PKG825 Exam 1 - Basic Structure of Polymers
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is a thermoplastic?
Flow more easily under heat and pressure. They can be reshaped after melt.
What are examples of thermoplastics?
PE, PS, PP, PET
What are thermosets?
They can be initially molded, but they are hard and cannot be reshaped.
What are examples of thermosets?
Rubber, starch, silicone
All plastics are polymers, but not all polymers are plastics (T/F)
True
Do thermosets or thermoplastics have a higher Tg?
Thermosets (due to cross linked and 3D structure)
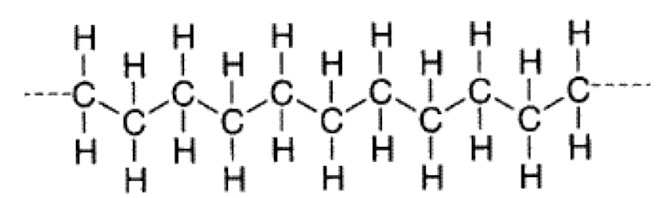
What is an example of a linear polymer?
Polyethylene
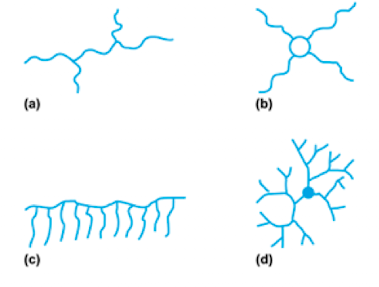
What are branched polymers?
Have side chains (lower crystallinity)
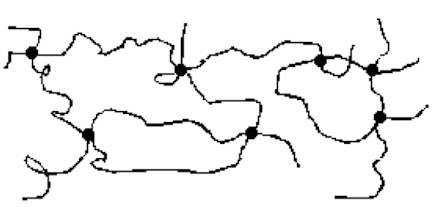
What are cross-linked polymers?
polymer chains are interconnected
What is a homopolymer?
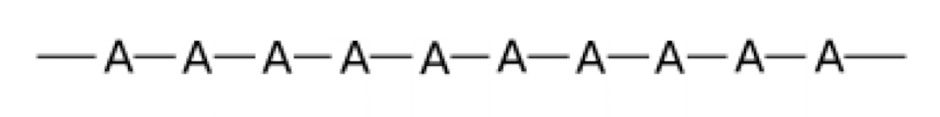
What is a copolymer?

Alternating copolymer
The two monomers are arranged in an alternating way
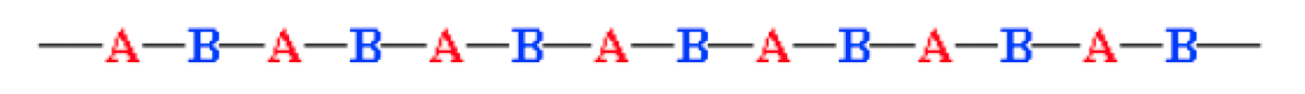
What is a random copolymer?
the two monomers are aligned in any order

