Stage 1 SACE Biology Topic 3
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
cardiovascular
- body system that consist of the heart,blood vessels, and blood
- also called circulatory system
heart
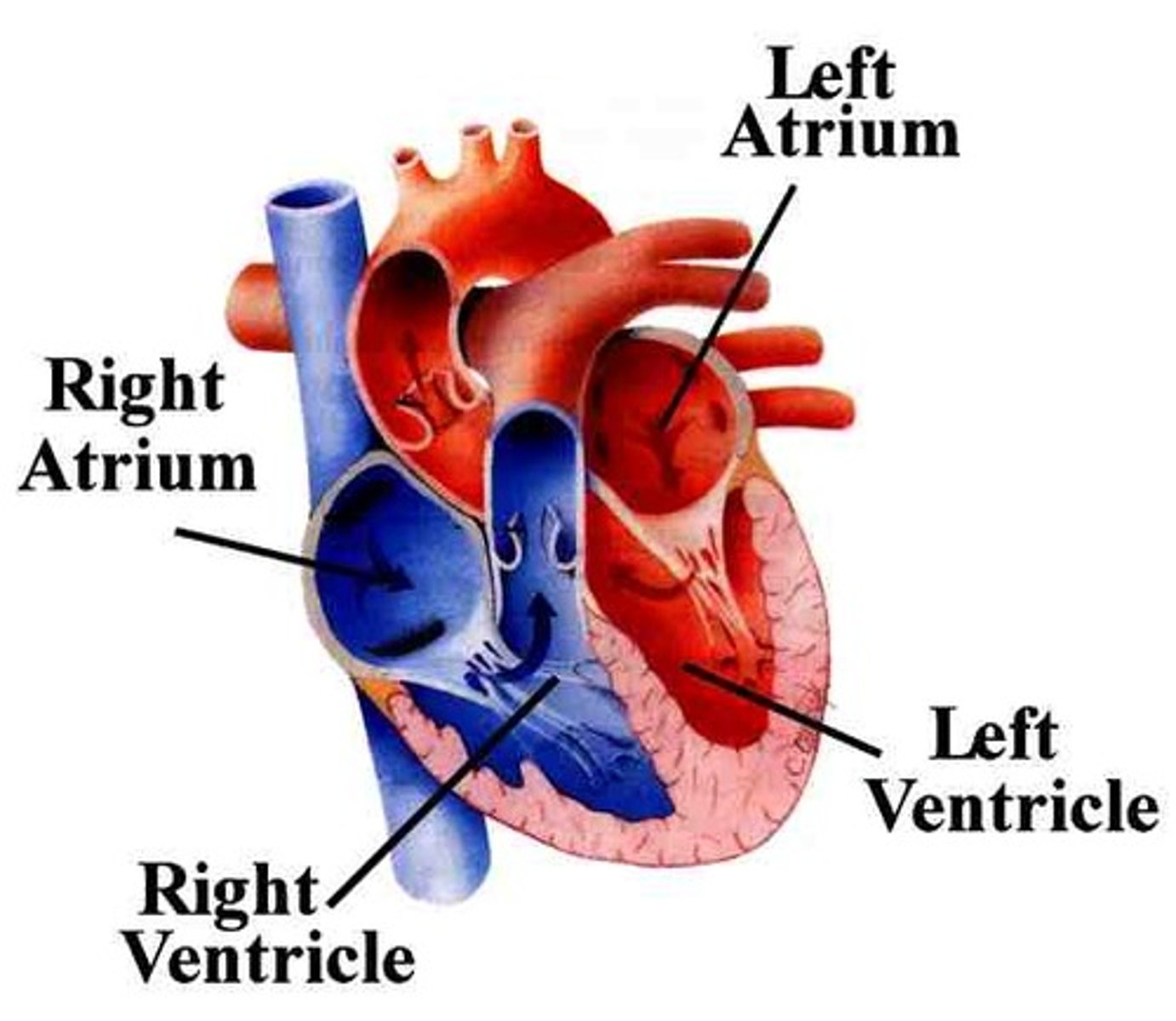
a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body
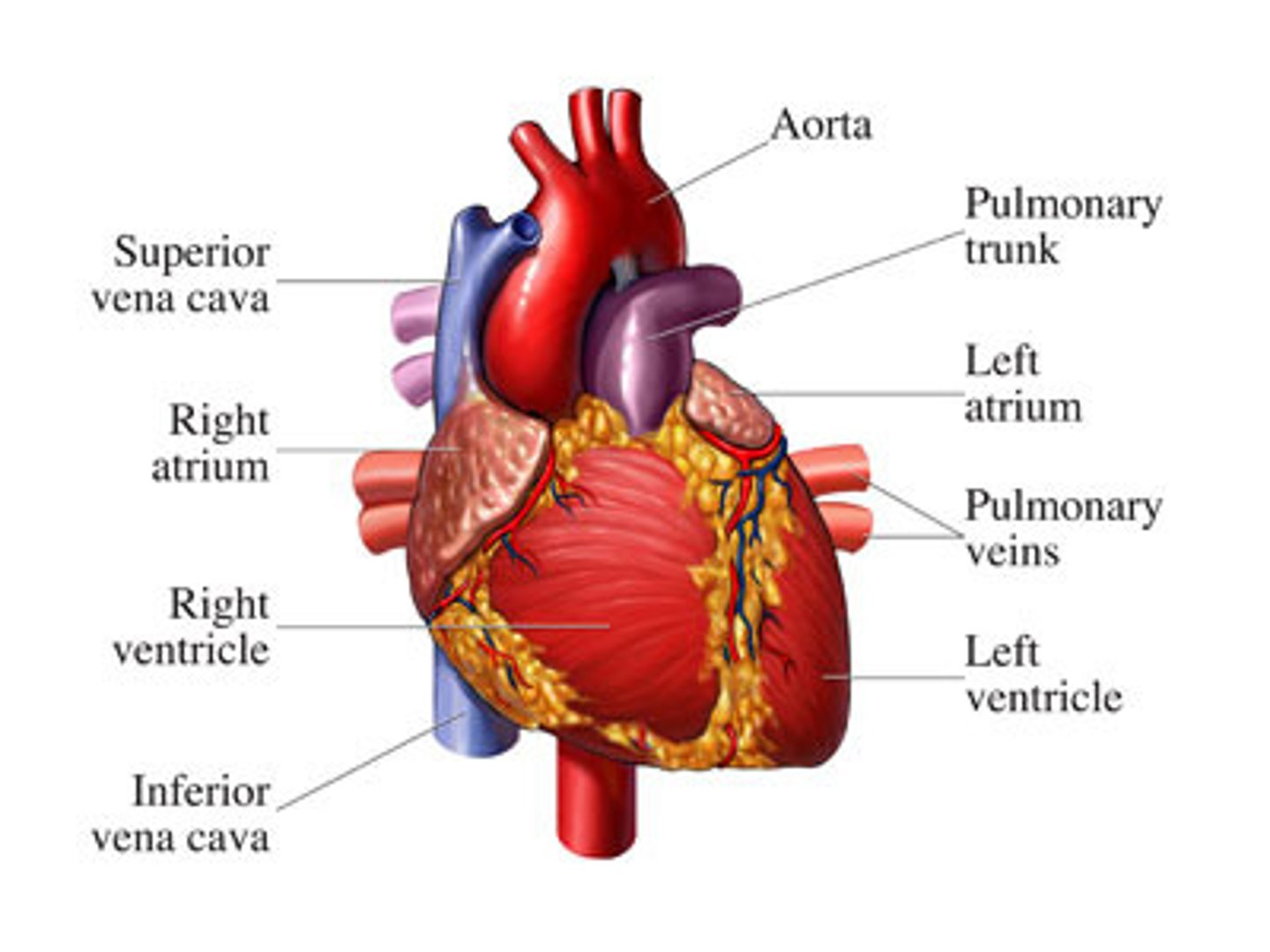
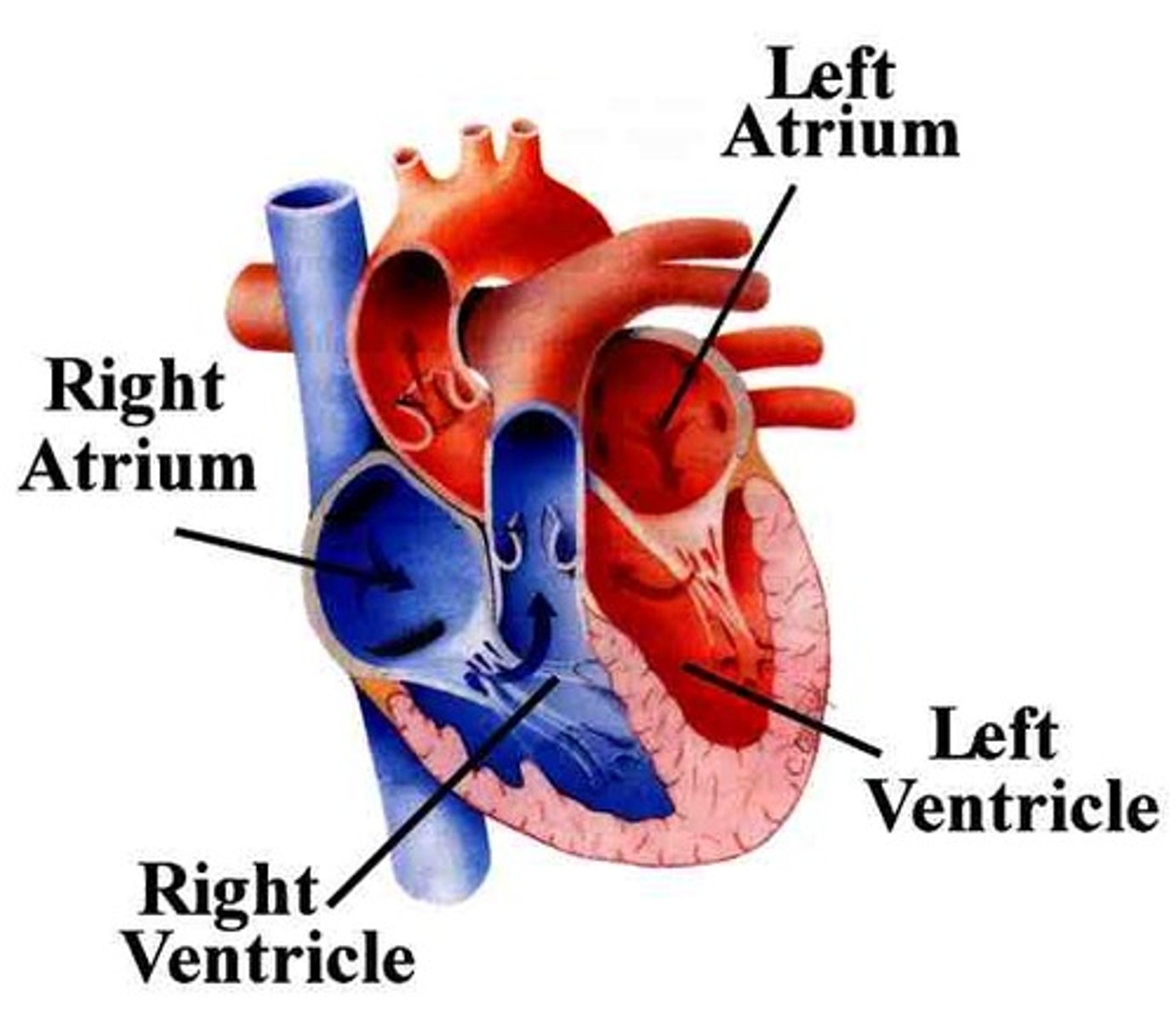
atrium
each of the two upper chambers of the heart that receives blood that comes into the heart
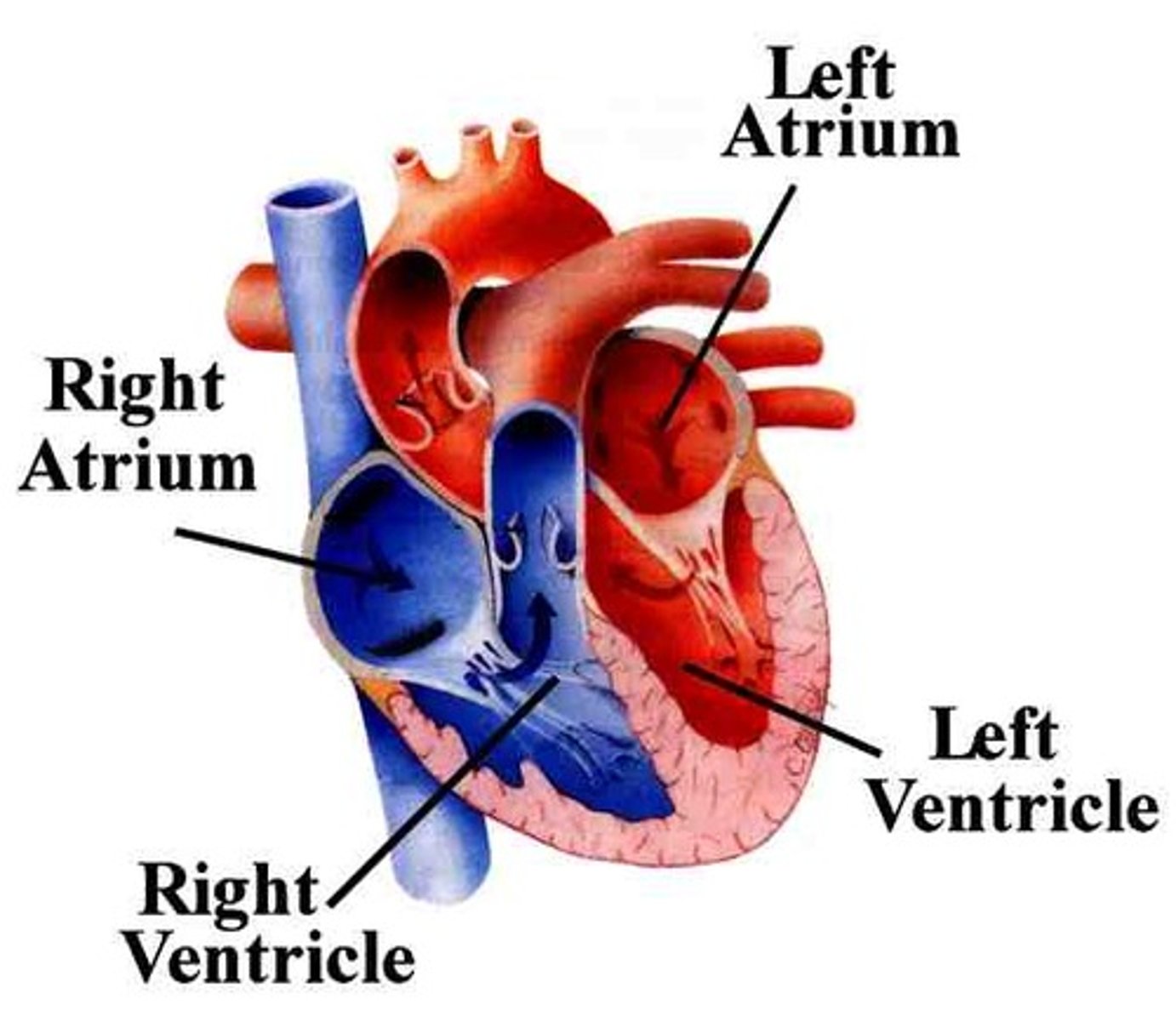
ventricle
each of the two lower chambers of the heart that pumps blood out of the heart
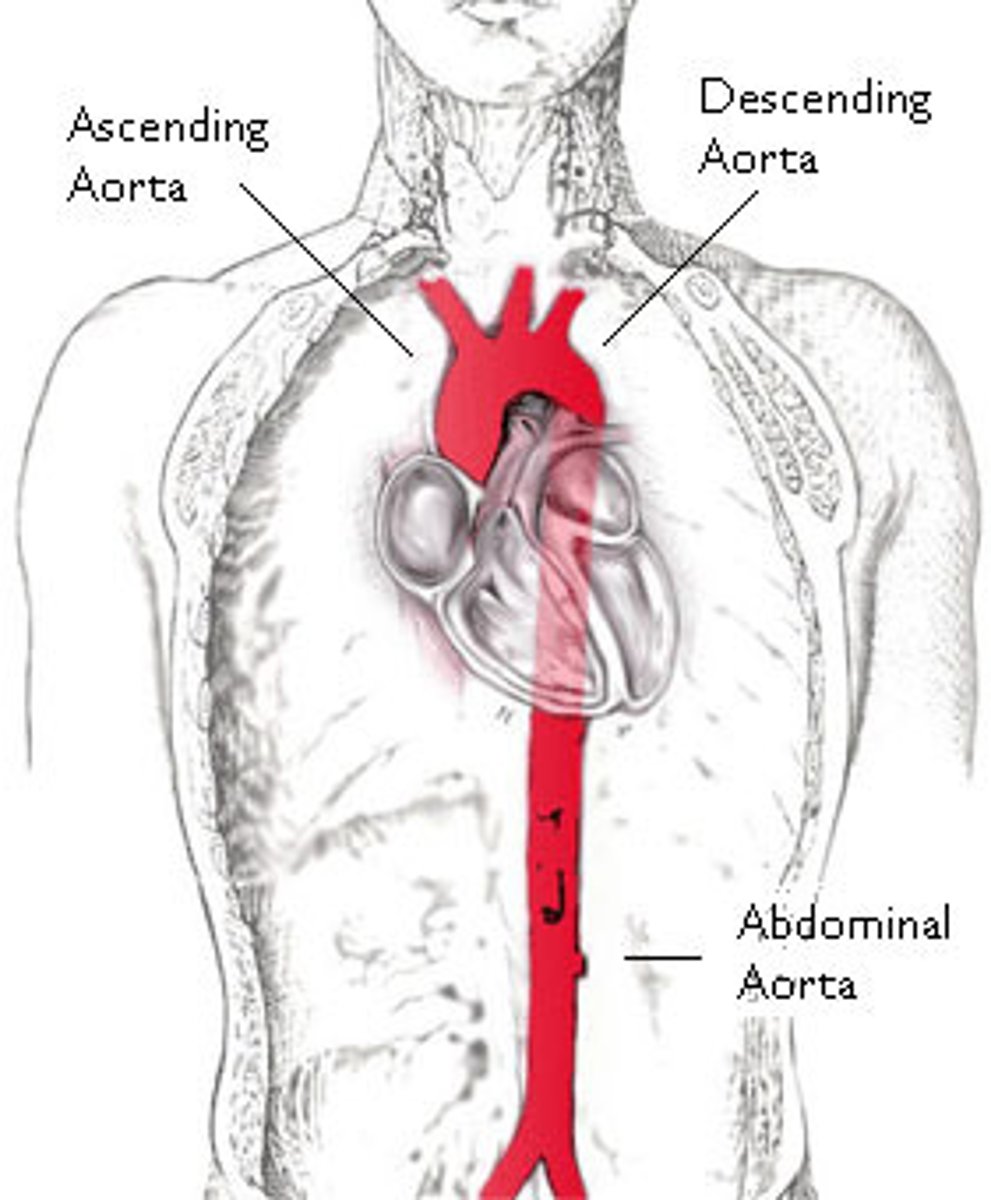
aorta
- the largest artery in the body
- receives blood from the left ventricle
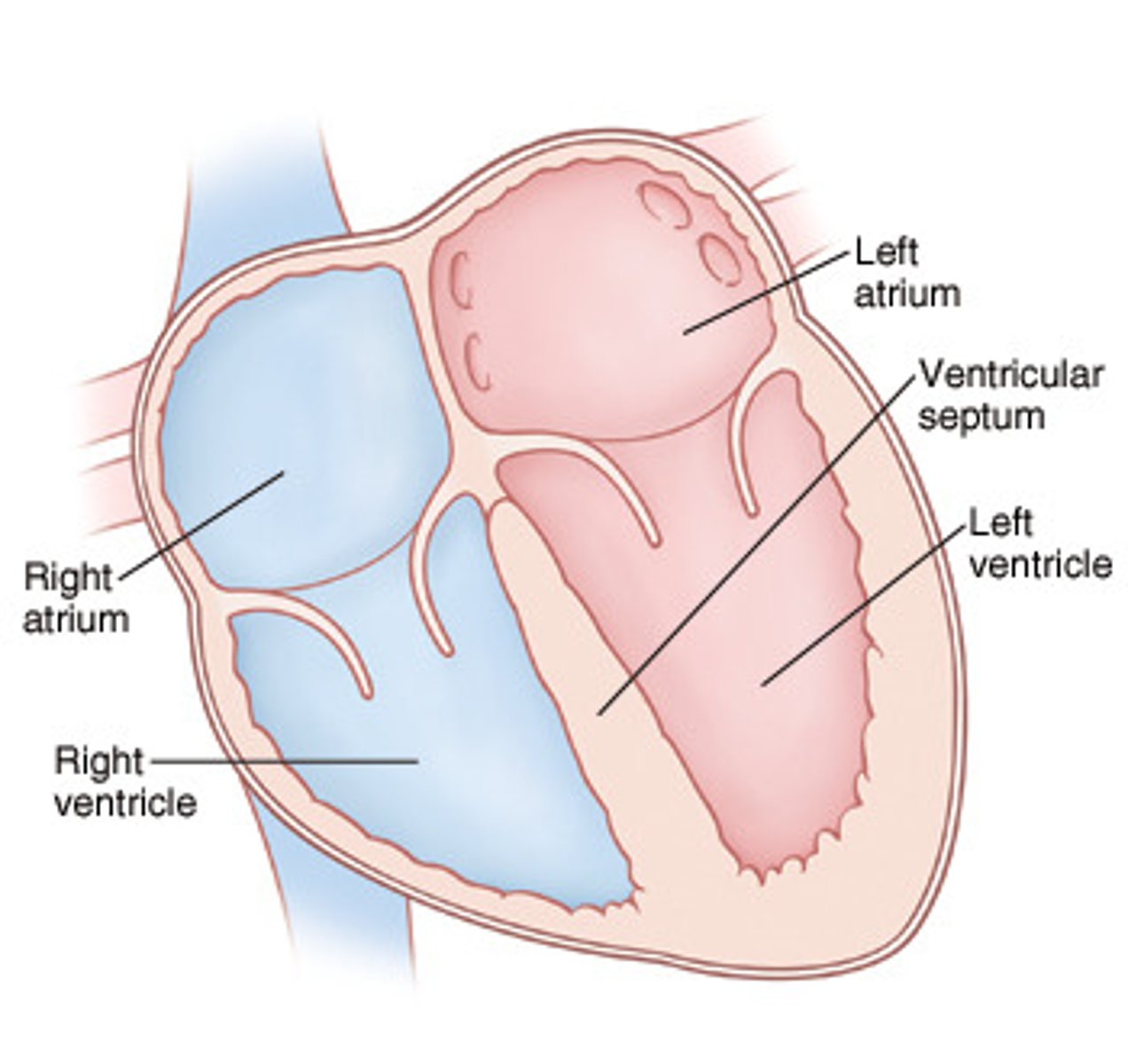
septum
the wall of tissue that separates the right side of the heart from the left side of the heart
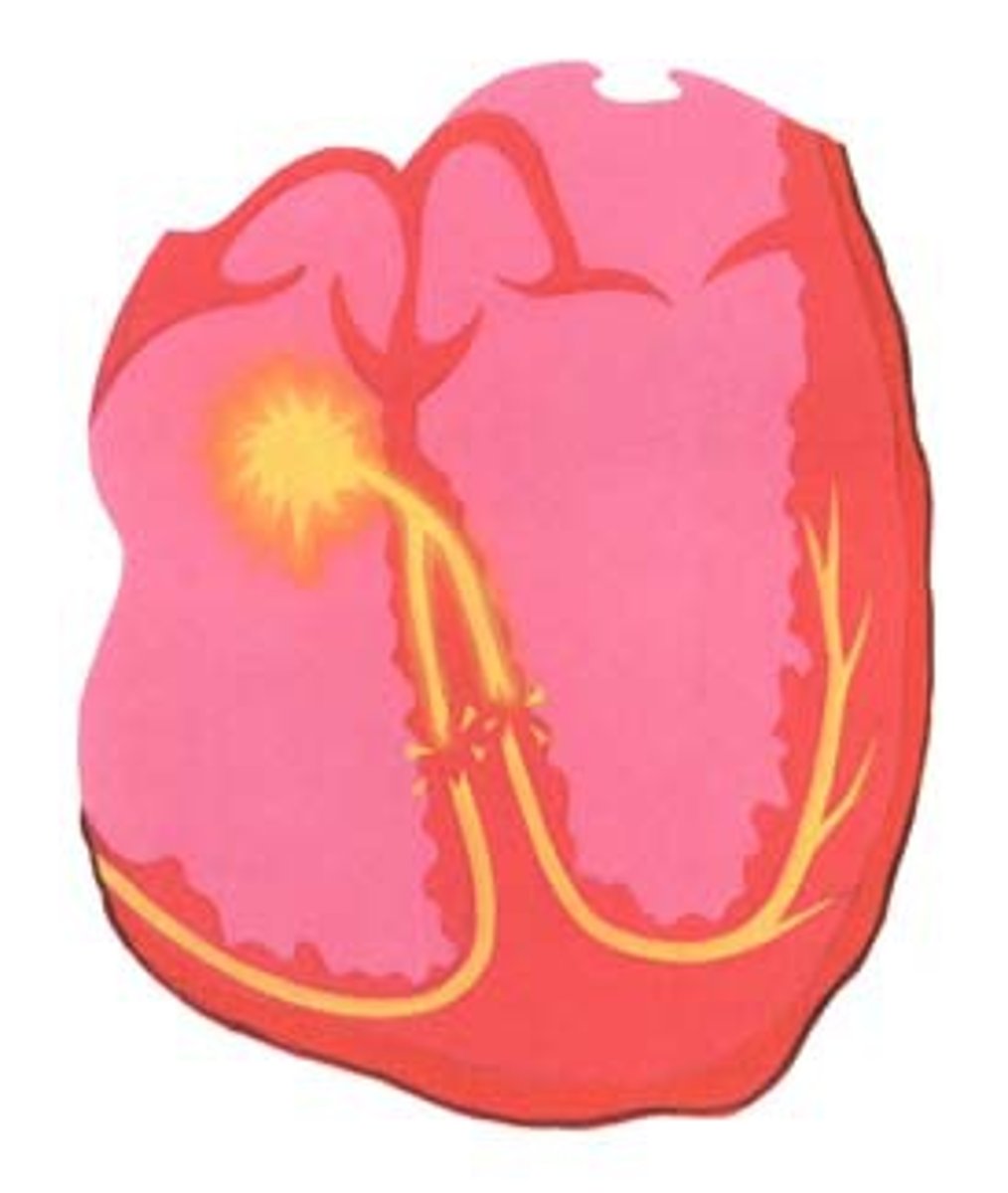
pacemaker
a group of cells located in the right atrium that sends out signals that make the heart muscle contract and that regulate heart rate.
