the motor unit and graded muscle contractions
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 4 unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
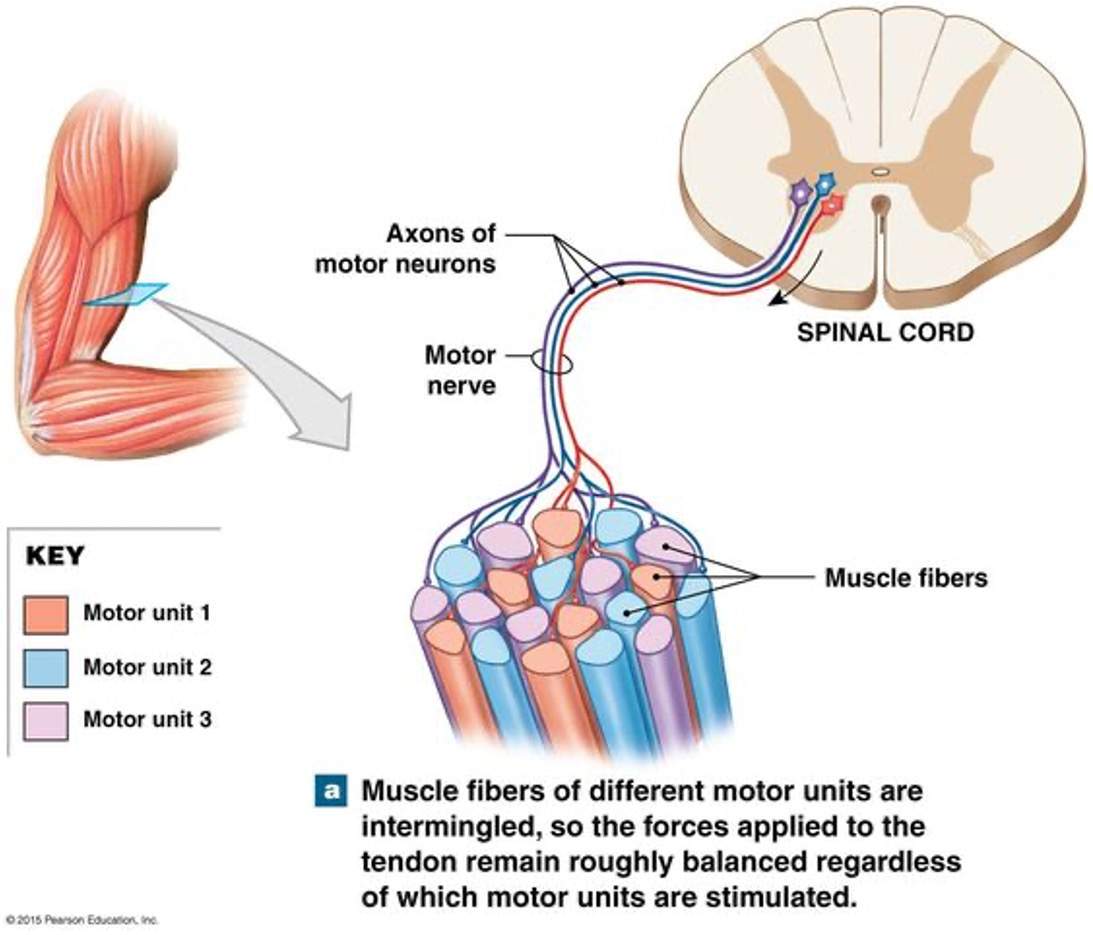
what is the motor unit
the motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates form the motor unit
action potential in neuron
in an ap is generated in one of the (purple) neurons, then an ap will be generated in all the purple skeletal muscle cells it innervates. same rule for the rest of the motor units
one ap in the motor neuron results in
one ap in all the muscle fibers it innervates
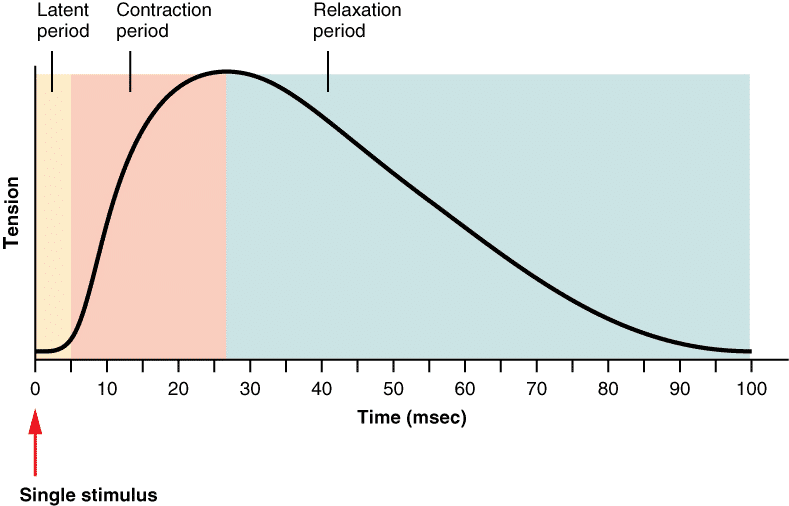
muscle twitch
a contraction in response to one ap on the motor unit
muscle twitch can be as short as 10ms or as long as 100ms
what are the periods/phases of a single muscle twitch
latent period, contraction period, and relaxation period
latent period ( muscle twitch period)
a short 1-2 msec delay from when the ap was generated in muscle cell
to when tension can be measured in the muscle
delay is due to the time it takes for calcium to be released from sr into cytoplasm
to reach and bind to troponin c, causing tropomyosin to shift and expose the myosin binding site on actin and formation of cross bridges
motor unit ordering
