Energy transfers - Energy and ecosystems
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is an ecosystem?
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment
What factors do ecosystems contain?
Abiotic and biotic factors
What do trophic levels mean?
They are a label for elements of a food chain e.g. producer is level 1 and tertiary consumer is level 4
What is autotrophy?
Self feeding (done by producers)
What is photoautotrophy?
Where something makes its own food via photosynthesis
What is biomass?
- Total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level/organism
- Amount of chemical energy stored in the bonds of molecules that an organism contains
When is energy transferred in a food chain?
When one trophic level consumes another
How do you measure biomass?
Calculate the dry organic mass of an organism. This is done by burning, drying and weighing an organism to get its mass when there is no water. The mass of carbon in the organism is usually 50% of the total dry mass
What can we use to measure the amount of chemical energy stored in a sample of biomass?
Calorimetry via the equation Q = mc(delta T)
How can we use calorimetry to measure chemical energy stored?
Bomb calorimetry (less wasted energy). Sample is burned to release kinetic energy which is used to heat water. The change in temp of the water is used to calculate energy released
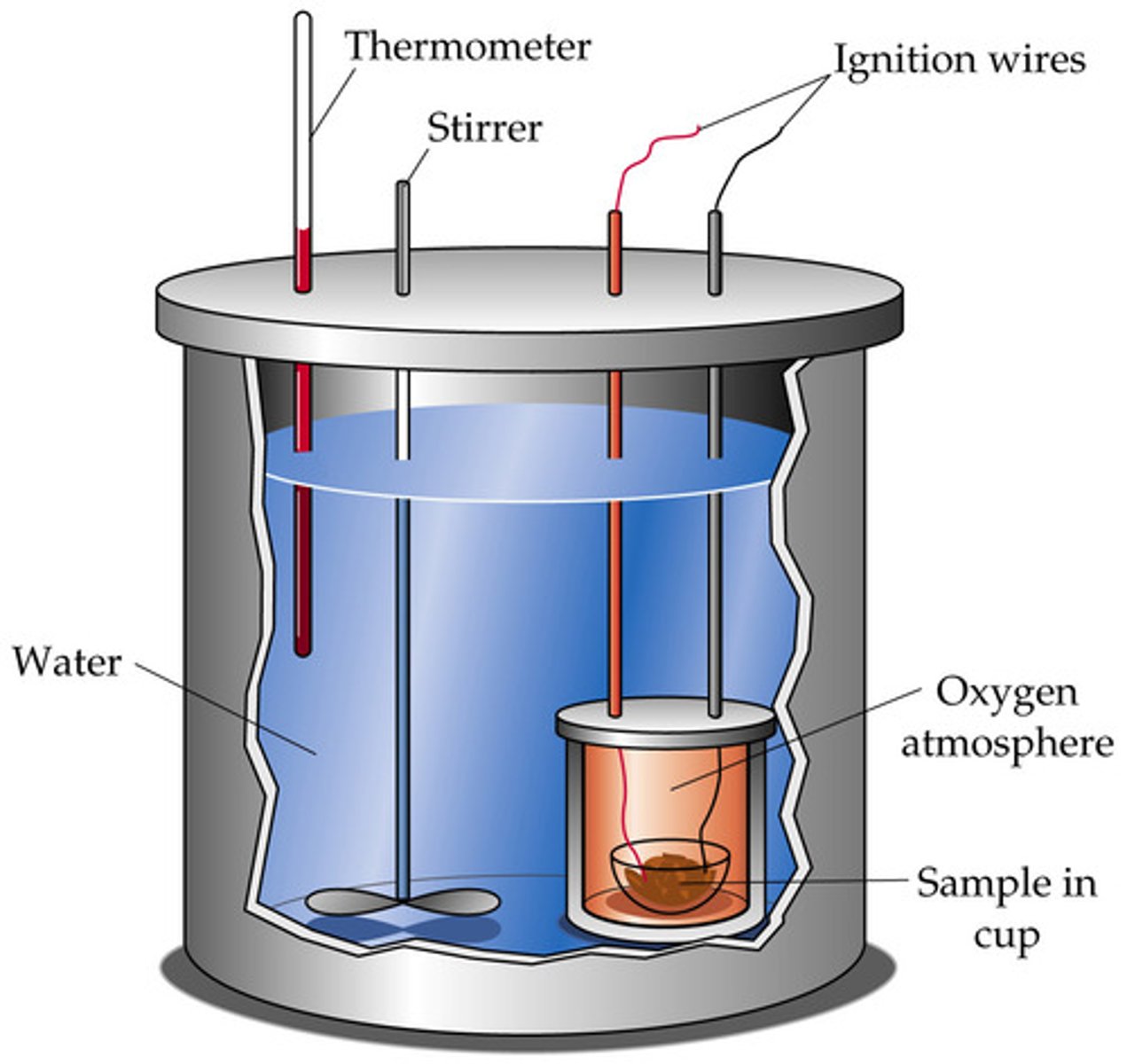
What is energy measured in?
Joules (J)
What is the specific heat capacity of water?
Energy required to heat 1 g of water by 1°C - it
is approximately 4.2 J/g/°C
What is net primary productivity (NPP)?
The chemical energy store in plant biomass after respiratory losses to the environment have been taken into account
What is gross primary productivity (GPP)?
The chemical energy store in plant biomass, in a given area or volume
What is respiratory loss (R)?
Energy produced during photosynthesis that is lost as heat when the plant respires
What is the equation for NPP?
NPP = GPP - R
What does NPP tell us?
- The energy available for the plant to use to grow and reproduce
- The energy available to the next trophic level should they be comsumed
What is net consumer productivity (NP)?
Estimates the total amount of organic matter that is stored in a given area in a consumer.
Where do consumers get their energy?
From eating or consuming other organisms
Roughly how much energy in a trophic level is available to the next level?
10%
Why is only 10% of the available energy from a trophic level gained by the next level?
- Not all of the organism available to the consumer is ingested/eaten (bones, plant roots etc.)
- Some of the biological molecules are not digestible (cellulose, connective tissue etc.)
- Much of the energy taken in by the consumer is lost to the environment as respiratory losses or through the excretion of urine
What is the equation for NP?
NP = I - (F + R)
What do I, F and R stand for in the NP equation?
I = Energy available in ingested food
F = Energy lost as faeces or urine
R = Respiratory loss
What is the fundamental difference between a food chain and web?
Food chains are far more simplistic and don't consider the different things consumers eat like webs do (webs are more realistic)
How is the efficiency (E) of energy transfer between trophic levels measured?
E = (NP/NP-1) x100 - gives percentage
What is NP-1?
The net productivity of the pervious trophic level.
What do farmers aim to do in terms of energy and farming?
They want to increase the amount of available energy for humans by increasing the NPP of crops and NP of livestock
How do farmers increase NPP of crops?
Remove pests (simplifies food webs - more energy preserved)
How to farmers increase NP of livestock?
Reduce the amount of heat lost by respiration in animals. This includes keeping them in warm environments and stopping them moving as much
What are the units for productivity?
It is measured as biomass in a given area in a given time eg kJ ha-1 year-1