Unit 3 - Biology
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Cell membrane
Barrier around a cell
Cell membrane function
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Chemical structure of the cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer
Simple diffusion
Transport of molecules from high to low concentrations without proteins
Facilitated diffusion
Transport of molecules with the help of transmembrane proteins
Osmosis
Facilitated diffusion of water
Isotonic
When the concentration of two solutions is the same
Hypertonic
When the concentration of one solution is greater than another
Hypotonic
When the concentration of one solution is less than another
Protein channel of osmosis
Aquaporin
Active transport
Energy-required diffusion from low to high concentrations
Endocytosis
Active transport where cells take in substances from outside the cell and enfolds it in a vesicle
Exocytosis
Active transport where cells release substances into the cell exterior
Cell specialization
Process that develops cells to perform different tasks
Cell specialization & homeostasis
Makes organs and organ systems that use individual tasks to maintain a internal environment
Hydrogen bonding
Bonds between hydrogen atom and oxygen atom of another water molecule
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
Attraction between molecules of two different substances
Solution
Mixture of a solvent and a solute
Solute
Substance being dissolved
Solvent
The liquid the solute dissolves in
Suspension
Solution where the solute hasn't dissolved in the solvent
pH scale
Measurement scale for acidity by hydrogen ion concentrations
Acid
Compound that forms hydrogen ions (H+) in solution
Base
compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH+) in solution
Biomolecule
Large organic molecule
Monomer
Small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
Polymer
Large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Carbohydrates
Short term energy storage
Lipids
Long term energy storage
Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules that help build up DNA/RNA
Proteins
Provides structure to cells and tissues
Benedict's Test
Test for reducing sugars
Iodine Test
Test for detecting the amount of starch
Biuret Test
Test for detecting the amount of proteins
Sudan IV
Test for detecting the amount of lipids
Activation Energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
Catalyst
Lowers the activation energy for a chemical reaction to speed up
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
Active Site
the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
Inhibitor
A substance that blocks the substrate
Cell
Smallest unit of life
Cell Theory
