The Behavior of Interest Rates & Bond Markets w8
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on The Behavior of Interest Rates & Bond Markets
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Asset
Anything that can be owned and has value.
Wealth
The total resources owned by the individual, including all assets.
Expected Return
The return expected over the next period on one asset relative to alternative assets.
Risk (in finance)
The degree of uncertainty associated with the return on one asset relative to alternative assets.
Liquidity
The ease and speed with which an asset can be turned into cash relative to alternative assets.
Bond Demand
At lower prices (higher interest rates), the quantity demanded of bonds is higher, indicating an inverse relationship.
Bond Supply
At lower prices (higher interest rates), the quantity supplied of bonds is lower, indicating a positive relationship.
Market Equilibrium
Occurs when the amount people are willing to buy (demand) equals the amount that people are willing to sell (supply) at a given price.
Income Effect
A higher level of income causes the demand for money at each interest rate to increase, shifting the demand curve to the right.
Price-Level Effect
A rise in the price level causes the demand for money at each interest rate to increase, shifting the demand curve to the right.
Liquidity Effect
An increase in the money supply will lower interest rates.
determinents of asset demand
wealth, expected returns, risk, and liquidity.
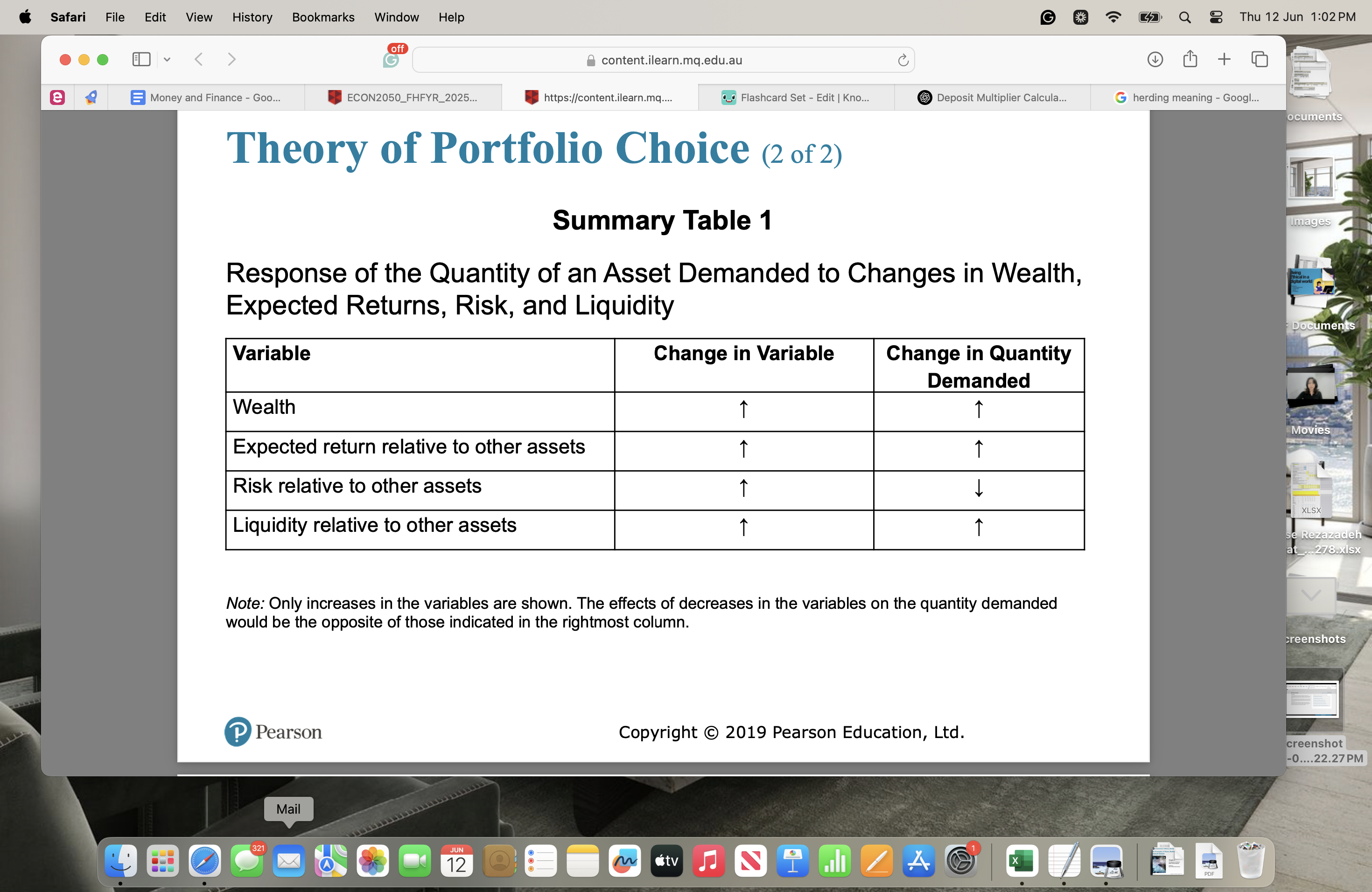
Response of the Quantity of an Asset Demanded to Changes in Wealth, Expected Returns, Risk, and Liquidity
affects of price on quanitity demand and supply of bonds
At lower prices (higher interest rate), the quantity demanded of bonds increases, while the quantity supplied decreases,
Excess supply
S > d which leads to a decrease in price. and increase in interets rates
Excess demand
D > S which leads to an increase in price and a decrease in interest rates.
an increase in the demand curve shifts the curve to the ——
right, indicating that at each price level, a greater quantity of bonds is demanded.
an increase in the supply curve shifts the supply curve to the—.
right, indicating that at each price level, a greater quantity of bonds is supplied.
