mega fat ultra quizlet
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Aposematic Coloration
"warning coloration", used by noxious organisms to signal their unprofitability to potential predators
EX: poisonous frogs be hella colorful

Batesian Mimicry
a harmless species mimics a harmful one

Biomanipulation
deliberate alteration of an ecosystem by adding/removing species, especially predators
Biomass
total quantity of weight of organisms in a given area or volume
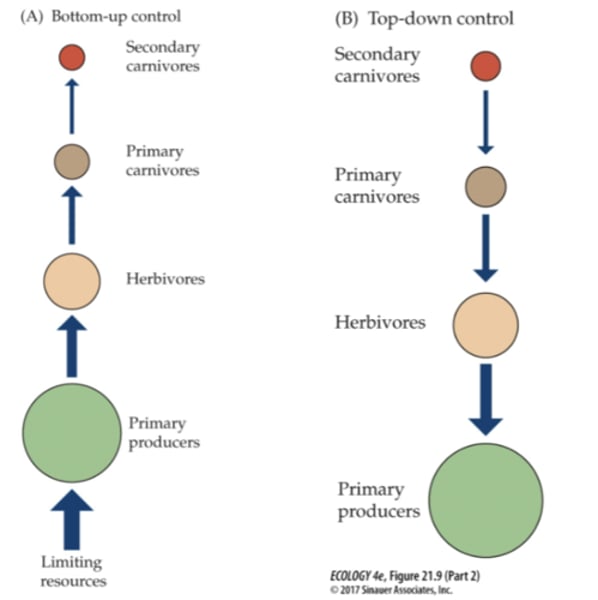
Bottom-Up Model
system design approach where parts of a system are defined in details
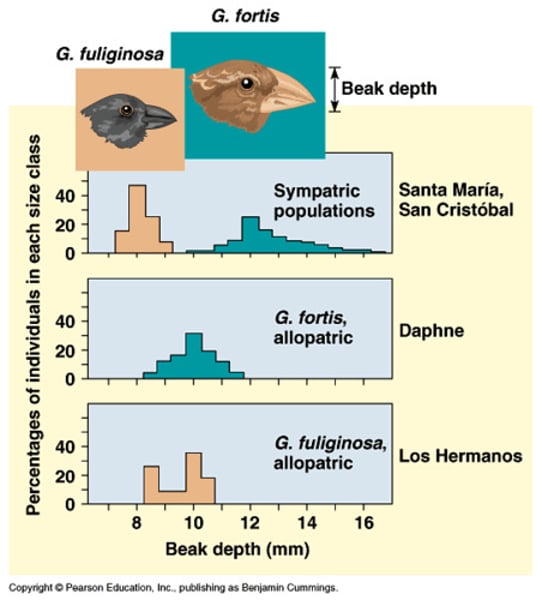
Character Displacement
phenomenon where differences among similar species whose distributions overlap geographically are accentuated in regions where species co-occur, but minimized when not
Commensalism
(+/0 interaction), one species benefits, other is neither harmed nor helped
Competition Exclusion
caused by strong competition, local elimination of a competing species
Cryptic Coloration
camouflage, making prey difficult to spot

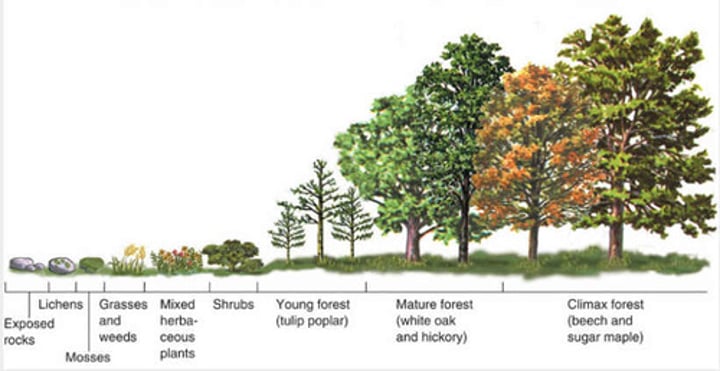
Ecological Succession
process by which an ecosystem or community experiences changes
Ecosystem Engineer
any species that creates, significantly modifies, maintains or destroys a habitat
Energetic Hypothesis
the length of a food chain is limited by the inefficiency of energy transfer along the chain
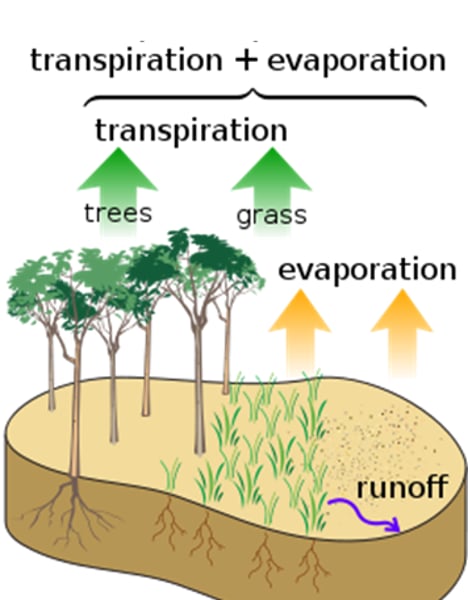
Evapotranspiration
process of water transferring from land to the atmosphere by evaporation from soil and other surfaces and by transpiration from plants
Facilitation
when one species positively impact the fitness of another
Food Chain
linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another
Food web
diagram showing transfer of energy through multiple different organisms in an area
Herbivory
(+/- interaction), refers to an interaction in which an herbivore eats parts of a plant or alga

Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
local species diversity is maximized when ecological disturbance is neither too rare nor too frequent
Interspecific Competition
when species compete for a resource in short supply, (-/- interaction)
EX: hyenas and lions compete for same food source
Interspecific Interaction
relationship between different species in a community
Invasive Species
organism that causes ecological or economic harm in a new environment where it isn't native
Keystone Species
organisms that other species in the ecosystem depend upon and whose disappearance would devastate their biological communities
EX: if leandros dimitropoulos kapsogeorgos disappeared it would devastate ian and oliver's bio grade because we depend on him in our community
Mullerian Mimicry
2 unpalatable species mimic each other

Mutualism
(+/+ interaction), interspecific interaction that benefits both species (obligative or facultative)
Parasitism
(+/- interaction), one organism (the parasite) derives nourishment from another organism (its host), which is harmed in the process
Predator
organism that consumes all or part of the body of another - living or recently killed - organism (its prey)
Prey
any animal that serves as food for another animal
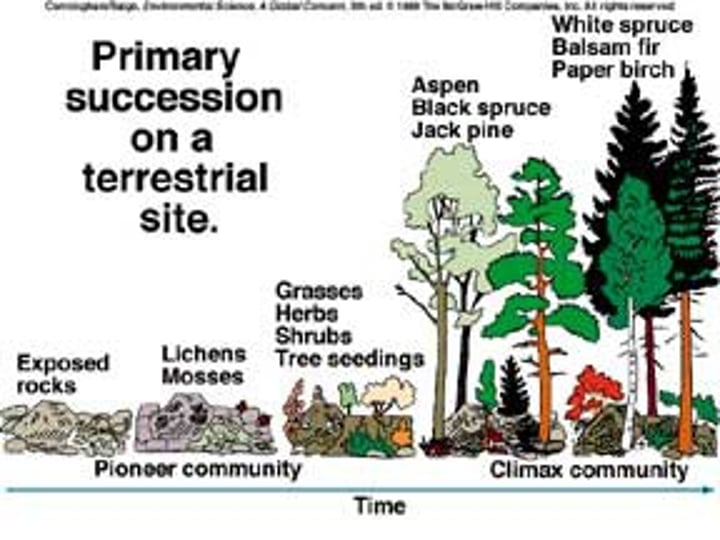
Primary Succession
when a new area of land is populated by a group of species for the first time
Production Efficiency
percentage of energy not used for respiration but stored in assimilated food
Relative Abundance
evenness of distribution of individuals among species in a community
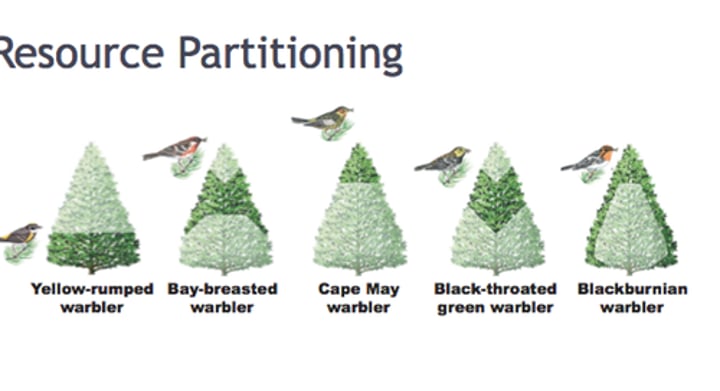
Resource Partitioning
when different organisms in 1 ecosystem split up an area so as not to compete for same resources. Enables similar species to coexist in a community
Secondary Successsion
a previously occupied area that is re-colonized following a disturbance that kills much of or all of its community :(
Species Diversity
the variety of organisms that make up a community
Species Richness
number of species present
Symbiosis
relationship where two or more species live in a direct and intimate contact with each other 😳
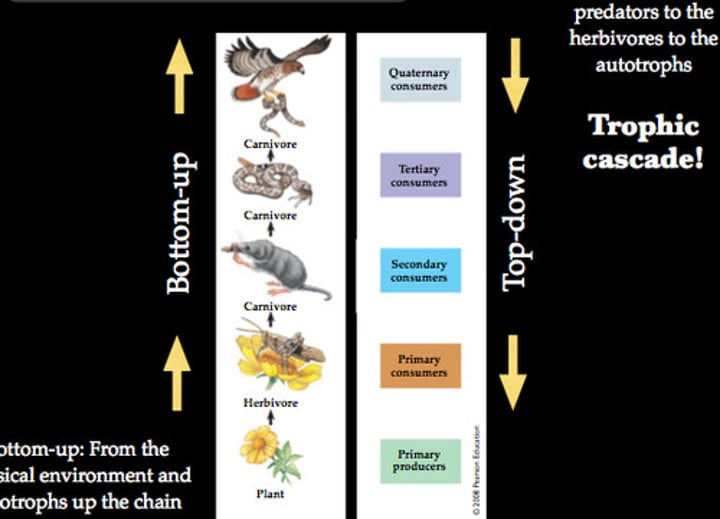
Top Down Model
basically says the influence on a community structure flows from top, the predators, down to the herbivores, then the vegetation and finally, nutrients
Trophic Structure
consists of the primary producer, a primary consumer, and a secondary consumer
Vector
a DNA molecule that is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a cloning or recombinant DNA technique
Altruism
any individual acting in a way that reduces their own fitness while increasing the fitness of the group
ex: insects that form colonies are largely unable to reproduce but instead gather and donate much of their resources to those who can

