PHA3003 Exam 1 Study (Reactions & enzymes)(Metabolism)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Phase 1 Reactions
Oxidative
Reductive
Hydrolytic (hydrolysis; uses H2O)(includes esterases and amidases)
Phase 1 Polar Groups
OH, COOH, NH2
Phase 1 Purpose
to add polar groups to make drug more water soluble [should decrease log P]
Aromatic Hydroxylation
an OH is added to an aromatic ring (Phase 1 Reaction)
* often occurs para (opposite) to another substituent on a ring
* often occurs on activated (O, C, N) rings... not so much on deactivated (with C=O, X, N=O, S=O)
activating groups
the following groups as a substituent on a ring
OH, OCH3, NH2, NHR, CH3, CH2CH3
(like anything that has H or C attached after it)
deactivating groups
the following groups as a substituent on a ring
F, Cl, Br, NO2, SO2NHR, COR
(anything that has a double bond attached after it, or a halogen)
Aliphatic Hydroxylation
an OH is added to an alkane (Phase 1 Reaction)
Oxidation
an OH is converted into a C=O, then a COOH (Phase 1 Reaction)(by enzyme: Oxidoreductases)
O-demethylation
an ester (R-O-CH3) looses its methyl group to become an OH, and the methyl becomes a H2C=O (Phase 1)(because the bigger drug R group got an alcohol)(Oxidation)
N-deethylation
an amine (R-NH-CH2-CH3) will loose the ethyl and result in R-NH2 and H3C-HC=O) (Phase 1)(Oxidation)
Reduction (3 types; names not specified)
a carbonyl (C=O) will become an alcohol (OH)
a nitro (NO2) will become an amine (NH2)
an AZO group (N=N) will become amines (NH2 and NH2)
(Phase 1)(notice how double bonds are broken and replaced with H's, not O's)
Phase II Purpose
combination type reactions (A + B = AB); can either attach more polar groups... OR lower/terminate biological activity [can result in higher or lower Log P]
Phase II Reactions
- Glucuronic Acid Conjugation
- Sulfate Conjugation (Sulfation)
