental procedures, especially maxillary cheek teeth?
Maxilla: Maxillary, infraorbital
Mandibula: Mandibular, mental
Which nerve block is near the eye?
Auriculopalpebral
Where in the limb are local anaesthetics injected for distal limb nerve blocks?
Perineural
What is the sexual repercussion of using drugs like acepromazine?
Priapism (penis prolapse).