bio finals formatives - unit 6
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
mitosis
consists of one nuclear divisions (1 PMAT)
mitosis
produces daughter cells that are genetically identical
mitosis
occurs during asexual reproduction
mitosis
produces 2 diploid cells
meiosis
consists of two nuclear divisions (2 PMAT's)
meiosis
produces daughter cells that are unique
meiosis
produces 4 haploid gametes
meiosis
occurs during sexual reproduction
A chromosome contains hundreds of genes, which are composed of DNA
What is the relationship between DNA, a gene, and a chromosome?
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase/cytokinesis
What is the order of the steps in mitosis?
- normal cell functions
- cell growth and organelle synthesis
- DNA replication
Which of the following occurs in interphase?
-Normal cell functions
- Cell growth and organelle synthesis
- Formation of a zygote
- DNA replication
interphase
what step is this?
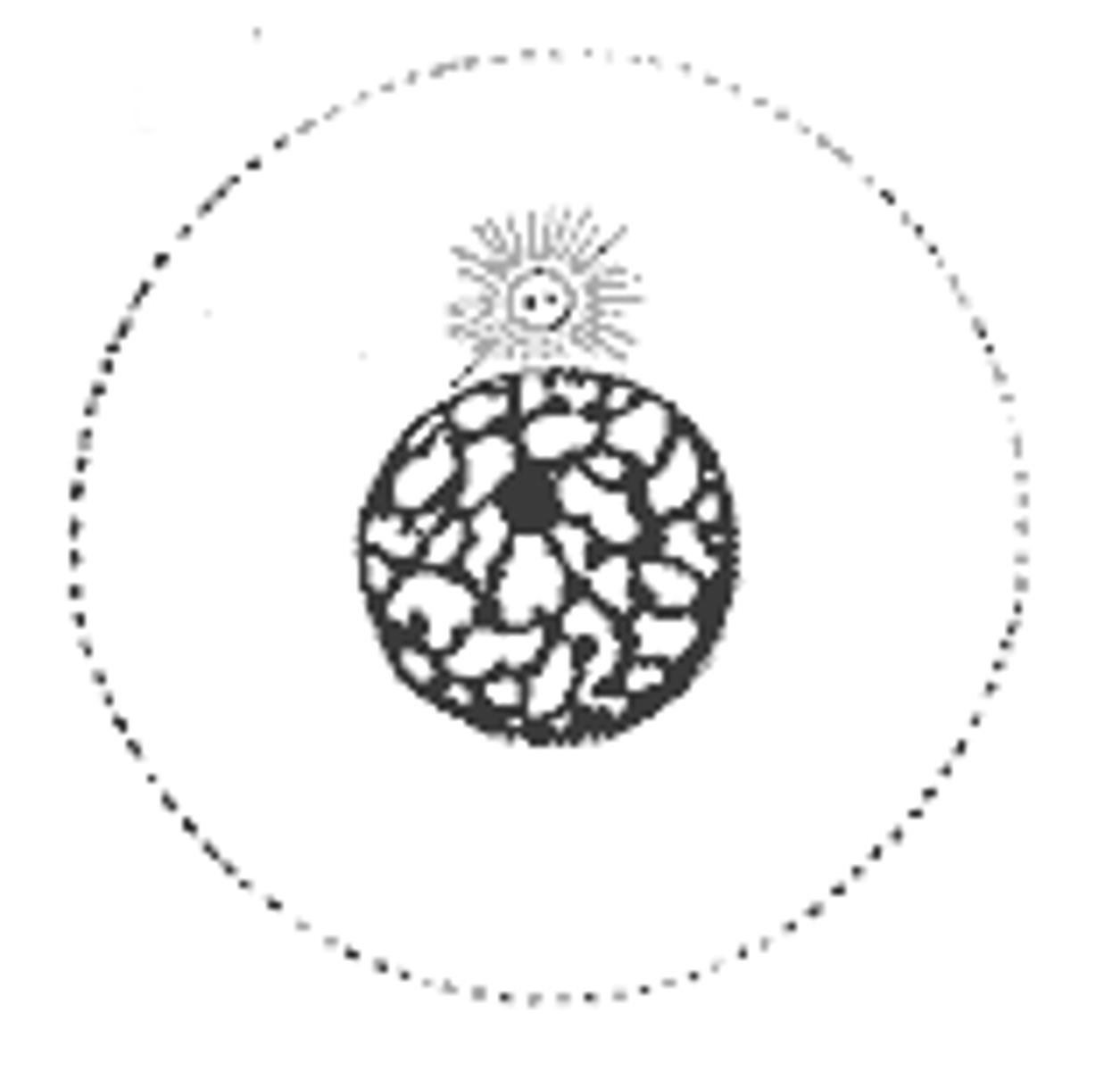
prophase
what step is this?

