The Circulatory System & The Heart
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Open circulatory system (definition)
Heart pumps blood into vessels that are open ended, blood leaves the vessels and flows around the cells before re-entering blood vessels.
Open circulatory system (Examples)
Insects, spiders, snails, slugs
Closed circulatory system (definition)
Blood remains in a continuous system of blood vessels e.g. animals
Advantages of a closed system
Blood can be pumped faster (nutrients & oxygen delivered faster, allows organism to be more active). Blood flow rate to different organs can be changed
Name the three blood vessels
Arteries. Veins. Capillaries
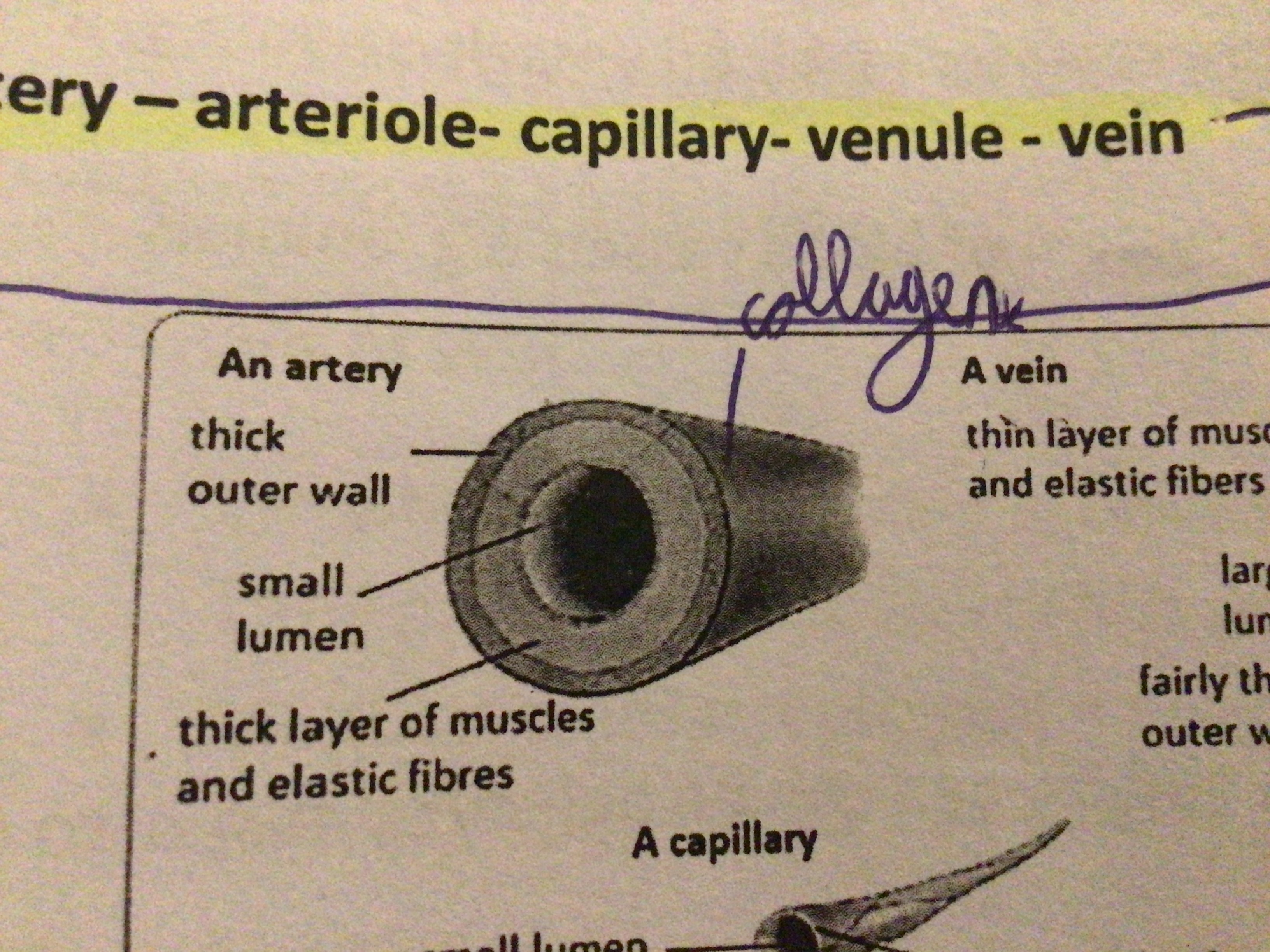
Artery Structure
No valves. Narrow lumen. Thick wall
What is the outside, inelastic layer of blood vessels made of?