- Amino Acid Conjugation
- Methylation
- Acetylation
- Glutathione Conjugation (GSH)
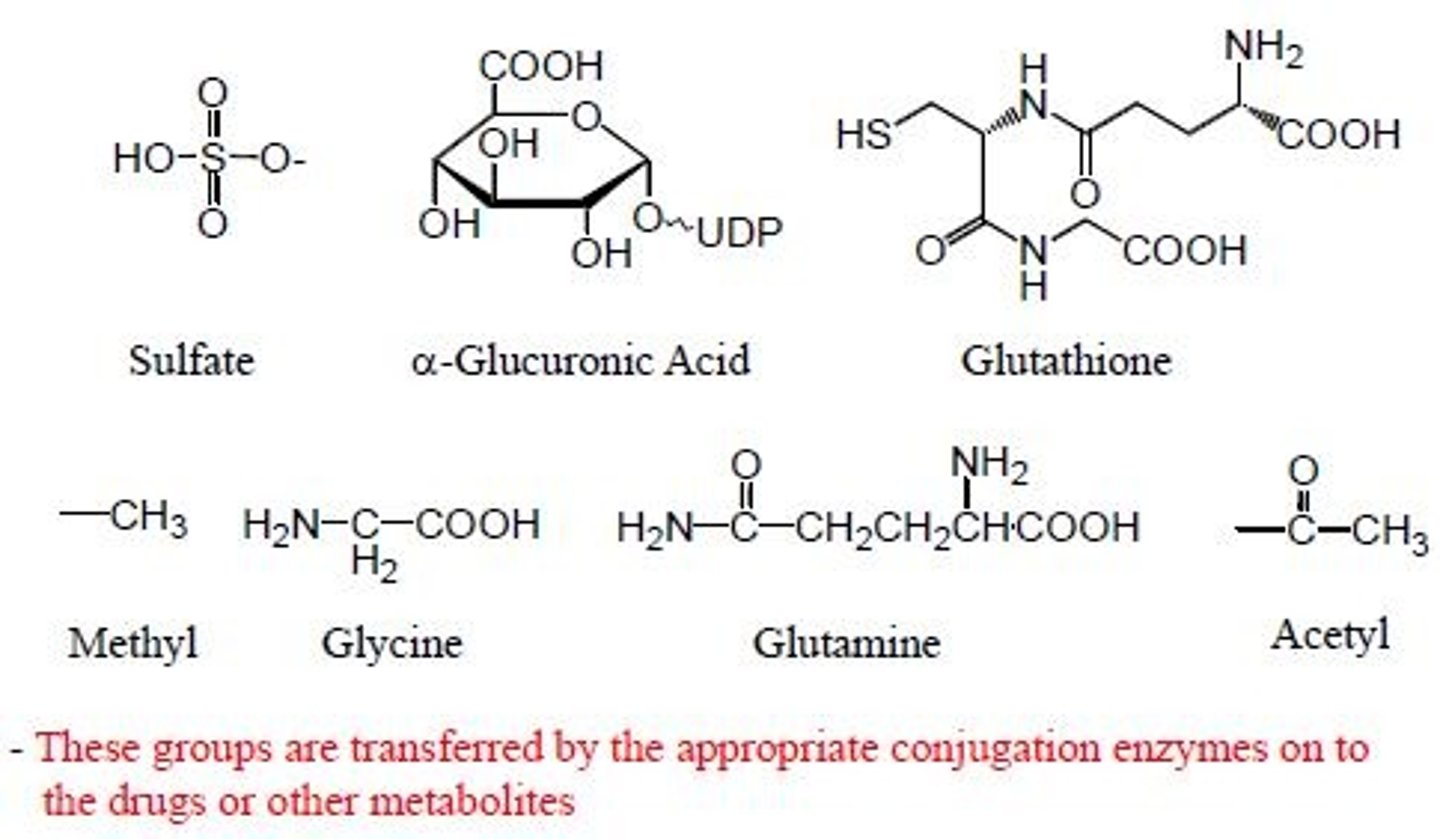
Phase II groups
sulfates, alpha glucuronic acid, glutathione, methyl, glycine, glutamine, acetyl
reacting with
phenol, COOH, OH, NH2, amides, sulfonamides, SH, amines, C-
Glucuronic Acid Conjugation
A phase I metabolite (such as a R-COOH or R-OH) will react with UDP- alpha glucuronic acid to form a beta glucuronide by an ETHER or ESTER bond (the R-COOH will replace the UDP group) by the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase (UGT)
(Phase II)(more aqueous soluble)
Sulfate Conjugation (Sulfation)
a phase I metabolite (such as phenol) is reacted with PAP-SO4H to form phenol-SO4H (the OH is replaced by SO4H)
an R-NH2 is reacted with PAP-SO4H to form R-NH-SO3H
(Phase II)
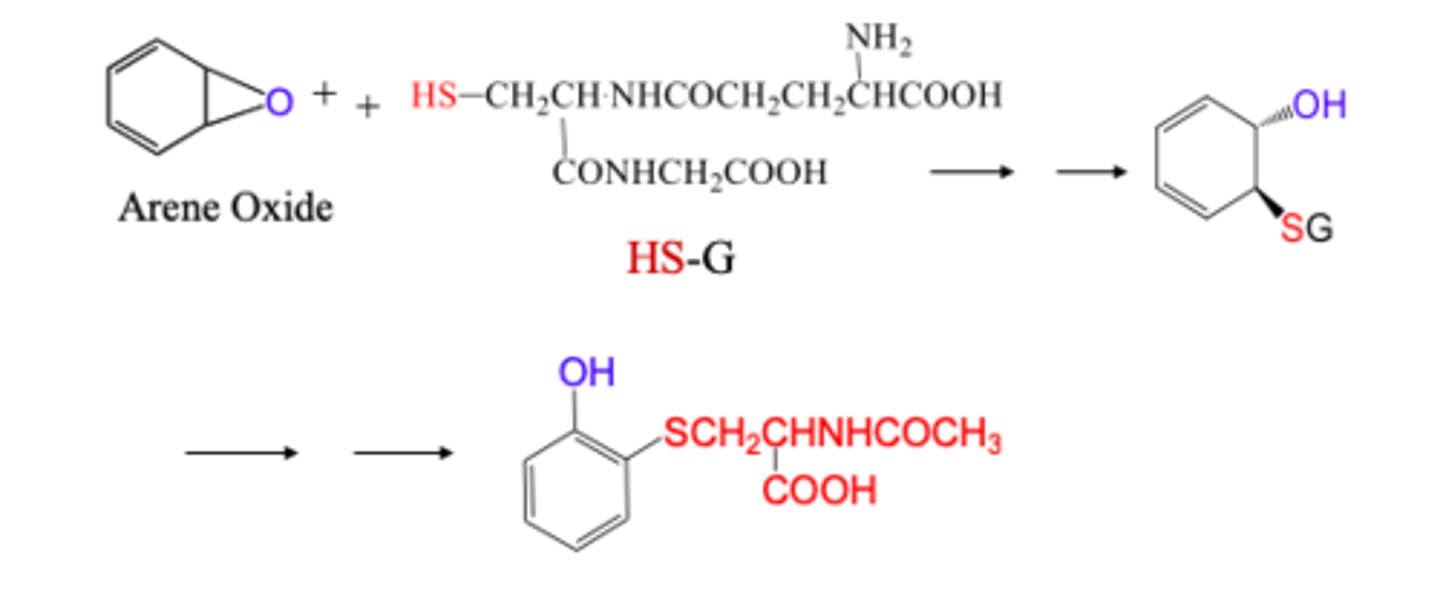
Glutathione Conjugation (GSH)
* this serves as a protective mechanism against electrophilic species
A C-X will become C-SG. (G is glutathione)
ALSO:
An arene oxide / epoxide will react with glutathione (a tripeptide of Gly-Cys-Glu) so break the epoxide into an OH and an S-glutathione)
in other words, the arene that has an epoxide ester will break into two separate attachments, an OH on one side of the original epoxide, and a thioester bond on the other where S connects to the arene and to the glutathione (Phase II)(more aqueous soluble)
Amino Acid Conjugation
an R1-COOH will react with an amino acid (H2N-CH(R2)-COOH) to make R1-(C=O)-NH-CH(R2)-COOH)
in other words, the COOH metabolite will attach to the NH2 on the amino group (like a polypeptide bond) to make an amide
(Phase II)(uses an N-acyl transferase to put amino acid onto the carbonyl)
Methylation
an R-OH will react with O-methylation and COMT to become R-O-CH3
(Phase II)(terminate activity)(increases lipid solubility)(inactivation)