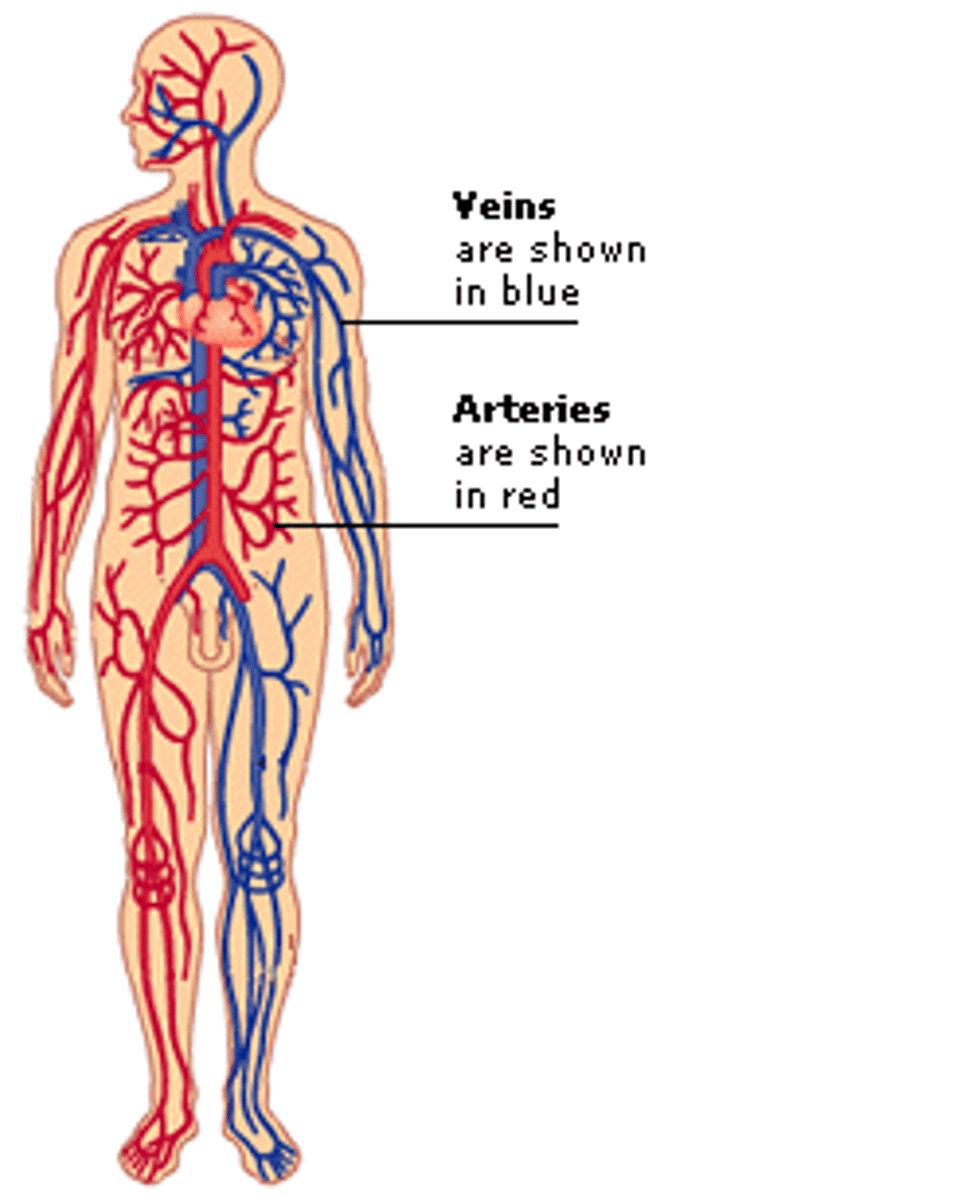
arteries
blood vessels that carrie blood away from the heart.
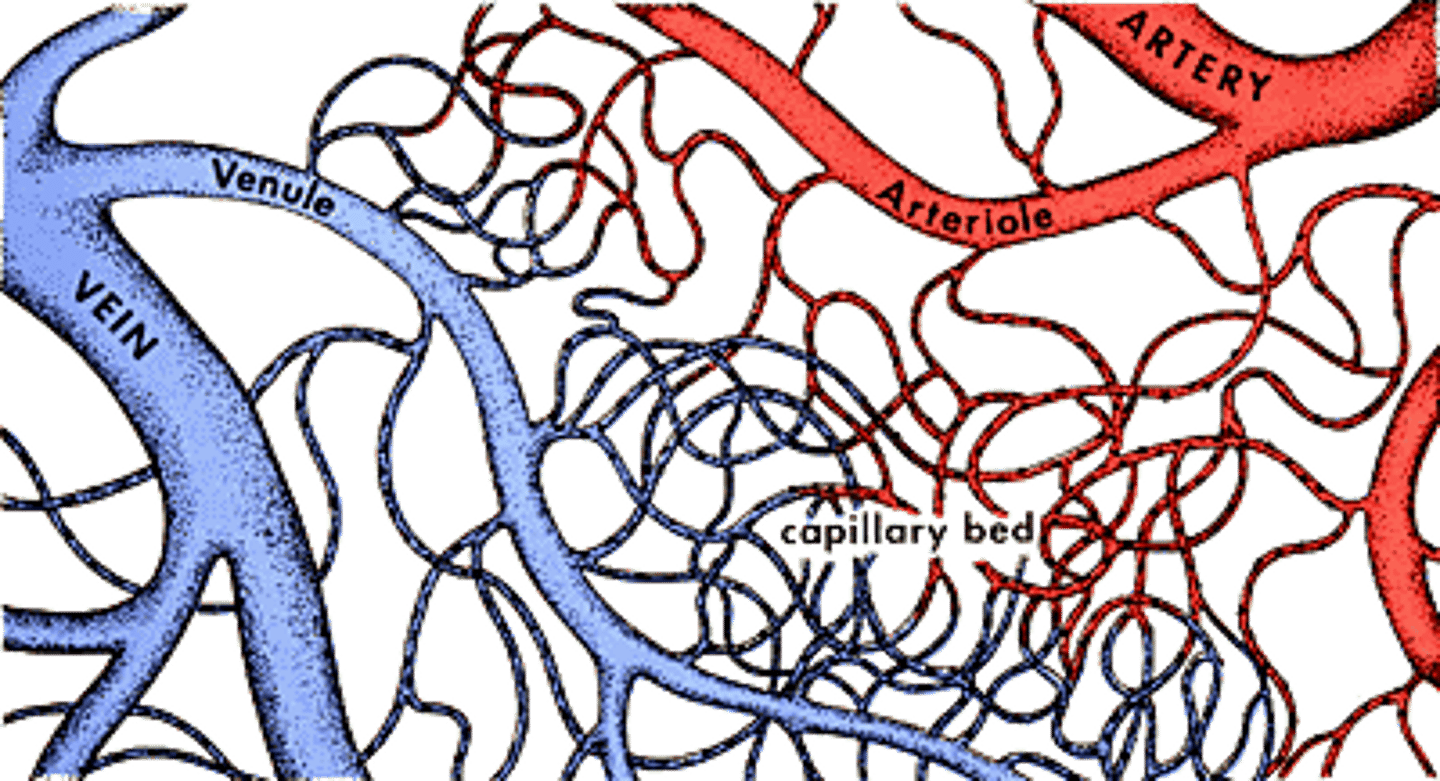
capillaries
tiny blood vessels where substances are exchanged between the blood and the body cells
veins
blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
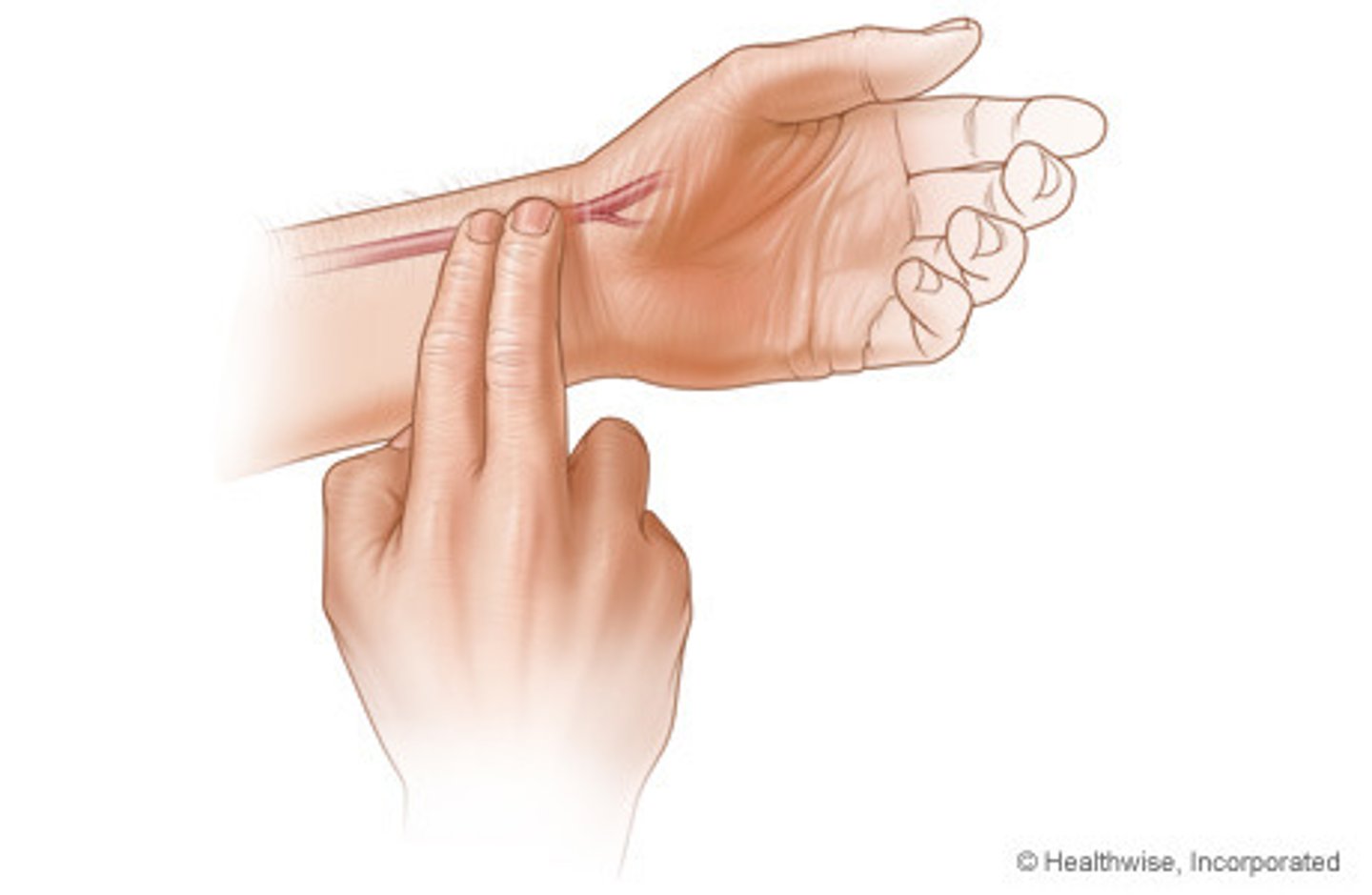
pulse
the alternating expansion and relaxation of an artery wall as blood travels through an artery
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels.
