IB SL Bio Correction
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms


26
D
explain each of the feeding types:
Autotrophs (chemoautotrophs, photoautotrophs)
Heterotrophs (consumers, detritoveres, saprotrophs)
Mixotrophs
CAutotrophs (“self-feeders”)
• Organisms that synthesize their own organic molecules from simple inorganic substances (e.g., CO₂ and water).
• Examples: Plants, algae, some bacteria.
Types of Autotrophs:
a) Photoautotrophs → Use light energy to synthesize organic molecules.
• Example: Plants, cyanobacteria (photosynthetic bacteria).
b) Chemoautotrophs → Use chemical energy from inorganic compounds (e.g., sulfur, iron).
• Example: Nitrifying bacteria in soil.
2. Heterotrophs (“other-feeders”)
• Organisms that obtain organic molecules by consuming other organisms.
• Examples: Humans, animals, fungi.
Types of Heterotrophs:
a) Consumers → Ingest living or recently killed organic material.
• Example: Humans, lions, cows.
b) Detritivores → Ingest non-living organic matter (decomposing plant/animal material).
• Example: Earthworms, dung beetles.
c) Saprotrophs → Externally digest dead organic material by secreting digestive enzymes and absorbing nutrients.
• Example: Fungi, bacteria.
3. Mixotrophs (“both-feeders”)
• Organisms that can switch between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
• Example: Euglena (a unicellular organism that photosynthesizes but can also consume food).
Different stages of meiosis
Meiosis
• Purpose: Produces genetically unique haploid gametes (sperm/egg).
• Occurs in: Sex organs (ovaries/testes in humans).
• Phases:
1. Interphase: DNA replication (chromosomes double).
2. Meiosis I:
• Prophase I: Homologous chromosomes pair up & crossing over occurs (genetic variation).
• Metaphase I: Homologous pairs line up in the middle.
• Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate.
• Telophase I & Cytokinesis: 2 daughter cells form.
3. Meiosis II: (Like mitosis but with half the DNA)
• Prophase II: No DNA replication.
• Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up.
• Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate.
• Telophase II & Cytokinesis: 4 genetically unique haploid cells form.