Acetylation
an R-NH2 will react with N-acetylation and an acyl group to form R-NH-acyl (an amide!) (where the acyl is (C=O)CH3)
(Phase II)(terminate activity)(increases lipid solubility)(inactivation)
N-transferase
enzyme that will transfer an N
O-transferase
enzyme that will transfer an O
(ex: an O-methyltransferase will replace OH with OCH3)
S-transferase
enzyme that will transfer an S
(ex: glutathione s-transferase will convert an R-OH into an R-S-glutathione)
N-acetyltransferase
enzyme that will turn an amine into an amide by adding the H3C-C=O from acetyl CoA (H3C-C(=O)-S-CoA) to the N
NADPH
a coenzyme used in reactions that include enzymes such as oxygenase
it will accept & deliver electrons (2 e)
in oxidation, NADPH becomes NADP+
Cytochrome P-450
an enzyme that is responsible for transferring an O to the Substrate (this is oxidation)(they are primarily phase 1 enzymes)
COMT (catechol-o-methyl-transferase)
enzyme responsible for the degradation (or the removal of one of the OH groups into a OCH3) of catecholamines (like dopamine, epinephrines)
Olefinic Oxidation
a C=C in a conjugated ring will form into alcohols (oxidative biotransformation)
Benzylic Carbon Oxidation
the benzylic carbon gets turned into COOH (oxidative biotransformation)
Allylic Carbon Oxidation
the allylic carbon (the carbon once removed from a double bond, such as the first C in CH3-C=C) gets an OH group (oxidative biotransformation)
Oxidation of Carbon Atom alpha to C=N
the carbon once removed form a C=N bond (the carbon once removed from the double bond, such as the first C in CH3-N=C) will become an alcohol (oxidative biotransformation)
Alicyclic Hydroxylation
the H of a cyclohexane will become an OH (oxidative biotransformation)
Oxidative N-Dealkylation
the alkyl groups on the N will be removed to become NH2 (smaller R groups are removed first) (oxidative biotransformation)