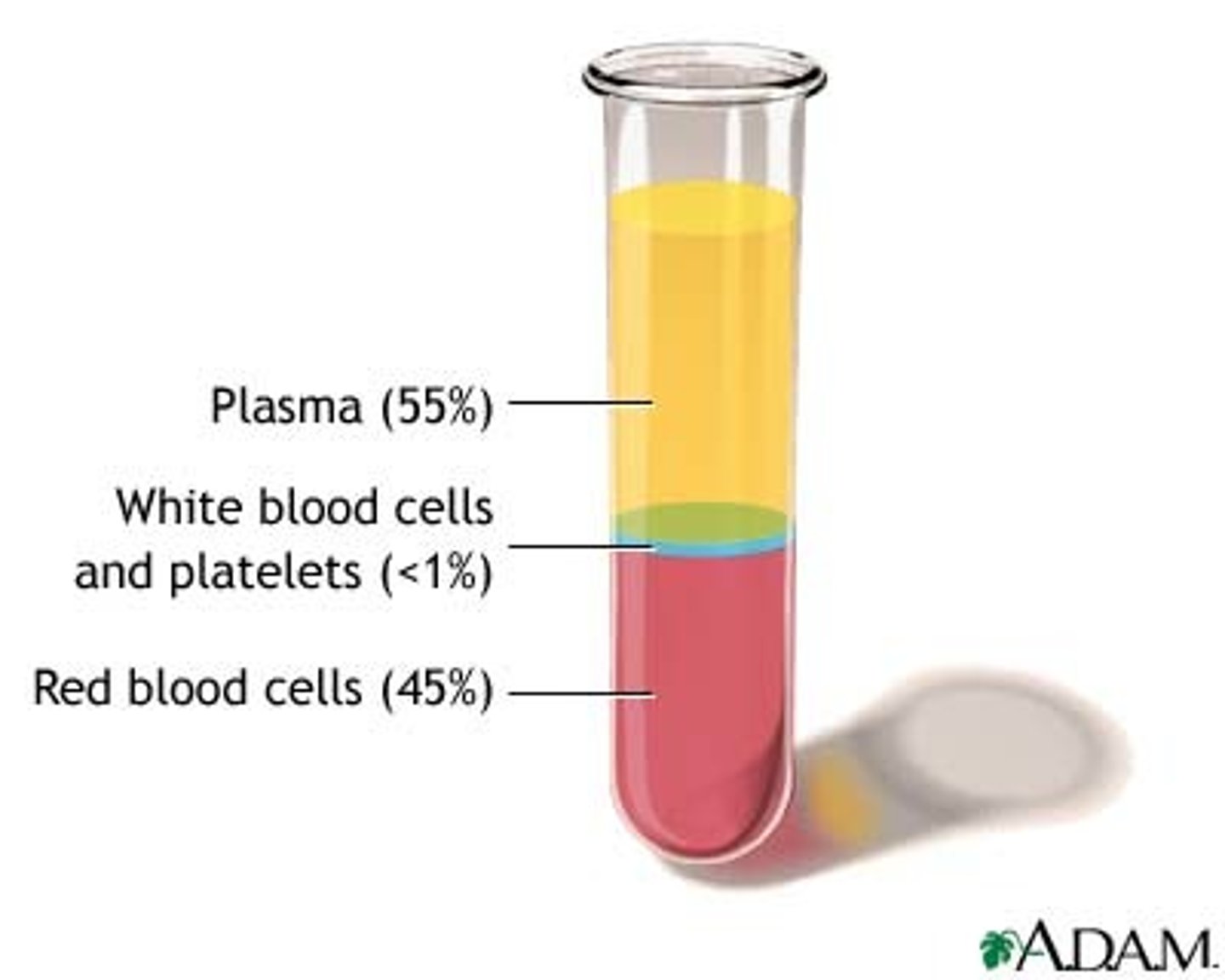
plasma
the liquid part of blood
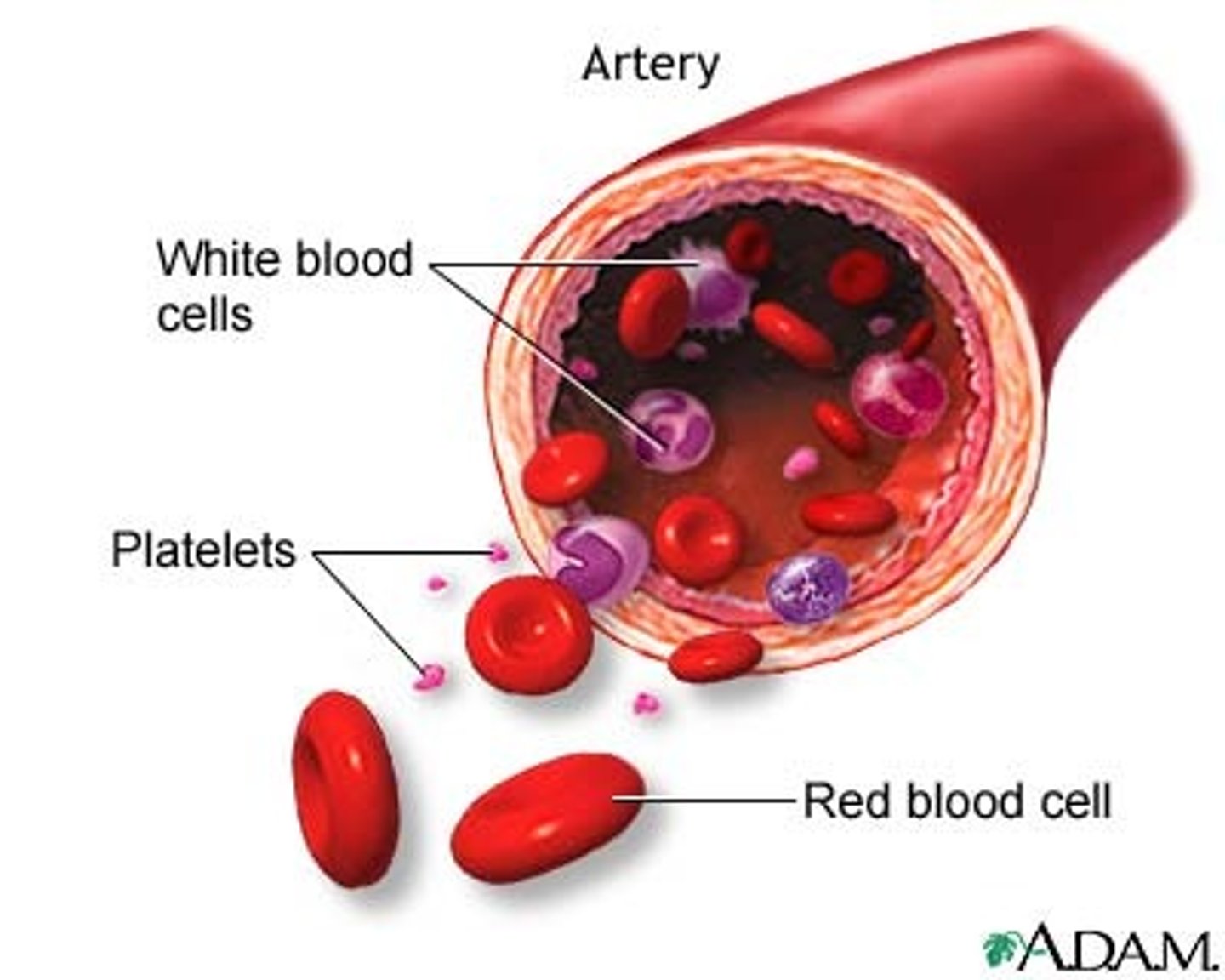
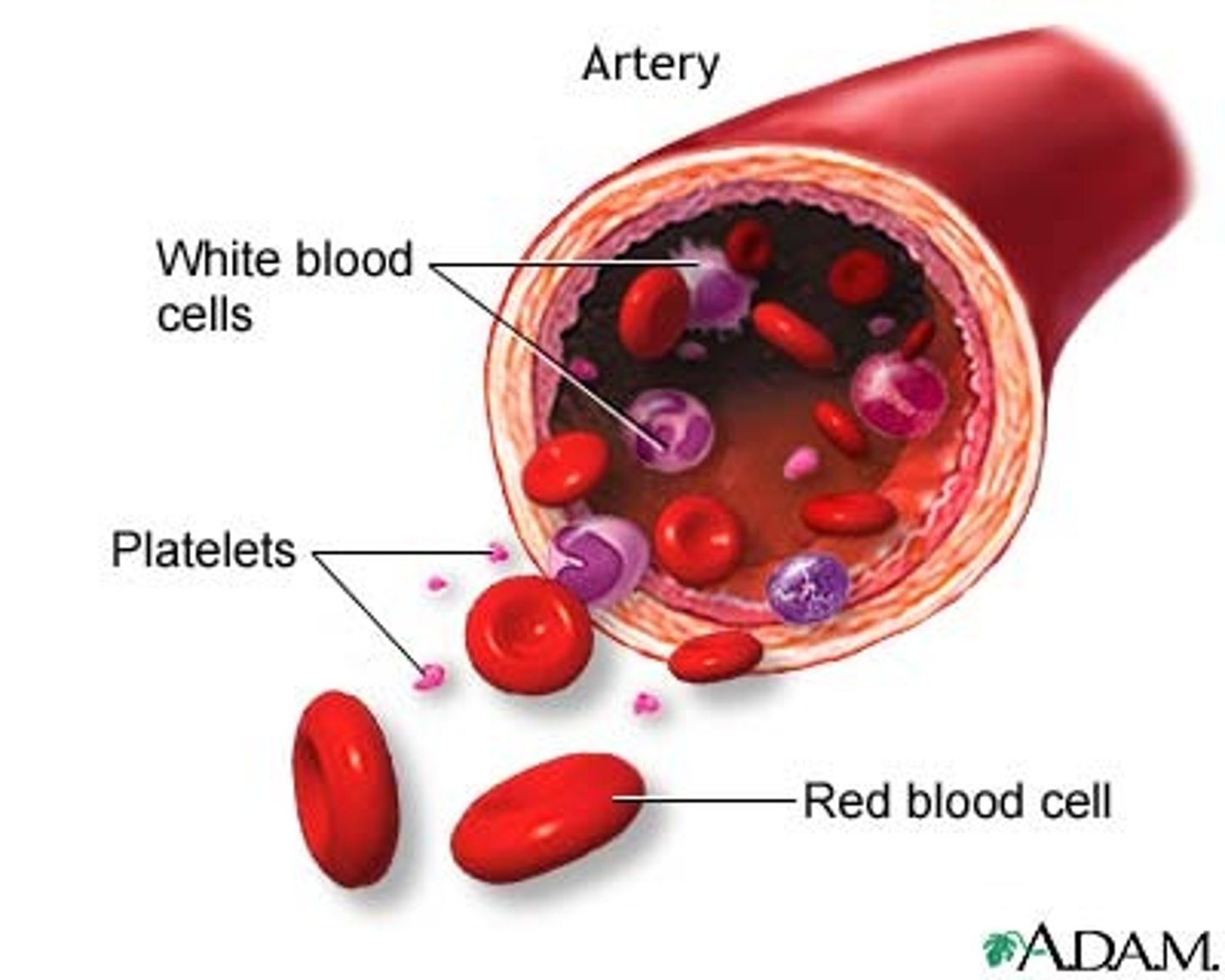
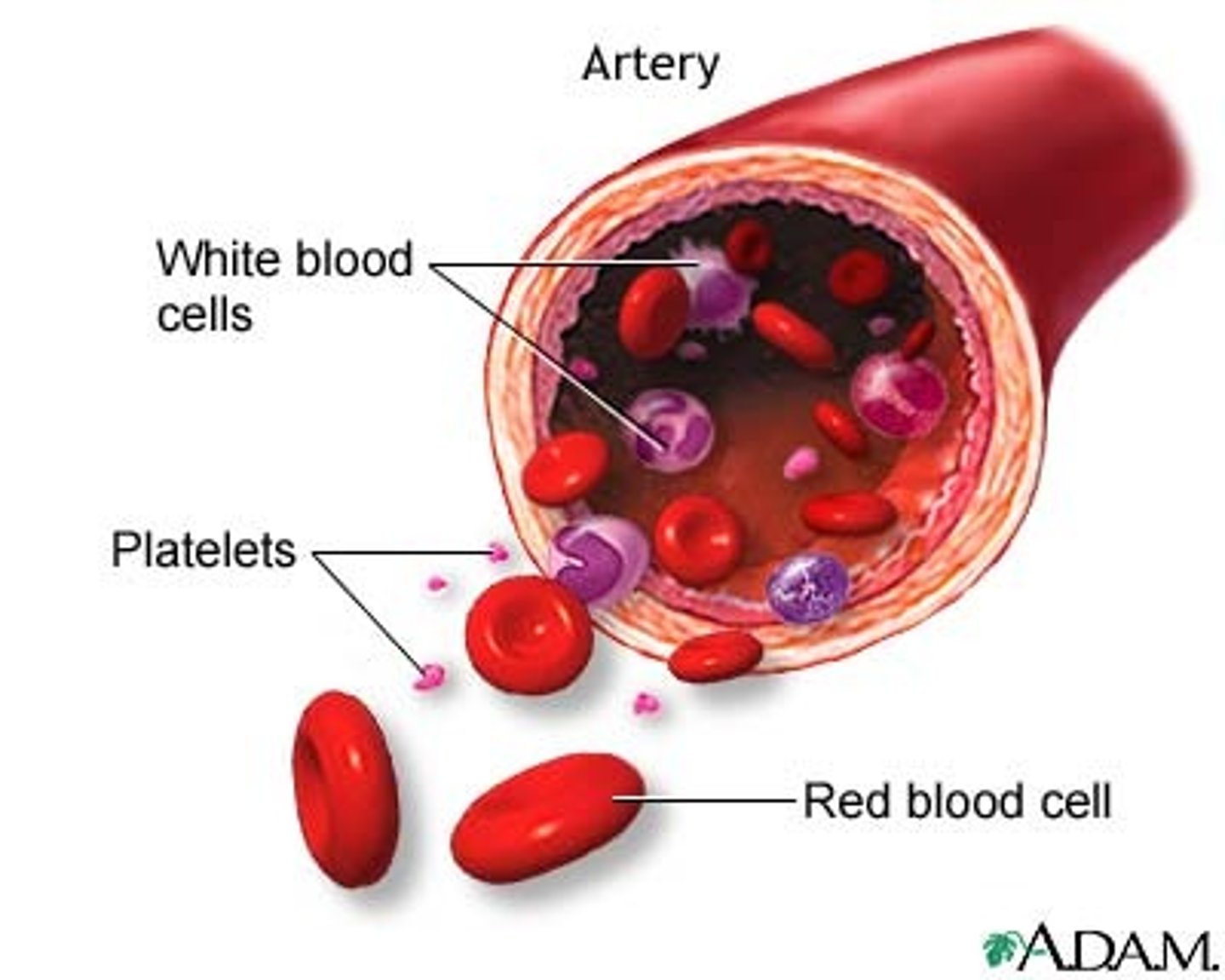
red blood cells
a cell in the blood that takes up oxygen in the lungs and delivers it to cells elsewhere in the body.
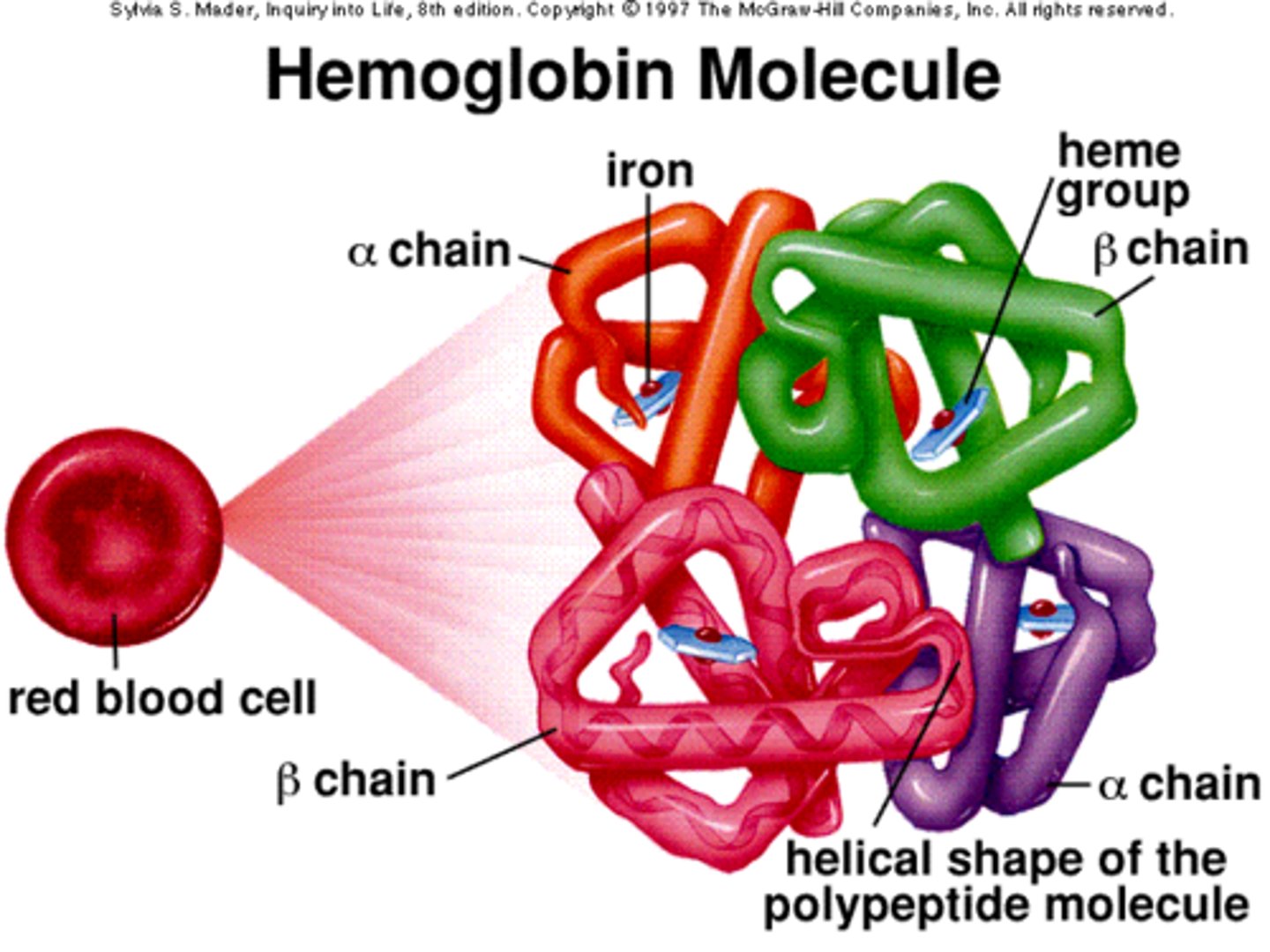
hemoglobin
- an iron-containing protein that binds chemically to oxygen molecules
- makes up most of red blood cells
white blood cells
a blood cell that attacks "foreign" or harmful particles that are found in the bloodstream
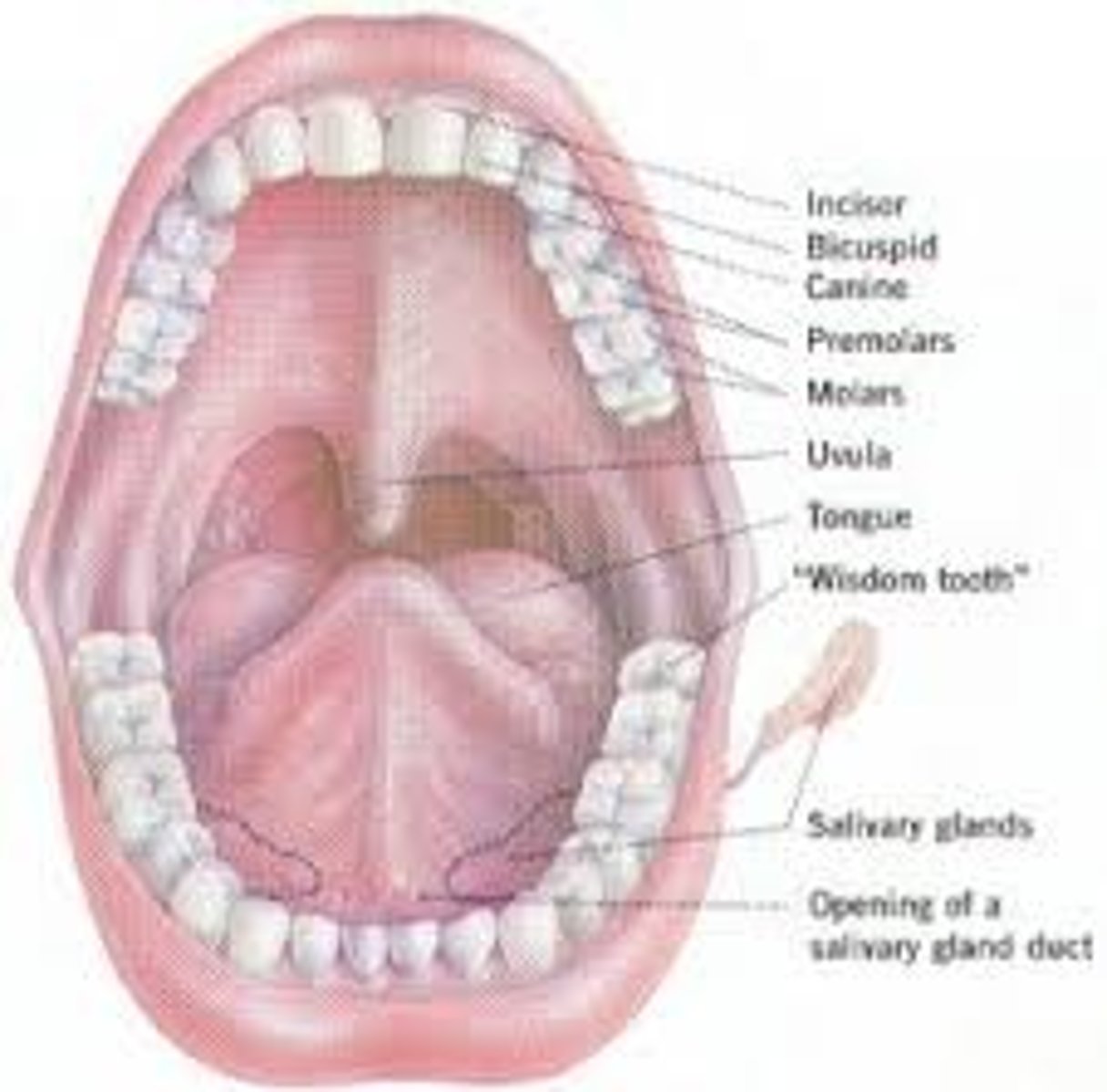
Ingestion (eating), taking in nutrients.
What is the 1st stage of digestion?
platelets
cell fragments that play an important part in forming blood clots
lymphatic system
a network of veinlike vessels that returns the fluid that leaks out of blood vessels to the bloodstream
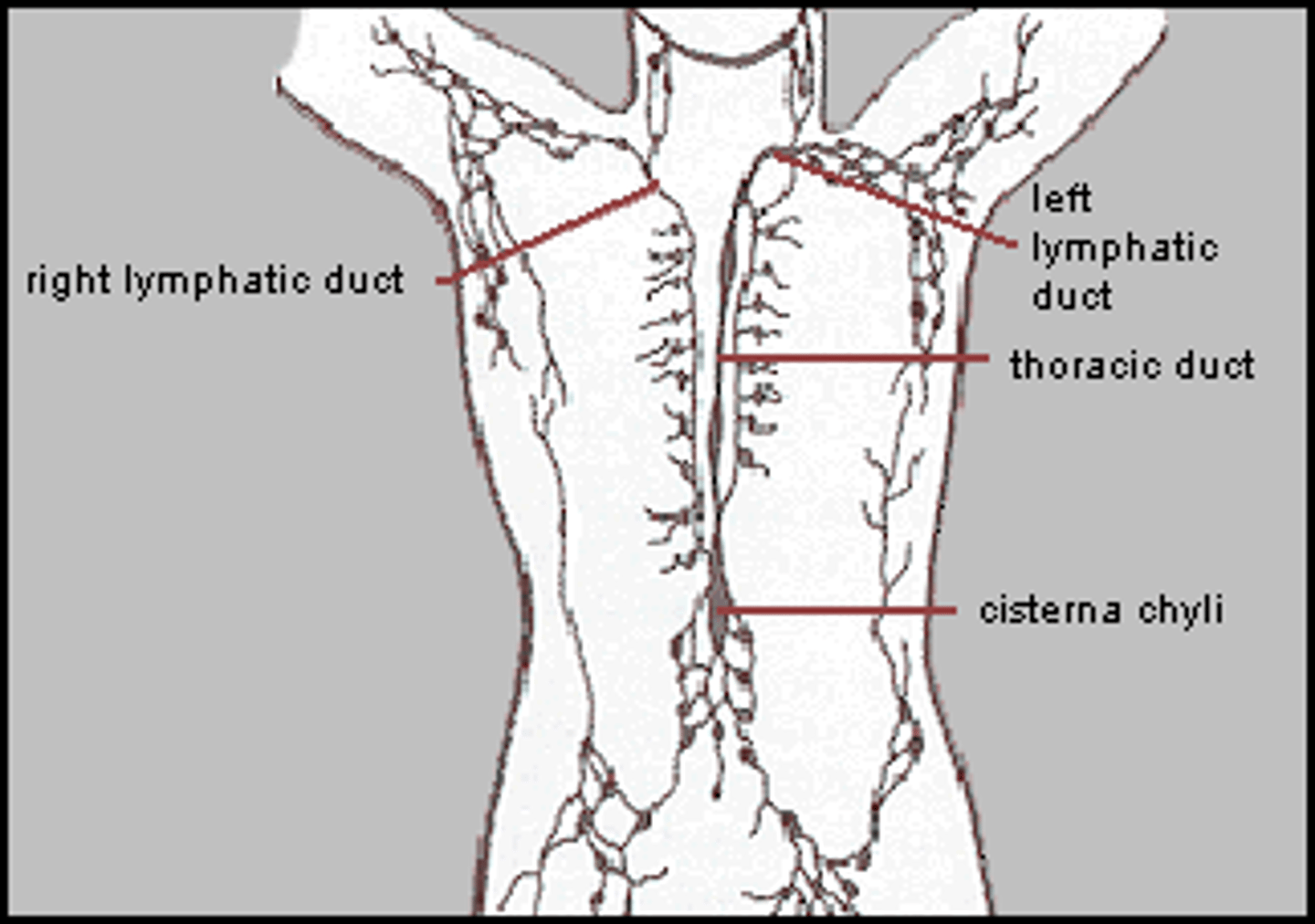
lymph nodes
a small knob of tissue in the lymphatic system that filters lymph, trapping bacteria and other microorganisms that cause disease
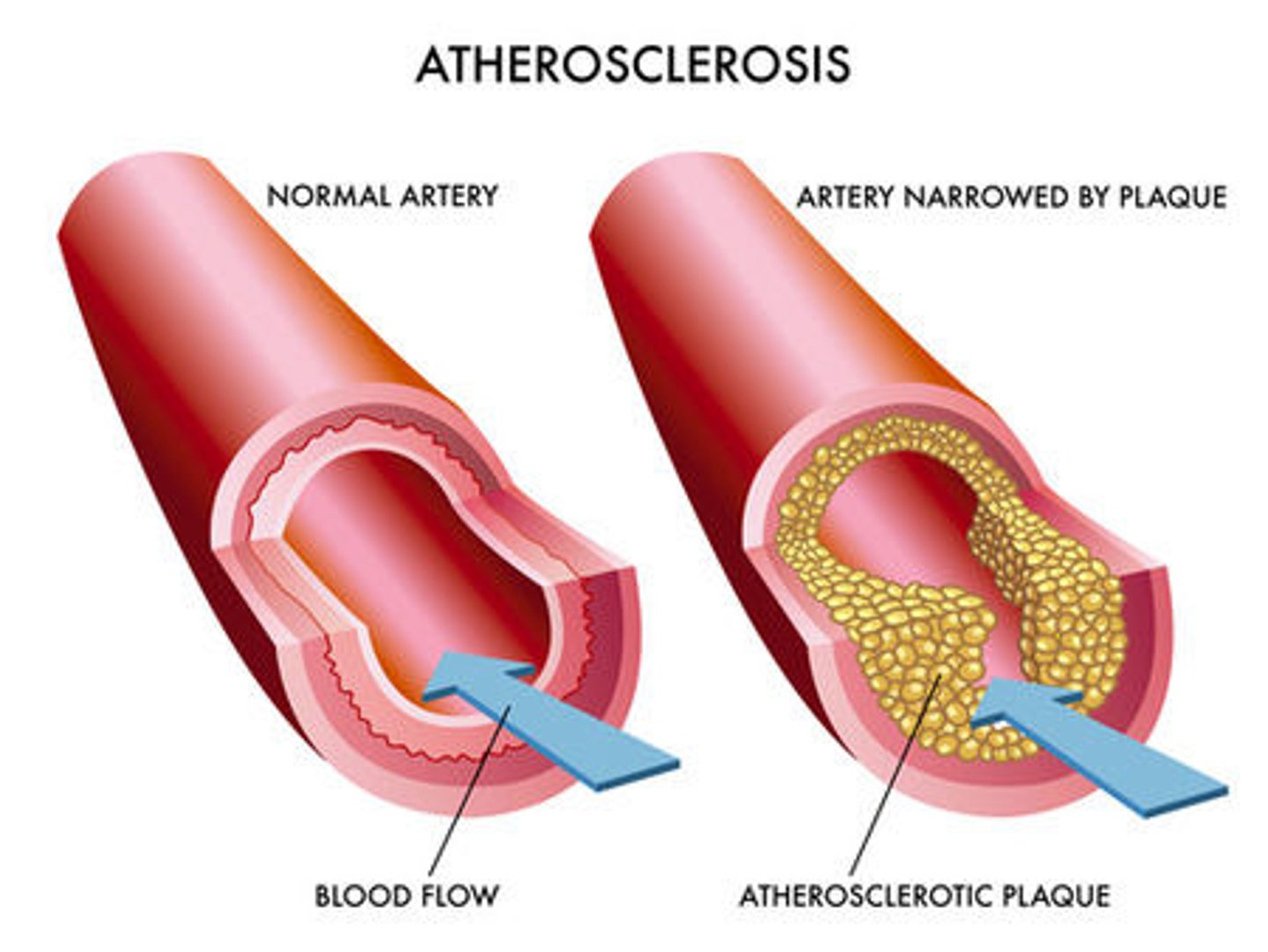
atherosclerosis
a condition in which an artery wall thickens as a result of the buildup of fatty materials
heart attack
a condition in which blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing heart cells to die

hypertension
a disorder in which a person's blood pressure is consistently higher than normal;also called high blood pressure.