Cells are the basic unit of life, all living things are made up of cells, all cells come from other cells
Prokaryotic Cell
cell lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotic Cell
cell that has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
Nucleus
Stores genetic information and is the control center of a cell
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Ribosomes
Synthesizes proteins by linking amino acids
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membranes with ribosomes that help in protein synthesis
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesizes lipids and detoxifies certain chemicals in a cell
Golgi Apparatus
Packages proteins and lipids for transport
Vacuoles
Stores food, water, wastes, and other materials
Vesicles
Sacs made of membrane
Lysosomes
An organelle containing digestive enzymes
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments that provide structure to the cell
Microfilaments
Thin protein fibers that help with cell movement and shape
Microtubules
Protein tubes that help maintain cell shape
Chloroplast
Organelles in plant cells that perform photosynthesis
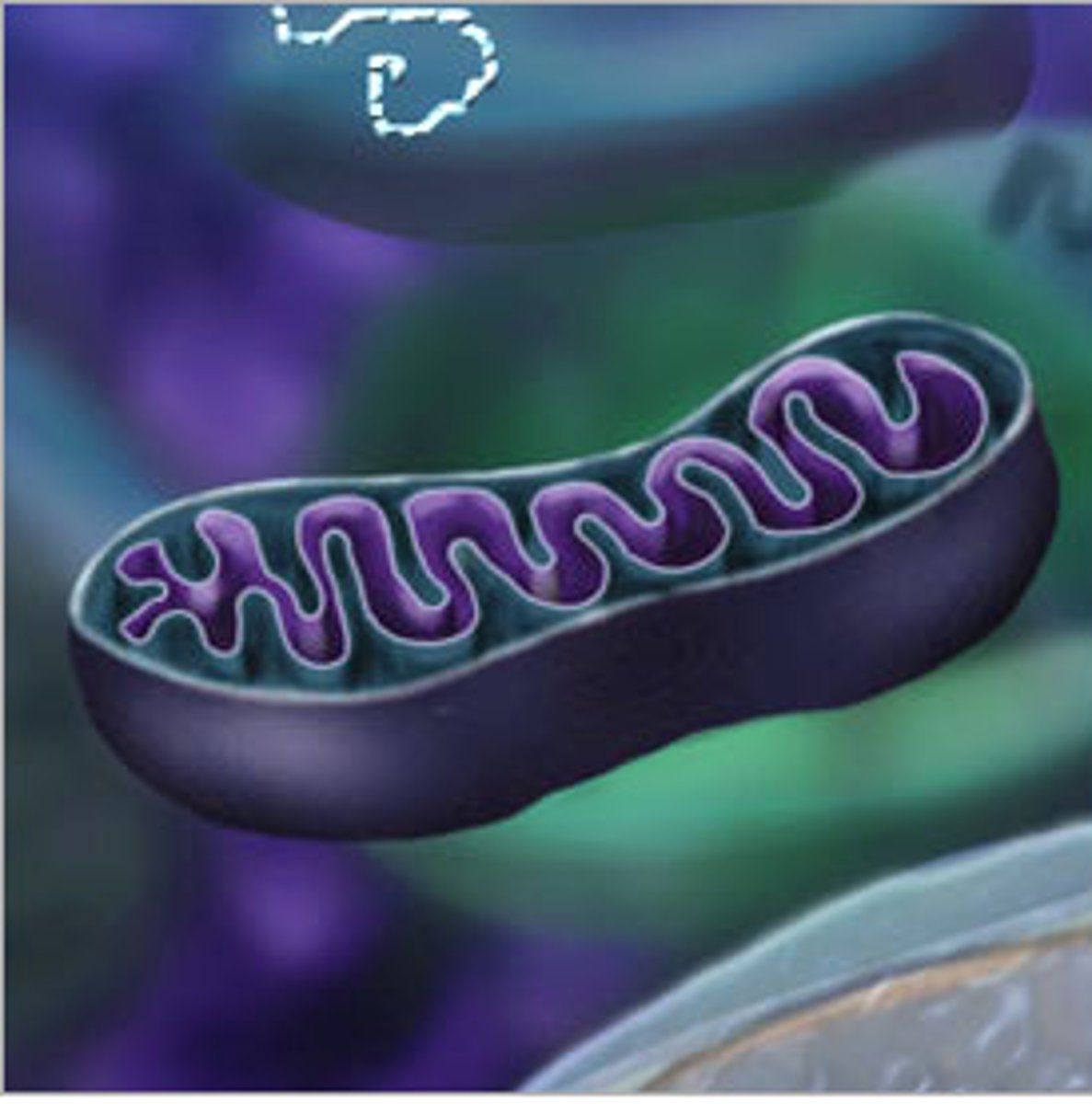
Mitochondria
Powers the cell, generates ATP through cellular respiration
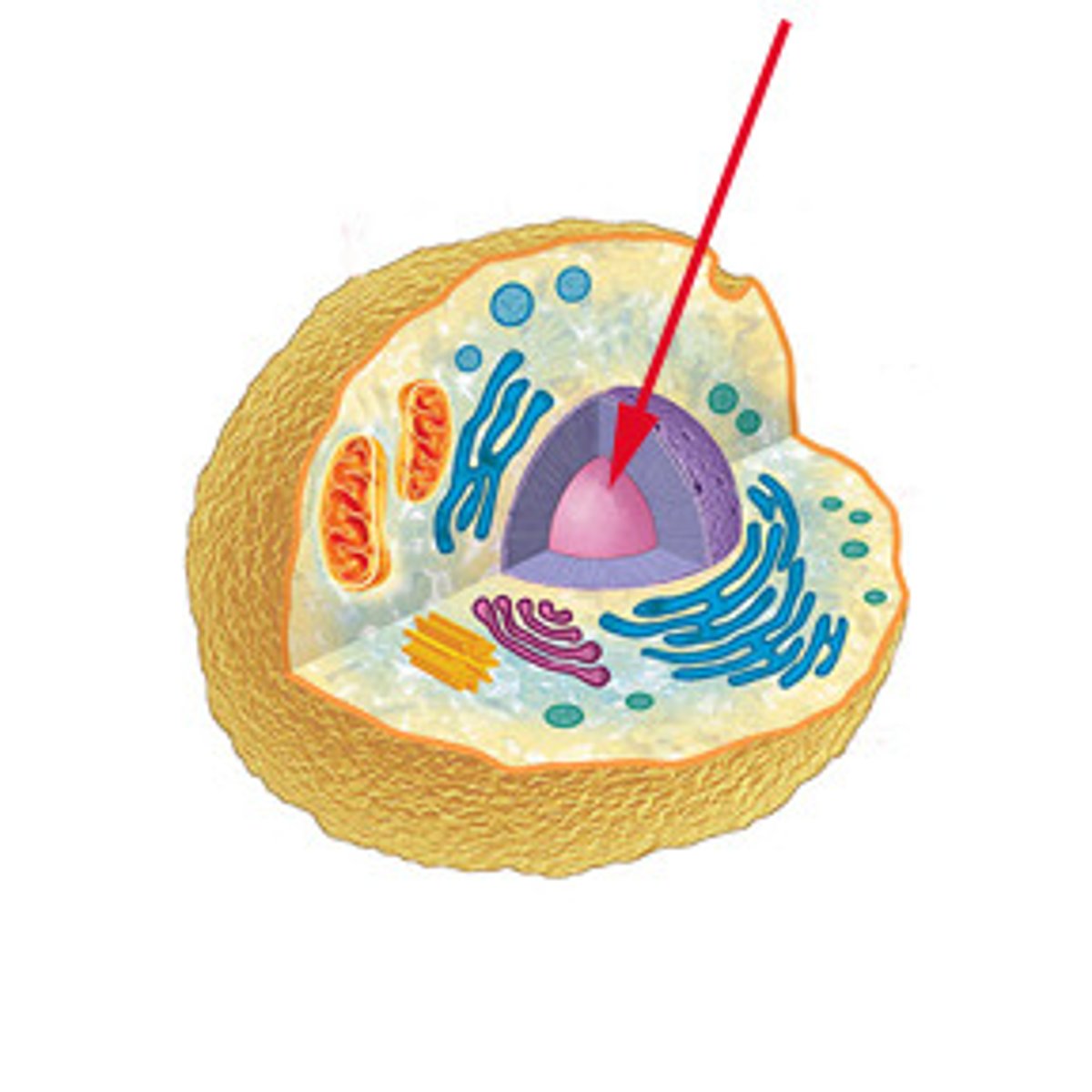
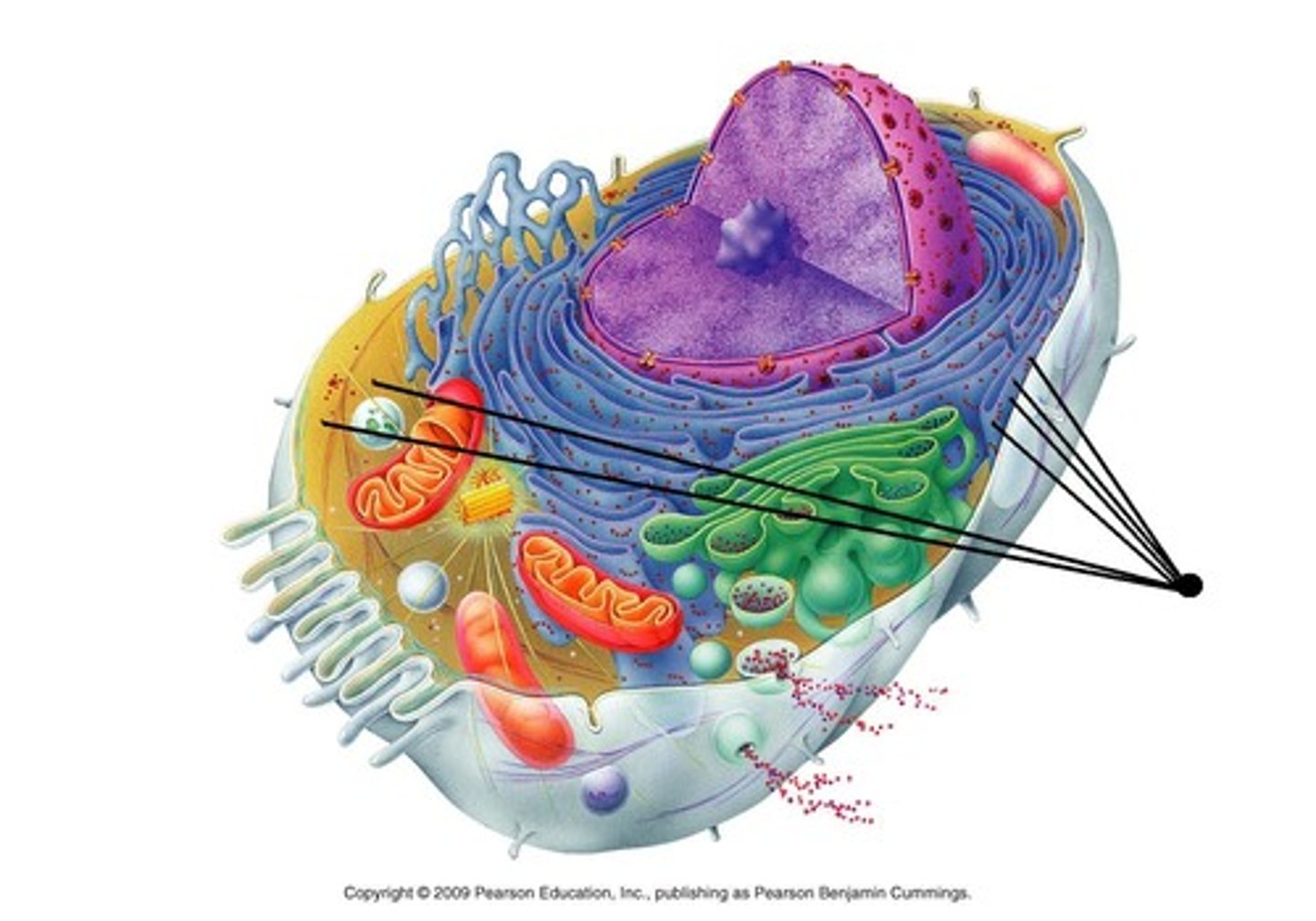
What is this?
Nucleus
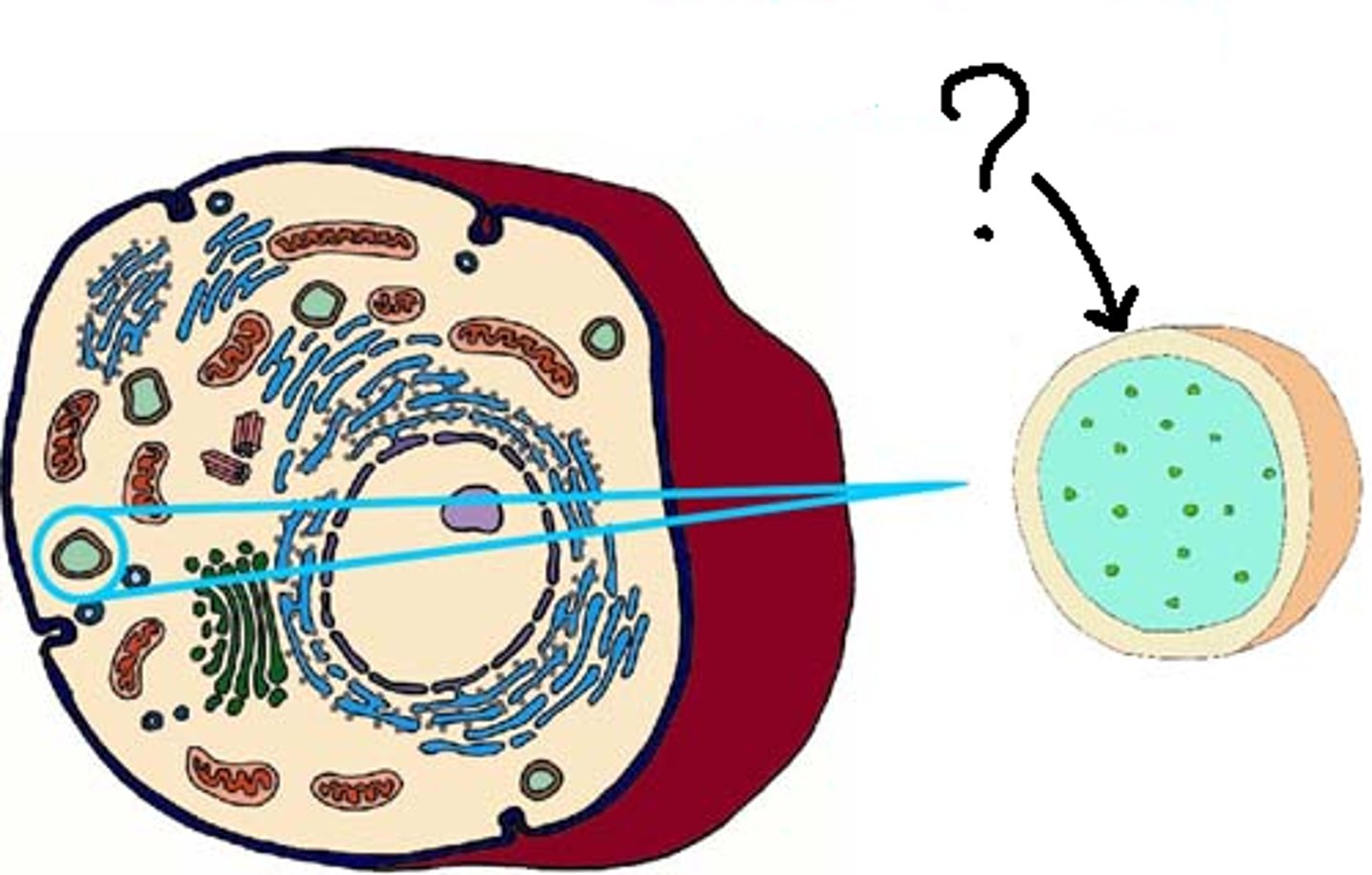
What is this?
