Preparing for a Physical Examination
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Physical Examination
A systematic assessment of a patient's body to identify any signs of disease or health issues.
Inspection
The visual examination of the body to assess the condition of the skin, posture, and overall appearance.
Palpation
The use of hands to feel the body's organs and tissues to assess their size, shape, and consistency.
Percussion
A technique involving tapping on the body to determine the underlying structure's density and presence of fluid.
Auscultation
The act of listening to internal body sounds, typically using a stethoscope, to assess the heart, lungs, and other organs.
Comprehensive Assessment
A thorough evaluation that includes a complete health history and physical examination, often used for new patients.
Focused Assessment
A targeted examination that addresses specific concerns or symptoms, often used for follow-up visits.
Patient Comfort
The state of physical and emotional well-being of the patient during an examination, crucial for accurate assessment.
Environmental Conditions
Factors such as lighting and noise level that can affect the quality of the physical examination.
Cardinal Techniques
The four primary methods used in physical examination: inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation.
Approach to the Patient
The manner in which a healthcare provider interacts with a patient, emphasizing calmness, organization, and professionalism.
Lighting Adjustments
Modifications made to the examination area to enhance visibility and facilitate accurate assessment.
Test Sequence Planning
The strategic organization of examination steps to ensure a systematic and efficient assessment.
Patient Positioning
The arrangement of the patient in a way that maximizes comfort and accessibility during the examination.
Hygiene Practices
The protocols, such as handwashing, that are followed to maintain cleanliness and prevent infection during examinations.
Reassurance Techniques
Methods used to comfort and alleviate patient anxiety during the examination process.
General Impression
The initial assessment of a patient's overall health and condition, observed as they enter the examination room and throughout the examination.
State of Consciousness
The level of awareness and responsiveness of a patient, which can range from alertness to coma.
Glasgow Coma Scale
A scoring system used to assess a patient's level of consciousness based on eye, verbal, and motor responses.

Signs of Distress
Observable indicators of a patient's discomfort or medical emergency, including respiratory, cardiac, or pain-related symptoms.
Height and Build
Physical measurements and observations regarding a patient's stature and body structure, which can indicate underlying health conditions.
Weight Assessment
Evaluation of a patient's body mass, which can reveal nutritional status and potential health risks.
Respiratory Distress
Symptoms indicating difficulty in breathing, such as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, or use of accessory muscles.
Cardiac Distress
Signs that may indicate heart-related issues, including chest tightness, sweating, and pallor.
Mental Disturbances
Cognitive or behavioral changes that may arise from acute or chronic conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or confusion.
Patient Instructions
Clear and polite communication of what is expected from the patient during the examination process.
Physical Examination Etiquette
Practices such as closing doors and curtains to ensure privacy and comfort for the patient during the examination.
Facial Expressions
Non-verbal cues that can indicate a patient's emotional state or level of discomfort.
Posture and Gait
Observations of a patient's body position and manner of walking, which can provide insights into their physical health.
Body Odor and Breath
Observable characteristics that can indicate underlying health issues or hygiene status.
Chronic Illness Indicators
Signs that suggest a patient may have long-term health conditions, affecting their overall appearance and behavior.
Acute Illness Indicators
Symptoms that suggest a sudden onset of health issues, requiring immediate attention.
Symmetry in Body Structure
The balanced proportions of a patient's body, which can reveal abnormalities or health conditions.
Central Obesity
Excess fat accumulation in the abdominal area, often linked to metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
Turner Syndrome
A genetic condition characterized by short stature and other physical abnormalities, often detectable through height assessment.
Marfan Syndrome
A genetic disorder that affects connective tissue, often resulting in tall stature and long limbs.
Cushing's Syndrome
A hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels, often indicated by central obesity and specific body fat distribution.
Weight Loss
A significant decrease in body weight that can indicate underlying health issues or changes in fluid balance.
Pallor
A pale appearance of the skin often associated with anemia or reduced blood flow.
Cyanosis
A bluish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to insufficient oxygen in the blood.
Jaundice
A yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood.
Skin Turgor
The skin's elasticity and hydration level, assessed by the speed at which a skin fold returns to its original position.
Body Odor
A characteristic smell that can indicate various health conditions, such as infections or metabolic disorders.
Vital Signs
Measurements of essential body functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature.