What are the four components of blood?
1. Plasma
2.red blood cells
3.white blood cells
4. Platelets

List three things to keep your cardiovascular system stay healthy
1. Exercise
2. Diet
3. Avoid smoking, drugs and excessive drinking

What does the circulatory sytstem consist of?
1. heart
2. blood vessels
3. blood
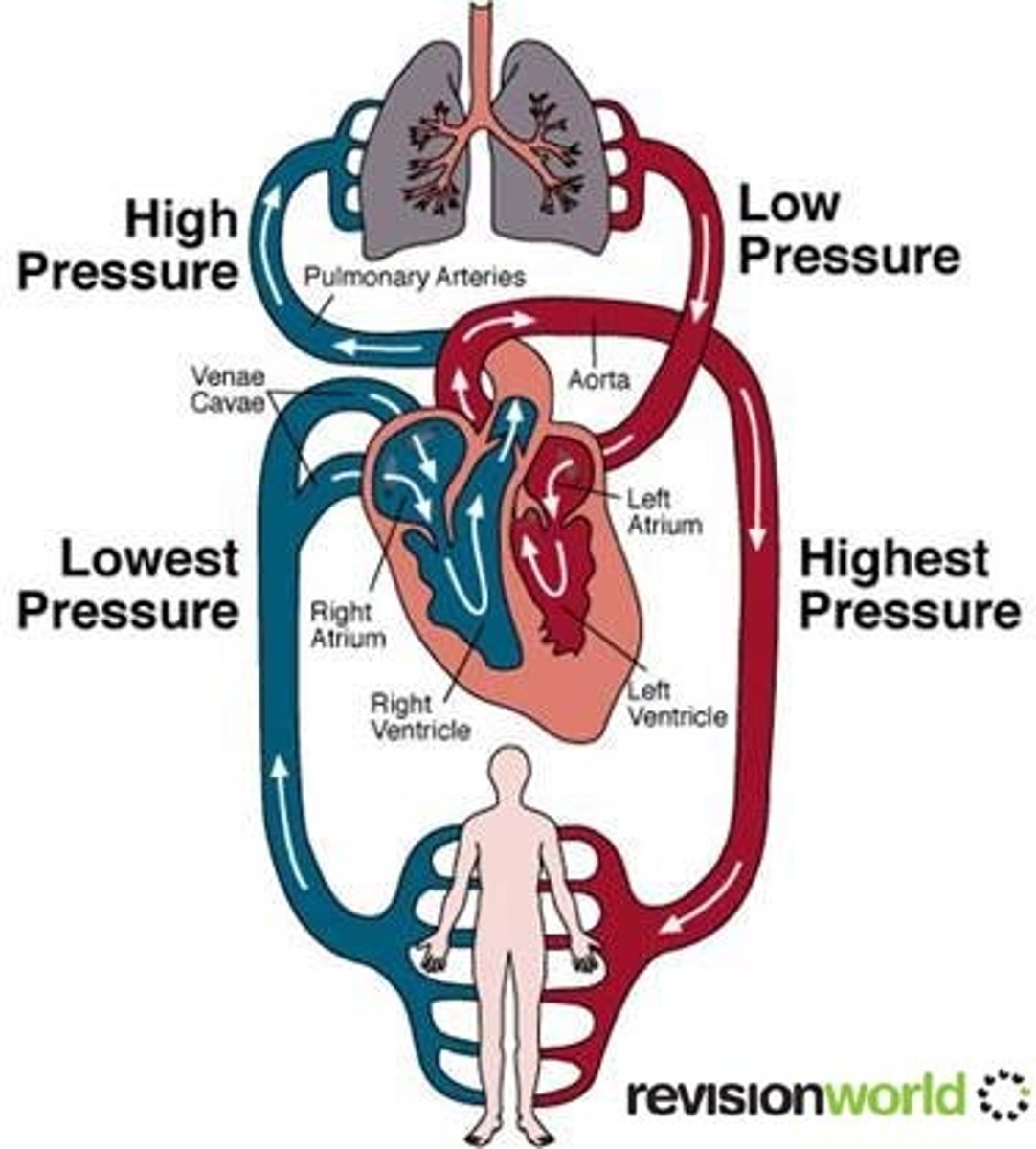
What three functions does the cardiovascular system perform
1. Delivering needed materials
2. Removing waste products
3. fighting disease
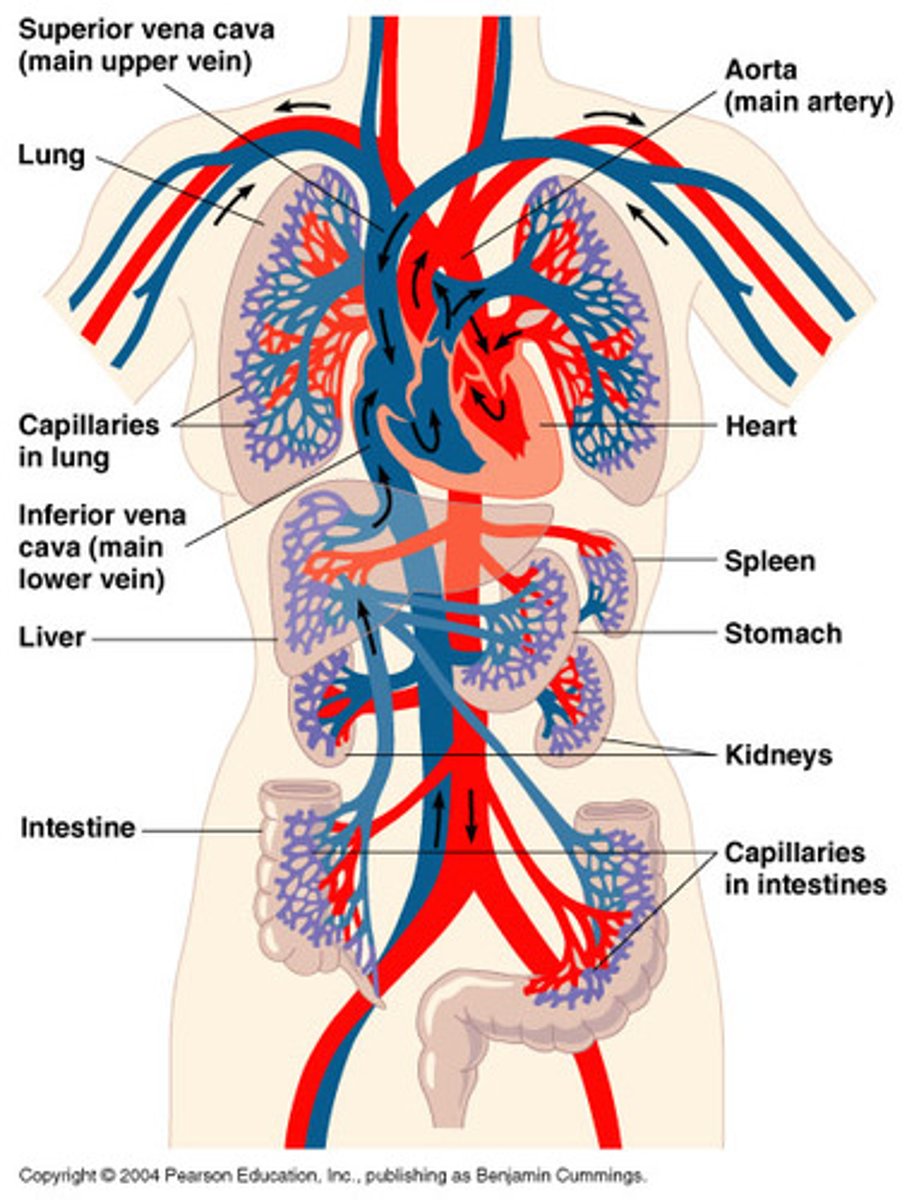
Explain the patterns of blood flow
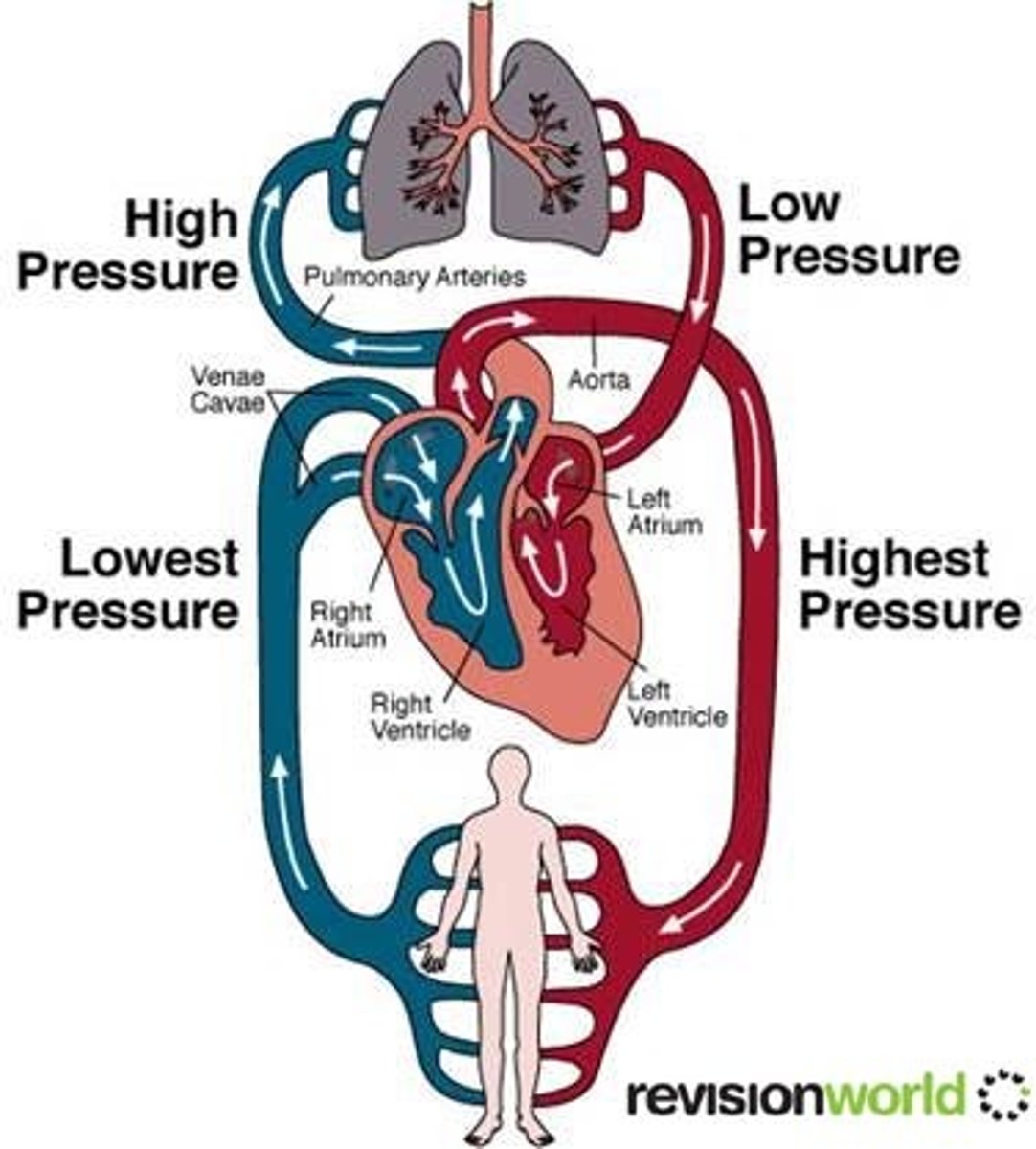
* Overall pattern of blood flow is something like figure eight
1. First loop blood travels from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart
2. Second loop, blood is pumped from the heart thoughout the body and then returns again to the heart.
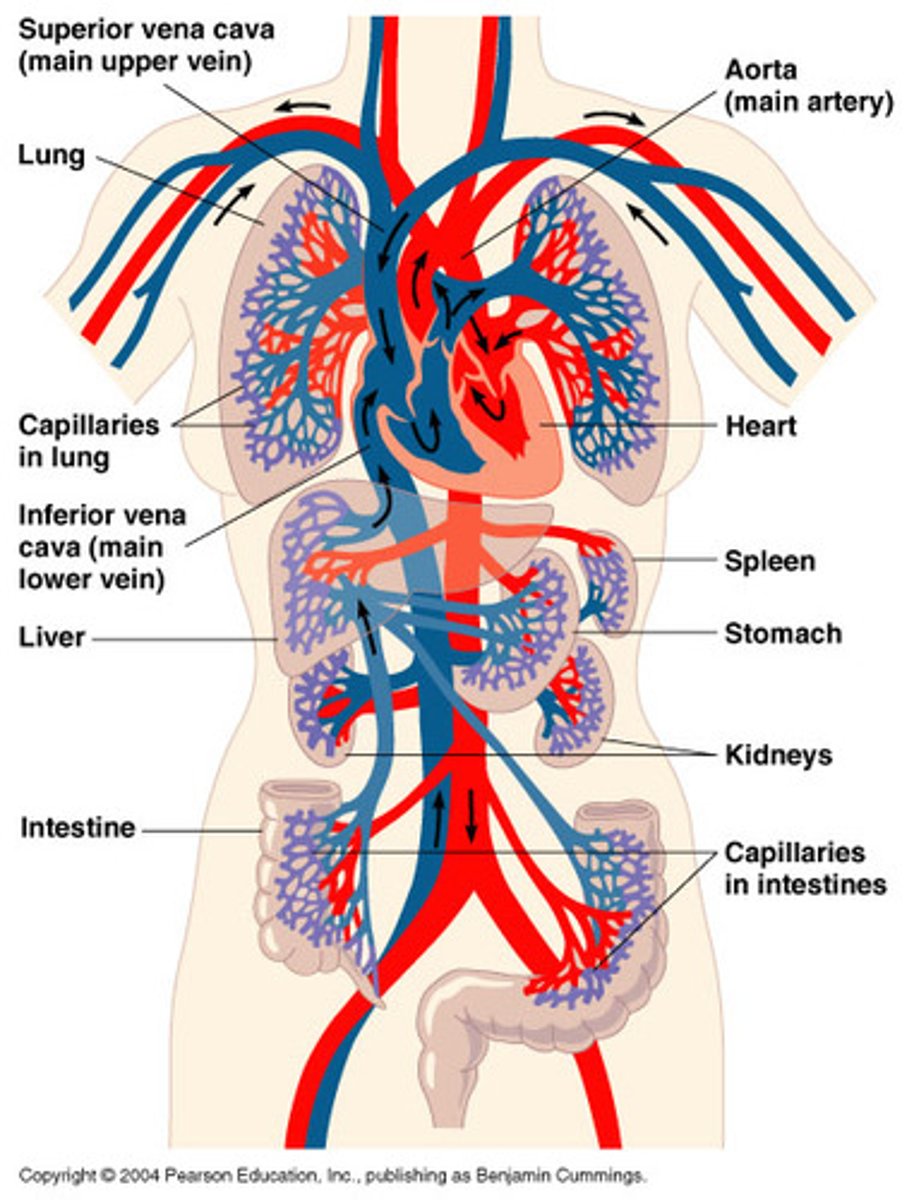
Where does the blood go in each?
Loop One:
1. right atrium
2.right ventricle
3.lungs
4.capillaries
Loop Two:
1. left atrium
2.left ventricle
3.pumped into aorta
4. tiny capillaries---Travels to parts of body (brain,liver,legs)
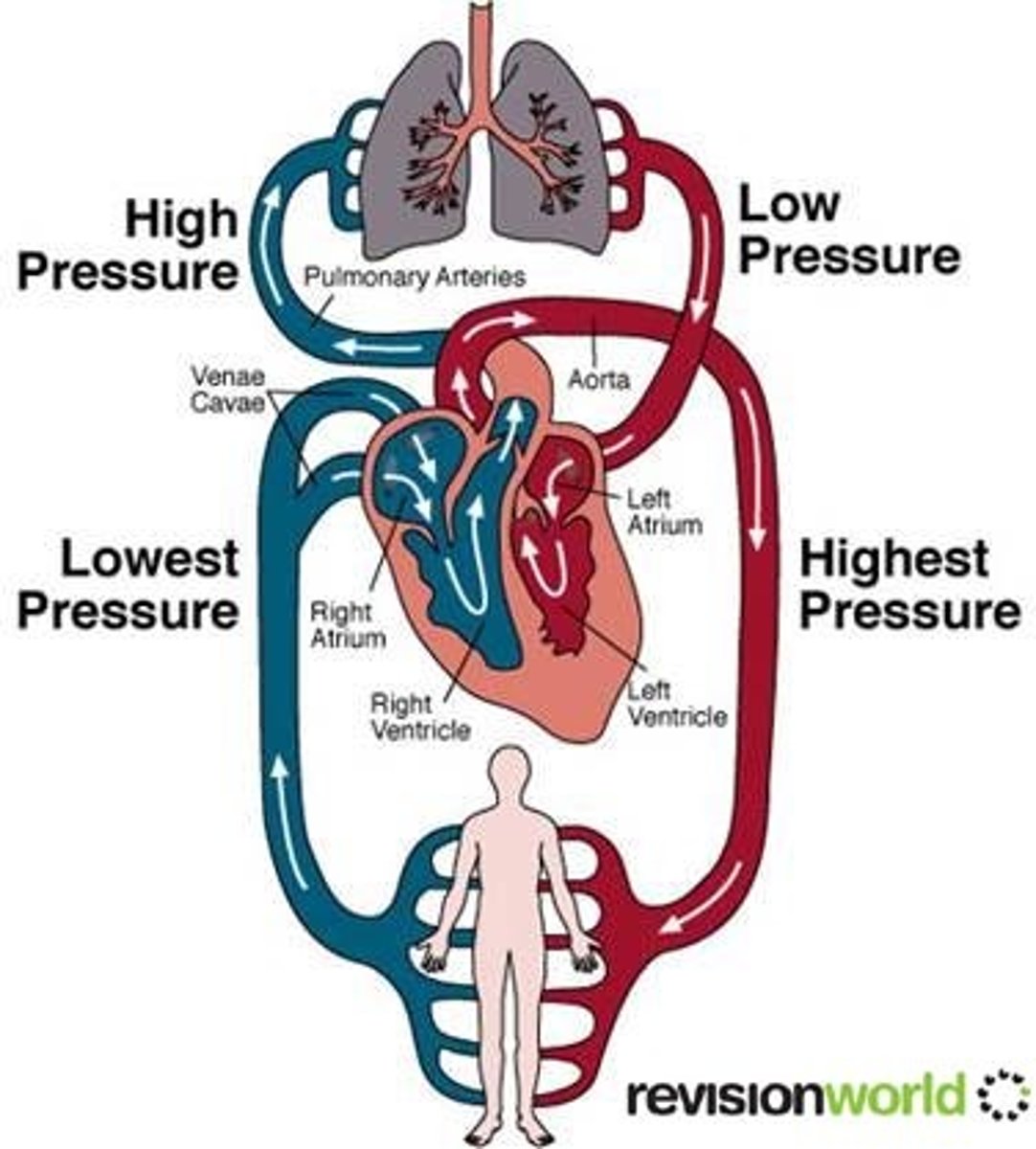
What causes blood pressure?
1. The force with which the ventricles contract
In which direction do your arteries carry blood?
1. Right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs
2. Left ventricle pumps blood to the aorta
Note. arteries always go away from the heart.
