Pathology of Liver + Pancreas | Quizlet
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is fatty liver?
(hepatic lipidosis)
Excessive lipid accumulation in hepatocytes
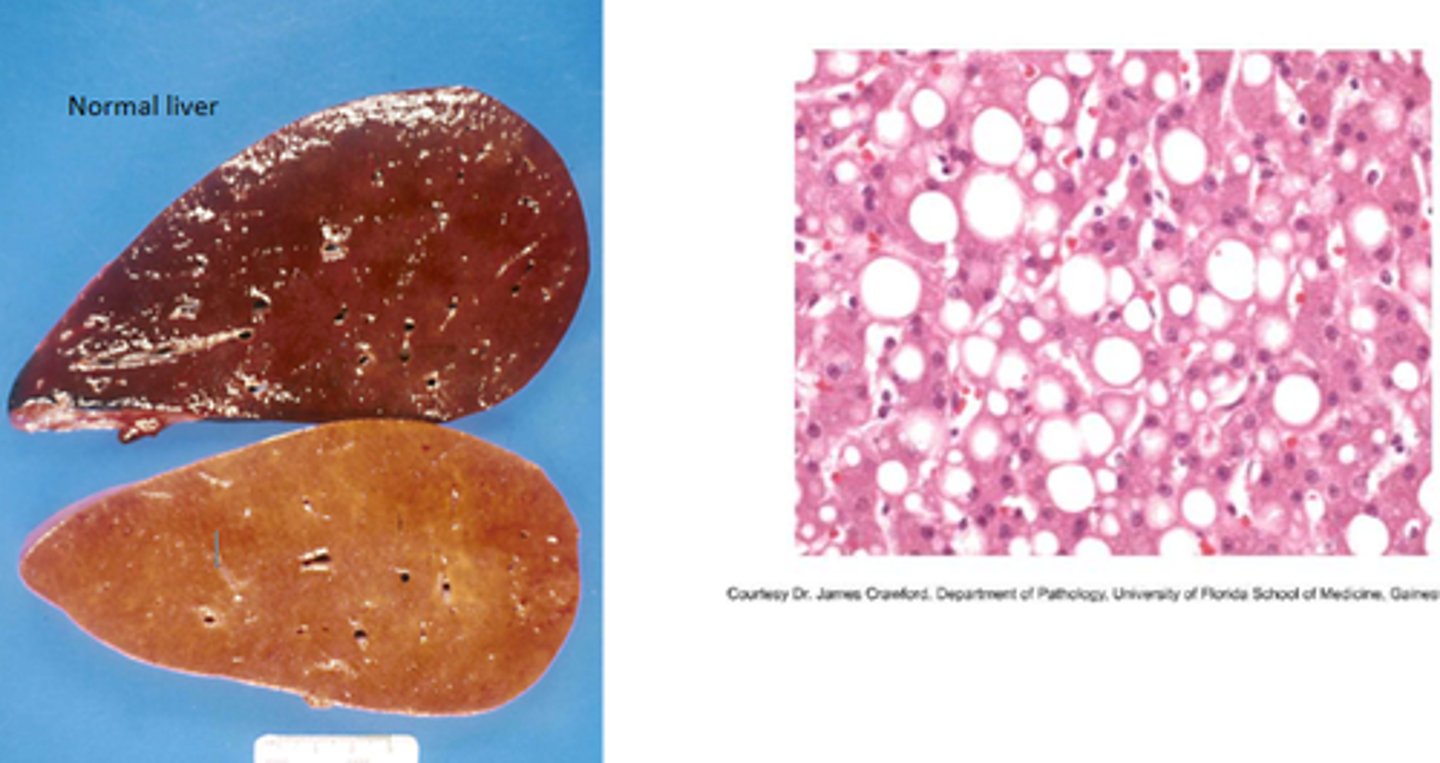
List causes of fatty liver
1. ↑ lipid uptake by hepatocytes.
2. Excessive dietary fat intake.
3. Impaired hepatocyte metabolism.
4. ↓ apoprotein synthesis.
5. Impaired lipoprotein secretion.
6. Genetic lipid metabolism defects (lipidoses).
Describe the pathomorphology of fatty liver
- Liver enlarged, yellow, greasy.
- May float in water.
- Cut surface oozes fat.
What is a nutmeg liver?