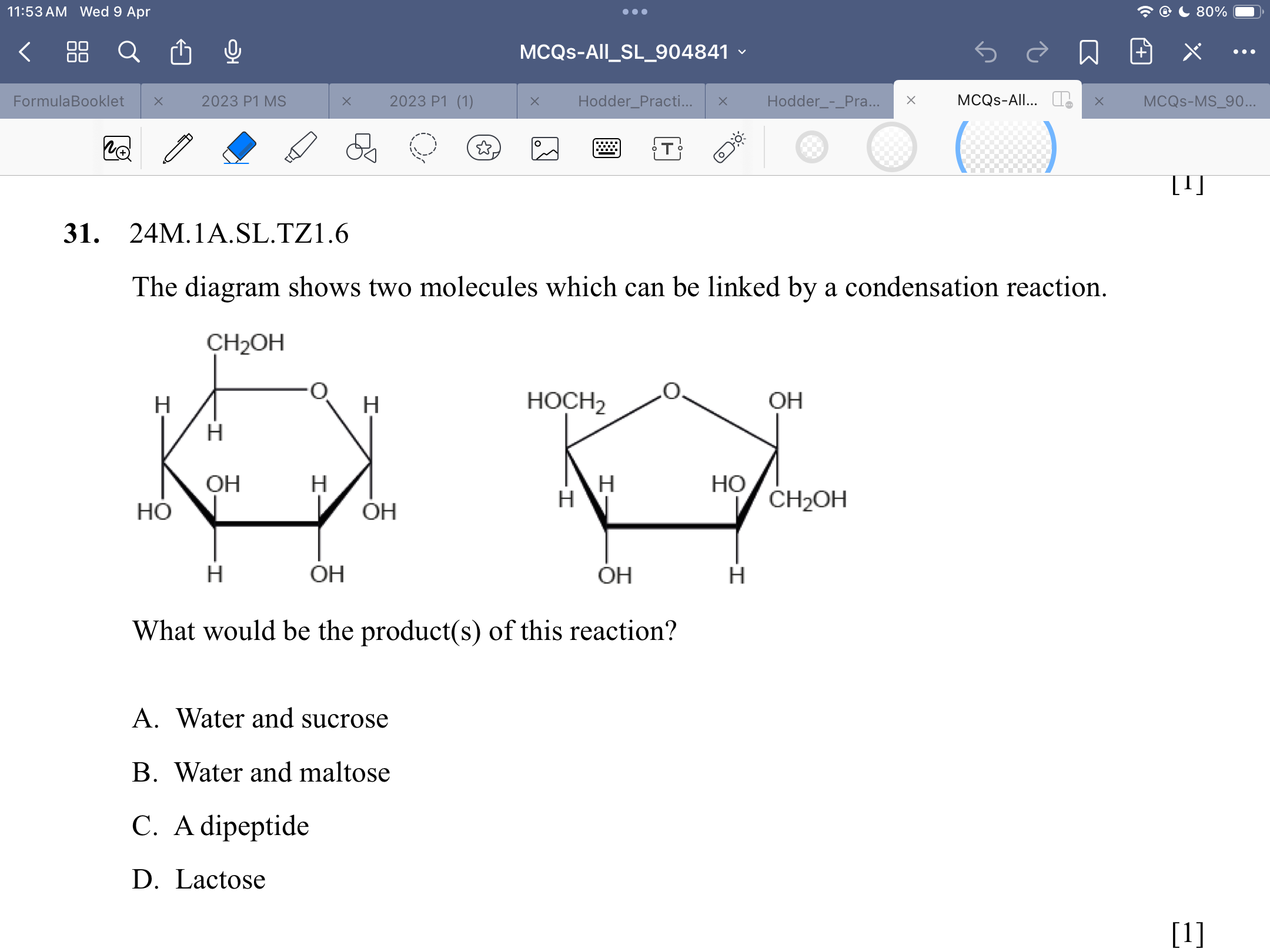
A (maltose is made of two glucose molecules, while sucrose is made of one glucose and one fructose molecule. in the diagram, molecules are different)

A
B
C

C

A
Describe where the potassium and sodium ions are at different phases of nerve impulse translation
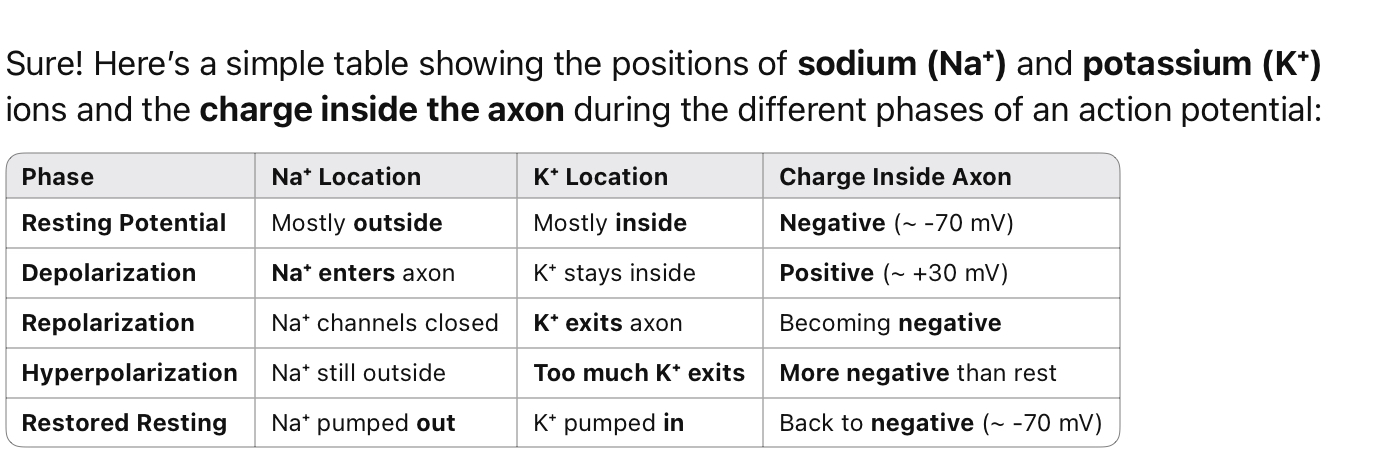
A
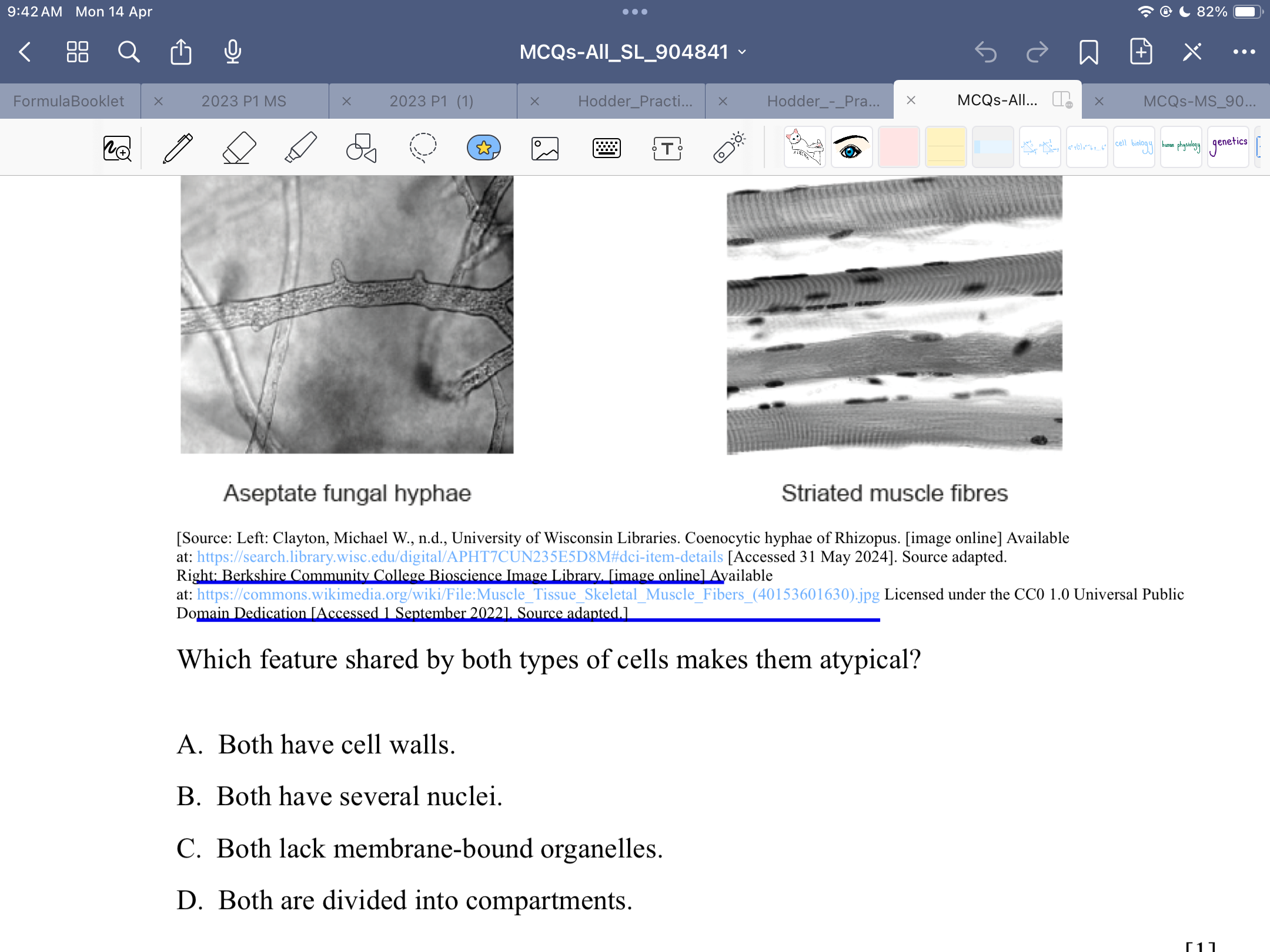
B
C

B
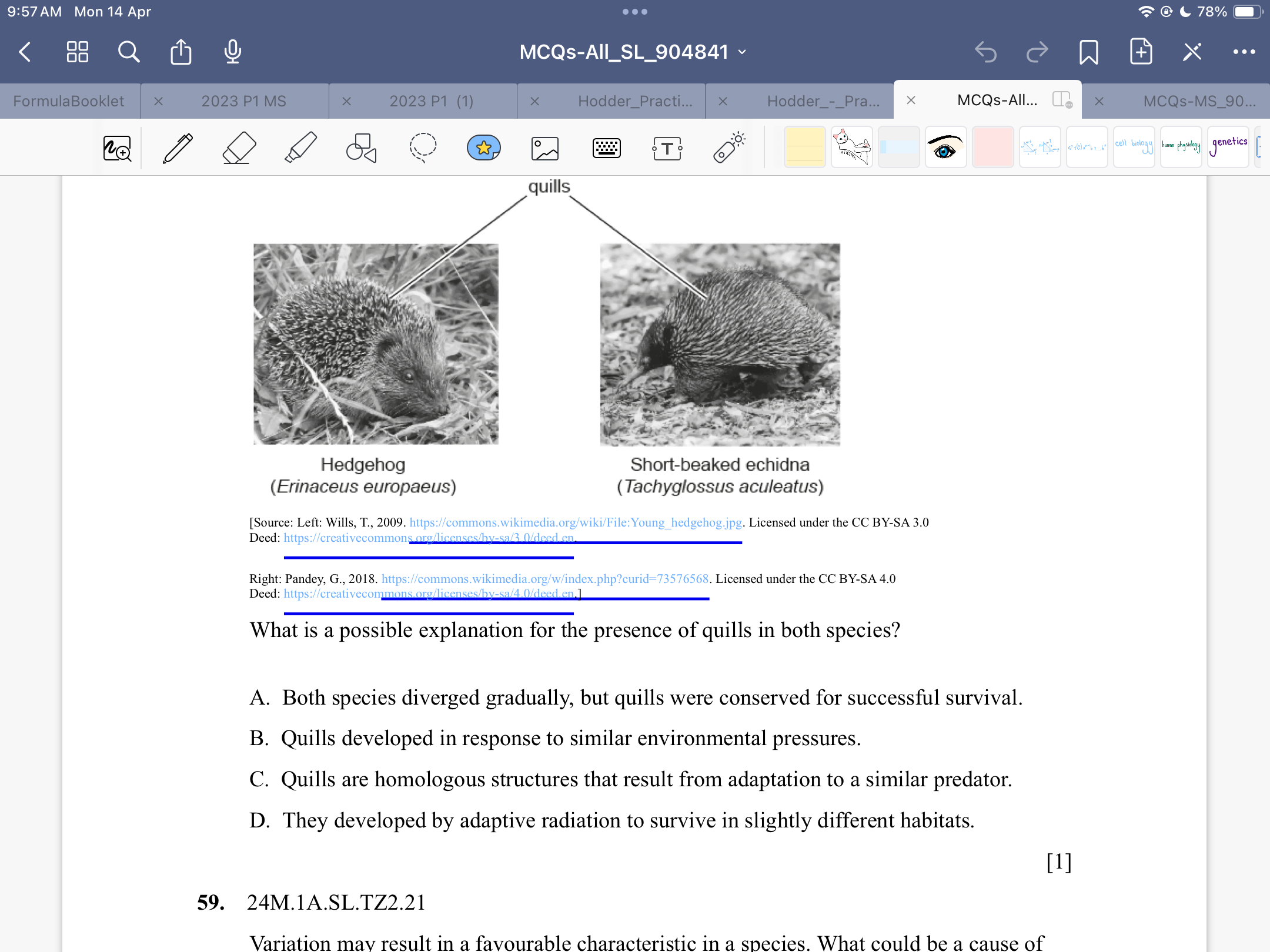
B
detail blood clotting step by step
platelets (detect damage, release clotting factors)
clotting factors (activate enzymes leading to thrombin production)
thrombin (enzyme, converts fibrinogen to fibrin)
fibrinogen (soluble protein, becomes fibrin)
fibrin (insoluble protein, forms clot through fibrin mesh)
People Can Take Funny Falls
Where is FSH secreted from and what is is role
Pituitary gland + stimulates follicle development in ovaries and estrogen
Where is estrogen from and what does it do
Developing follicle + rebuilds uterine lining, inhibits FSH, stimulates LH
Where is LH from and what does it do