metaphase
what step is this?
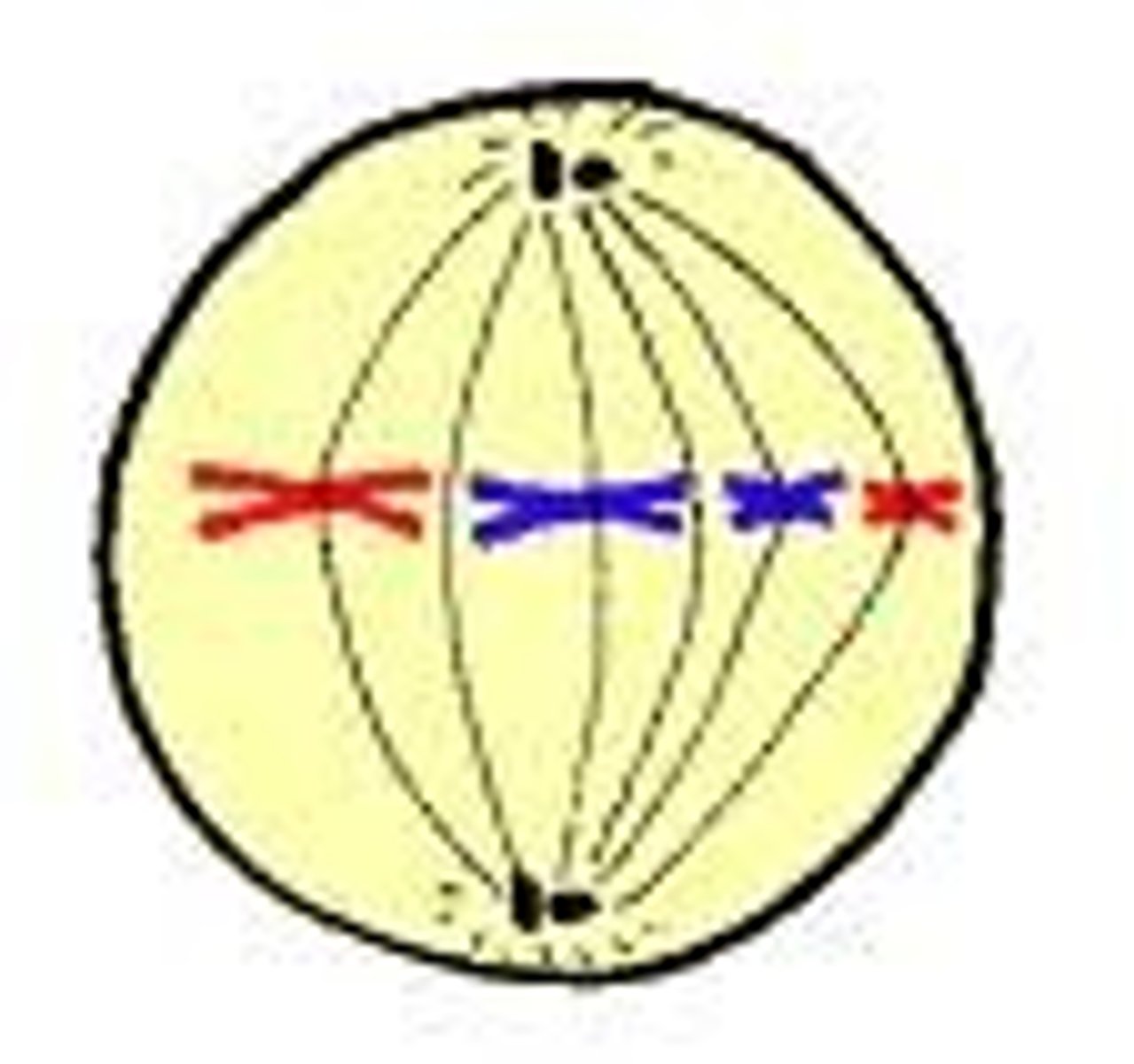
anaphase
what step is this?