Lysosome
What is this?
Golgi apparatus
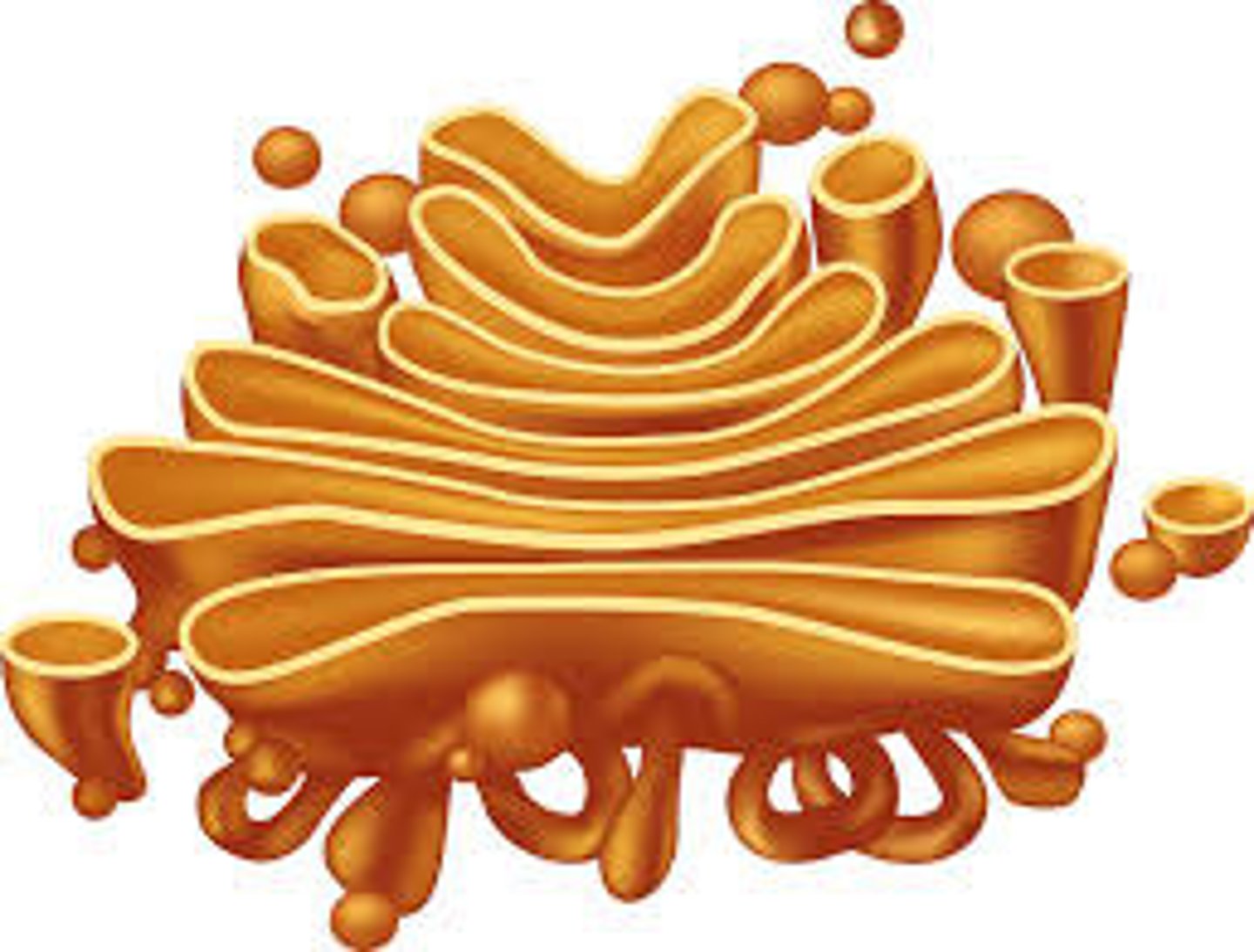

What is this?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