Associative Learning
animals associating one feature of their environment with another
EX: if someone puts their hand on a hot stove and hurts themselves, they may learn to associate hot stoves with pain
Behavior
an action carried out by muscles under control of the nervous system in response to a stimulus
EX: an animal releasing a scent to mark its territory
Coefficient of Relatedness
the probability that a gene in one individual is identical-by-descent (IBD) to a gene in another individual
EX: no f ucking clue
Cognition
process of knowing that may include awareness, reasoning, recollection, and judgement
EX: honeybees can distinguish same from different
Fixed Action Pattern
a sequence of unlearned acts directly linked to a simple stimulus
EX: dog sees a cat run away from them and instinctively chases after them
Foraging
searching for food and balancing energy costs
EX: storks using long beaks to search bottom of freshwater marshland for food
Hamilton's Rule
an animal will engage in altruistic behaviour only when the indirect benefits that it derives from such behaviour are greater than the direct reproductive cost that it incurs.
simply: it's about how altruistic behaviors can evolve if they benefit relatives enough to outweigh the personal cost
EX: in insect colonies, workers exhibit altruistic behaviors such as sacrificing their own reproductive potential to benefit closely related individuals like the queen

Imprinting
behavior that includes a specific critical period learning and innate components and is generally irreversible
EX: newborn ducklings instinctively follow and bond with the first moving object they see, often their mother
Inclusive Fitness
individual's overall genetic contribution to the next generation, including not only its own offspring but also the offspring that its relatives produce as a result of shared genes
EX: bird that foregoes its own reproductive opportunities to help raise its siblings. Although the bird may not directly pass on its genes through its own offspring, it increases the likelihood of those shared genes being passed on by aiding in the survival and reproduction of its relatives. This behavior enhances the bird's inclusive fitness by contributing to the success of genetic relatives
Innate Behavior
developmentally fixed and under strong genetic influence/inborn
EX: the moment they hatch, some birds instinctively know how to construct nests using materials found in their environment, following specific patterns and techniques characteristic of their species
Kin Selection
occurs when an animal engages in self-sacrificial behaviour that benefits the genetic fitness of its relatives
EX: squirrel detects predator coming, squirrel emits alarm to alert other squirrels but draws attention to itself
Learning
modification of a behavior based on specific experiences
Migration
a regular, long-distance change in location