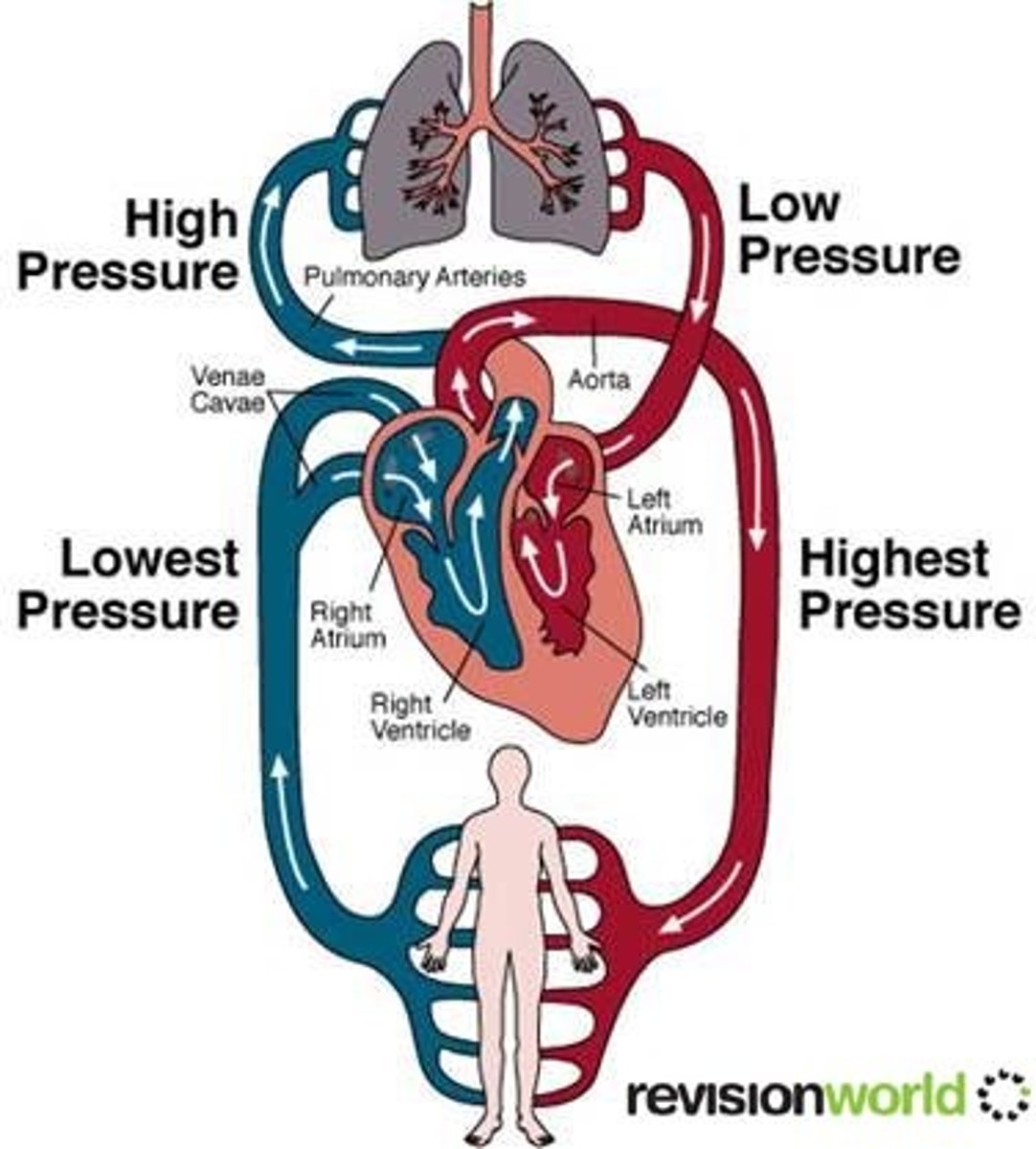
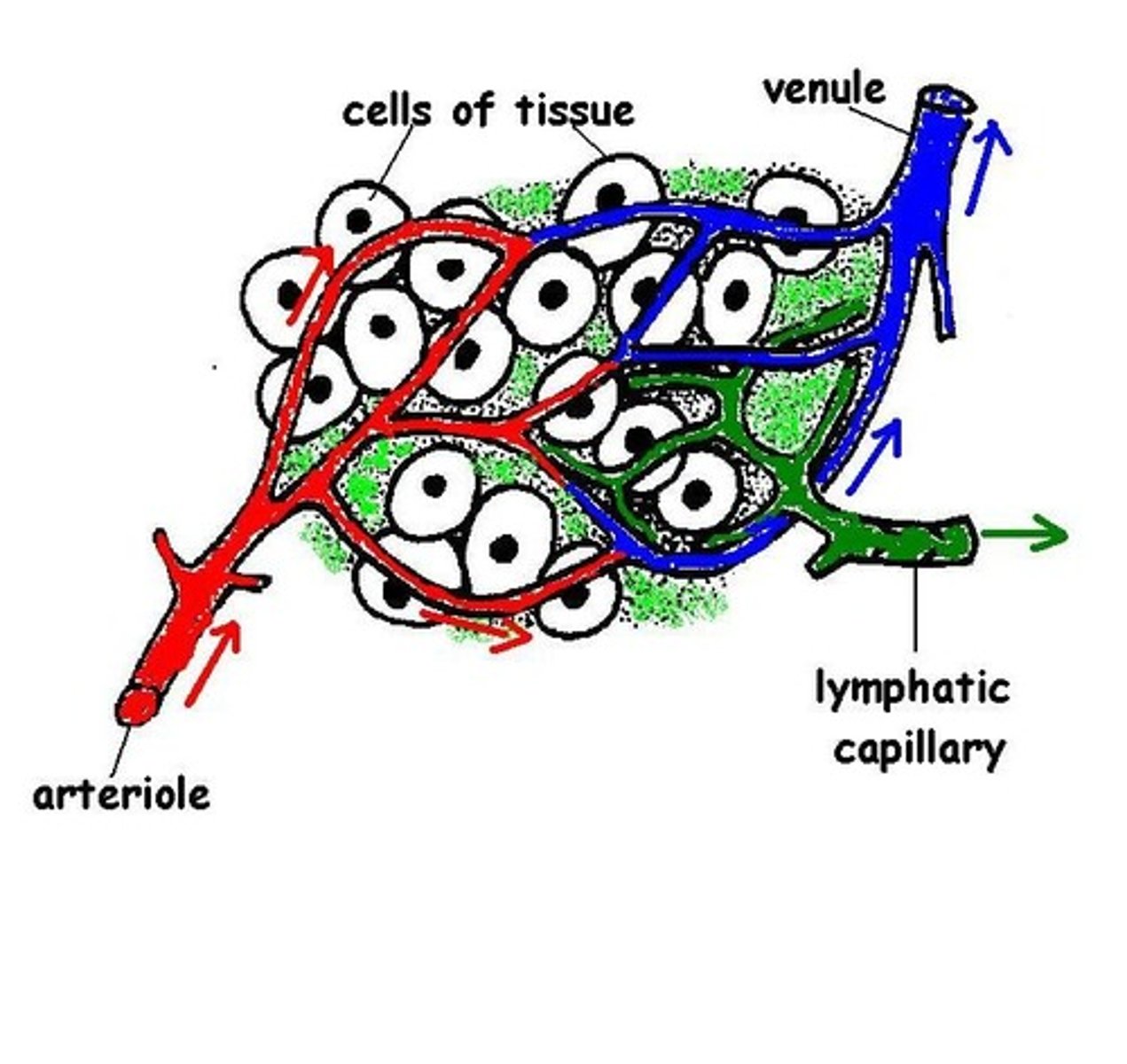
What is the function of capillaries in the body?
- capillaries are where materials are exhanged between the blood and the body's cells. Such as oxygen and glucose
What function does the heart perform?
1. The heart pumps blood throughout the body.
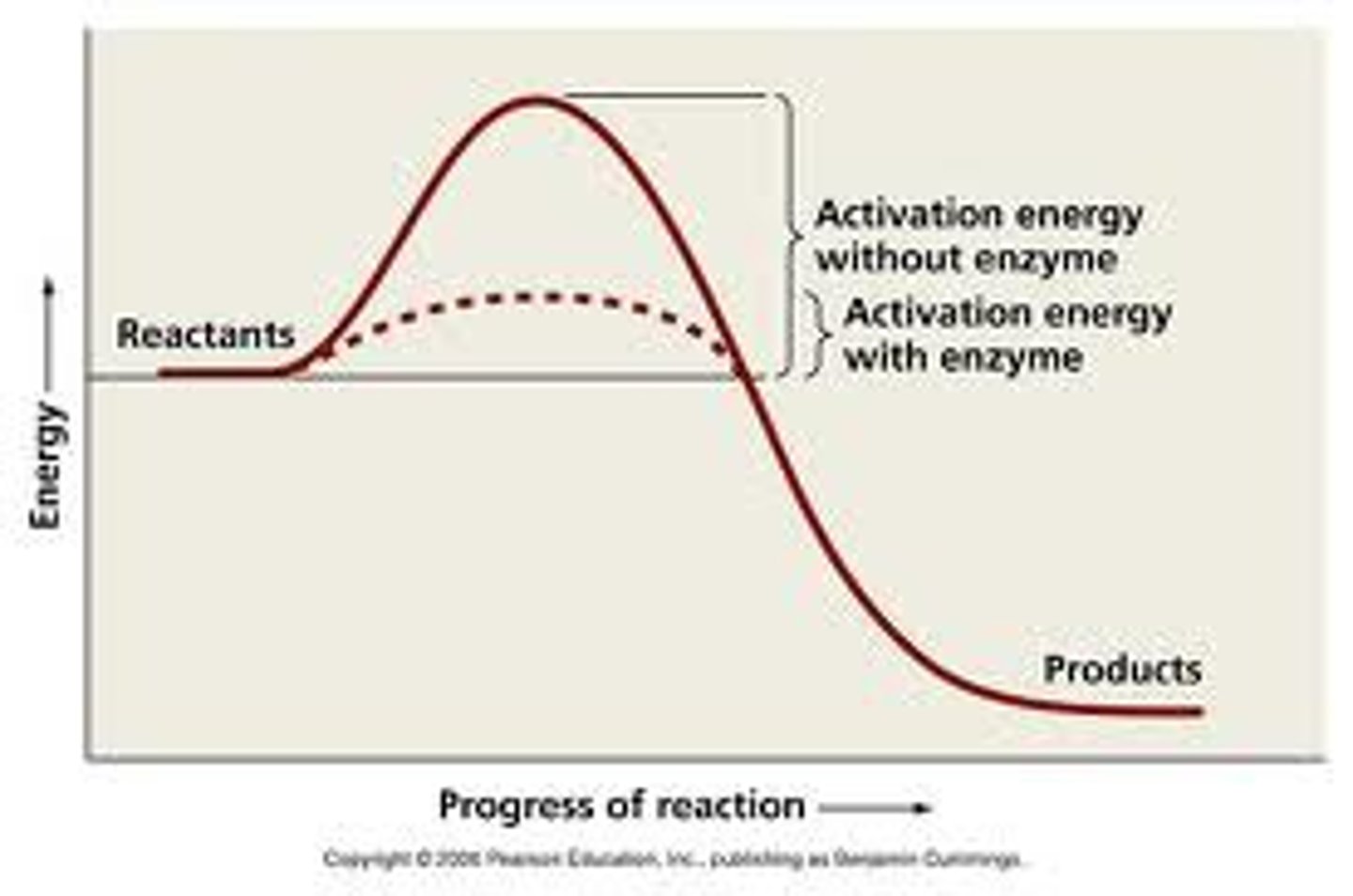
How do enzymes catalyze reactions?
by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur
True or False: Enzymes start chemical reactions.
FALSE. Enzymes don't start reactions- they SPEED UP reactions that would occur eventually.
Enzyme substrate
The reactant that an enzyme acts on
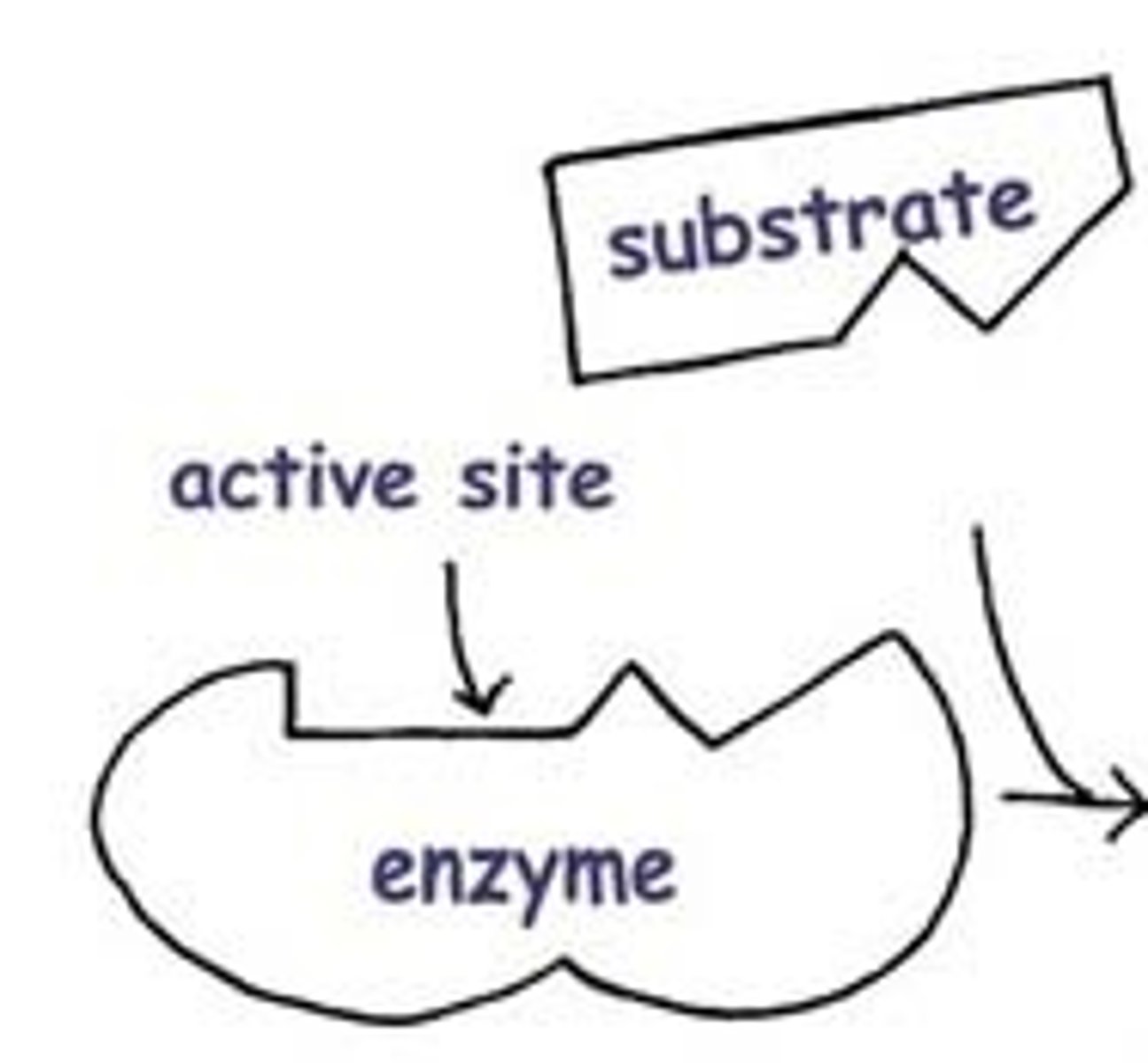
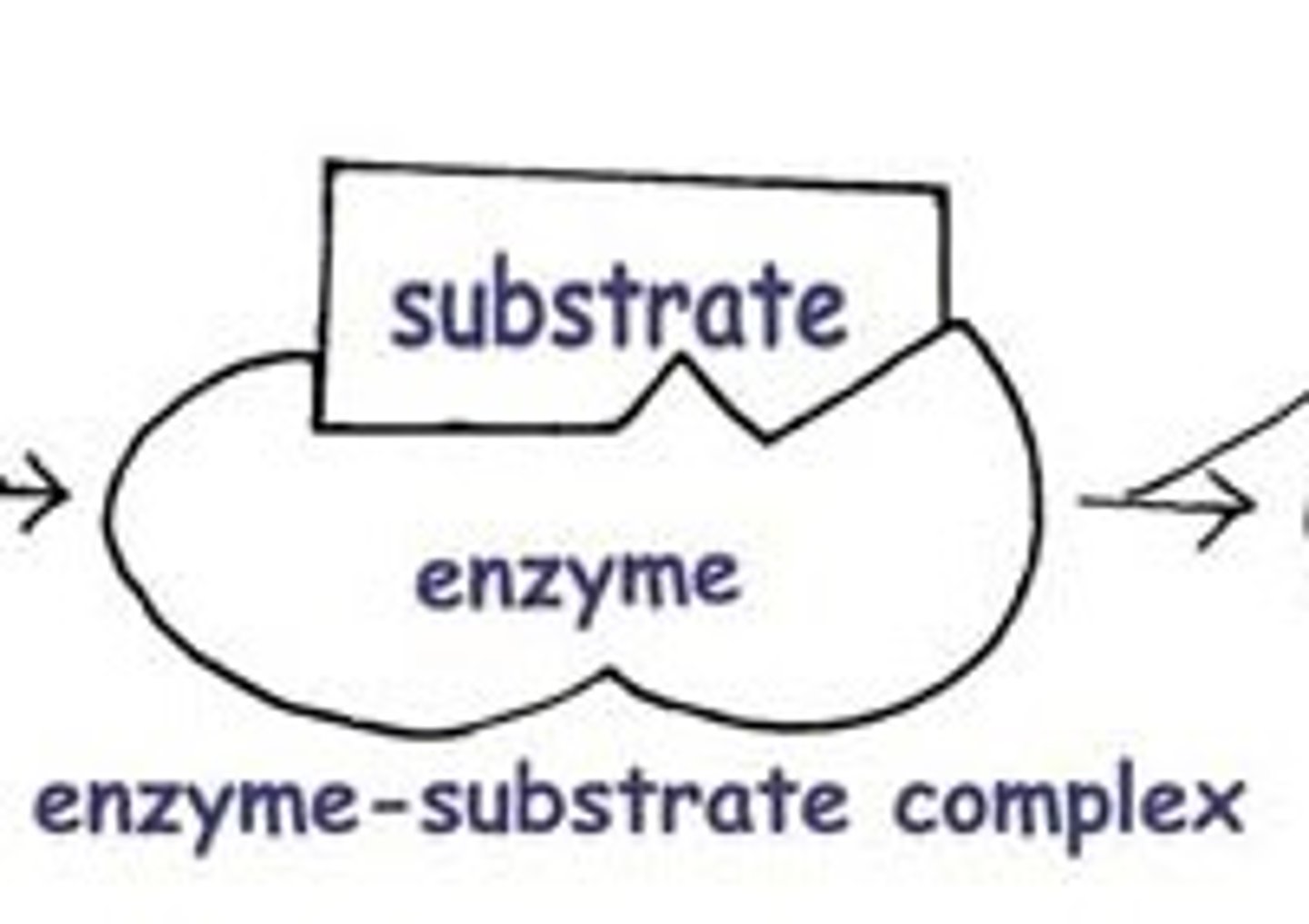
The enzyme binds to its substrate, forming what?
Enzyme-substrate complex
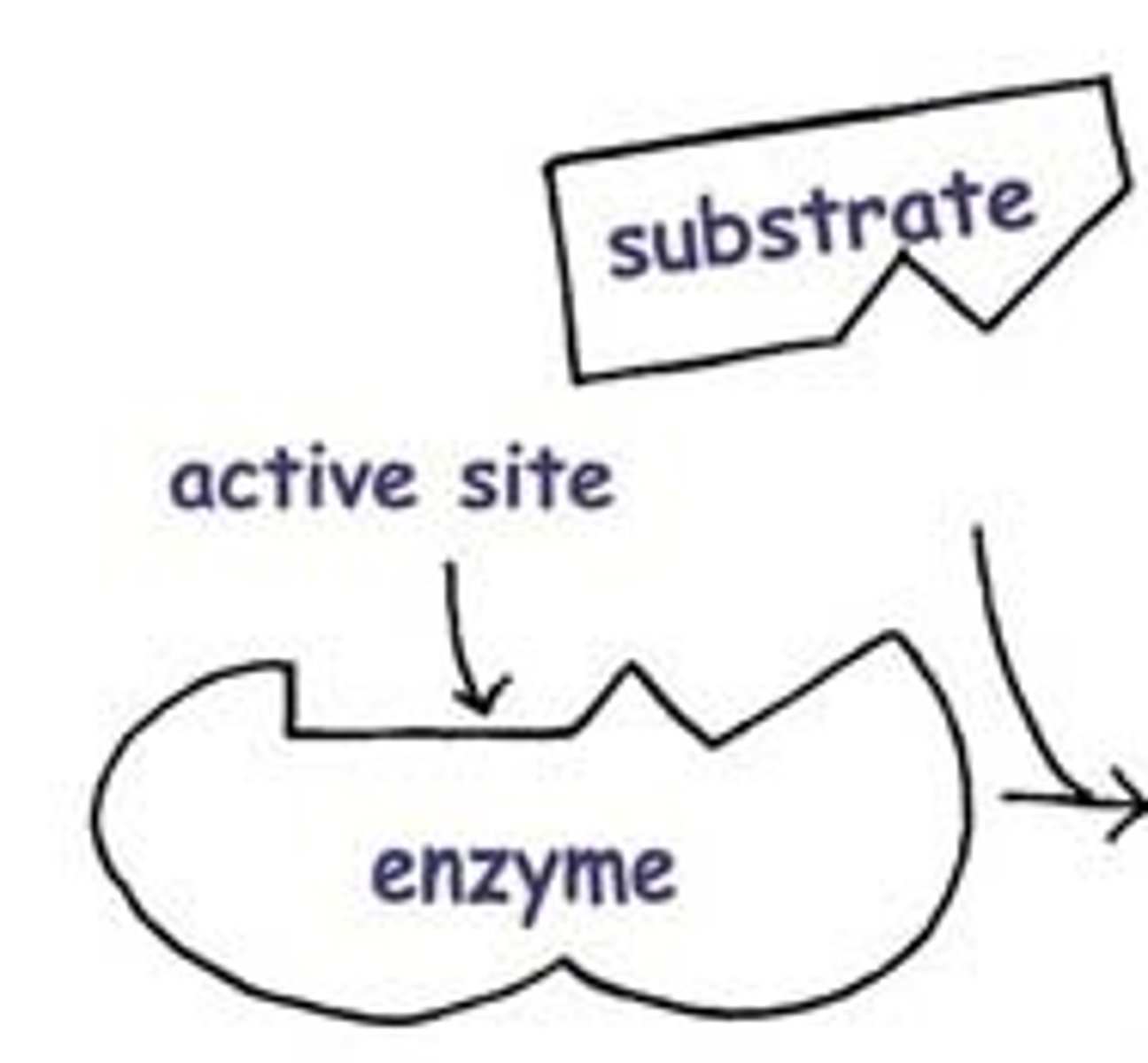
What is the active site?