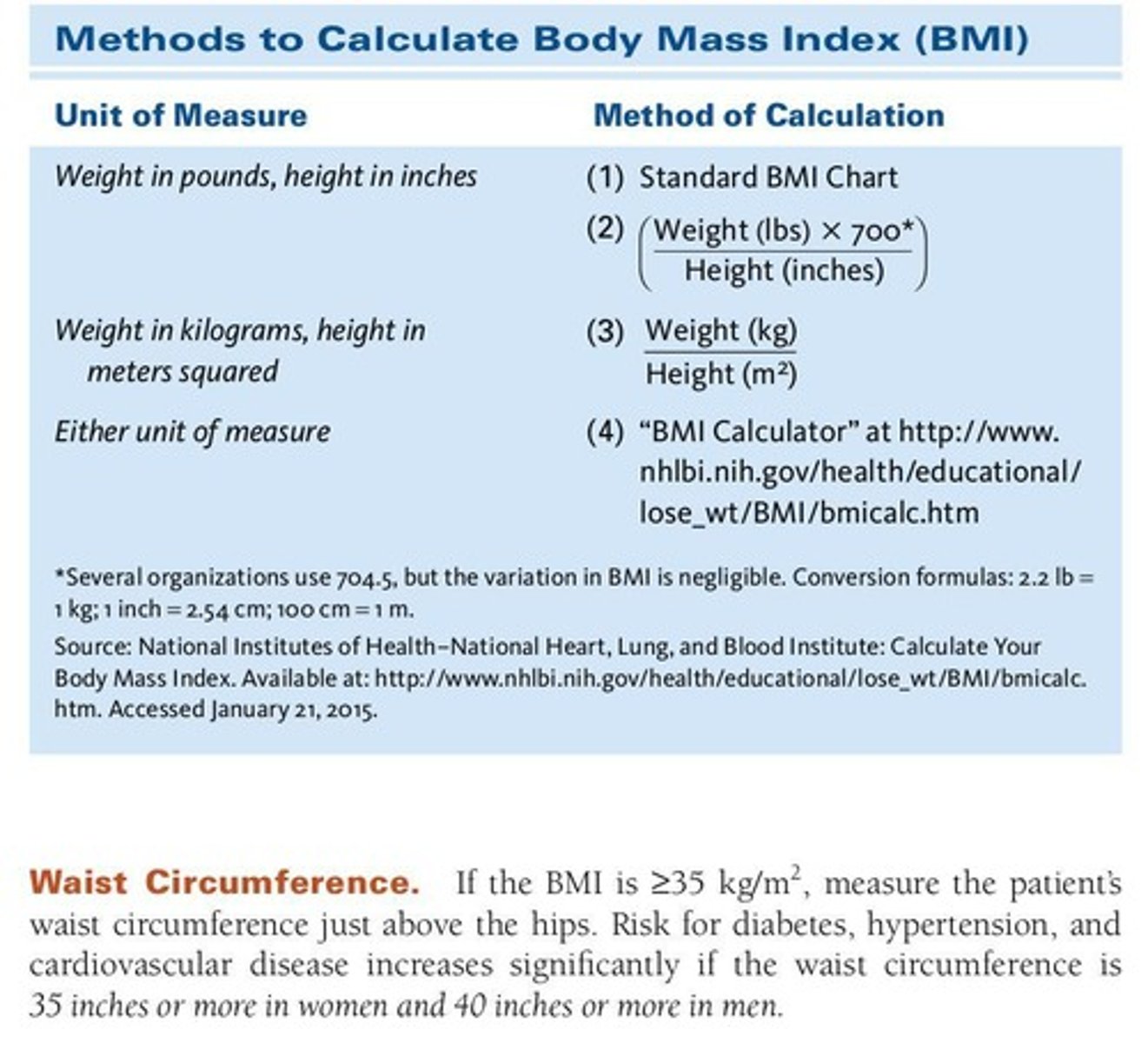
BMI (Body Mass Index)
A numerical value calculated from height and weight, used to classify individuals as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Blood Pressure
The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Posture
The position in which someone holds their body while standing or sitting, which can provide insights into their health status.
Gait
The manner or pattern of walking, which can indicate neurological or musculoskeletal conditions.
Edema
Swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues, often affecting the skin.
Acetone Breath
A fruity odor on the breath, commonly associated with diabetic ketoacidosis.
Temperature Regulation
The body's ability to maintain its internal temperature, which can be affected by various health conditions.
Facial Expression
The outward appearance of emotions on a person's face, which can provide clues to their mental state or health.
Mobility
The ability to move freely and easily, which can be affected by various medical conditions.
Skin Texture
The surface quality of the skin, which can be described as dry, oily, rough, or smooth.
Abdominal Circumference
A measurement around the abdomen used to assess abdominal obesity, which is a risk factor for various diseases.
Resting Position
The preferred position of a patient when at rest, which can indicate comfort or discomfort.
Involuntary Movements
Uncontrolled movements that may indicate neurological disorders or side effects of medication.
Hypertension
A condition characterized by consistently elevated blood pressure, specifically readings above 140/90 mm Hg.
Isolated Systolic Hypertension
A type of hypertension where only the systolic blood pressure is elevated, while diastolic pressure remains normal.