Liver with mottled red + yellow appearance due to chronic passive congestion + central lobular hypoxia
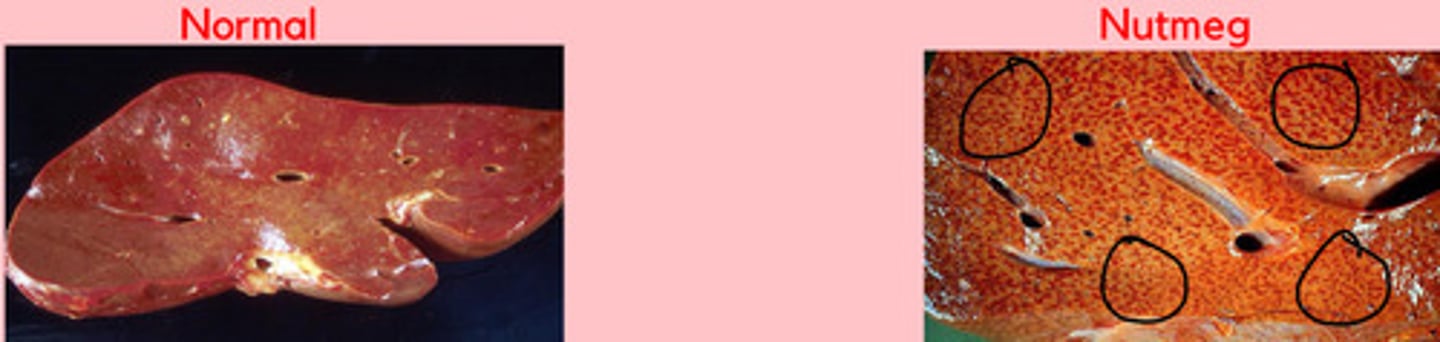
List causes of nutmeg liver
1. Chronic right-sided heart failure.
2. Chronic hepatic congestion.
Describe gross lesions of nutmeg liver
- Enlarged organ with rounded edges.
- Dark red depressed centers (central veins) + pale fatty periphery.
What is hepatic cirrhosis?
End-stage liver with fibrosis and architectural distortion forming abnormal regenerative nodules

List causes of hepatic cirrhosis
1. Chronic hepatitis.
2. Chronic toxicity.
3. Chronic passive congestion.
Describe lesions of hepatic cirrhosis
- Fibrous scar tissue replaces parenchyma.
- Regenerative nodules form within fibrosis.
- Irregular shrunken liver.
- Thickened capsule.
Describe microscopic changes in hepatic cirrhosis
- Bridging fibrosis.
- Regenerative nodules.
- Loss of normal lobular structure.
What is acute hepatic congestion?
Circulatory disturbance due to acute right heart failure
Describe lesions of acute hepatic congestion
- Enlarged, dark red liver
- Blood-filled cut surface
- Enhanced lobular pattern
What is chronic hepatic congestion?
Long-term venous stasis due to chronic right heart failure
Describe lesions of chronic hepatic congestion
- Nutmeg appearance.
- Rounded lobe edges.
- Firm texture.
- Thickened capsule.
- Common in older 🐶 with endocardiosis.
What are hepatic tumors?
Primary or metastatic neoplasms of liver parenchyma or mesenchyme
List clinical signs of hepatic tumors
- Nonspecific
- Anorexia, vomiting, lethargy
- Abdominal enlargement
- Hepatic encephalopathy
List the morphologic forms of hepatic tumors
1. Massive: single large mass in one lobe.
2. Nodular: multiple nodules in several lobes.
3. Diffuse: numerous nodules in all lobes.
List histologic types of hepatic tumors
1. Hepatocellular adenoma/adenocarcinoma
2. Cholangiocellular carcinoma
3. Mesenchymal tumors (hemangiosarcoma, fibrosarcoma)
Describe metastases to the liver
- Common from GI, pancreas, or mammary tumors.
- Multifocal pale nodules scattered throughout parenchyma.
What is acute pancreatitis?
Necrotizing and inflammatory disease of pancreas due to enzyme activation
List causes of acute pancreatitis.
1. Duct obstruction (calculi, parasites).
2. Acinar cell injury (mycotoxins, zinc toxicosis).
3. Disturbed enzyme trafficking.
4. Trauma (e.g. road accidents).
Describe the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.
- Activated pancreatic enzymes digest parenchyma (autodigestion).
- Enzymes destroy tissue, fat, + vessels causing necrosis and hemorrhage.
Describe gross lesions of acute pancreatitis.
- Edematous or hemorrhagic pancreas.
- Bloody peritoneal fluid.
- Fibrinous peritonitis with adhesions.
- In severe cases: DIC, vascular injury, shock.
What is chronic pancreatitis?
Long-standing inflammation causing fibrosis + atrophy of pancreatic tissue
List causes of chronic pancreatitis.
1. Recurrent acute pancreatitis.
2. Duct obstruction.
3. Zinc toxicosis (🐱).
4. Parasitic migration or bacterial infection (🐴).
Describe gross lesions of chronic pancreatitis.
- Shrunken nodular pancreas.
- Fibrosis + distortion.
- Firm adhesions to surrounding tissue.
Describe microscopic lesions of chronic pancreatitis.
- Fibrosis replacing acini.
- Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
- Atrophy of exocrine tissue.
- Possible endocrine islet hyperplasia.