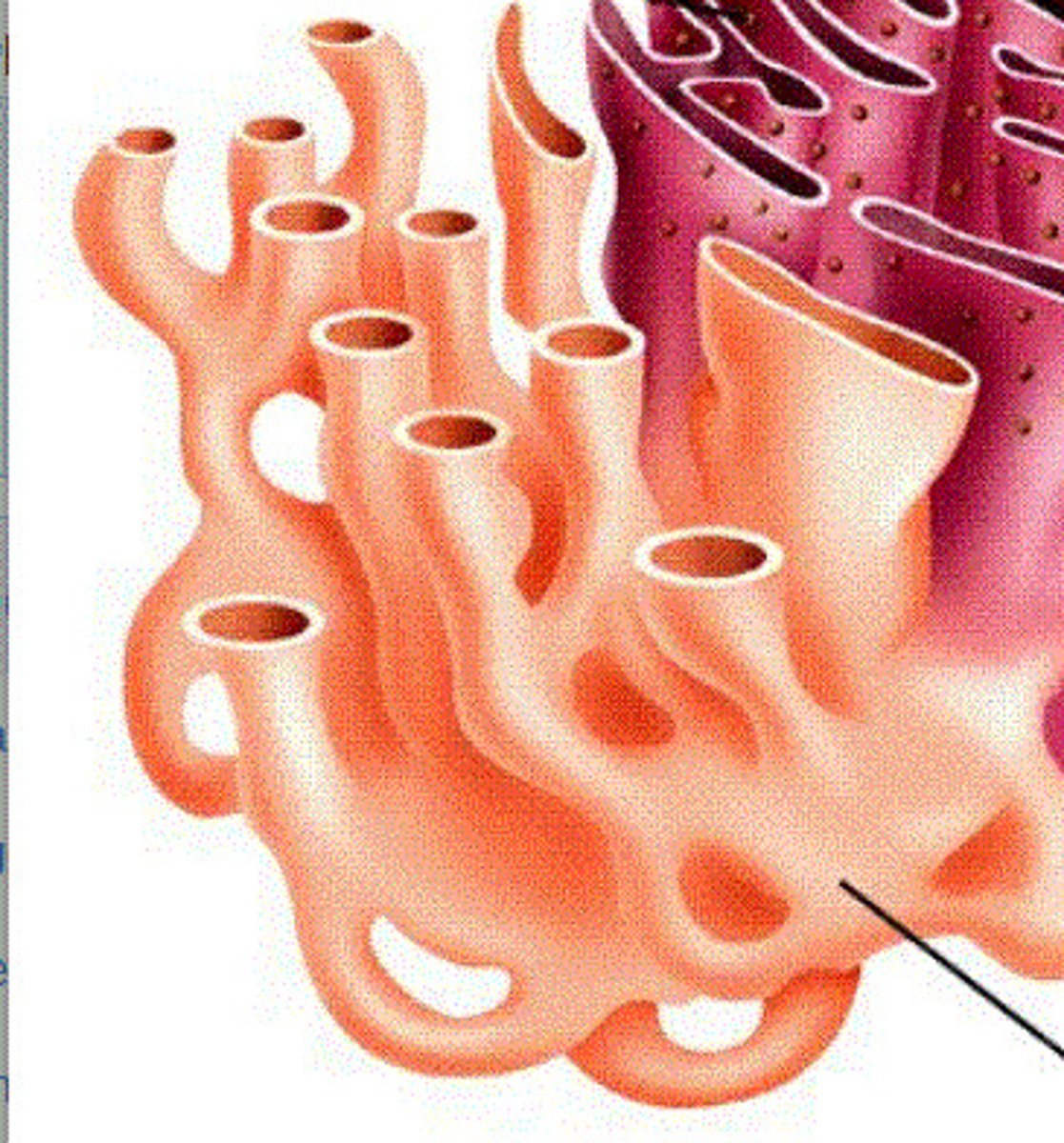
What is this?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
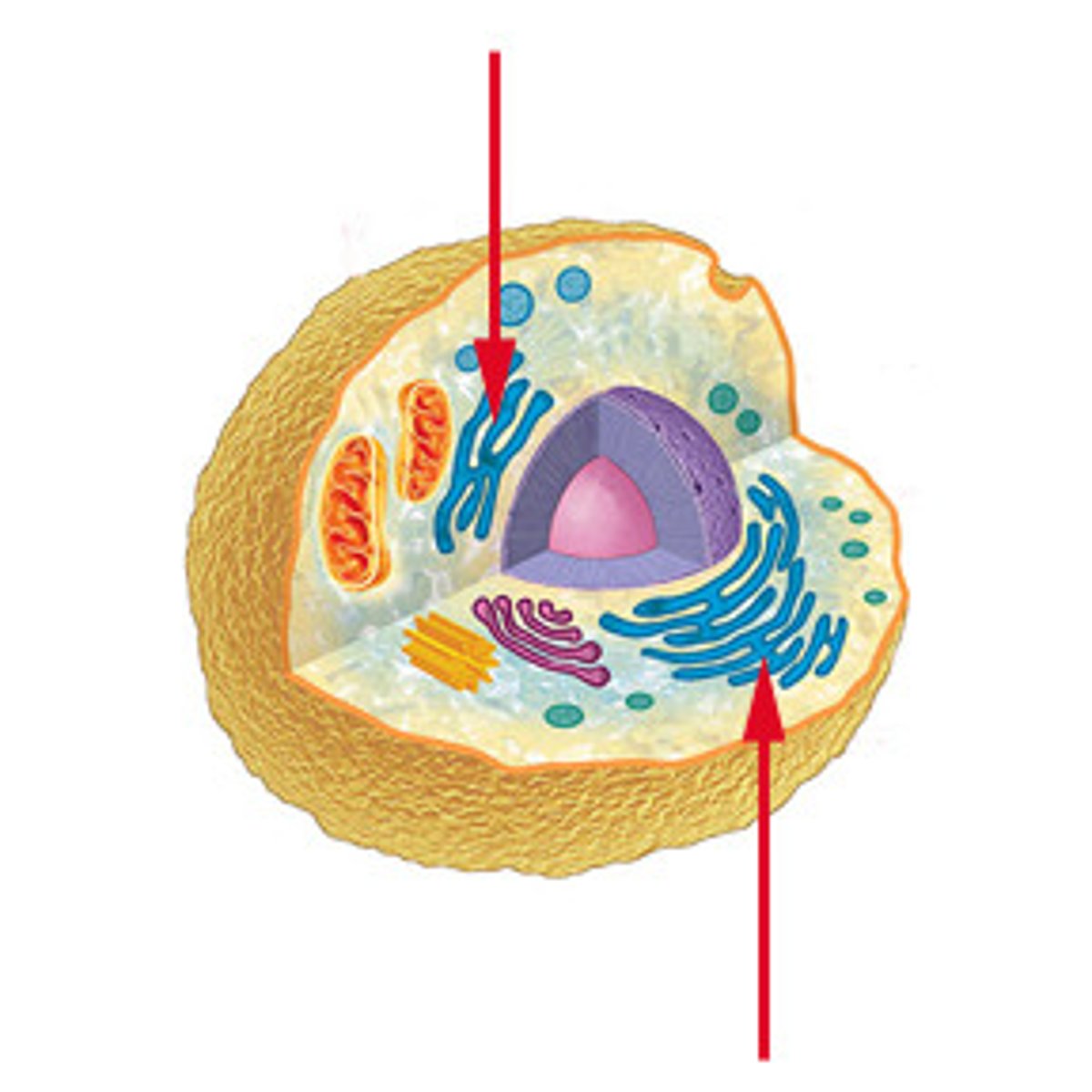
What is this?