Pituitary gland + triggers ovulation, promotes corpus luteum
Where is progesterone from and what does it do
Corpus luteum + maintains endometrium, inhibits LH and FSH
Explain the menstruation phase (when, what happens with dif hormones)
Days 1-5
low estrogen + progesterone —> uterine lining sheds
FSH rises —> new follicle starts developing
Explain the follicular phase (when and what)
days 1-13
FSH stimulates follicle growth
Estrogen rises, rebuilding endometrium lining
Describe ovulation (when and what)
Day 14
High estrogen, LH sugre, egg released
Explain the literal haste (when and what)
Days 15-28
LH causes follicle to become corpus luteum
CL secretes progesterone, which maintains lining
If no fertilisation progesterone and estrogen fall
Exalting how enzymes lower activation energy
Stabilising transition state of a reaction
Weakening bonds in a sbstrate so they are broken more easily
Explain why DNA replication is semi-conservative
Each new DNA molecule is mad of one original strand and one new synthesised strand
C
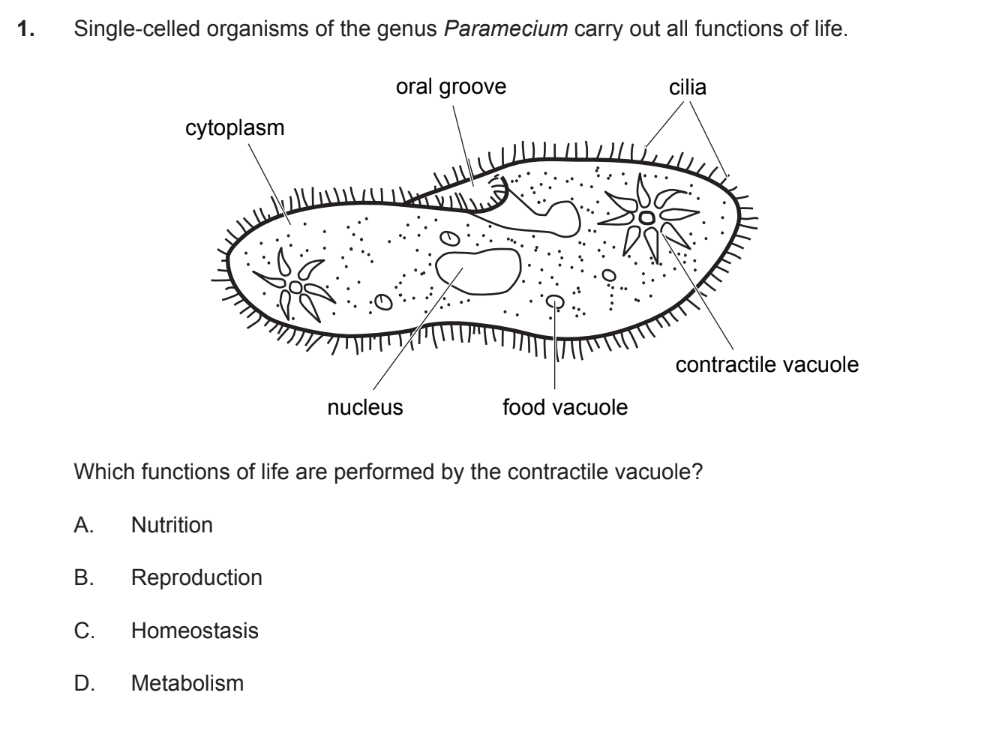
B
What does the RER do?