Business cycle expansion
occurs when economic activity increases, leading to growth in employment, income, and production.
leads to a shift in the bond demand curve to the right and shifts the bond supply curve to the right
This leads to a decrease in bond price and an increase in the equilibrium interest rate.
The liquidity preference framework
It is a theory that explains how interest rates are determined by the supply and demand for money, factoring in people's preference for liquidity.
keynesian model
states that there are two main categories of wealth: money and bonds
as interest rates goes up the oppurtunity cost of holding money increases and relatuve expected return of money decreases. This leads to a decrease in the demand for money and an increase in the demand for bonds, resulting in higher interest rates.
formula of total wealth in the economy
BS - BD = MD - MS
If the price of gold becomes less volatile, then, other things equal, the demand for stocks will ________ and the demand for antiques will ________.
decrease; decrease.
If wealth increases, the demand for stocks ________ and that of long-term bonds ________, everything else held constant.
increases; increases
When the interest rate on a bond is ________ the equilibrium interest rate, in the bond market there is excess ________ and the interest rate will ________.
above; demand; fall
When the expected inflation rate increases, the real cost of borrowing ________ and bond supply ________, everything else held constant.
decreases; increases
During business cycle expansions when income and wealth are rising, the demand for bonds ________ and the demand curve shifts to the ________, everything else held constant.
increases, right
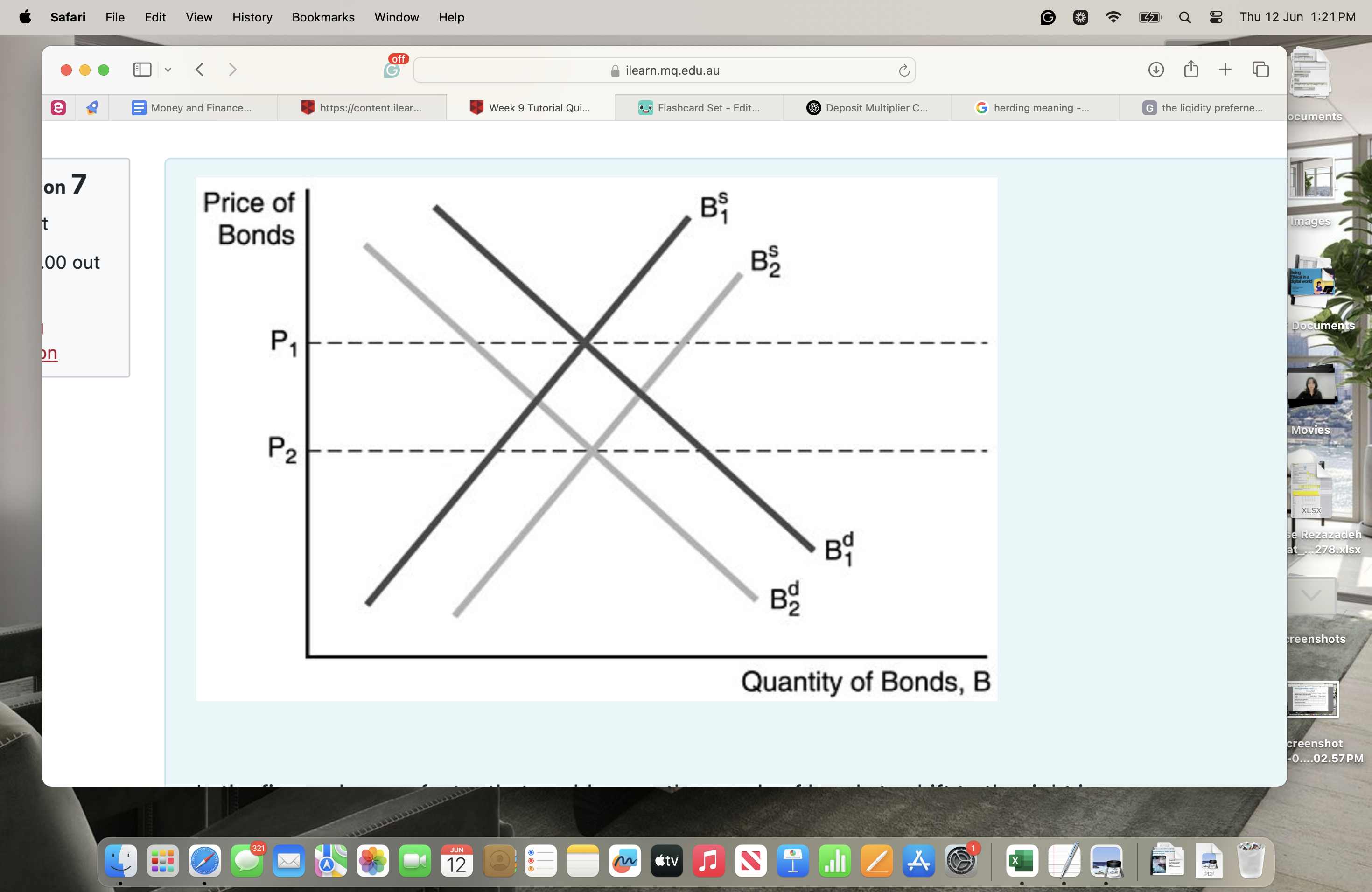
In the figure above, a factor that could cause the supply of bonds to shift to the right is ——
a business cycle expansion.
When the growth rate of the money supply is increased, interest rates will fall immediately if the liquidity effect is ________ than the other money supply effects and there is ________ adjustment of expected inflation.
larger, slow
What is the impact on interest rates when the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply by selling bonds to the public?
Bond supply increases and the bond supply curve shifts to the right. The new equilibrium bond price is lower and thus interest rates will increase.