Mitochondria
What is this?
Ribosome
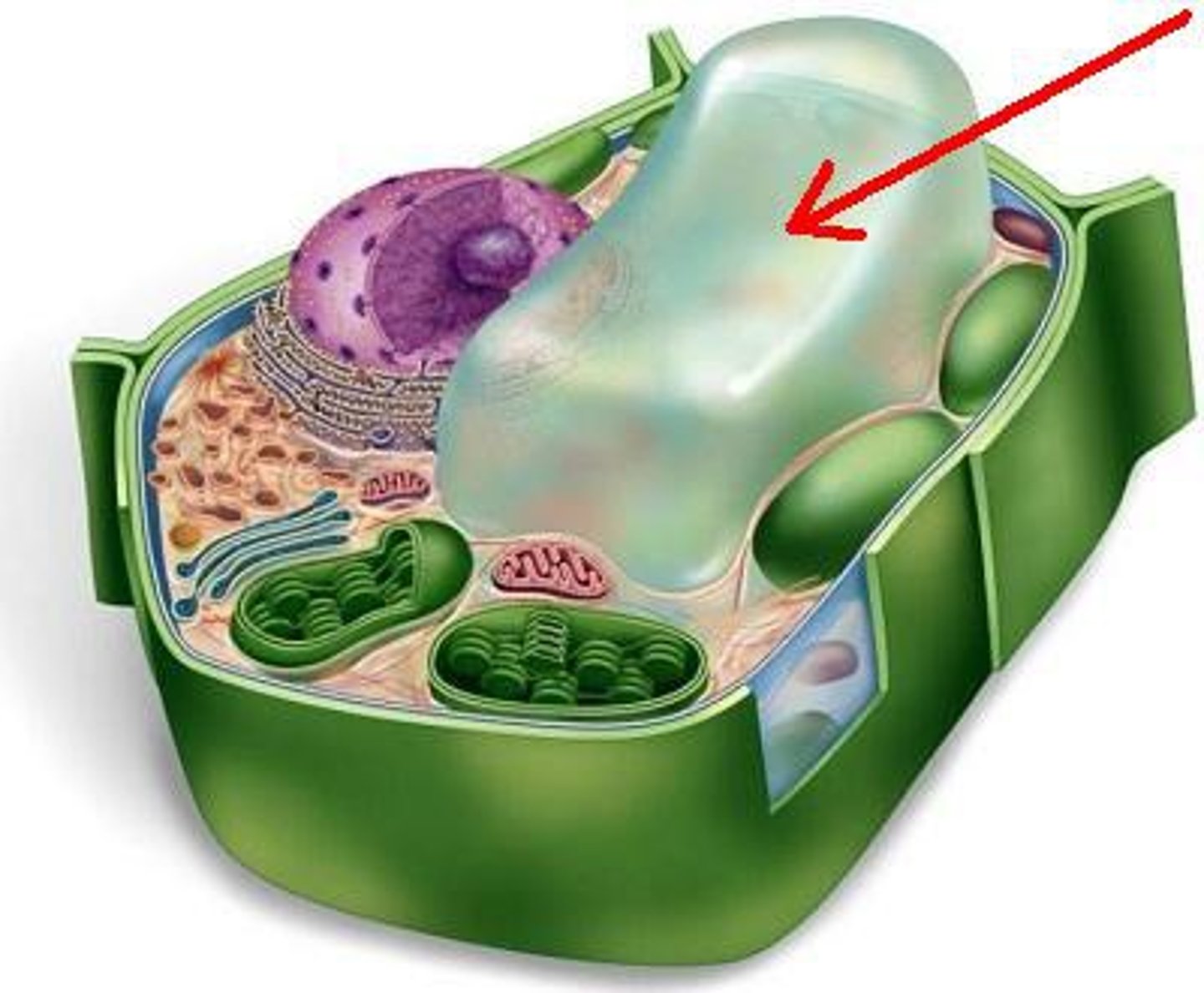
What is this?
Vacuole
What is this?