The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds.
True or false: Enzymes fit with any shape of molecules.
FALSE. Each substrate/reactant has a unique shape. The have a specific substrate the work on
An enzyme's activity can be affected by what three factors?
Temperature, pH and Concentration of the Substrate
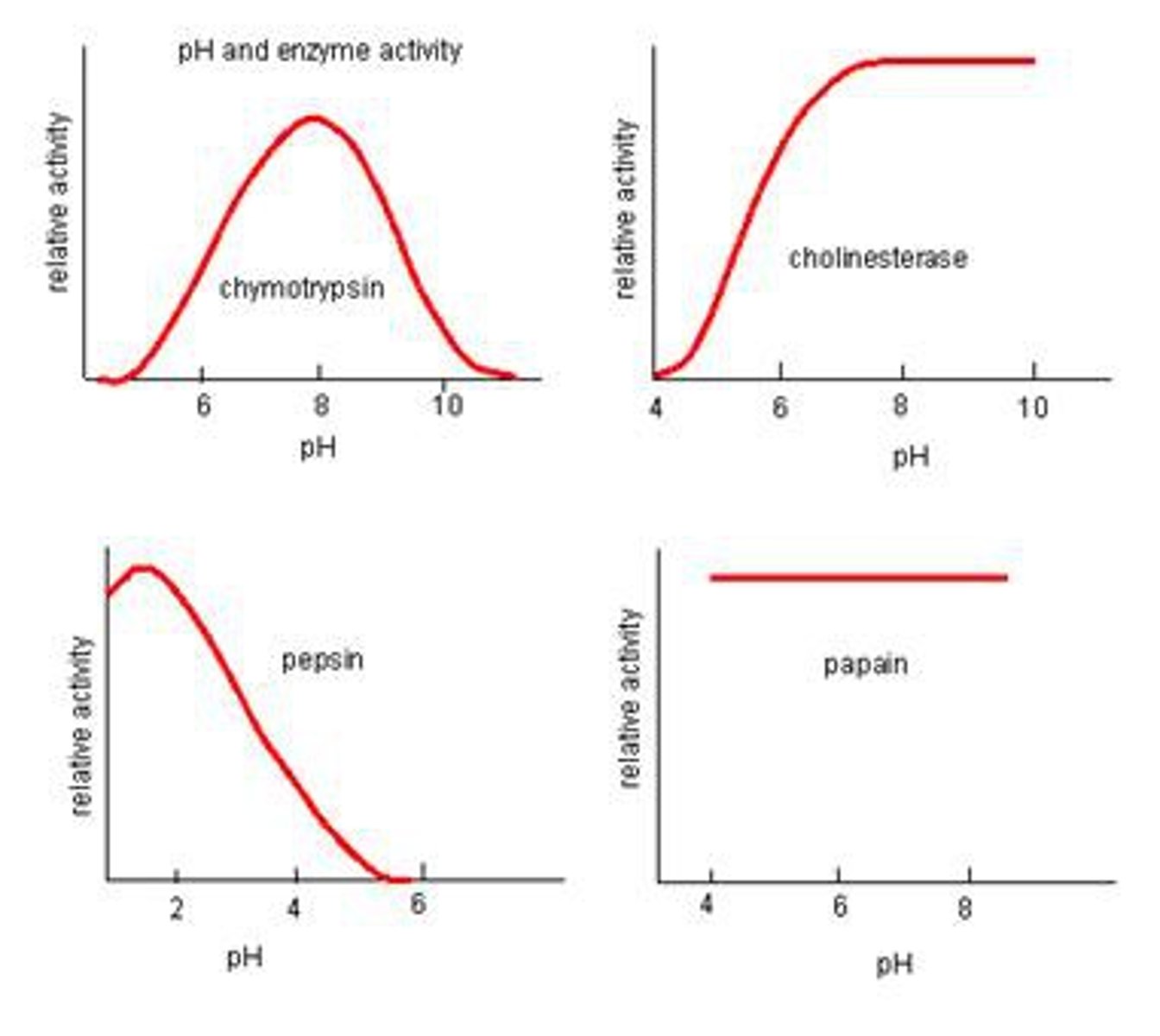
Each enzyme has an optimal _________ and _________ in which it can function.
Temperature / pH
Some enzymes reside in specific organelles, such as...
Enzymes for cellular respiration are located in mitochondria
The names of enzymes mostly end in
" ASE" Protease
Exception: Pepsin
Amylase enzyme works on what substrate?
Starch in the human mouth
Lactase works on what substrate?
Lactose in the human small intestine
Pepsin works on what substrate?
Protein in the human stomach
Catalse works on what substrate?
Blood and human cells creating H2O2 Hydrogen Peroxide
Lysomsomes
Contain enzymes that digest waste and damaged organelles so the cell can dispose of them
Activation Energy
The energy required to initiate a reaction.
Optimal Enzyme Temperature Graph
The temperature at which each enzyme specifically works at. In this graph it is 37 degrees C or 98.6 degrees F.
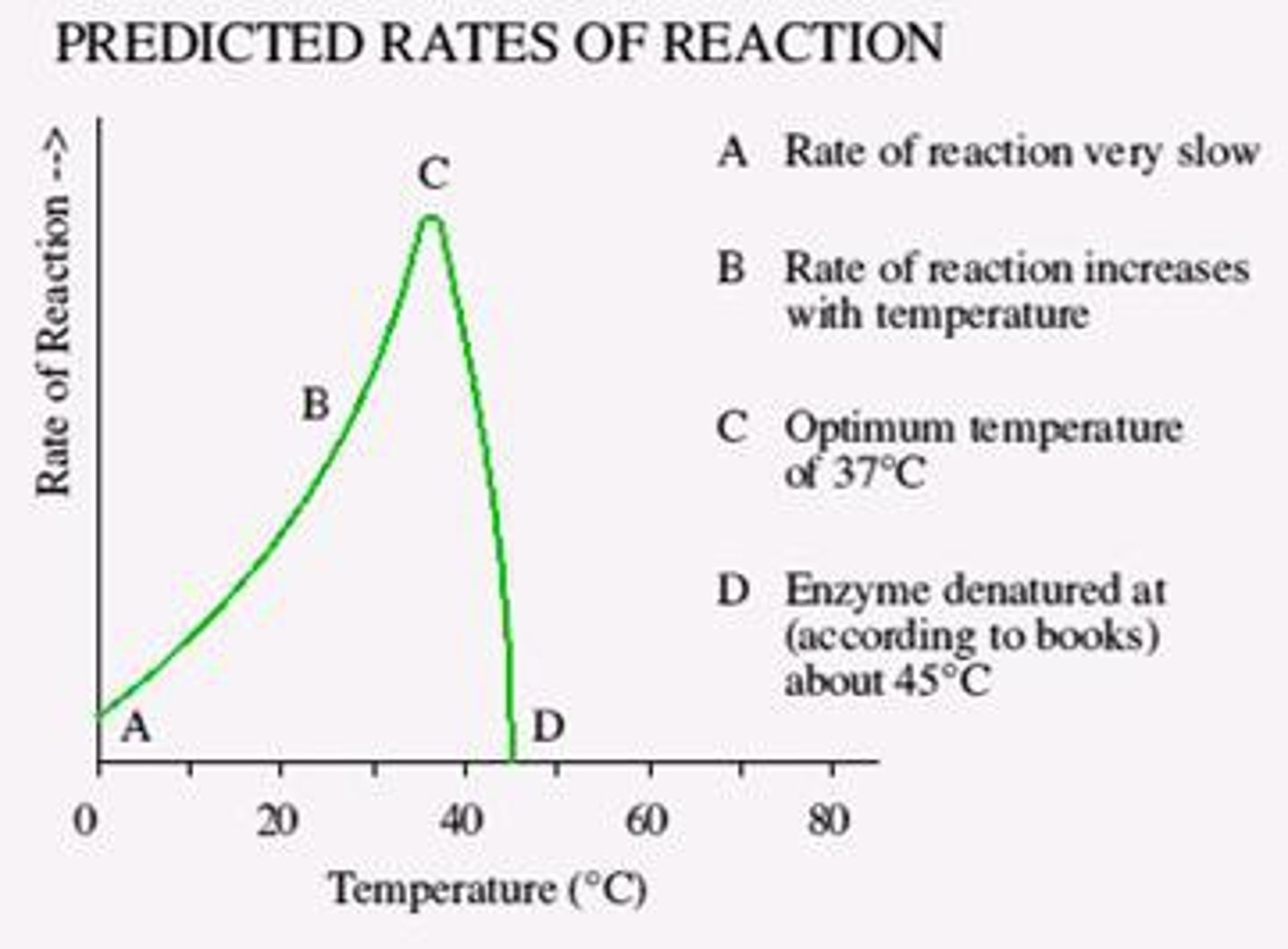
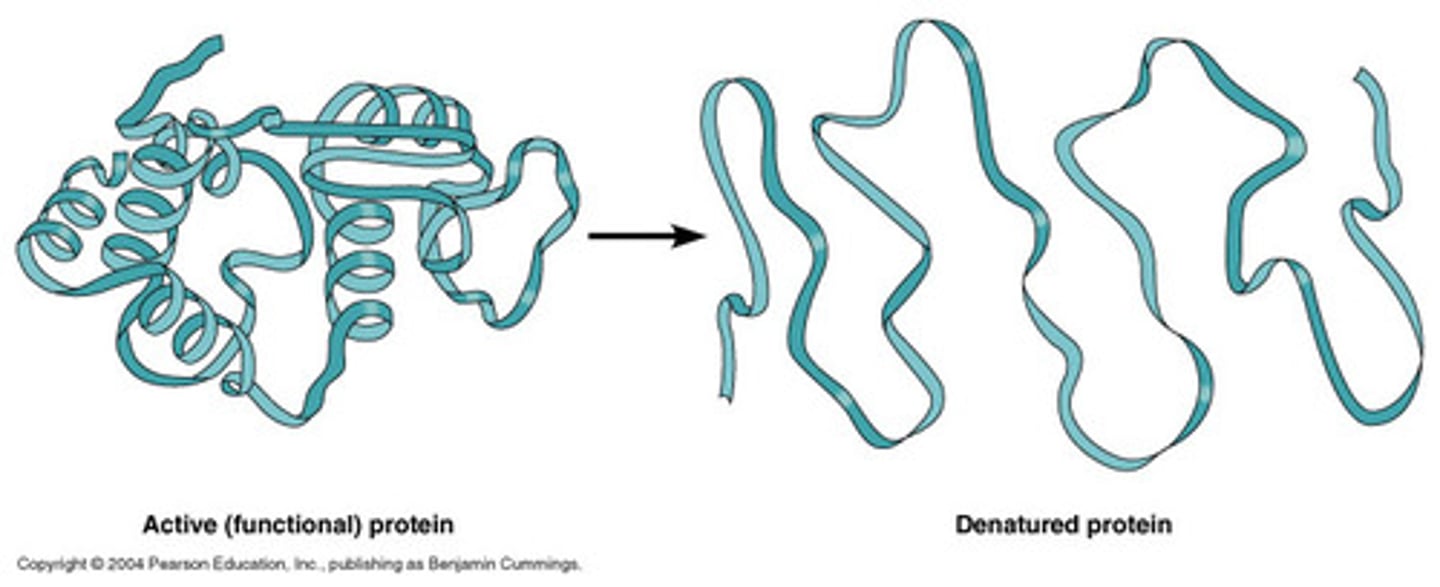
to Denature (verb)
to destroy the characteristic properties of (a protein or other biological macromolecule) by heat, acidity, or other effects that disrupt its molecular conformation.
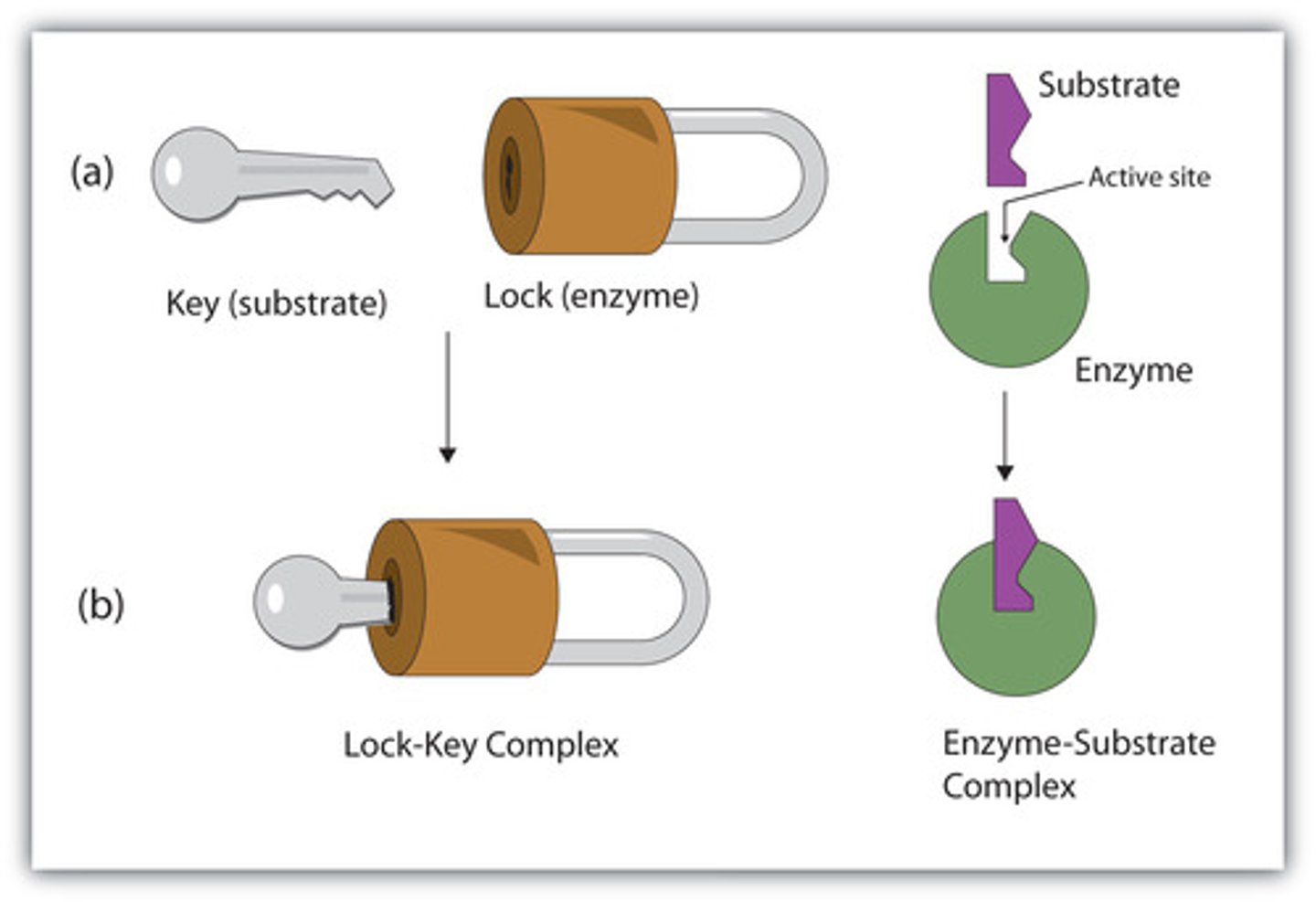
Lock and Key Model
Enzymes are specific. The only wok on the substrate that they "fit." Just like a lock has a specific key to open it.
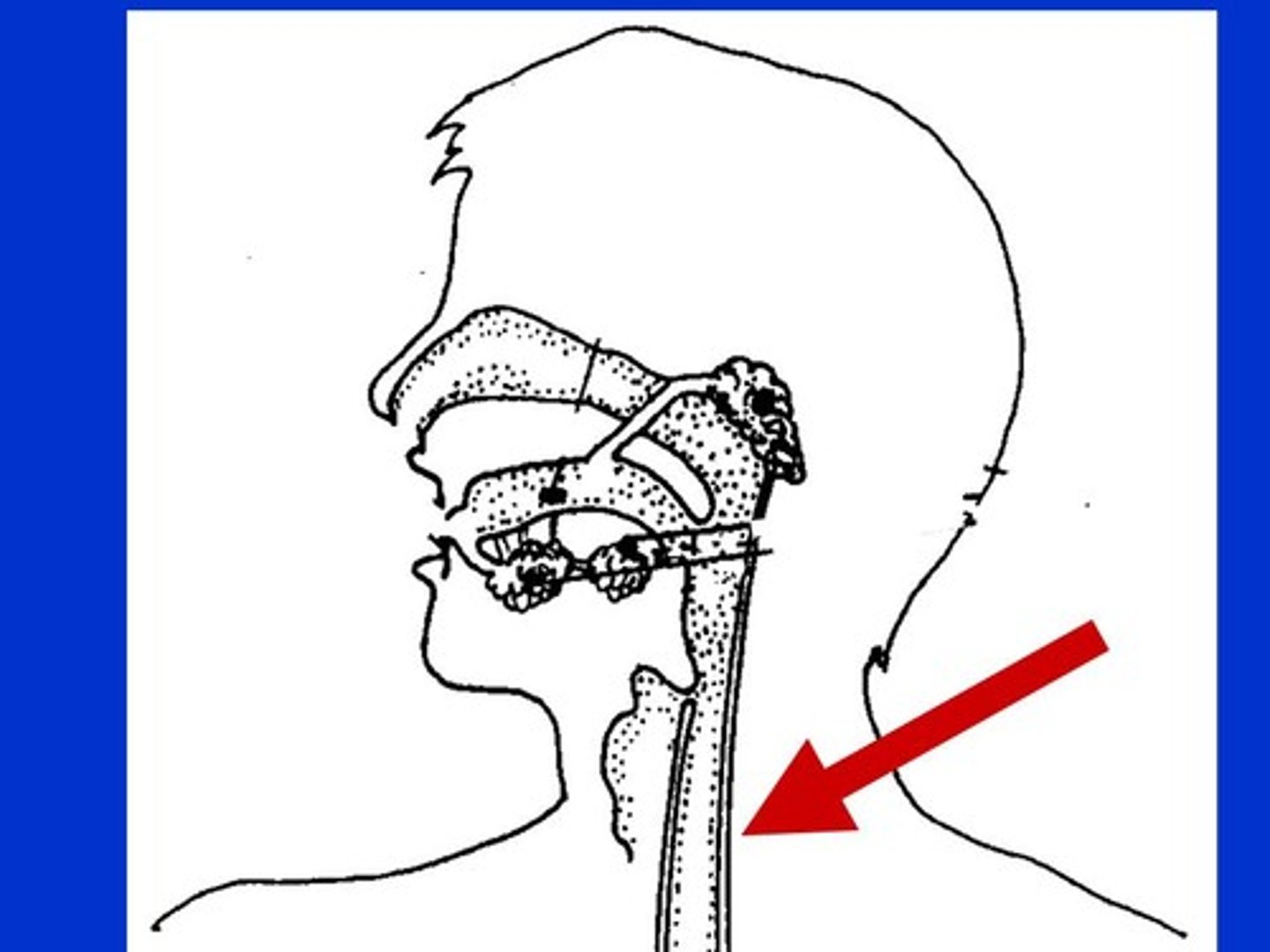
Nasal passages
The hollow spaces in the nose through which air flows from the nostril to the pharynx, responsible for filtering, moistening and warming air.
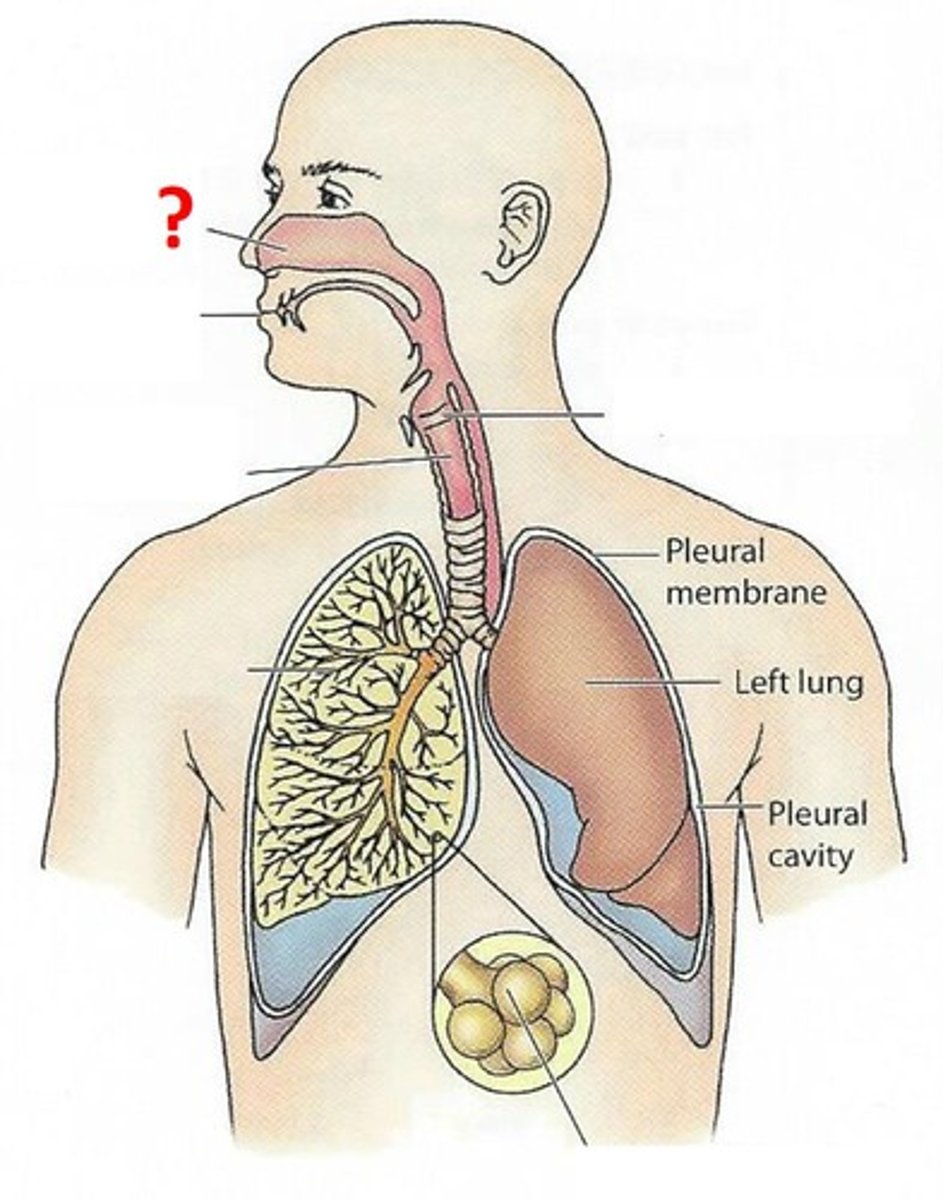
Mouth
starting point of the digestive system and secondary starting point of the respiratory system after the nasal passage. Has a tongue that helps to shape sounds produced in the larynx.