Monogamous
relationship where one male mates with one female

Optimal Foraging Model
generates quantitative predictions of how animals maximize their fitness while they forage
Pheromone
odor emitted (usually in low concentrations) as a way for many animals to communicate
Polygamous
relationships where an individual of one sex mates with several individuals of the other sex

Reciprocal Altruism
reciprocal altruism is a behaviour whereby an organism acts in a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism's fitness, with the expectation that the other organism will act similarly at a later time
Sign Stimulus
external cue that is a trigger for fixed action patterns
Social Learning
learning by observing and mimicking others
Sociobiology
the systematic study of how biology affects human social behavior
Spatial Learning
more complex modification of behavior based on experience with spatial structure
EX: wasps use landmarks to locate their nest
Abiotic
physical rather than biological
Abyssal Zone
one of the levels that the ocean is divided into (~3,000 - 6,000 meters below the surface)
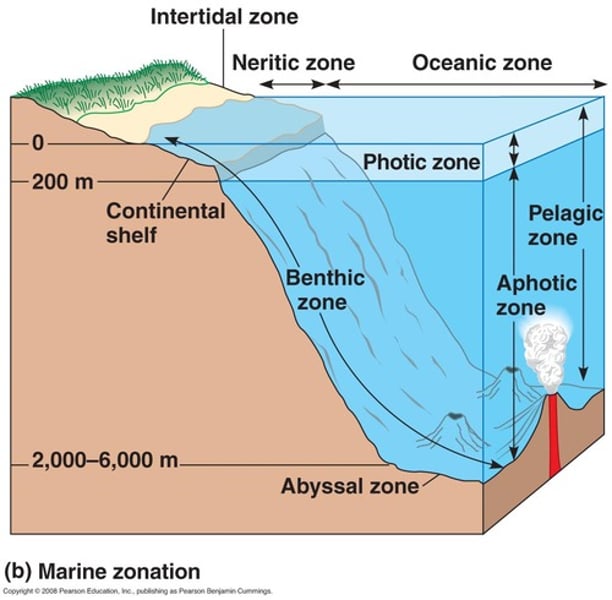
Aphotic Zone
portion of lake with little or no sunlight
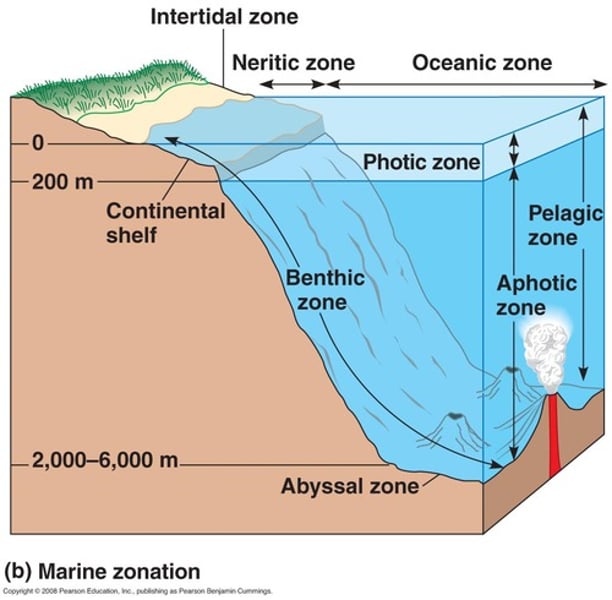
Benthic Zone
lowest ecological zone in a water body
Biome
major ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions and/or water

Biosphere
the global ecosystem, the sum of all the planet's ecosystems
Biotic
relating to or resulting from living things
Climograph
time-based graph presenting a location's average temperature & precipitation
Community Ecology
group of populations of different species in an area (including interspecific interactions, succession, and trophic strucutre)
Detritus
dead particulate organic matter
Dispersal
movement of individuals away from centers of high population
Disturbance
temporary change in environmental conditions causing pronounced change in an ecosystem
EX: drought, fire tornado, blizzard

Ecosystem
community of organisms in an area and physical factors with which those organisms interact

Ecology
scientific study of interactions between an organism and environment
Ecotome
transition area between 2 biological communities where they meet and integrate
Estuary
transition area between river and sea (salinity varies between rise and fall of tides)