Collagen
What is the middle layer of blood vessels made of?
Muscle and elastic fibre
What is the name of the cells that surrounds the lumen?
Endothelium
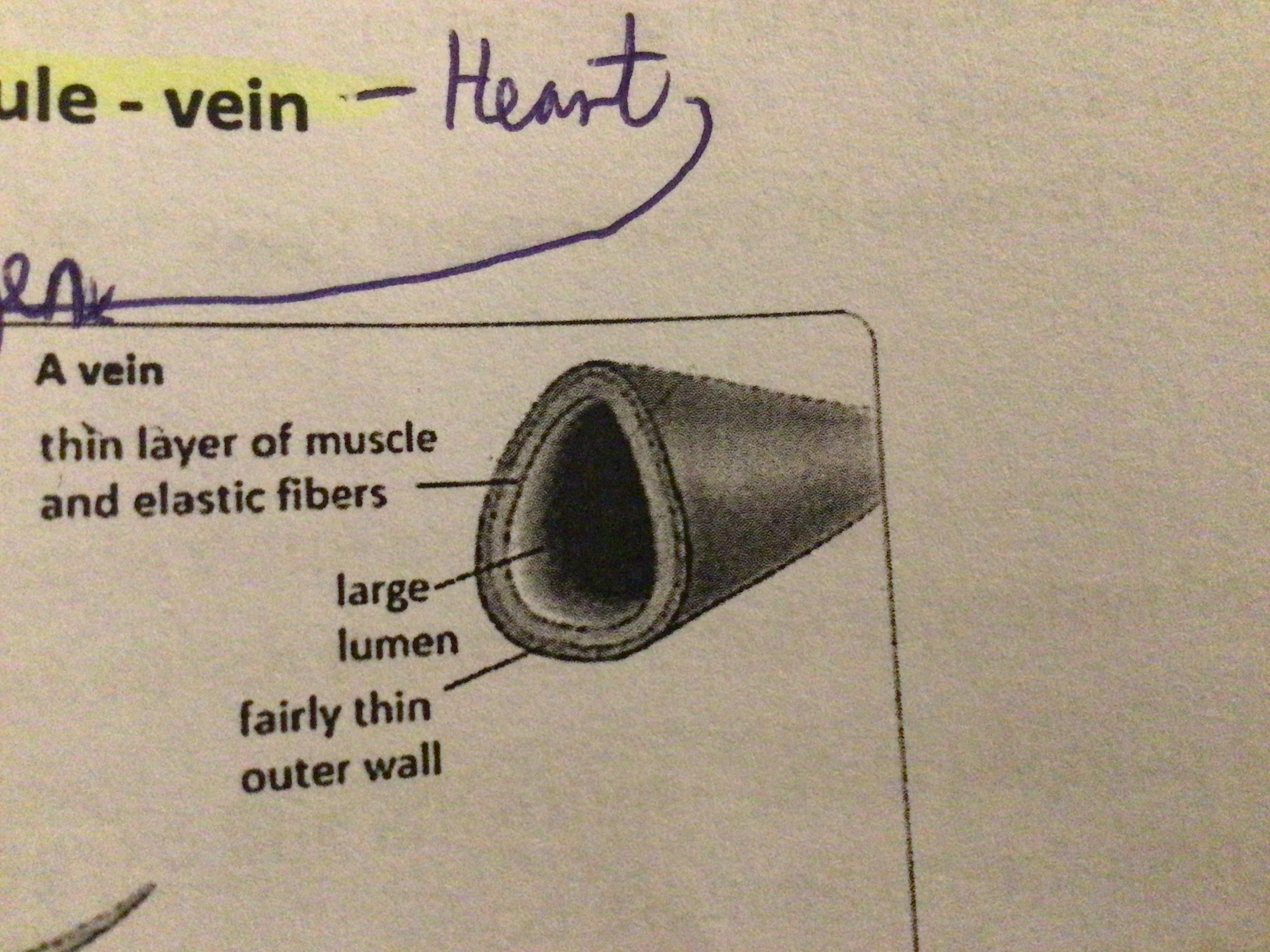
Vein Structure
Wide lumen. Thin walls. Has valves
Function of valves
Prevent the backflow of blood
Capillaries (Structure & Function)
Thin walls (One cell thick to exchange materials between blood and cells). Connects veins to arteries
Name the places blood goes as it travels through the body, starting at the artery
Artery - arteriole - capillary - venule - vein - heart
Draw a diagram of a vein
…
Draw a diagram of an artery
…
Where is the heart located?