Orthostatic Hypotension
A form of low blood pressure that occurs when standing up from sitting or lying down, indicated by a significant drop in blood pressure.
Systolic Blood Pressure
The pressure in the arteries during the contraction of the heart muscle, typically measured with a sphygmomanometer.
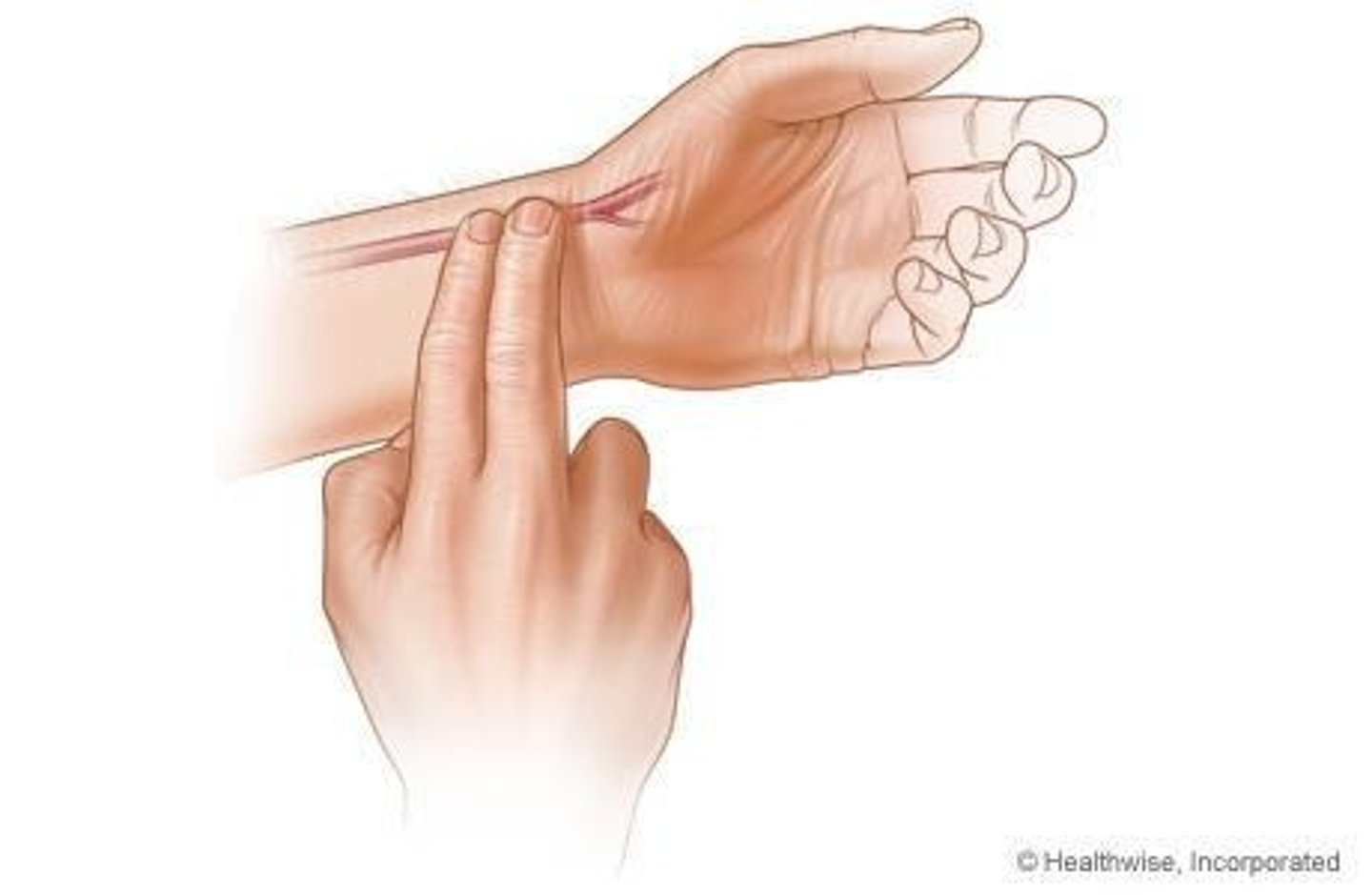
Radial Pulse
The pulse felt at the wrist, used to assess heart rate and rhythm.
Heart Rate
The number of times the heart beats in one minute, typically measured in beats per minute.
Atrial Fibrillation
An irregular and often rapid heart rate that can lead to poor blood flow and increased risk of stroke.
Respiratory Rate
The number of breaths taken per minute, used to assess respiratory function.

Normal Breathing Rate
The typical range of breaths per minute for a resting adult, which is 14-20 breaths.
Body Temperature
A measure of the body's ability to generate and dissipate heat, typically around 37 degrees Celsius when measured orally.