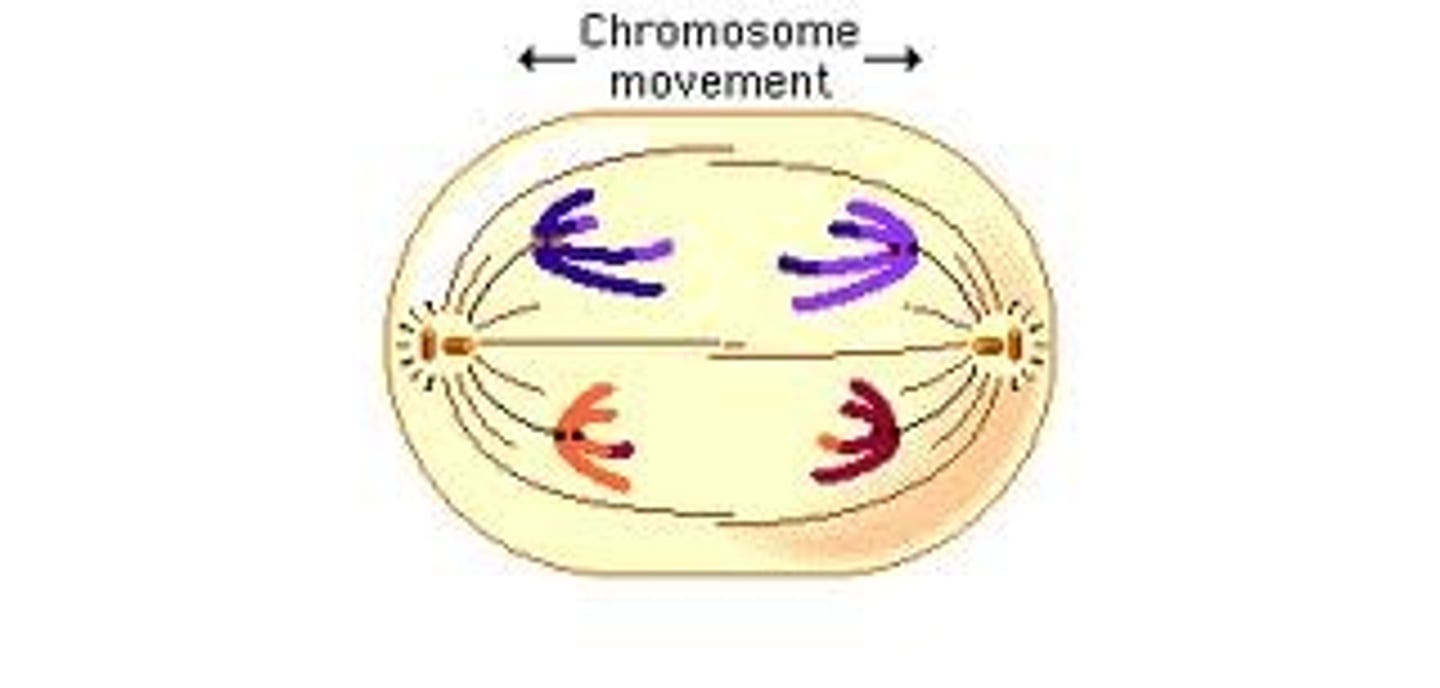
telophase/cytokinesis
what step is this?
Interphase
During which phase does a cell spend most of its life?
To generate gametes for sexual reproduction.
What is the primary function of meiosis in organisms?
Four genetically diverse haploid cells.
What is the outcome of meiosis?
Meiosis II, which separates sister chromatids.
What immediately follows the end of meiosis I?
Homologous chromosomes pair, crossing over occurs, and the nuclear envelope dissolves.
What is a key feature of prophase I in meiosis?
Chromosomes condense and become visible in both processes.
How are prophase I and prophase in mitosis SIMILAR?
Homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
What occurs during "crossing over"?
Homologous pairs line up along the metaphase plate.
What happens in Metaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
What is the main event of Anaphase I?
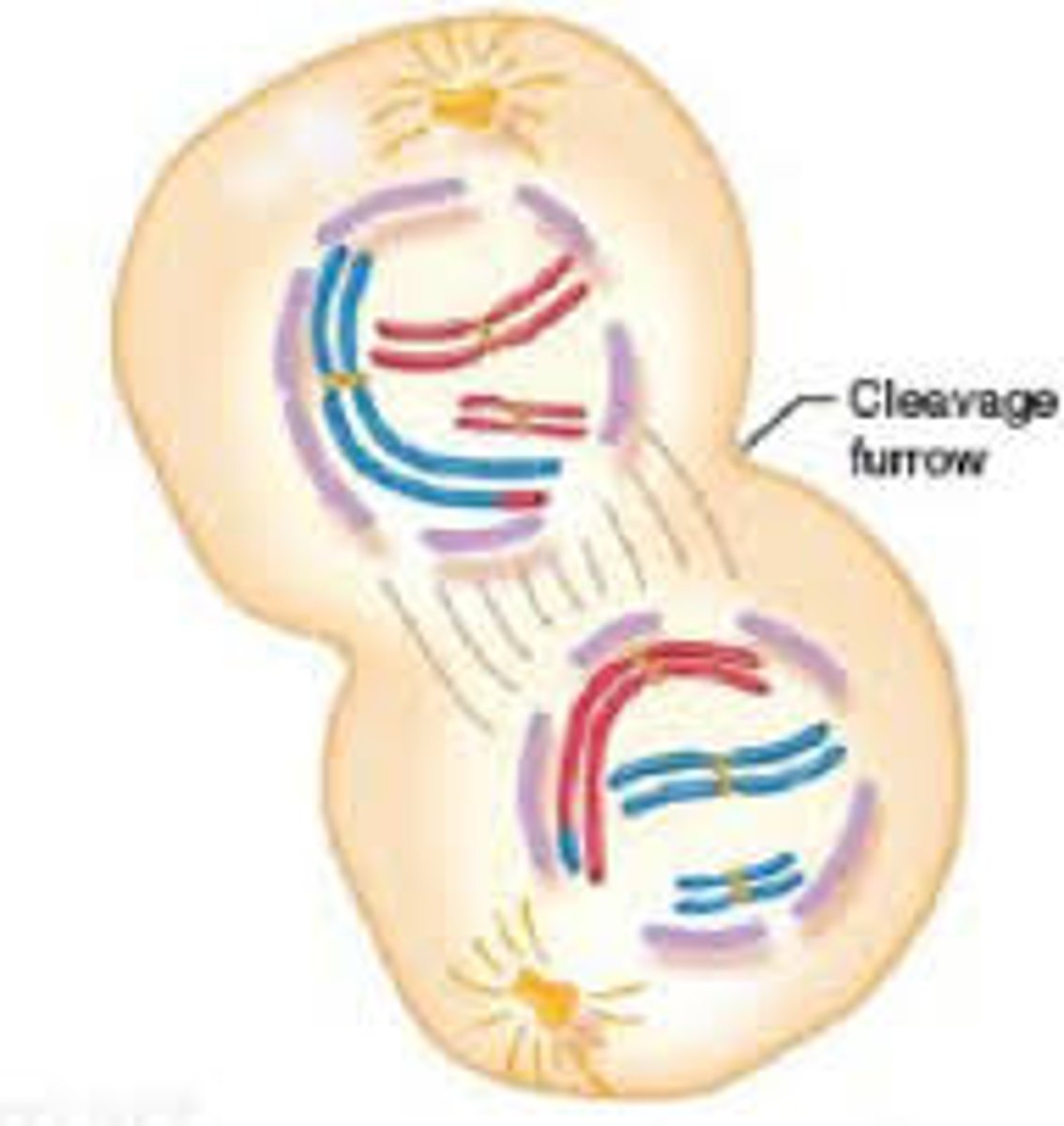
Cells divide into two daughter cells with duplicated chromosomes.
What happens during Telophase I?
telophase II
What phase of meiosis is indicated by this picture?