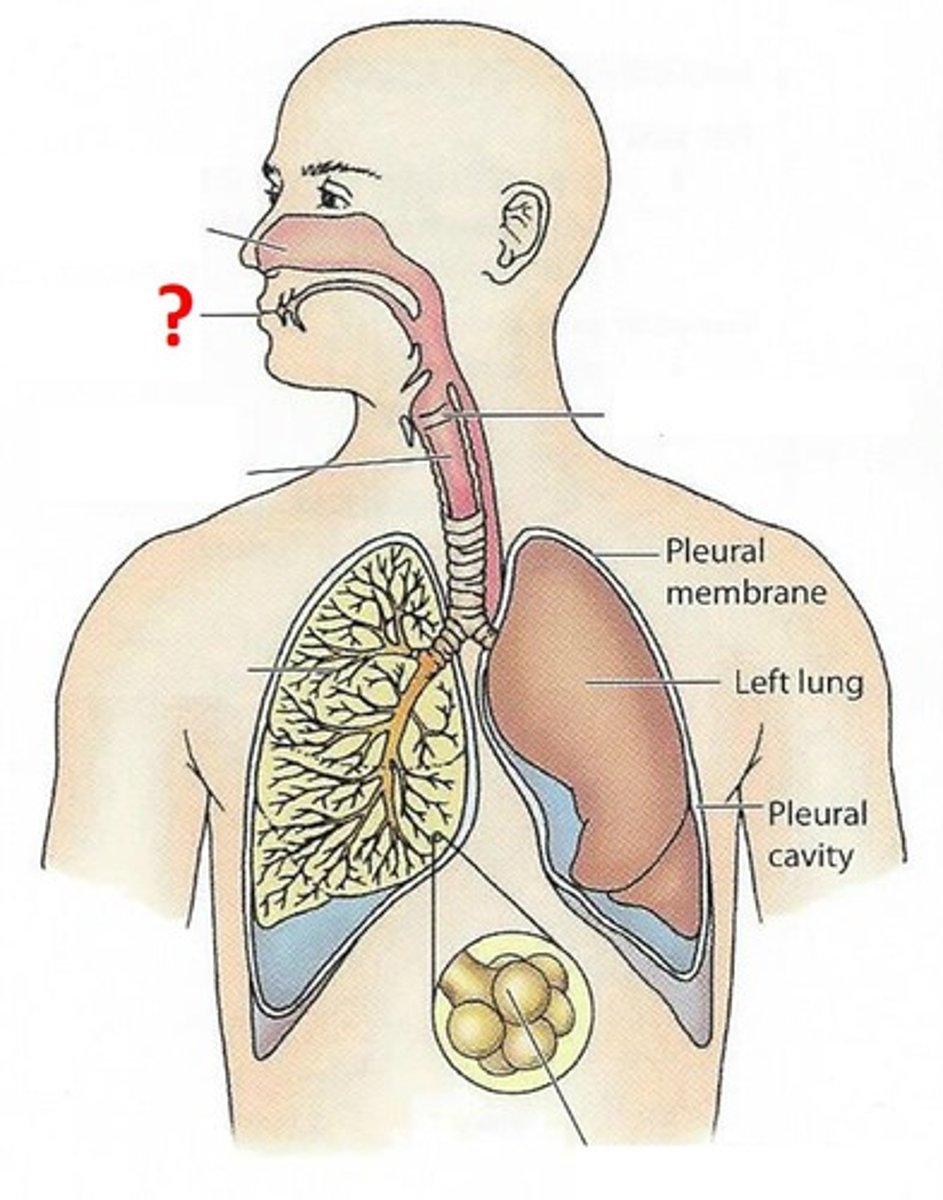
Larynx
the area of the throat that contains the vocal cords and produces vocal sounds.

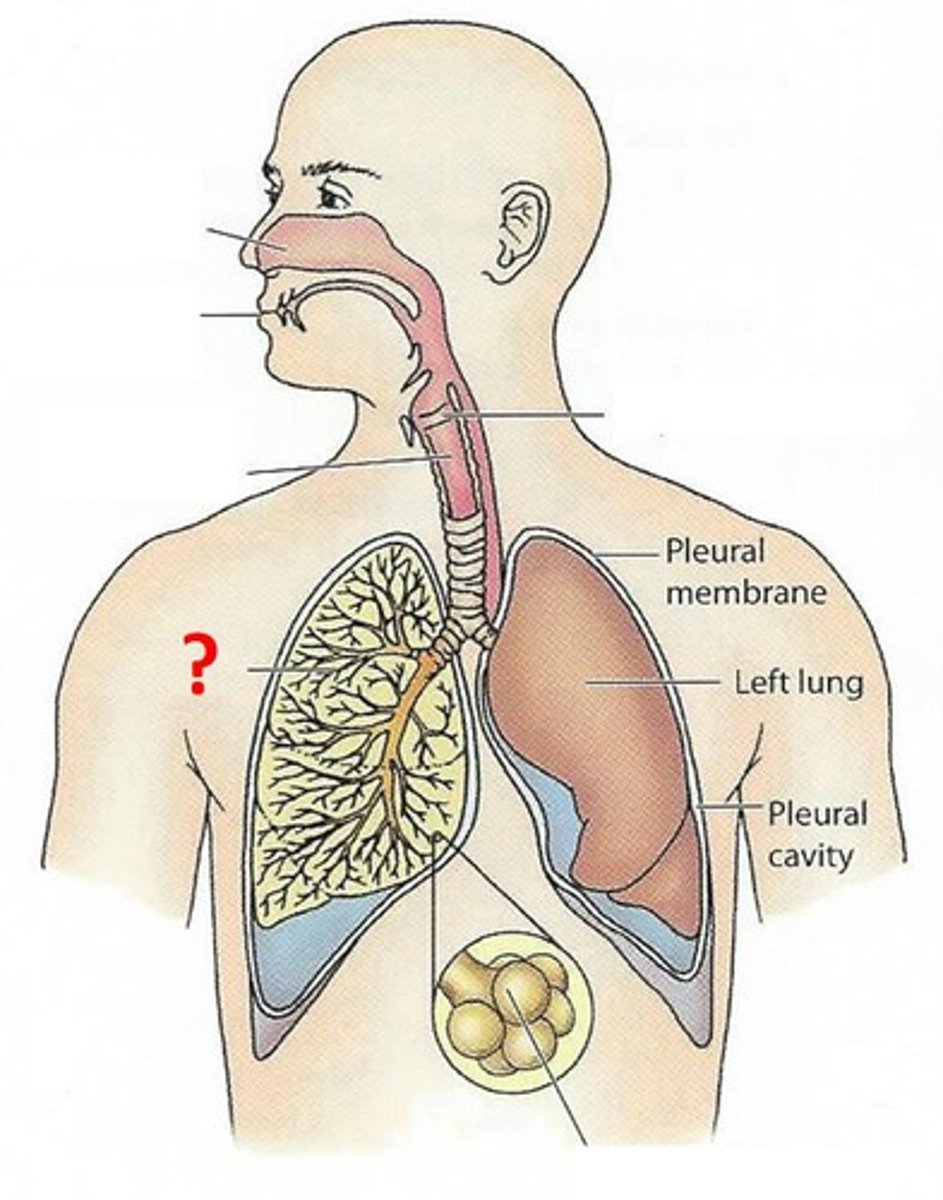
Lung
organs through which an animal gets oxygen from the air.
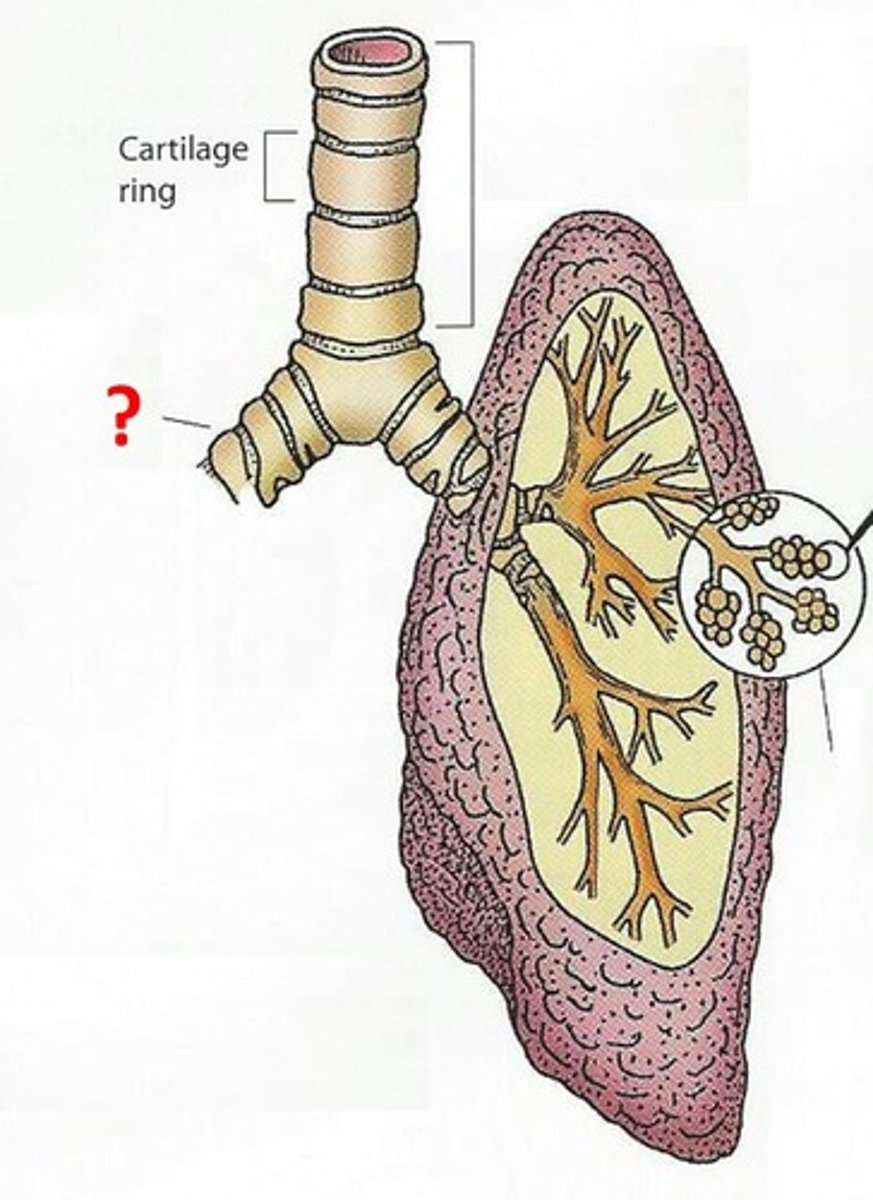
Bronchus
one of the two tubes (bronchi is plural) that connect the lungs with the trachea.
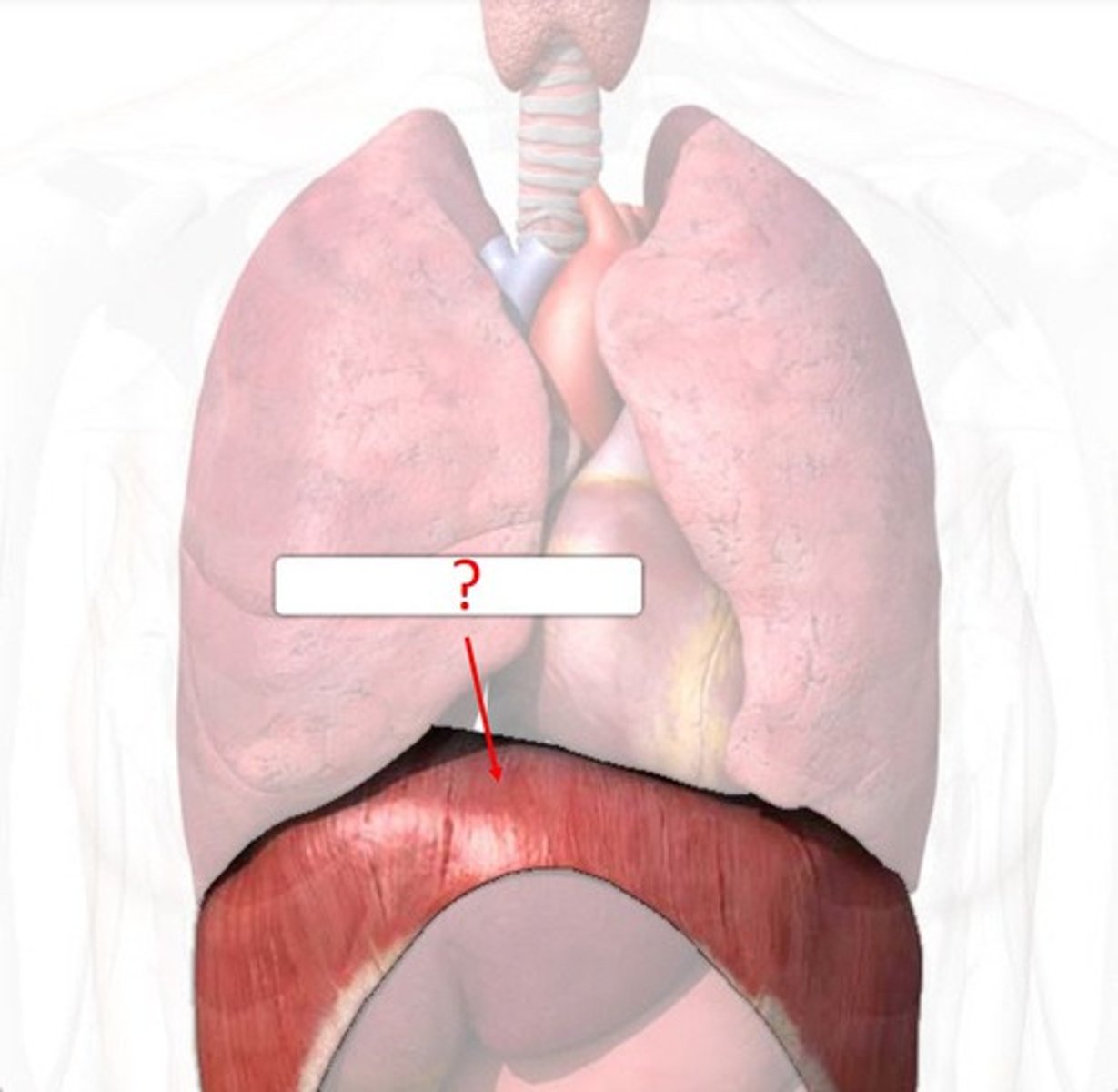
Diaphragm
a dome-shaped muscle beneath the lungs that helps with breathing.
Pharynx
a passage from the mouth to the larynx and esphogus.
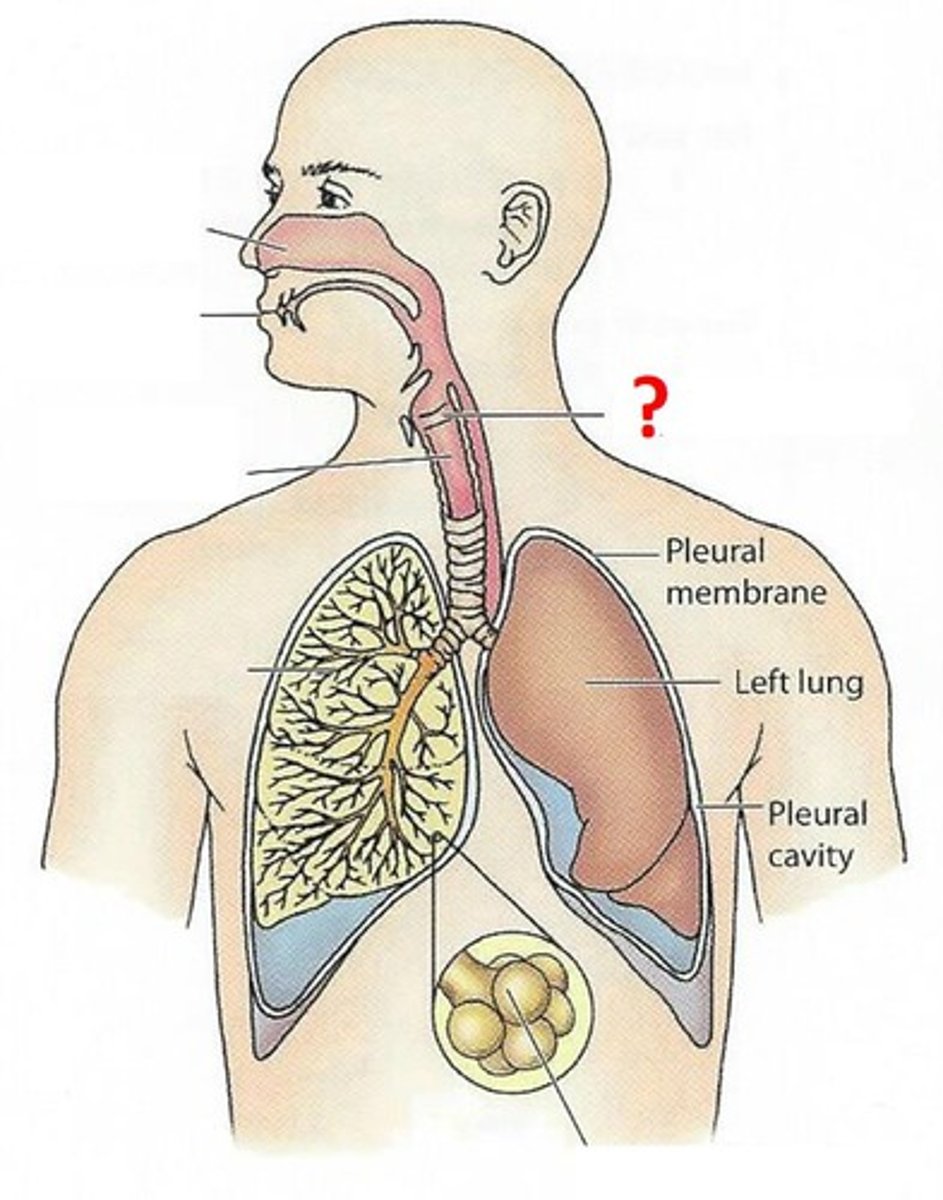
Trachea
the tube that connects the larynx to the lungs.