Eutrophic Lake
nutrient rich, oxygen poor standing bodies of freshwater
Landscape
mosaic of connected ecosystems
Macroclimate
patterns on the global, regional, and local level
Microclimate
very fine patterns
EX: community of organisms underneath a fallen log
Photic Zone
uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight
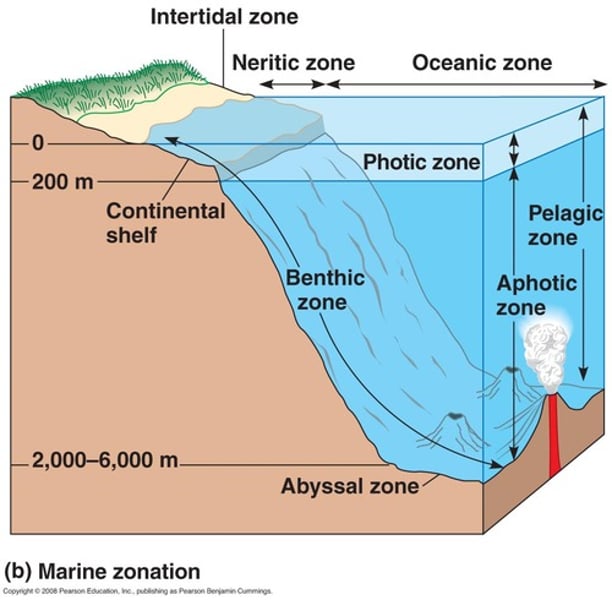
Thermocline
temperature boundary that separates warm upper layer from cold deeper water

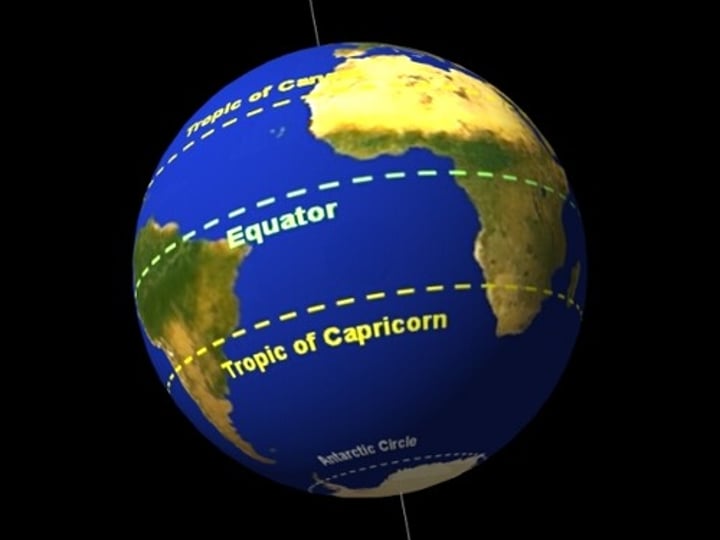
Tropics
regions of Earth surrounding the equator
Turnover
rapid mixing of lake water
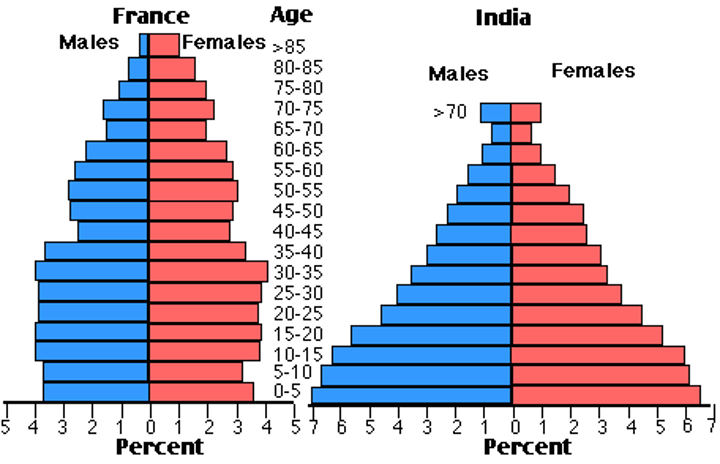
Age Structure
composition of a population in terms of proportion of individuals of different ages
Carrying Capacity
max # of individuals of a species that can exist in a habitat indefinitely without threatening other species in that habitat