Synthesizes and processes proteins for export or membrane insertion.
Studded with ribosomes.
what does the SER do
4. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Synthesizes lipids, steroids, and detoxifies drugs.
No ribosomes attached.
what does the golgi apparatus do
5. Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins/lipids into vesicles.
Involved in secretion and lysosome formation.
what does the centriole do
13. Centrioles (animal cells)
Involved in cell division (spindle formation).
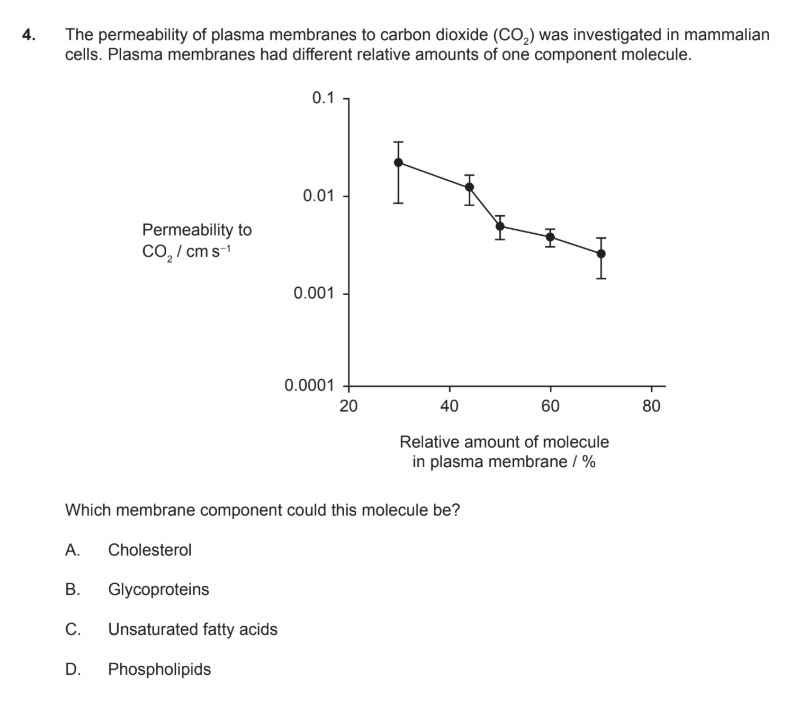
A
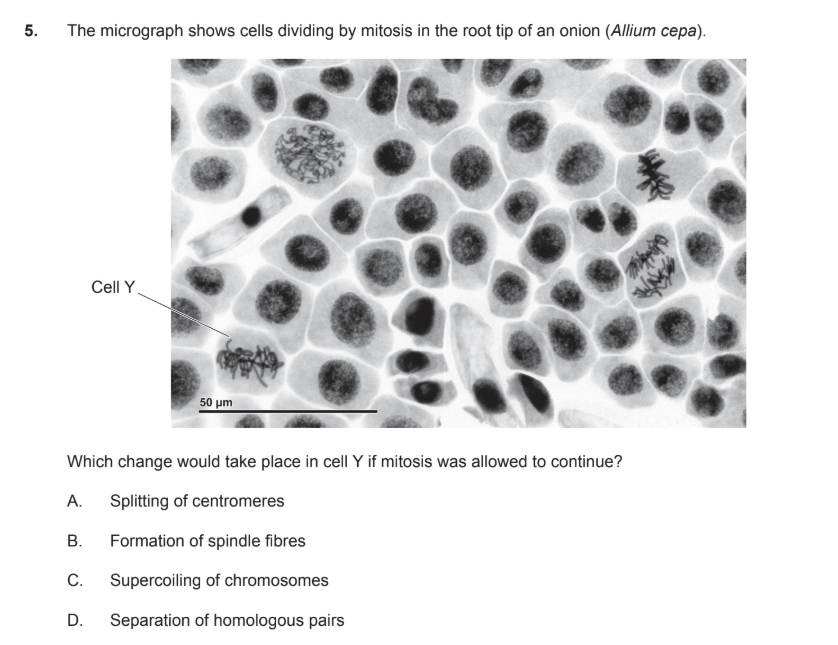
A
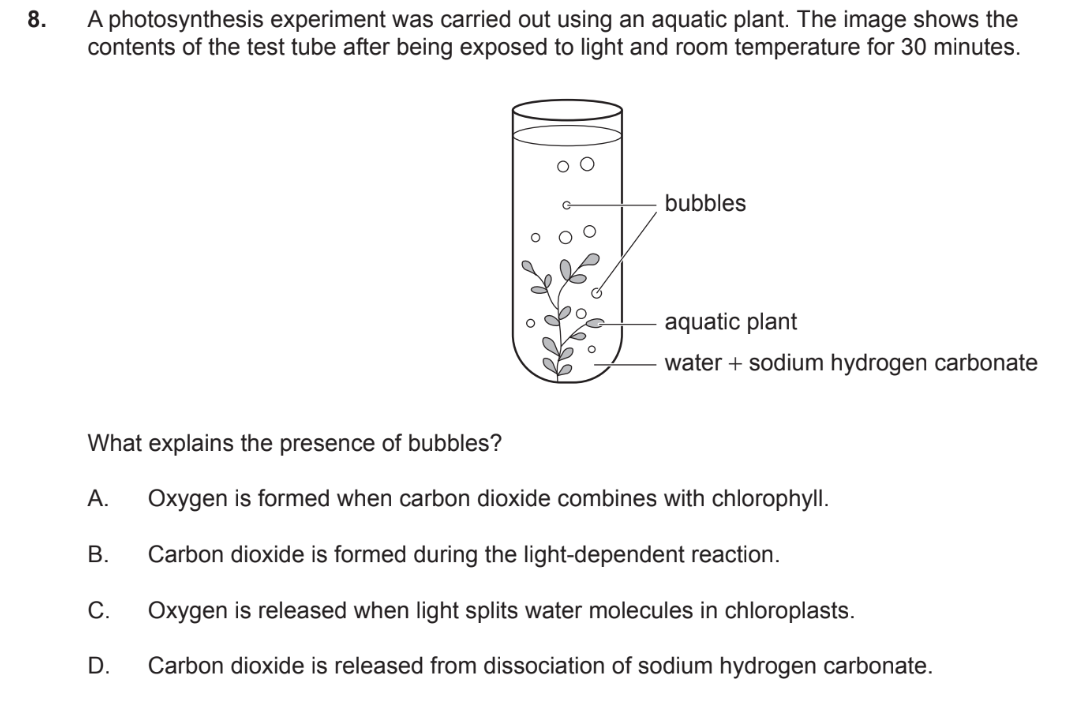
C
Outline how a dipeptide is formed
two amni acids form during a condensation reaction
the amine group (-NH(2) of one amino acid and the carboxyl group (-COOH) of another
forms a peptide bond and releases water
