BIOL 319 Lee - Exam 4
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
neuron
an individual specialized cell that conducts nerve impulses and that are found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
nerve
a bundle of neurons along with their connective tissue sheaths, blood vessels, and lymphatics
nervous tissue and muscle tissue
what are the two excitable tissues (meaning they have action potentials)?
3 major parts of the brain
- forebrain (prosencephalon)
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
brain stem
made up of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla
medulla oblongata
contains the BP, HR, RR centers as well as blood flow, swallowing, and vomiting
evolutionary significance of sulci/fissures
the wrinkles increase the surface area of the brain
cerebellum
- means "little brain"
- muscle tone
- spatial equilibrium
- balance and posture
- coordination (fine motor skills, hand-eye coordination)
- one of the first centers hit by ethanol
reticular activating centers
- contained within the midbrain
- caffeine hits receptors here
- essentially responsible for wakefulness/sleep-wake cycles
forebrain (prosencephalon)
houses the diencephalon and telencephalon
diencephalon
consists of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus
hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
houses the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the cerebellum
pons
controls balance and posture
multitasking
- what the female brain is better than the male brain at doing
- enlarged corpus callosum and higher number of synapses firing in the female brain allow this to be better
substantia nigra
- Latin for "black area"
- basal ganglia structure in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement
- contains dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta
Parkinson's disease
characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta
pyramidal tracts
looks like a pyramid in the brain and connects longitudinal association fibers, commissural fibers (corpus callosum), and projection fibers within the midbrain
limbic system/paleomammalian cortex
- made up of the amygdala, mamillary bodies, the stria medullaris, central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden
- functions to process and regulate emotions, manage behaviors, control motivation, form memories, influence autonomic nervous system, plays a key role in fight or flight, etc.
basal ganglia
what the limbic system interacts with when you see something scary
it helps build memory/learn
why is it important that we have an emotional response and brain re-wiring when experiencing something scary?
frontal lobe
- voluntary movement and thought
- cognition (think, reason, cause and effect)
- long term memory
parietal lobe
- taste (gustation)
- pressure
- touch
- temperature
- vibration
temporal lobe
- auditory
- short term memory
- emotions
- speech
- smell (olfactory)
occipital lobe
mainly involves/control vision
midbrain
controls consciousness (sleep/wake cycles)
caffeine
- binds to reticular activating center receptors to inhibit sleep
- inhibits ADH/vasopressin production which increases urine production
spinal cord
- muscle and tendon reflexes
- walking
- urination
- sex organ function
primary motor cortex
- anterior to central sulcus
primary somatic sensory cortex
- posterior to central sulcus
Broca's area
associated with speech formation and execution
Wernicke's area
associated with speech/language comprehension and interpretation
hypothalamus
- houses the satiety receptors (FULL)
- where the posterior pituitary hormones are made
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- functions to cushion the brain and provide nutrients
- located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater and the ventricles of the spinal cord
meninges
- the dura matter, the arachnoid matter, and the pia matter
- the primary function is to protect the central nervous system
epidural
- injection between L3 and L4 into the epidural space
- numbing from the waist down
- contains local anesthetics (-caines), vasoconstrictors, opioids, and alpha-agonsists
peptide hormones
- hydrophilic
- rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi to be vesicalized (stored)
- released when needed
- bind to cell surface receptor (2nd messenger)
- effects are FAST (seconds to minutes)
- ex: adrenaline/epinephrine
steroid hormones
- come from cholesterol (type of lipid)
- hydrophobic
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum (made AND released)
- "-one" or "-ol"
- bind to an intracytoplasmic receptor (dimer when bound)
- affect TXPN (genes turn ON and OFF)
- takes time, slow effect (hours to days)
- ex: testosterone (T, C19H28O2)
meningitis
signified by white blood cells being present in the CSF
filum terminale
pia matter that connects to the base of the sacrum and is ALSO a good source of CSF (should be fluid being no WBCs)
SSRIs
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- legal, by prescription only
- only block receptors in brain (takes about a month)
- antidepressants (block serotonin reuptake pump)
- serotonin will stay in the synapse because of blockage
SRIs
- serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- illegal, not prescribed
- include methamphetamines
- not just brain, all over body
- serotonin everywhere else goes way up so it goes way down in the brain (feel good first to feel bad later = feedback inhibition)
serotonin and dopamine
the two major feel-good neurotransmitters of the brain
opiates/narcotics
- types of systemic analgesics
- usually oral or IV
- massive hyperpolarization of pain centers in CNS (and centers in medulla oblongata)
- play into reward pathways of brain (addiction)
systemic analgesics
block pain no matter where the source is
local anesthetics
- pain killers
- "-caines"
- block at the source (wedge into VG Na+ channel like a doggie door)
- has to be injected into spot
- blocks depolarization which means A.P. can't start
guilian-barre' syndrome (GBS)
- largely idiopathic (don't know what causes it)
- sudden muscle weakness (hours to days, can lead to paralysis)
- prior to onset, there are a series of antecedent infections
antecedent infections (associated with GBS)
1. viruses (ex: mono)
2. bacterial infection (ex: tonsil infection)
3. respiratory infection (ex: pneumonia)
cranial nerves
1. olfactory nerve I
2. optic nerve II
3. oculomotor nerve III
4. trochlear nerve IV
5. trigeminal nerve V
6. abducens nerve VI
7. facial nerve VII
8. vestibulocochlear nerve VIII
9. glossopharyngeal nerve IX
10. vagus nerve X
11. spinal accessory nerve XI
12. hypoglossal nerve XII
inner ear fluid
within the semicircular canals of the ear and play a role in balance and detection of acceleration/deceleration (CN VIII)
proprioception/proprioceptors
- sensory function but motor nerves to muscles contain some of these types of afferent fibers
- the body's ability to ascertain body movements, direction, and position awareness
- muscles, tendons, and ligaments are mechanosensory neurons
CN II
cranial nerves associated with vision
CN III, IV, VI
cranial nerves associated with double vision
olfactory nerve I
- sense of smell (note that smell is linked to memory)
- lesions to it cause inability to smell
olfactory bulbs
larger in vertebrates that have a better sense of smell
chemoreceptors
consists of both smell and taste
optic nerve II
- vision
- blindness on the affected side when lesions to nerve occur
optic chiasm
- the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross
- found in all vertebrates located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus
oculomotor nerve III
- motor to eye muscles and upper eyelid
- parasympathetic to the sphincter of the pupil (causes constriction) and the ciliary muscle of the lens
- issues can cause double vision, blurred visions, and ptosis (eyelids drooping)
trochlear nerve IV
- motor to one eye muscle and the proprioceptive from that muscle
- contains some of the smallest motor units in higher vertebrates found within the muscles that control the eye
- injury can lead to double vision
- lens mineralize and cause cataracts
trigeminal nerve V
- mainly chewing (mainly V3) and give motor function to muscle of mastication
- sensory for teeth and gums, nasal cavity, scalp, forehead, nose, anterior two thirds of tongue, etc.