Thoracic cavity (between the lungs and above the diaphragm)
What is the heart made of?
Cardiac muscle
What is cardiac muscle?
An involuntary muscle that is slow to fatigue
What is the pericardium?
A double membrane that surrounds the heart
Function of pericardium fluid
Helps reduce friction when the heart beats
Why does the left ventricle have thicker walls?
Pumps blood all around the body
Why does the right ventricle have thinner walls?
Pumps blood to the lungs
Draw a diagram of the heart
…
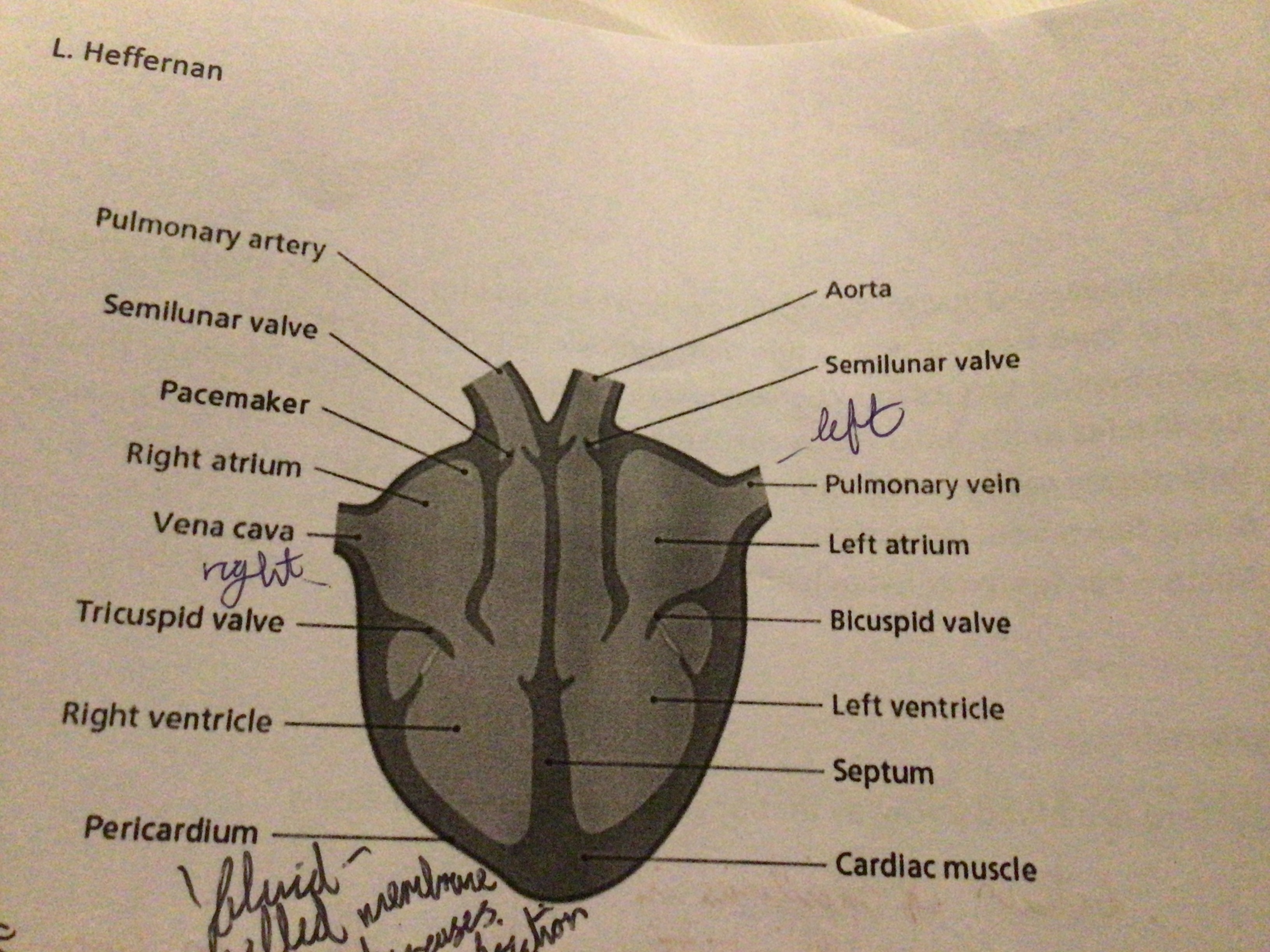
Aorta (What is it? & Function)
Main artery. Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body
Vena Cava (What is it? & Function)
Main vein. Carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
Pulmonary Artery (Function)
Carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Pulmonary Vein (Function)
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
What are the names of the two circuits?