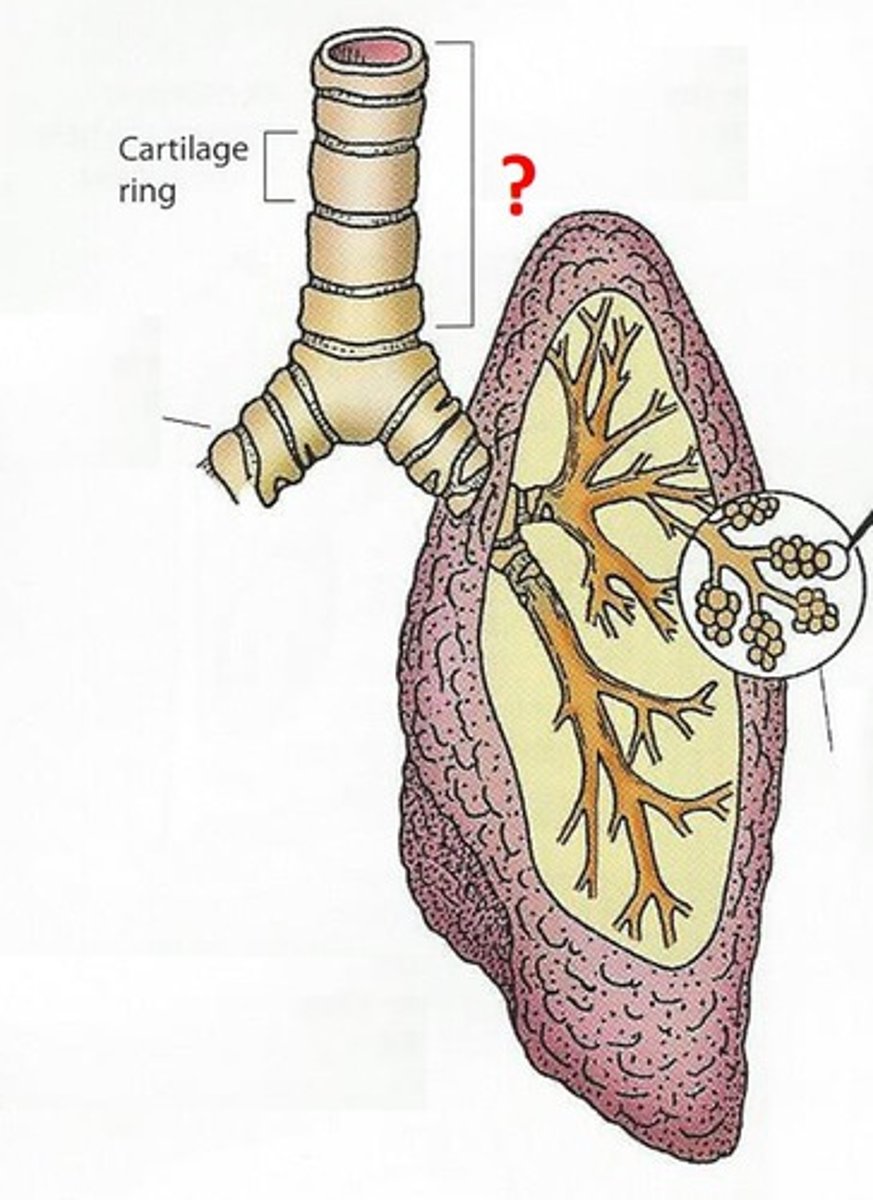
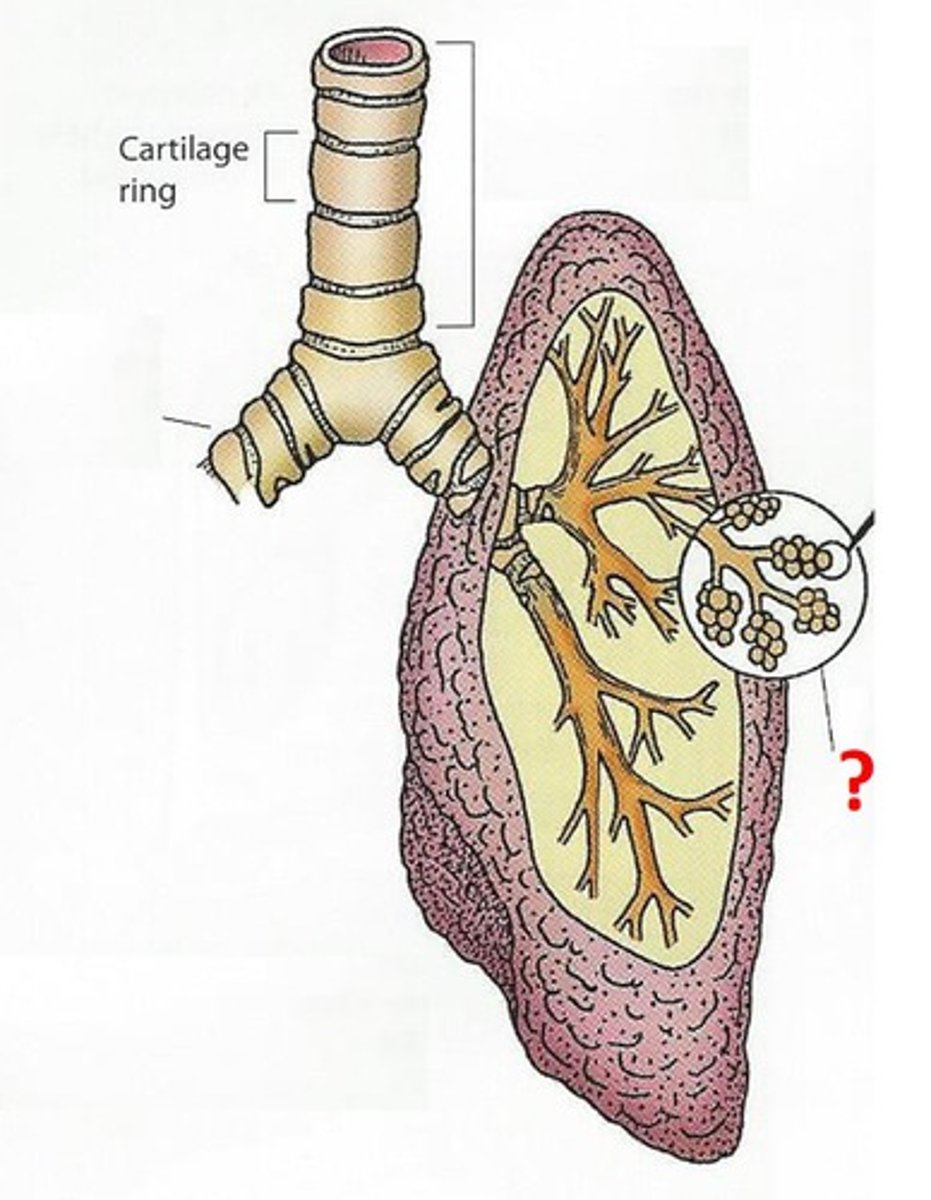
Bronchiole
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
Alveoli
any of the tiny air sacs of the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
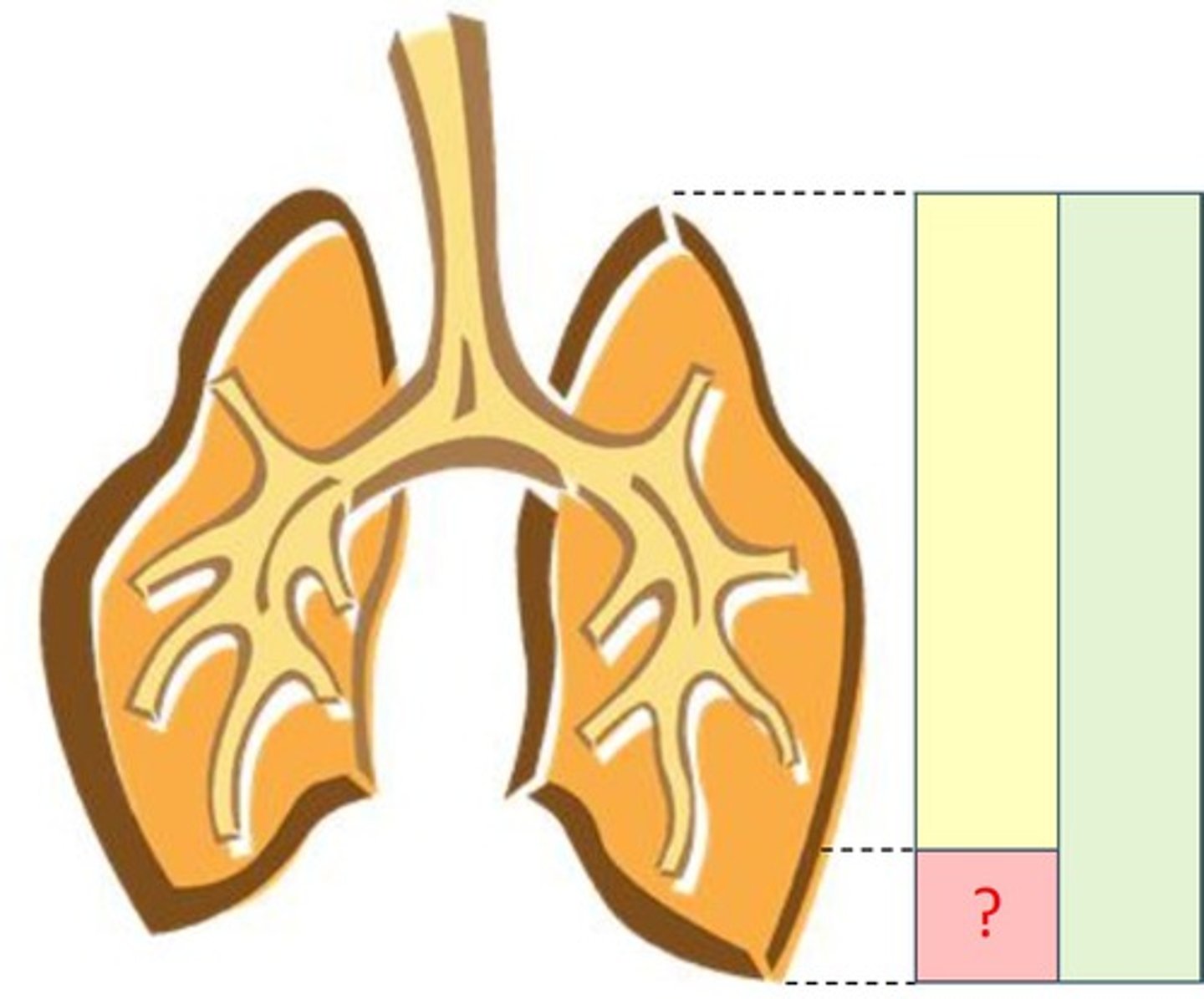
Total capacity
the total amount of air your lungs can hold.
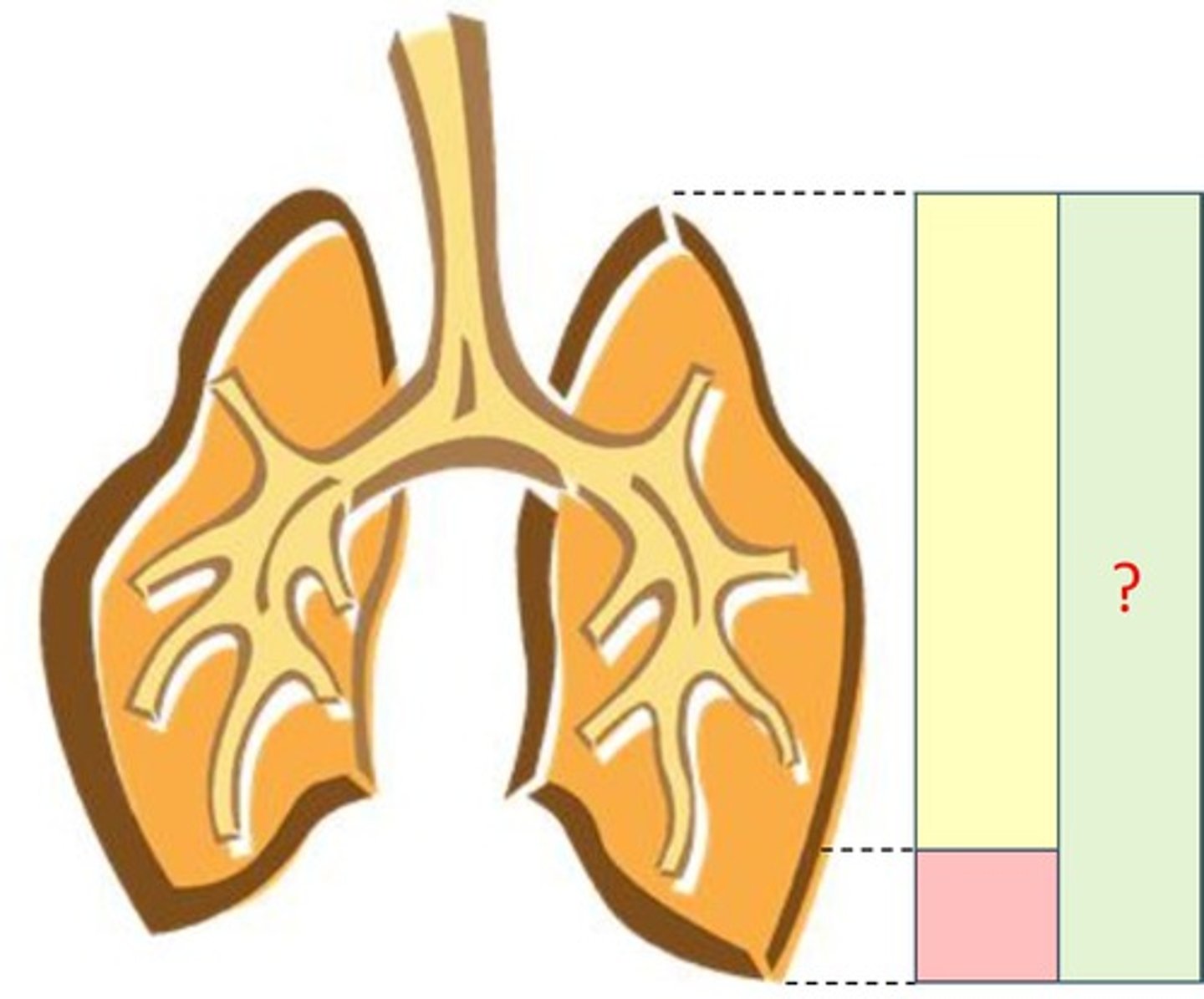
Vital capacity
the amount of air you can forcibly exhale from your lungs.
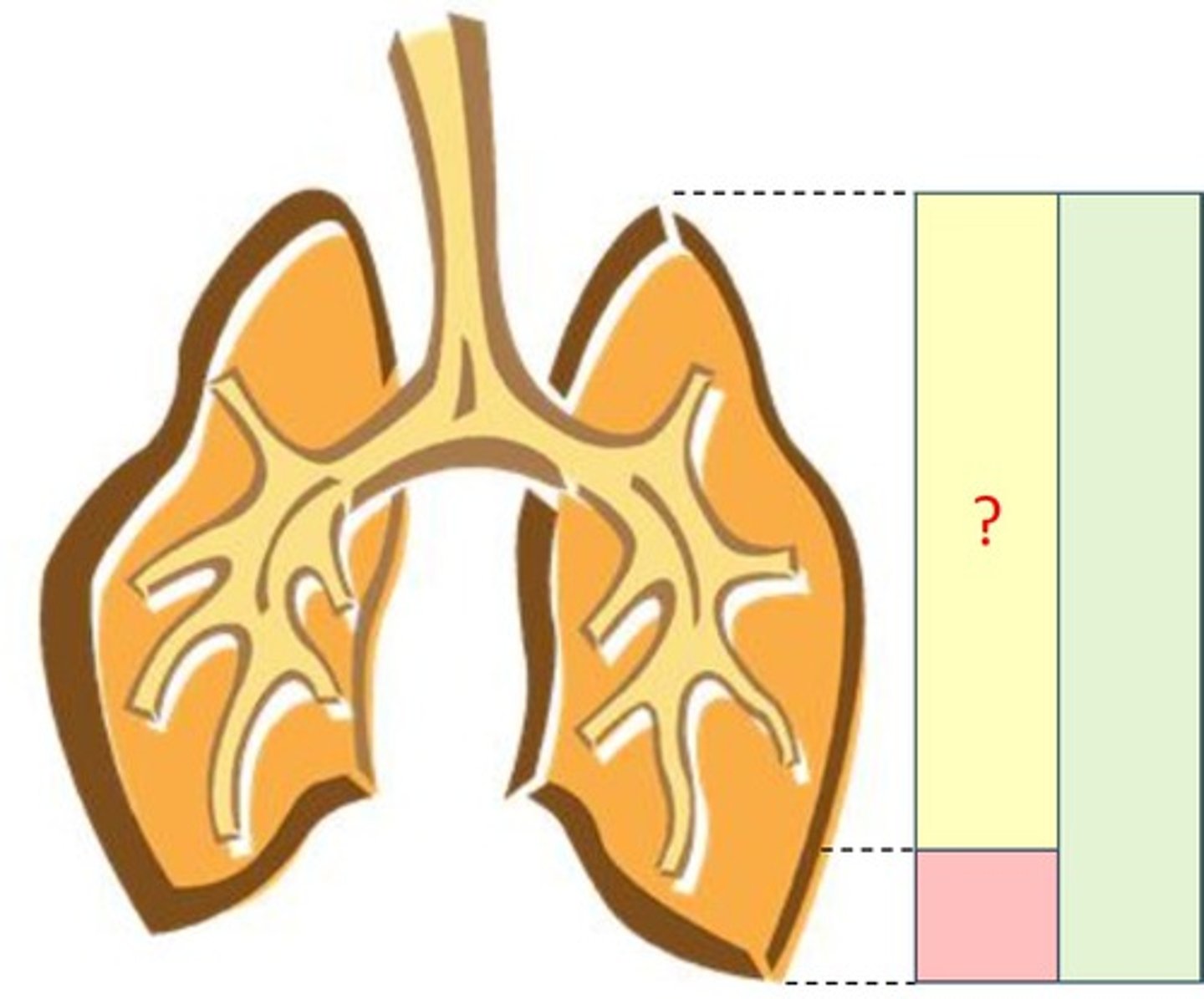
Residual capacity
the total amount of air remaining in your lungs after forcibly exhaling.
Cellular respiration
Is the process by which all living cells convert glucose (food) into ATP (energy).
Mitochondria/Cytoplasm
Site of cellular respiration.
All living organisms
are organisms that go through cellular respiration.
Cytoplasm
site of anaerobic respiration
Alcoholic Fermentation
Plants, yeast, and some micro-organisms break down pyruvic acid without oxygen to make 2 ATP and alcohol
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Animals (muscle cells) will break down pyruvic acid without oxygen to make 2 ATP and lactic acid.
Aerobic Respiration
Requires the use of oxygen.
Anaerobic Respiration
Does not require the use of oxygen
Krebs cycle
Occurs in the matrix, part of the mitochondria. Creates hydrogen ions that will later be used in the electron transport chain. The total number of ATP produced in this process is 2 ATP.
Electron Transport Chain
Occurs in the cristae part of the mitochondria. The total number of ATP produced is 32 ATP
2 ATP
total number of ATP from glycolysis
34 ATP
Total number of ATP produced in aerobic respiration
36 ATP
Total number of ATP produced for cellular respiration
Equation for respiration
(Note 36 ATP)

Three steps to respiration
Glycolysis
Kreb cycle
ETC (electron transport chain )
Energy source made in respiration
36 ATP
What does photosynthesis use from respiration
Co2 and H20
Reactants of respiration
oxygen and glucose
Products of respiration
CO2, H2O, and 36 ATP
Example of anaerobic respiration
Glycolysis
Alcoholic Fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the
Cytoplasm 2 ATP
Examples of Aerobic respiration
Krebs cycle
ETC
Produces hydrogen that will be later used
Krebs cycle
Process that takes hydrogen from Krebs to produces ATP
ETC
ETC occur in the
Cristae
Total number of ATP produced from ETC
32 ATP
Subatomic particle that stores energy
Electron
Specifically created by glycolysis
2 pryovic acid or pryovatic and 2 ATP
Were is energy stored?
Phosphate bonds
salivary amylase
Enzyme in the mouth that helps break down carbohydrates
bile
A secretion of the liver that emulsifies fats, preparing them for further digestion and absorption in the small intestine
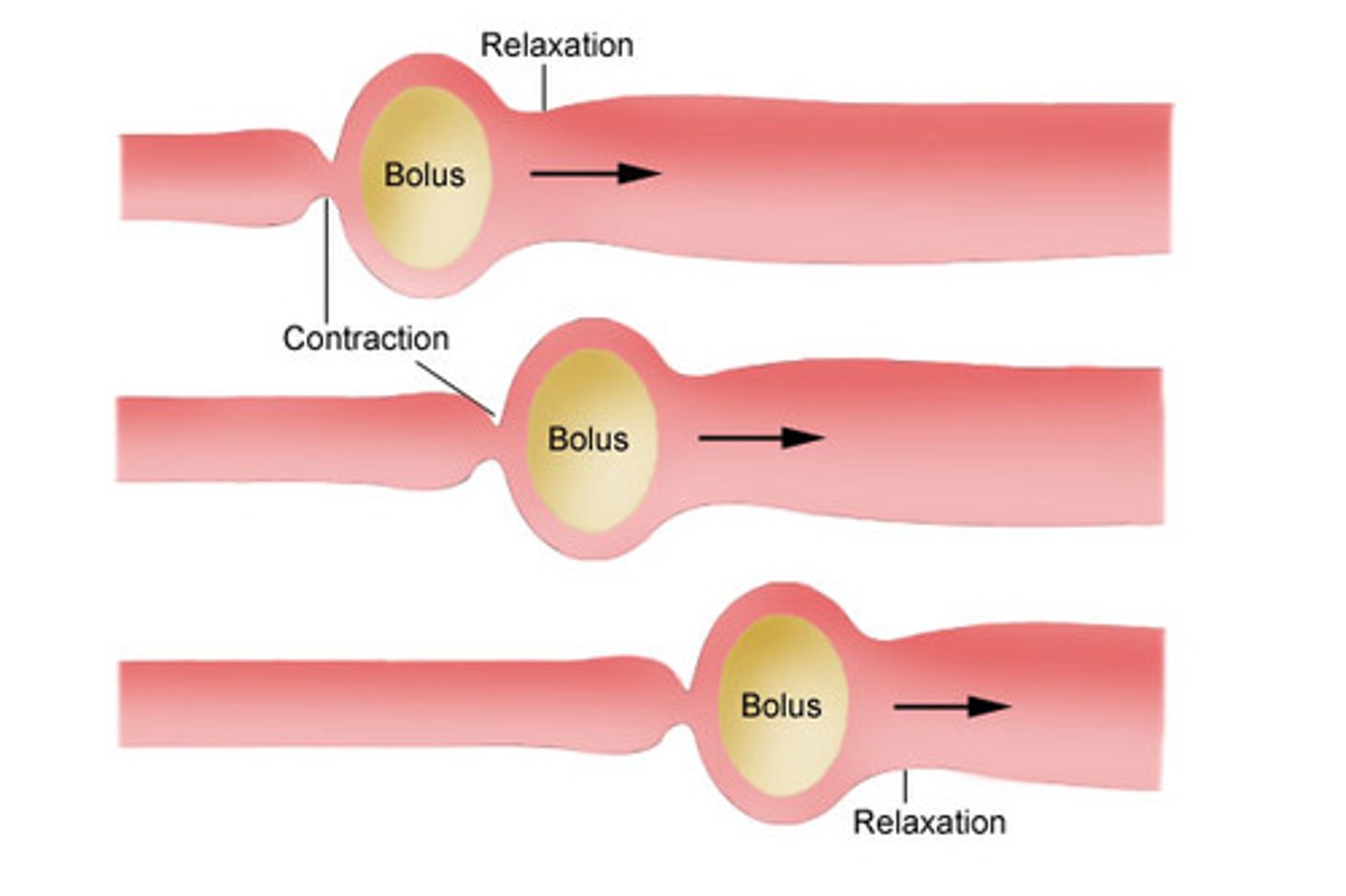
Peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
Lipase
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of fats and other lipids into individual fatty acids that can be absorbed into the bloodstream
mechanical digestion
Part of digestion that uses movement and muscles to break down food
oesophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.