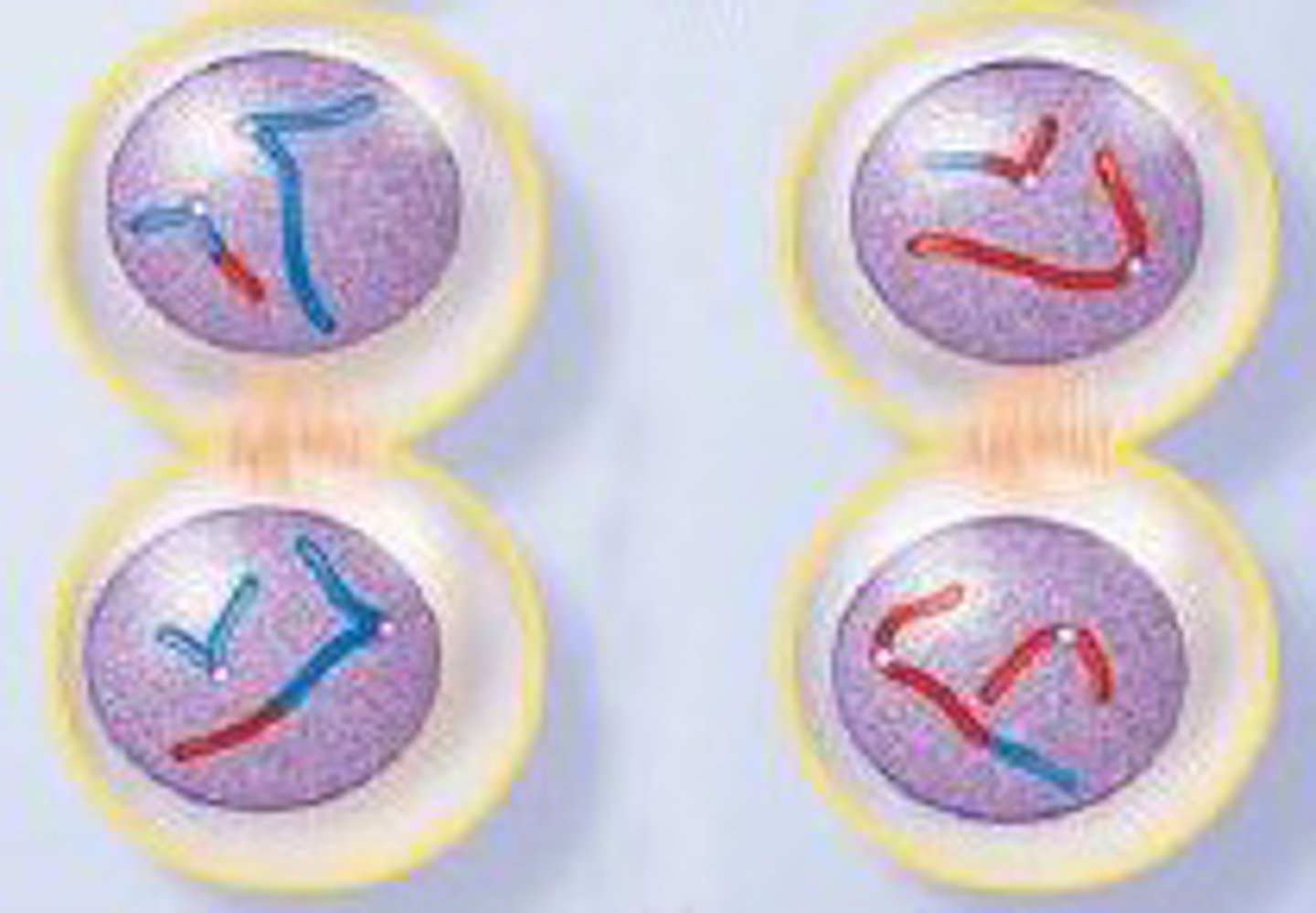
prophase I
What phase of meiosis is indicated by this picture?