Pulmonary circuit. Systemic circuit
Pulmonary circuit
Heart - pulmonary artery (right side) - lungs - pulmonary vein (left side) - heart
Advantages of two circuits
Allows for deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood to be kept separate. Ensures blood pressure remains high enough to reach all parts of the body
The superior and inferior vena cava
Split in two. One Vena cava collects blood from the head (superior vena cava). Other collects it from the rest of the body (inferior vena cava)
Anagram for remembering which side of the heart carries oxygenated/deoxygenated blood
LORD (Left Oxygenated, Right Deoxygenated)
What is a portal system?
A blood pathway that begins and ends in capillaries
What two parts is the hepatic portal system between?
Capillaries in small intestine and capillaries in liver
Function of hepatic portal system
Nutrients from small intestine move directly to the liver for processing
Hepatic artery (function)
Carries blood from aorta into the liver
Hepatic portal vein (function)
Carries nutrients from small intestine to liver
Hepatic vein (function)
Carries deoxygenated blood with nutrients away from the liver
What supplies oxygenated blood to the heart?
Coronary arteries
Where do the coronary veins return blood?
Directly into the right atrium
Where do coronary arteries originate?
Base of the aorta
What is a common cause of a heart attack?
Blockage of the coronary arteries
Bicuspid valve location
Between left atrium and left ventricle
Bicuspid valve function
Prevents back flow of blood into left atrium
Tricuspid valve location
Between right atrium and ventricle
Tricuspid valve function
Prevents back flow of blood into right atrium
Semi-lunar valves location
At the base of arteries
Semi-lunar valves function
Prevents back flow of blood into heart
What causes the flow of blood through the heart?
The alternate contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle
Alternate name for a heartbeat
Cardiac cycle
What is diastole?
Relaxation of cardiac muscle
What is systole?
The contraction of cardiac muscle
First stage of the cardiac cycle
Blood enters through the vena cava and pulmonary vein. Atria and ventricles are in diastole
Second stage of the cardiac cycle
Pacemaker (SA node) sends out waves of electric impulses across the walls of the atria.
Third stage of the cardiac cycle
Atria are in systole, pressure of blood causes bicuspid and tricuspid valves to open. Blood enters ventricles
Fourth stage of the cardiac cycle
AV node carries impulses to the ventricles. Ventricles now in systole. Pressure causes semi-lunar valves to open and blood enters the aorta and pulmonary artery. Ventricles relax
What is the full name of the SA node?
Sinoatrial node
What is the full name of the AV node?
Atrial-ventricular node
Where is the SA node located?
Embedded in the top of the right atrium
Where is the AV node located?
Located in the septum between the right atrium and right ventricle
where can the pulse be felt and why?
In the wrist or neck as the arteries are close to the skin
Blood pressure (definition)
The force exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels (mainly arteries)
What does high blood pressure (hypertension) indicate?
The blood is struggling to move freely throughout blood vessels
What causes high blood pressure?
Blockage in arterioles and small arteries
How do medical professionals take blood pressure?
Record the pressure needed to stop the flow of blood in the major artery in the upper arm
What is the average blood pressure?
120/80
How to maintain a healthy heart
Exercise regularly (strengthens heart). Reduce fat, sugar, salt in diet to reduce heart attack risks and obesity. Don’t smoke
How does smoking effect the heart?
CO (carbon monoxide) reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen. Nicotine increases blood pressure
Describe how blood is moved through the veins
Moved by the contraction of skeletal muscles and the opening and closing of valves