Chloroplast
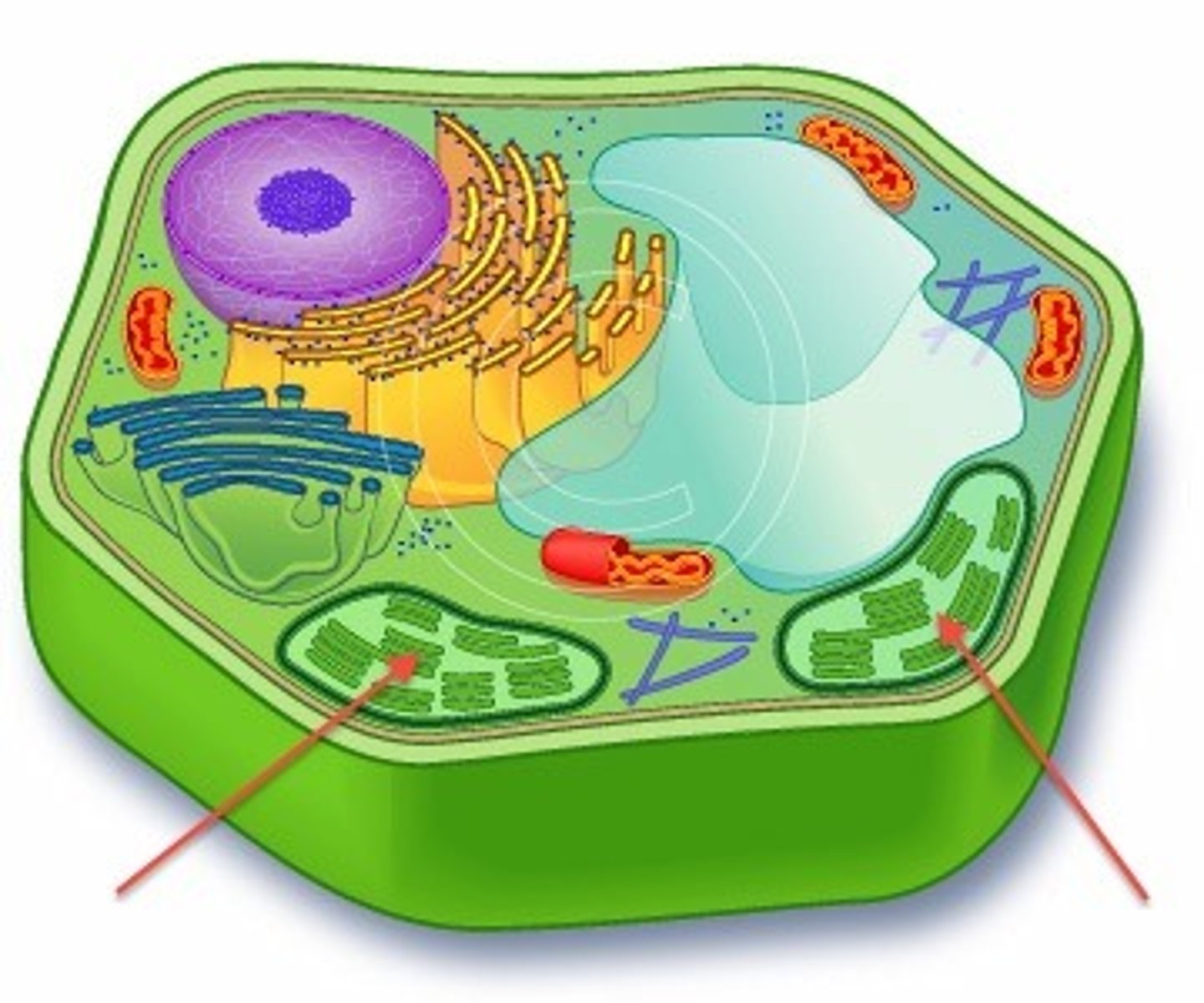
What is this?
Cell Wall
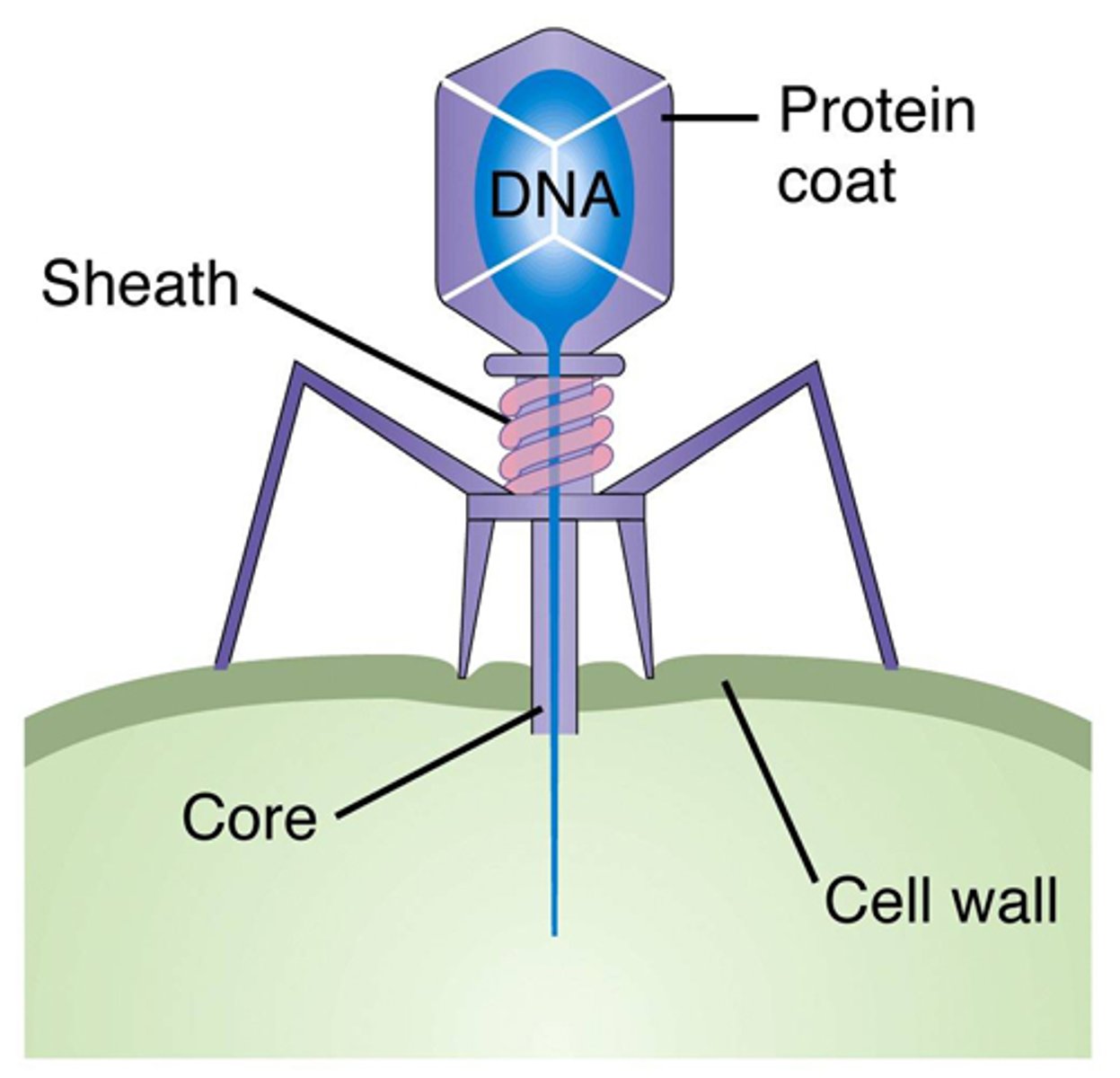
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
Fredrick Giffith
Discovered bacterial information
Oswald Avery
Proved that DNA is the genetic material of bacteria.
