IB 360 E1- Wk3 Evolutionary Hypothesis & Wk4 Phylogenies and Shared History
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the 3 major approaches to testing evolutionary hypotheses?
1) Experimental
2) Intraspecific (within-species) comparisons of adaptation
3) Phylogenetic comparative methods
How is the Experimental Approach Set Up?
manipulate independent variables to measure the dependent variable
keep all other variables the same
What is the goal of experimental approaches?
establish proximate causal links
What are the strengths of the experimental approach?
simple
establish clear causal links
What are weaknesses of the experimental approach?
typically not ethical to study in humans
limited in scopes
Intraspecific Comparisons of Data, Methods
correlates trait variation within a species with differences in environments and cultures to infer selection
Intraspecific Comparisons of Data, Goal
Identify conditions that may explain trait variation
can be used to inform future studies using experimental approach
Intraspecific Comparisons of Data, Strengths
uses existing natural experiments, more ethical
can test several covariates
Intraspecific Comparisons of Data, Weaknesses
correlation isn’t causation
confounding variables
Phylogenetic Comparative Methods
-uses information on the historical relationships of species (phylogenies) to tests evolutionary hypotheses
Phylogenetic Comparative, Goals
infer evolutionary history of some character across species
Phylogenetic Comparative, Strengths
allows us to account for shared evolutionary history (enhances accuracy)
can be applied to living and extinct organisms
Phylogenetic Comparative, Weaknesses
often assumes specific model of trait evolution
depends on quality and completeness of the phylogeny tree and data (could lead to biased results)
Tinbergen’s 4 Types of Biological Explanations
1) Development, Historical Sequence and Proximate Explanations (Ontogeny)
2) Evolutionary History, Historical Sequence and Ultimate Explanations (Evolution)
3) Mechanism, Slice in Time and Proximate Explanations (Causation)
4) Function, Slice in Time and Ultimate Explanations (Survival Value)
Benefits of Tinbergen’s Framework
helps identify hypotheses that are complementary
makes larger questions more tractable
Issues of Tinbergen’s Framework
modern techniques and understanding have blurred the boundaries of the categories
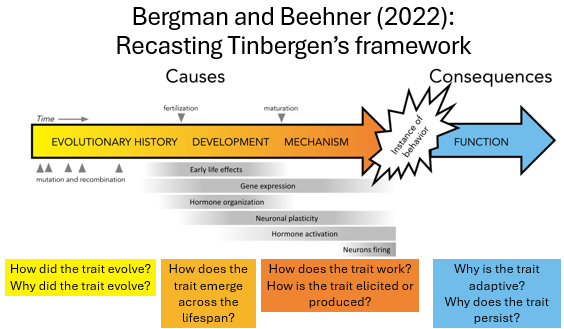
Draw Bergman and Beehner’s Recast of Tinbergen’s Framework
Contingency in Phylogeny
-existence of something depends on the existence of something else
Non-Independence in Phylogeny
-organisms share history, similarities between them can be due to shared ancestors who possessed those traits
Convergent Evolution in Phylogeny
-describes similarities that aren’t due to shared evolutionary history
Outgroups In Phylogeny
-allow the tree to be rooted
Nodes in Phylogeny
-represents a common ancestor
Branches in Phylogeny
-evolutionary connections between organisms
Terminal taxa in Phylogeny
-end points on phylogeny tree that represent the species being studied
What are phylogenies based on?
-built on shared traits (homologies) not homoplasy
-parsimony
What are 4 types of data used to construct phylogeny?
1) morphological
2) fossils
3) behavior
4) molecular
What region of DNA has the highest rates of nucleotide substitution?
-in regions that have the least effect on protein function noncoding
What are challenges in building phylogenies?
-homoplasy (convergent evolution)
-complex traits
-number of included taxa
Monophyletic Group
-includes the common ancestor and all the descendants
Paraphyletic Group
-includes the common ancestor and some but not all descendants
Polyphyletic Group
-includes organisms from different ancestors, no common ancestor