abducens nerve VI
- motor to one eye muscle and proprioceptive from that muscle
- lesions to nerve can result in double vision
facial nerve VII
- sensory, motor, and parasympathetic
- sense of taste, sensory from some external ear and palate
- proprioceptive from those muscles
- motor to muscles of facial expression, throat, and middle ear
- injury can cause loss of taste/sensation and decreased salivation
vestibulocochlear nerve VIII
- sensory
- special senses of hearing and balance
- injury can cause loss of hearing, balance and equilibrium, nausea, vertigo, and vomiting
- cochlea plays a role in hearing
glossopharyngeal nerve IX
- sense of taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
- carotid, sinus, and carotid body
- motor to pharyngeal muscle and proprioceptive from pharyngeal muscle
- parasympathetic increases salivary gland secretions
- injury causes loss of taste sensation and decreased salivation
vagus nerve X
- motor to intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- parasympathetic to thoracic and abdominal viscera
- goes all over the body
- parasympathetic to SA node of the heart (lowers HR using muscarinic ach receptors)
SA node of the heart
- brings the HR down
- will fire twice per second without the vagal tone
spinal accessory nerve XI
- most posterior cranial nerve in origin
- motor to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
- injury can cause difficulty elevating the scapula or rotating the neck
hypoglossal nerve XII
- motor to extrinsic tongue muscles (styloglossus, hypoglossus, and genioglossus)
- proprioceptive from those muscles
intrinsic tongue muscles
entirely WITHIN the tongue
extrinsic tongue muscles
attach the tongue to other structures
palsy
means paralysis
neuralgia
pain that is distributed to one or more nerves
phrenic nerve
- only spinal nerve
- innervates the diaphragm
brain vs spinal cord
gray matter on outside and white matter inside VS white matter outside and gray matter inside (butterfly shape)
respiration
involves the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles (especially inhalation)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves
- 12 pairs of cranial nerves
- somatic branch, autonomic branch, and enteric branch
- transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment
somatic branch of PNS
- voluntary
- afferent (sensory) nerves which go INTO spinal cord
- efferent (motor) nerves go away from spinal cord (skeletal muscle is only outward manifestation)
autonomic branch of PNS
- involuntary
- parasympathetic (rest and digest)
- sympathetic (fight or flight)
enteric branch of PNS
involves the GI tract (the most forgotten branch of the PNS)