Erwin Chargaff
discovered that A=T and G=C
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Determined that DNA is the genetic material
Rosalind Franklin
Produced X-ray images of the DNA's helix shape
James Watson and Francis Crick
Stole Rosalind Franklin's work, made the diagram of the DNA's helix
Roles of DNA
storing, copying, and transmitting information
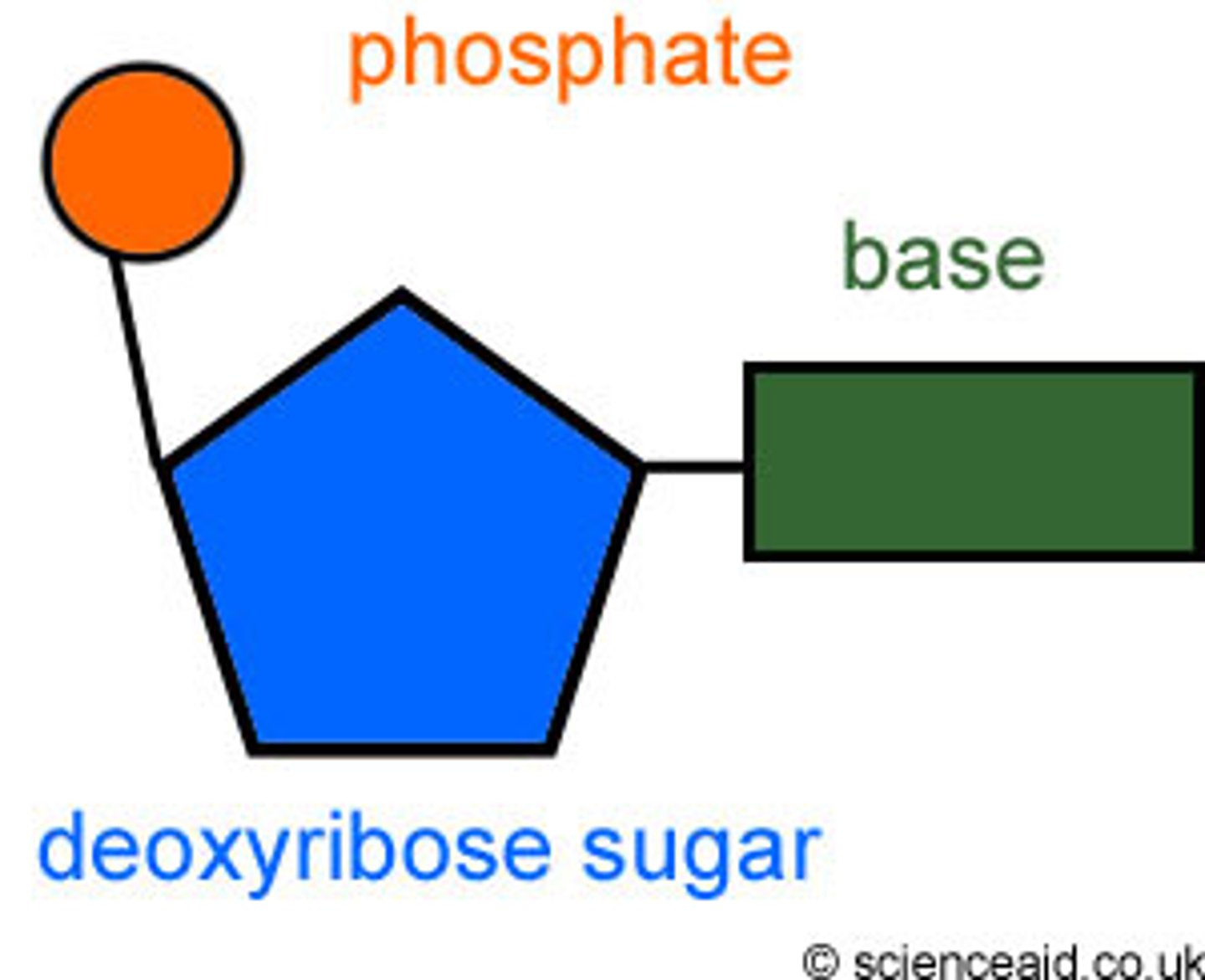
Nucleotide
Building block for DNA/RNA
Nucleotide parts
sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base