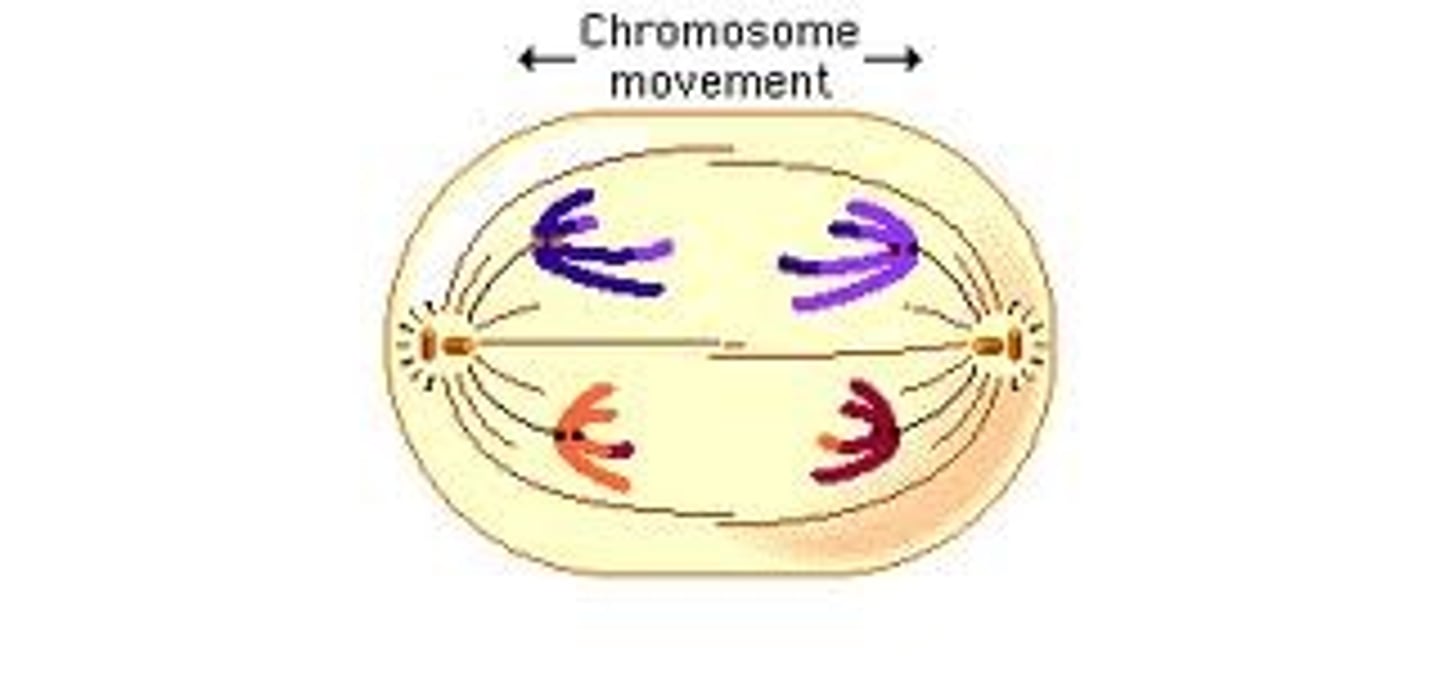
anaphase I
What phase of meiosis is indicated by this picture?
Four viable sperm cells.
What is produced at the end of spermatogenesis?
One egg and three polar bodies.
What is the end result of oogenesis?
haploid
What is the PLOIDY of a gamete (egg or sperm)?
diploid
What is the PLOIDY of a fertilized cell (zygote)?
Failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly.
What causes nondisjunction during meiosis?
Presence of only one chromosome from a pair.
What is monosomy in terms of chromosome presence?
More than the normal number of chromosomes for one pair.
What characterizes polysomy in chromosomes?
Organism has more than the normal number of sets of chromosomes.
What does polyploidy mean in terms of chromosome number?
An abnormal number of chromosomes in gametes.