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
saltatory conduction
when the A.P. jumps from node to node over the myelin sheaths (nodes of ranvier)
myelination
- PNS: Schwann's cells
- CNS: oligodendrocytes
- increases A.P. conduction velocity (APCV)
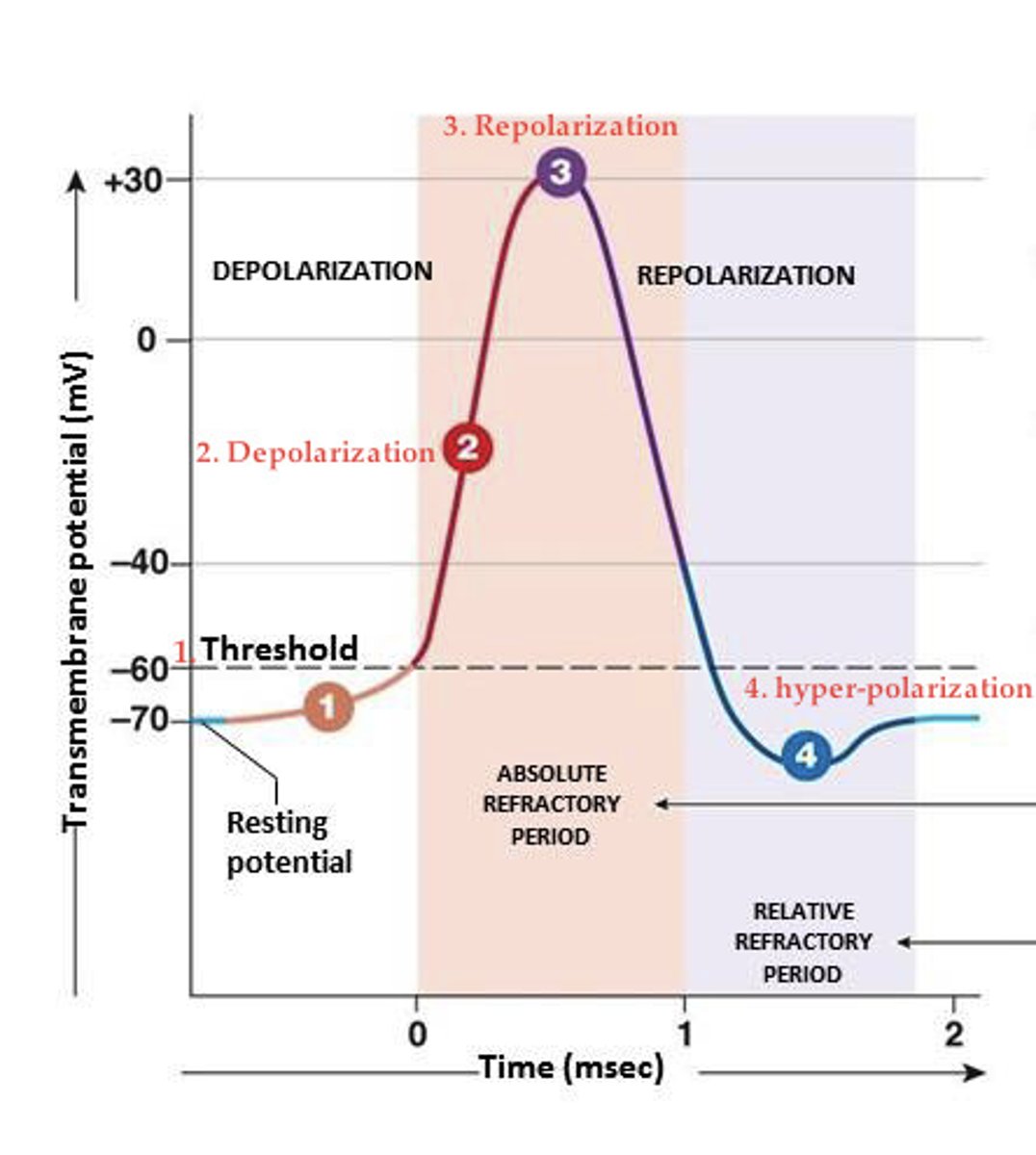
refractory periods
- absolute (no new AP generated during this time, time when VG Na+ channel gates are resetting)
- relative (can generate a new AP during this time, need a stronger stimulus to get back to T)
sympathetic nervous system
- fight or flight
- not default
- stronger and faster due to sympathetic chain and epinephrine/adrenaline
- thoracolumbar nervous system (middle of vertebral column sandwich)
- control skeletal muscle
parasympathetic nervous system
- rest and digest
- default system
- weaker and slower
- craniosacral nervous system (bread of vertebral column sandwich)
- control of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands
pre-ganglionic fiber and post-ganglionic fiber
both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system have them
ganglion
a group of cell somas/bodies that are OUTSIDE the CNS
acetylcholine within nervous system
- the pre- and post-ganglionic NT of parasympathetic system
- the pre-ganglionic NT of the sympathetic nervous system
norepinephrine
- post-ganglionic NT of sympathetic nervous system in the brain
- hormone in the blood is stronger that NTs
the numbers are higher
why are hormones stronger than NTs?
example of sympathetic nervous system when scared
- blood flow increases in brain and skeletal muscle
- blood flow decreases in GI and reproductive organs
blood flow to skin when scared
- initially goes down to prevent bleeding out
- overheating occurs so then it goes up
- sweat will also increase (side note)
fiber lengths in parasympathetic
- pre-ganglionic nerve is long
- post-ganglionic nerve is short
fiber lengths in sympathetic
- pre-ganglionic nerve is short (form a little chain which makes it stronger)
- post-ganglionic nerve is long
- note that the adrenal medulla is a part of the short fiber (epinephrine/adrenaline)
5 layers of the epidermis (superficial to deep)
1. stratum corneum
2. stratum lucidum
3. stratum granulosum
4. stratum spinosum
5. stratum basale
5 regions of the bone growth plate (epiphysis to diaphysis)
1. cartilage (chondroblasts create cartilage)
2. proliferation (high levels of hyperplasia - # of cells increase)
3. hypertrophy (cells become bigger)
4. calcification (HA comes into play, cell with HA undergoes apoptosis but HA stays)
5. ossification (new diaphysis forms)
from diaphysis up to epiphysis
what direction does bone growth occur?