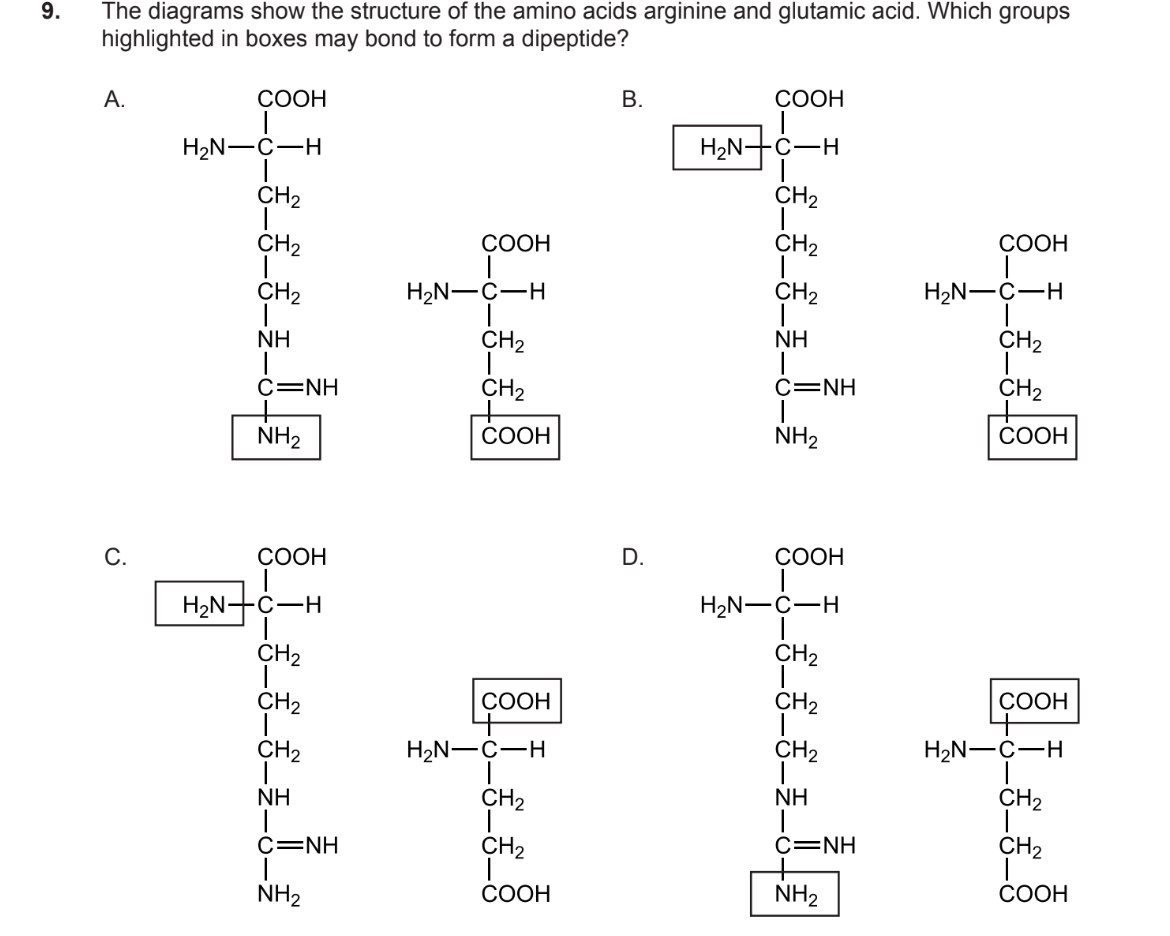
C
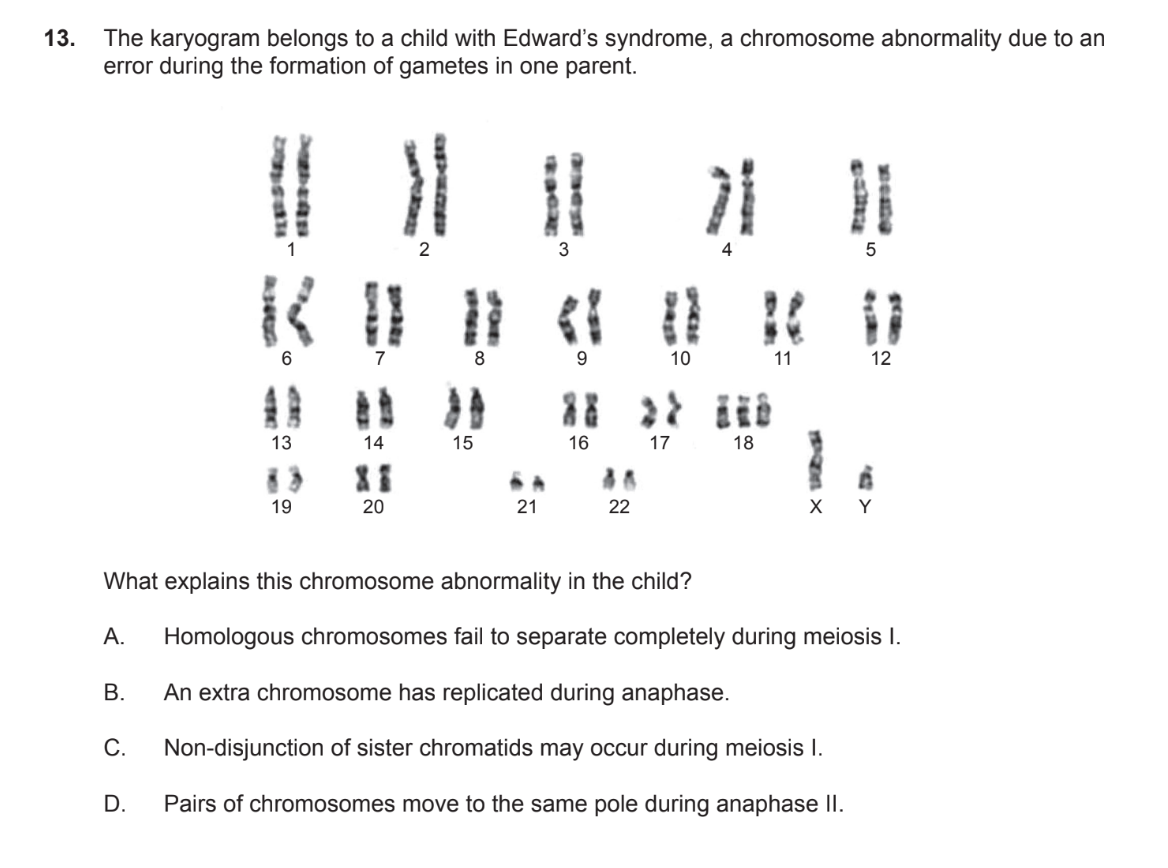
A
explain gel electrophoresis purpose and steps
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. The process involves the following steps:
DNA is extracted.
Isolation and amplification of DNA.
DNA is added to the gel wells.
Electric current is applied to the gel.
DNA bands are separated by size.
DNA bands are stained.