how our muscle move so smoothly even tho twitching is a period of contraction. the interpersed arrangement skeletal muscle cells ensures that the muscle contracts smoothly even though not all motor units contract at the same time
motor unit firing
if all motor units would contract at the same time, we would produce a jerky movement
however, the motor units fire asychronously (not firing all at the same time)
the relaxation period of one may overlap with the contraction period of another motor unit, therfore ensuring smooth movement
why is the relaxation period of the muscle twitch longer than the contraction period
relaxation period is dependant on calcium being pumped back into sr by calcium atpase at the end of contraction
rather than it does to be released from the sr, binding to troponin c, expose myosin binding site
during contraction period, calcium goes down its concentration gradient as its released from the sr.
during relaxation period, calcium is going against its concentration gradient
graded muscle contraction
the increase in muscle contraction force thru motor unit recruitment and/or summation of twitches
motor unit recruitment
as more motor units are recruited due to increase load or demand on the muscle to generate force,
more muscle fibers contract, leading to a higher contractile force
summation
as ap freq is increased, each muscle twitch cannot reach full relaxation before the next twitch occurs
as consequence, twitched start to stack up on one another, generating more force
force generated by the twitches add up on top of previous generated force, producing muscle summation
treppe
increase in ap freq increases the force of contraction in a stair like fashion referred to as treppe
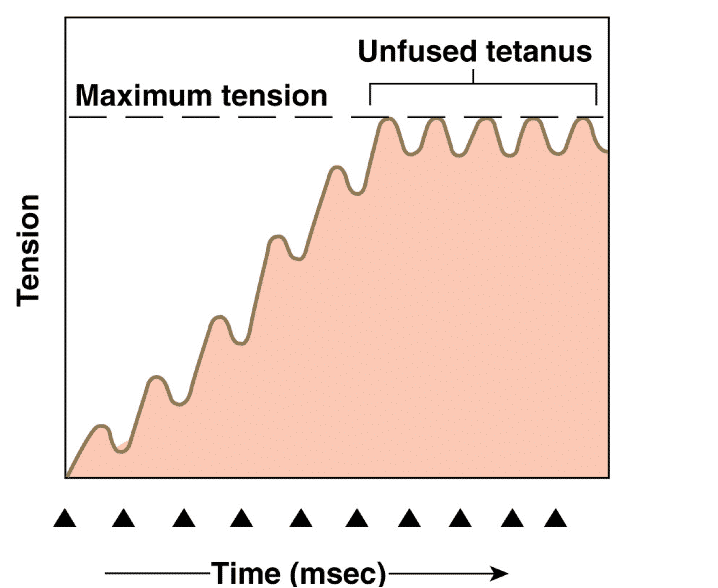
unfused tetanus
when the freq of the ap still allows for partial relaxation between twitches, the tension in the muscle plateaus
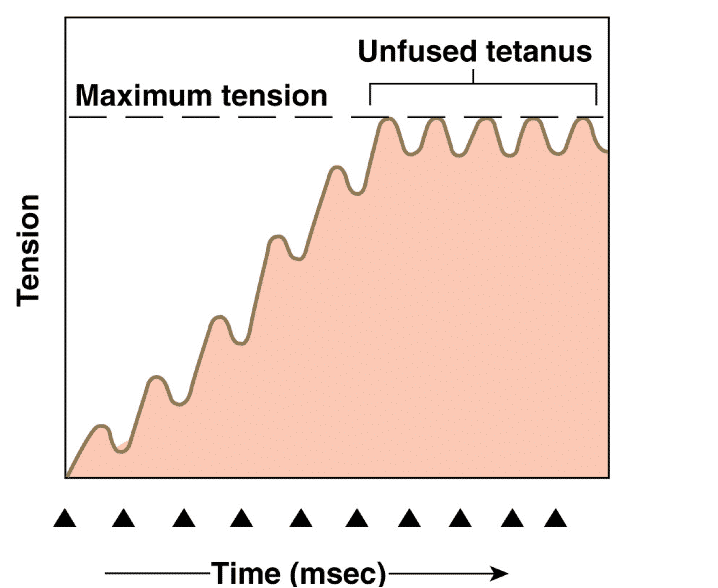
complete tetanus
when ap freq is so high that there is no relaxation between muscle twitches, the muscle is in complete tetanus. all the twitches summate to produce a smooth sustained contraction
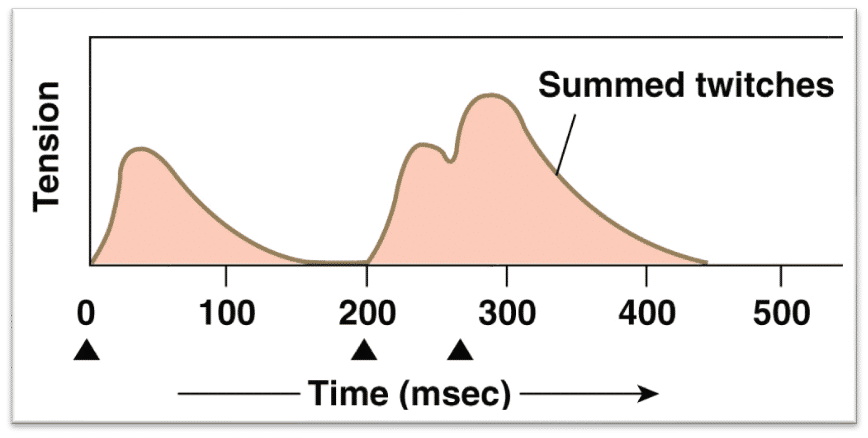
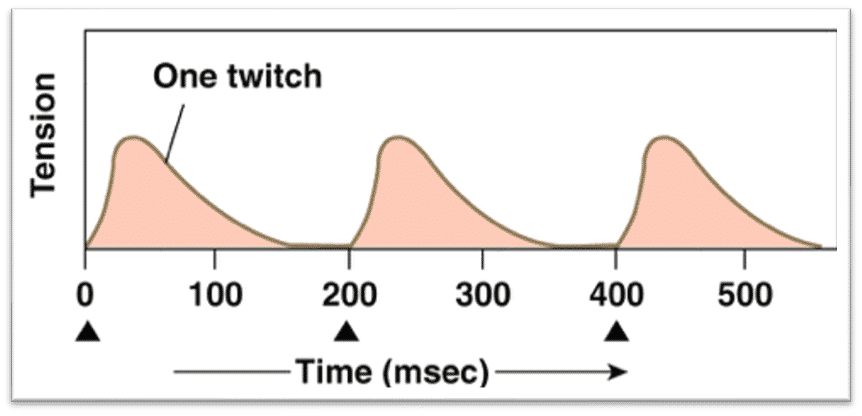
muscle twitches
each twitch occurs following an ap (black arrow). all twitches come to relaxation before next twitch starts. tension of power generated by each twitch is same
summed twitches
first twitch completely relaxes before the next twitch, following an ap.
second twitch completes contraction, but does not reach full relaxation before the third twitch begins
amplitude of the third twitch is higher than the previous ones as tension is increased due to summation
increase in ap freq= summation