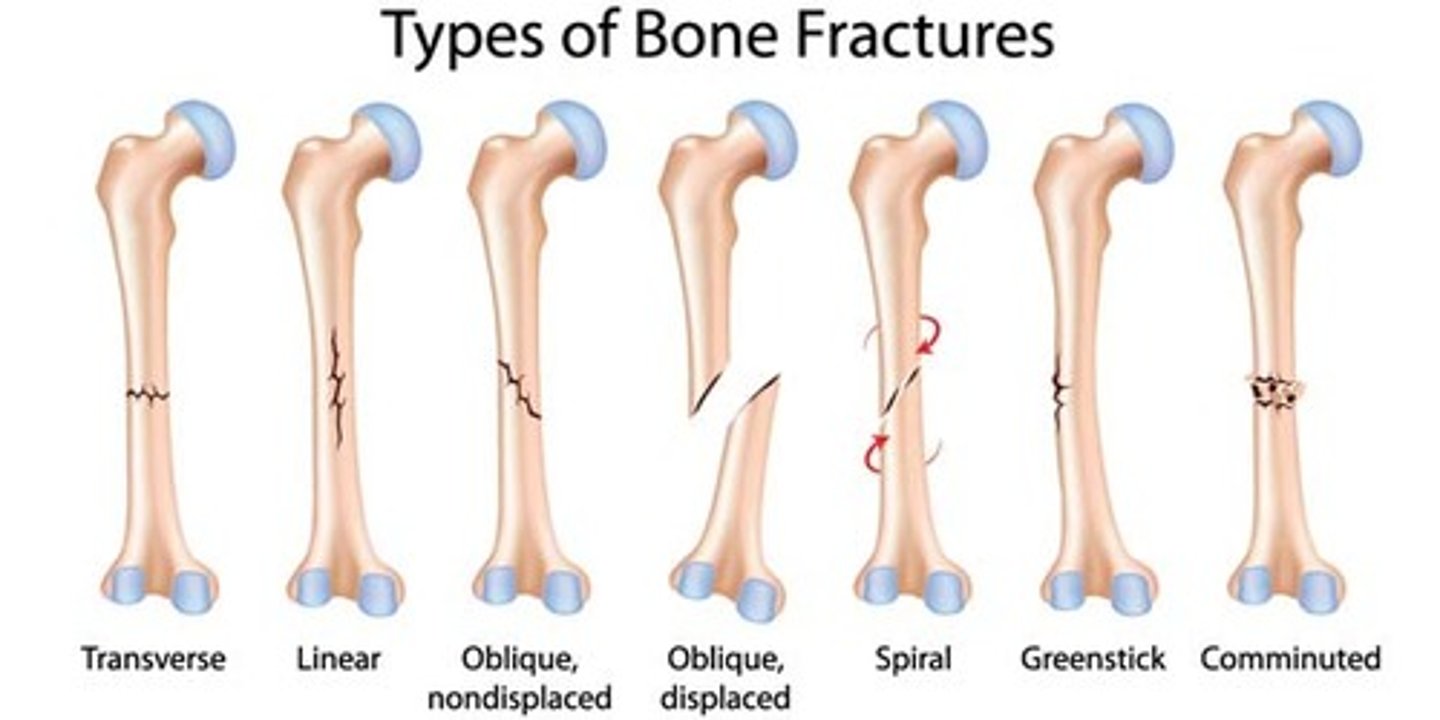
bone fractures
- remember that compound goes through the skin and is a full break