D
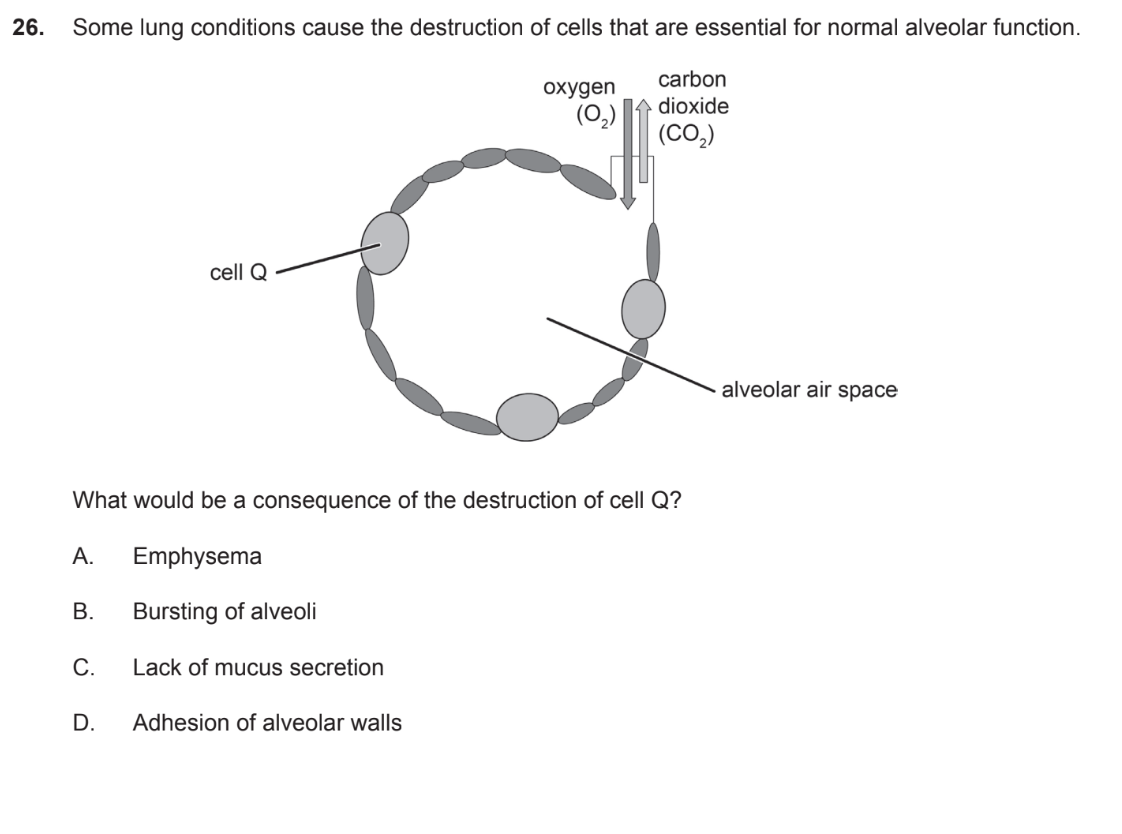
D
explain IVF process in terms of what happens in two steps (drugs, and artificial hormones)
Initial drug treatment:
Women are given drugs to suppress their natural menstrual cycle.
This prevents natural fluctuations in hormones like FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) and LH, so doctors can take full control.
Artificial hormone treatment:
High doses of FSH are given to stimulate multiple follicles to mature.
This leads to multiple ovulations, increasing the number of eggs that can be collected.
what makes maltose?
glucose + glucose
what makes sucrose
glucose + fructose
what makes lactose
glucose and galactose
describe the structure of amylose (its a starch)
linear, unbranched (slower energy). alpha, 1-4 glycosidic bonds. energy store in plants, stored in plants
describe the structure of amylopectin (its a starch)
branched, alpha 1-4 and alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds. more compact and branched (faster enregy). energy store in plants, stored in plants
describe glycogen structure (found in animals)
highly branched
alpha 1-4 and alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds
stored in animals
fast release energy
store energy in humans
the more branches = easier to break down = faster energy
describe cellulose structure
straight unbranched chains
beta- 1,4 glycosid
strucuturally differentiate between saturated fats and unsaturated fats
saturated = no double bonds, straight chains
unsatureated = at least one double bond, causing a kink, making them more fluid
explain one structural advantage of the phospholipid bilayer forming a membrane
has hydrophillic heads and hydrophobic tails, allowing it to form a selectively permeable barrier in an aqueos environment.
what is the role of aquaporins in cells?
channel proteins that facilitate rapid water movement acorss membranes
differentiate between niche and habitat
niche = role and position a species plays, (what it eats, where it lives, how it interacts)
habiitat = physical place it could survive
two features of desert plants to reduce evalporation / transpiration
thick cuticle (reduces evaporation)
sunken stomatoa (traps moisture to reduce transpiration)
list the main macromolecule bonds
carbohydrates —> glycosidic
proteins —> peptides
lipids —> ester
differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fats in regards to melting point, room temp state, found in, health impact, function, examples
melting point (s - higher, u lower)
room temp state (solid, liquid)
found in (animal fats/dairy, plant oils/fish fats)
health impact (increase ldl (bad), increase HDL (good)
function (energy storage/insulation, energy source/membrane fluidity)
examples (butter/ palm oil, nuts/seeds)
what’s an animal adaption to preveent wwater loss
kangeroo rats —> concentrated urine and few sweat glands