Cohort
group of individuals of the same age

Demographic Transition
long term trend of declining birth and death rates, resulting in substantive change in the age distribution of a population
Demography
study of vital statistics of populations and how they change overtime
Density Dependent
linear inverse relationship between population growth rate and population density (i.e population growth decreases as density increases)
Density Independent
force that affects population size regardless of population density
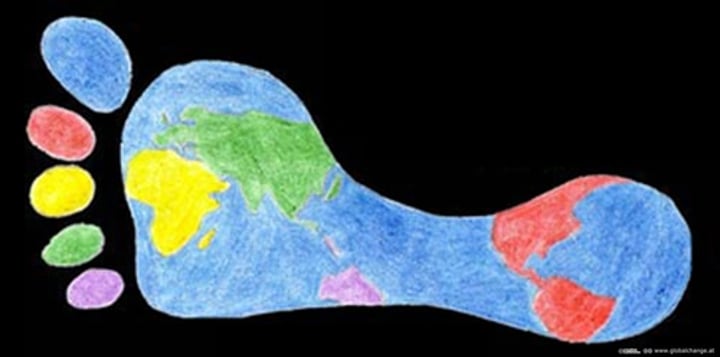
Ecological Footprint
method that determines how dependent humans are on natural resources
Ecological Niche
match of a species to a specific environmental condition
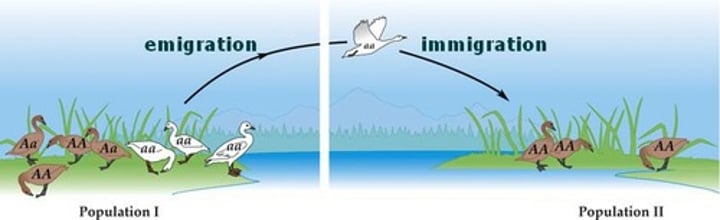
Emigration
act of leaving a habitat or place with the intent of moving to a different habitat or place
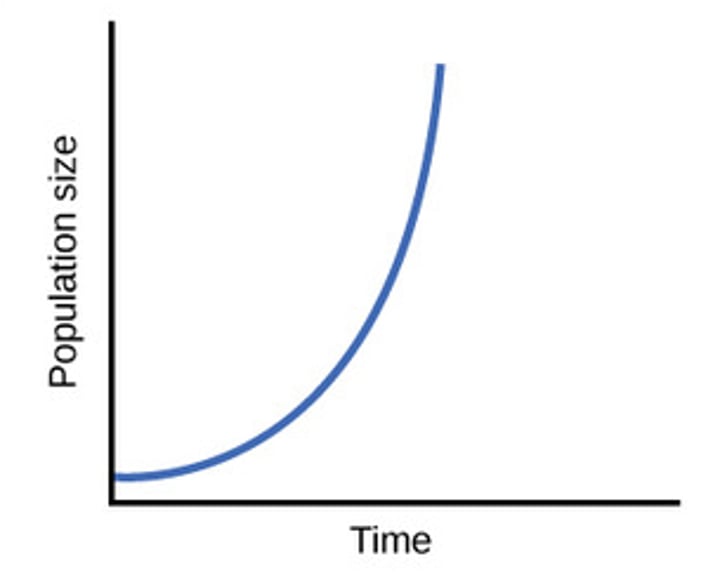
Exponential Population Growth
continuous increase/decrease in a population in which the rate of change is proportional to number of individuals at any given time
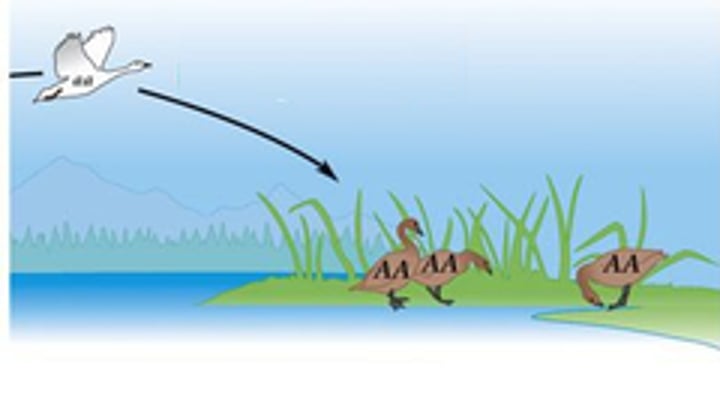
Immigration
movement of an organism to an area
Iteroparity
reproductive strategy characterized by multiple reproductive cycles over the course of a lifetime
K-Selection
reproductive strategy favoring quality over quantity, fewer offspring, higher parental care, suited for stable environments with little resources
Life History
the pattern of survival and reproduction events typical for a member of the species