- comminuted is little pieces
action potential in neuron and skeletal muscle
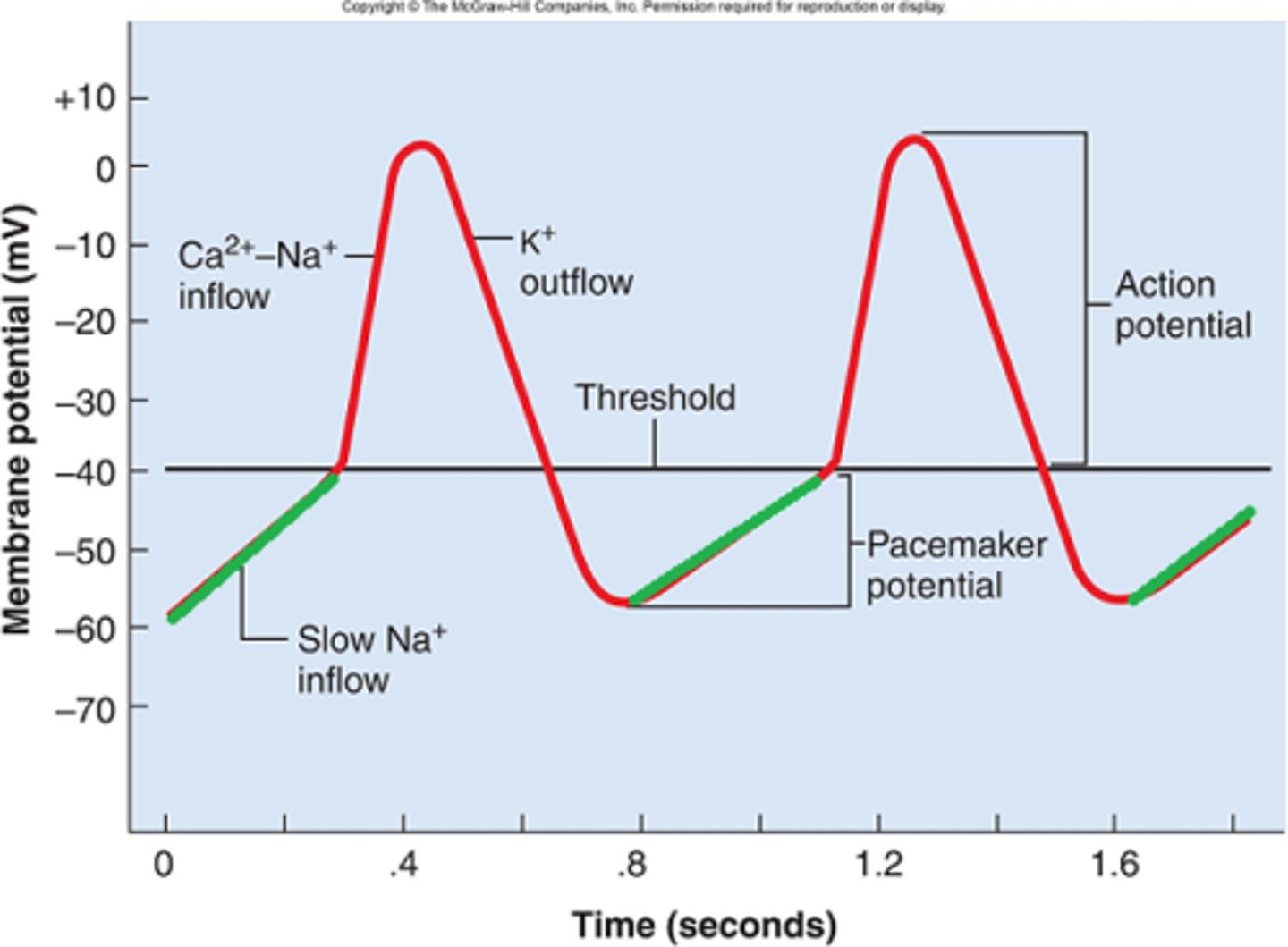
action potential in SA node