What is a common outcome of nondisjunction in meiosis?
deletion
Loss of a segment of DNA from a chromosome.
inversion
Reversing the order of chromosome segments.
translocation
A segment of a chromosome breaks off and moves to a non-homologous chromosome.
frameshift
Insertion or deletion alters reading frame of DNA, or the codon pattern; can't be seen on a karyotype
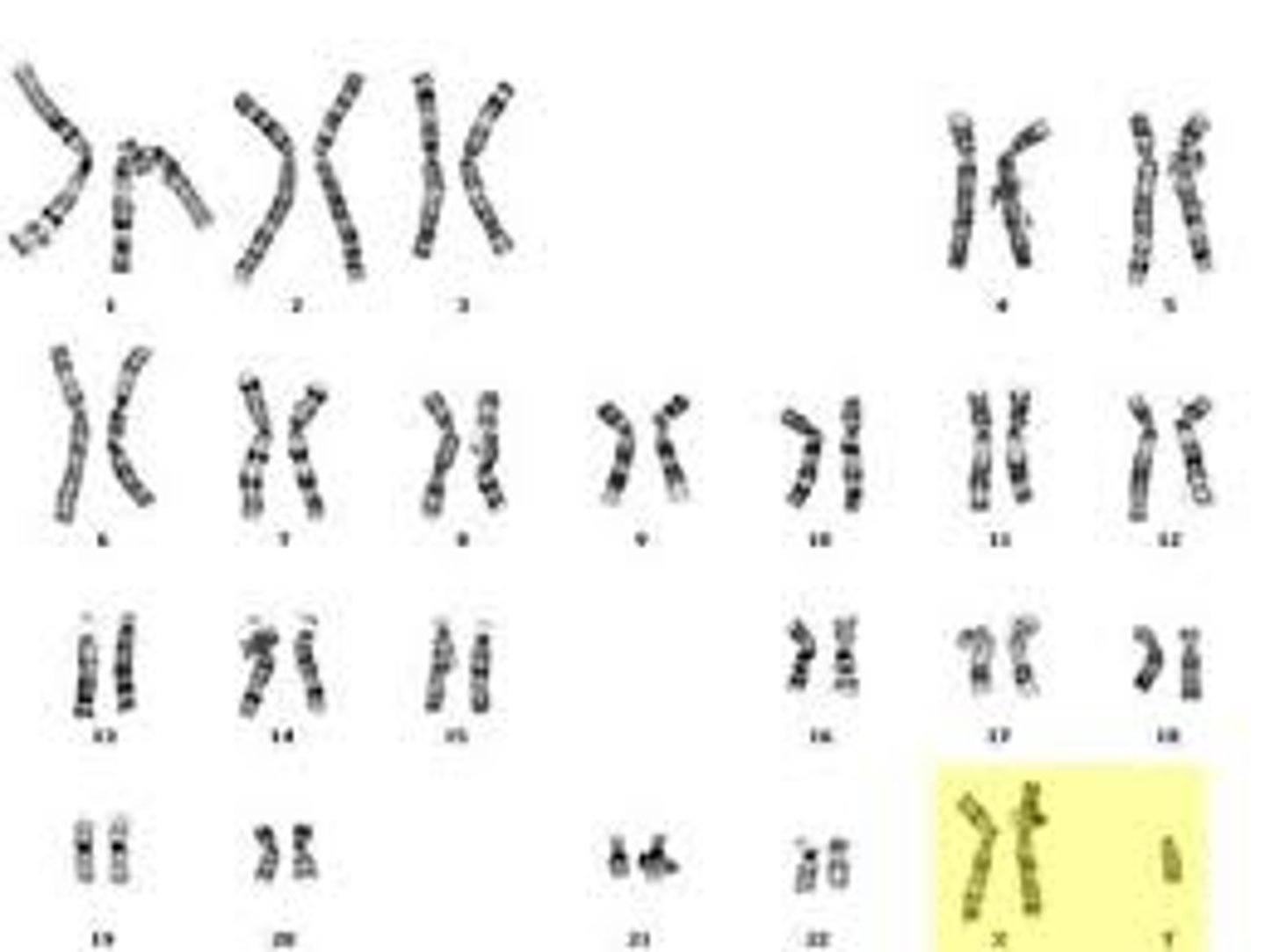
Males.
Which sex is affected by Klinefelter's syndrome?
47 chromosomes total, including an extra chromosome 21.
How many chromosomes are present in Down's syndrome karyotype?
One X chromosome
What is missing in a Turner's syndrome karyotype?
XXY sex chromosomes.
What is the chromosome composition in Klinefelter's syndrome?
Kleinfelter's Syndrome
What syndrome is represented by this karyotype?