Chap11 - Moral Hazard
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
moral hazard
tendency for insurance against loss to reduce incentives to prevent and minimize the cost of loss
(carelessness, fraud)
moral hazard with health insurance
insured people take risks with health that uninsured people would not take, and demand more expensive treatment from their doctors when they get sick
downside of health insurance
moral hazard, because it raises society’s level of healthcare expenditures
social loss
riskier behaviour creates a _____ because the costly event X occurs more than it would have without insurance.
Ex Ante moral hazard
behaviour changes that occur BEFORE an insured event happens and make that event more likely (such as leaving stove on)
Ex post moral hazard
behaviour changes that occur AFTER an insured event happens and make recovering from that event more expensive (knee replacement surgery instead of painkillers)
social loss caused by moral hazard
Price-consumption graph. Point A is socially efficient equilibrium, Point B is outcome with insurance. things between Qu and Qi result in more costs than they are worth
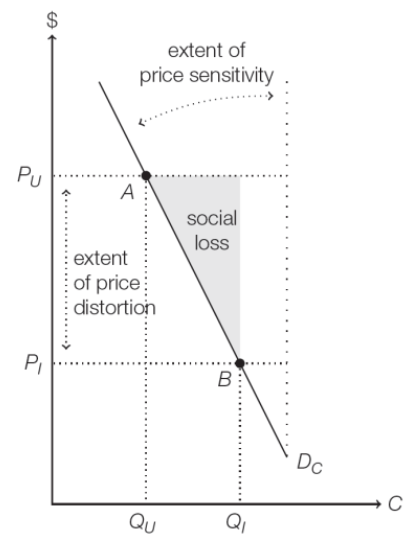
extent of price distortion
on price-consumption graph (PQ), the vertical distance between Pu and Pi
extent of price sensitivity
angle between demand curve (DC) and the vertical. larger angle —> more responsive behaviour is to price distortions and the larger the social loss from moral hazard
why price distortion
exists in insurance markets bc insurance companies cannot monitor everything patients fo and price their actions accordingly
moral hazard conditions
Cost of a risky or wasteful action to an individual is reduced, usually as a consequence of insurance
Asymmetric information prevents an insurer from adequately pricing the action
That individual responds to the price distortion
by changing his behavior—either by taking
more risks or demanding more covered goods
and services.
ways to reduce price distortion
coinsurance, copayment, deductibles, monitoring
coinsurance
insurance provision in which enrolees pay a percentage of each medical bill, and insurer covers the remaining portion
copayment
insurance provision in which enrollees pay only a fixed amount, called a copay
deductibles
set minimal levels of expenses below which the insurer does not help reimburse medical expenses
ex. insured with deductible of $1000 must pay that much himself then insurance will help pay for the rest
can eliminate moral hazard
deductibles can, unless its low enough
monitoring
insurance companies try to observe/guide the preventative measures their customers take, while others choose to supervise medical care that customers receive
rand hie
people on free plan more likely to show up at the hospital with broken bones or drug abuse (ex ante)
those on free plan more likely to visit hospital (ex post)
ghana
insured households less likely to use mosquito nets, key for preventing malaria (ex ante)
seguro popular
low-income mexicans assigned to receive free insurance were less likely to get a flu shot and cancer screenings (ex ante)
standford employees
after a change that required a new 25% copay, visits to doctor declined by 24% (ex post)
germany
introducing deductibles leads to greatly decreased health expenditures (ex post)
Canada
people with prescription drug coverage visit doctor more often (ex post)
private market
navigate the tradeoff between moral hazard and uninsurance to provide the optimal contract if they are perfectly competitive
public market
non-voluntary, lacks self-corrective features that make national insurance policy both more complex and more critical
extra preventative care
beneficial effect of moral hazard, people consume less than they should
income effect
insurance makes people “richer” by making expensive surgeries or treatments unaffordable without insurance