N-Oxidation (direct)
a tertiary N will become quaternary (+ charged) due to the addition of an O- to the N (oxidative biotransformation)
Oxidative Deamination
the C on a C-NH2 will become oxidated to a carbonyl, losing the NH2 (oxidative biotransformation)
O-Dealkylation
an ester will split into an OH and O=C (oxidative biotransformation)
S-Dealkylation
a thioester (R-S-R) will become a SH (oxidative biotransformation)
Desulfuration
a S=C bond will become O=C (oxidative biotransformation)
Oxidation of Sulfur (direct)
a thioester (R-S-R) will become a S=O
(differs from S-dealkylation where thioester becomes SH) (oxidative biotransformation)
aromatization
a C=O on a non aromatic cyclic molecule will become a C-OH and the ring will become aromatized; its a form of oxidation (oxidative biotransformation)
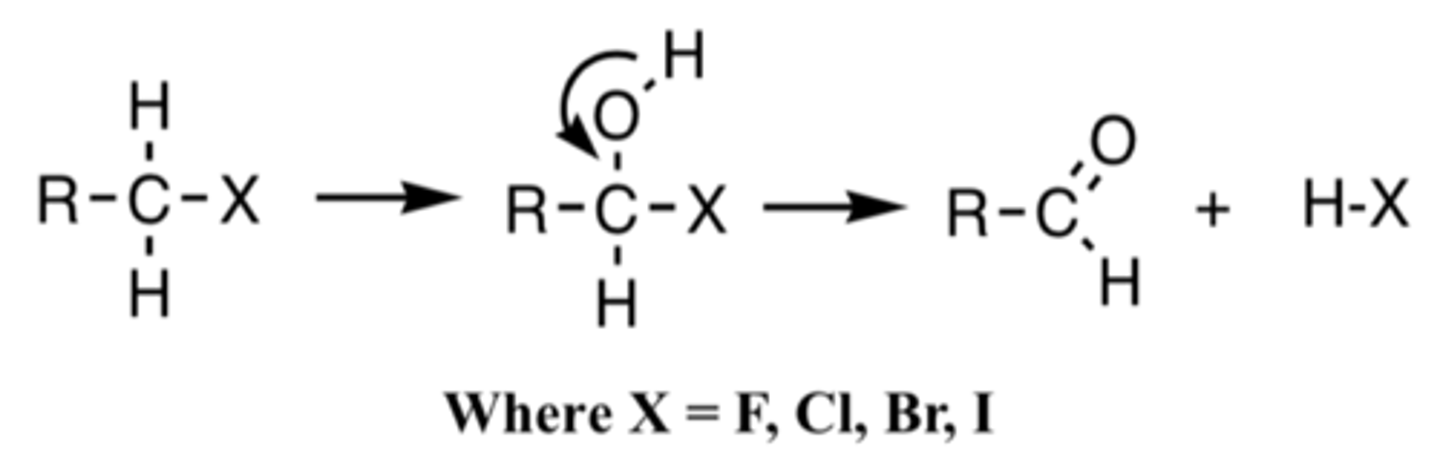
Dehalogenation
a C-X will loose the X and form a carbonyl C=O; its a form of oxidation (oxidative biotransformation)
Aldo-Keto Reductases (with NADPH)
an enzyme that will turn C=O into a C-OH (a reductive biotransformation)(Phase I)(Reduction)
Nitro reductase
an enzyme that will turn an NO2 into an NH3 (a reductive biotransformation)(Phase 1)(Reduction)
AZO reductase
an enzyme that will turn a N=N into amides (a reductive biotransformation)(Phase 1)(Reduction)
Esterases
an enzyme that turns esters into an OH and a COOH (hydrolysis of esters)(a hydrolytic reaction)
amidases
an enzyme that turns amides into an amine and a COOH (a hydrolytic reaction)(hydrolysis of amides)
thiol (AKA mercapto)
SH
esterification
turns a carboxylic acid into an ester (by reacting with an alcohol)

deamination
removes an amine
MAO (monoamine oxidase)
will deaminate (remove NH) and replace with =O (oxidation)(phase I)
what reactions use NADPH as a coenzyme
look in book