Block copolymer
all of one type of monomer are grouped together. a block copolymer could be considered as 2 homopolymers
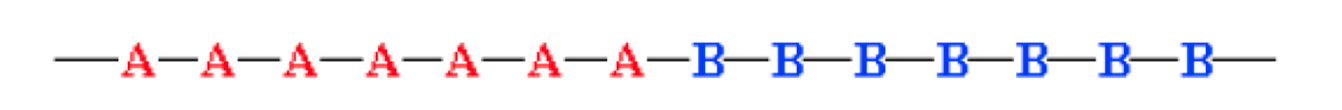
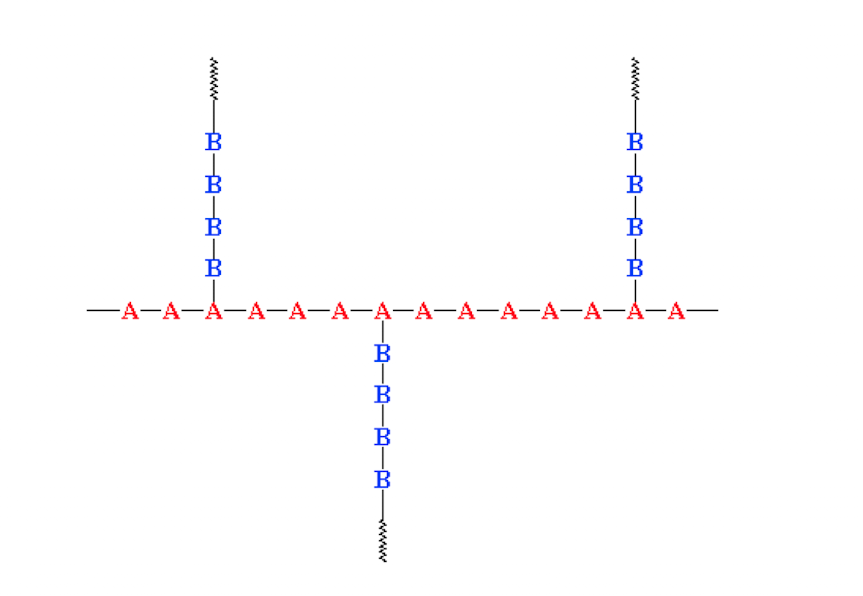
Graft copolymer
when chains of a polymer made of monomer B are grafted onto a polymer chain of monomer A. Composed of a backbone of one type of monomer with the branches of the other.
What are types of primary bonds?
covalent and ionic bonds w
What are types of secondary bonds?
Van der Waals (dispersion, induction, dipole), hydrogen bonds
What type of bonds form the backbone of the polymeric chain?
Covalent bonds (single/double/triple)
What is an aromatic bond?
six member carbon rings containing alternating single and double bonds that can switch positions with one another
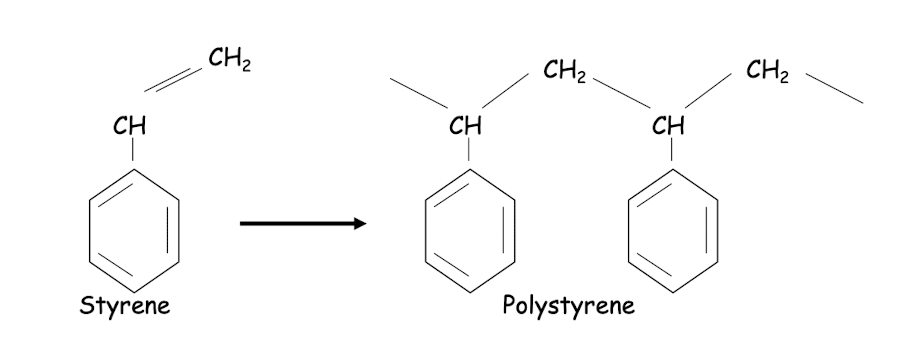
What is an example of an aromatic polymer?
Polystyrene
What is the difference between a polar and nonpolar covalent bond?
polar covalent bond: one atom has a higher affinity for the shared electron (C-Cl)
nonpolar covalent bond: sharing electron identical atoms (C-C)
What are examples of polar covalent bonding?
C-O, C-N, C-Cl, C-F (all have a higher affinity for electrons than C)
What are ionic bonds?
Formed when there is a complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom, resulting in two ions (one positive and one negative)
What is cohesive energy density?
measures secondary forces. The amount of energy required to move a molecule far enough away from its neighbors
What effect does molecule size have on intermolecular forces?
The bigger the molecule, the more molecule there is to exert an intermolecular force
What is London dispersion force?
A temporary electrostatic attractive force between the electrons of 2 adjacent atoms with temporary dipole
What force do all plastics have?
LDF
What are induction forces?
polar atoms creating a temporary polarity in the neighboring non-polar atoms, leading to electrostatic attraction between atoms
What is an example of a polymer with induction forces?
EVA (presence of polar atom (Oxygen) creates temporary polarity
What are dipole forces?
permanent attraction of molecules with positive and negative charges, present where ever there is a polar bond (C-Cl)
What is Tg?
Tg marks the onset of segmental mobility
below Tg, polymer is stiff
above Tg, polymer is flexible
higher Tg = more stiff polymer
What happens molecularly when the temperature reaches Tg?
There is enough energy to overcome the attractive forces occurring between the molecules.
How do intermolecular forces affect the Tg?
The stronger the intermolecular forces, the more energy is required for segmental mobility, the higher the Tg
How are Tm and Tg connected?
They are a linear relationship → lower conformational flexibility means increased Tm
How is the Tm affected in polymers that have strong intermolecular bonding (ex: PVDC)
PVDC has strong intermolecular bonding (two H-Cl bonds), so the Tm will be so high that the polymer is likely to burn before it melts
What is heat of vaporization?
the amount of heat that has to be added to separate the molecules
What is isothermic condition?
The amount of van der waals forces that held the molecules of liquid together

How do you know if two materials are miscible?
If their intermolecular attractive forces/CED values are similar