Integumentary System: Feathers, Hair, Glands, and Scales in Birds and Mammals
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Feather tracts
Pterylae
Apteric tracts
Featherless areas (apteria)
Melanins
One of the three groups of pigments found in feathers.
Carotenoids
One of the three groups of pigments found in feathers.

Porphyrines
One of the three groups of pigments found in feathers.
Pelage
Fur, hair, or wool found in most mammals.
Hypodermis
Subcutaneous space beneath the skin.
Equine skin
Skin structure in horses, magnified 40x.
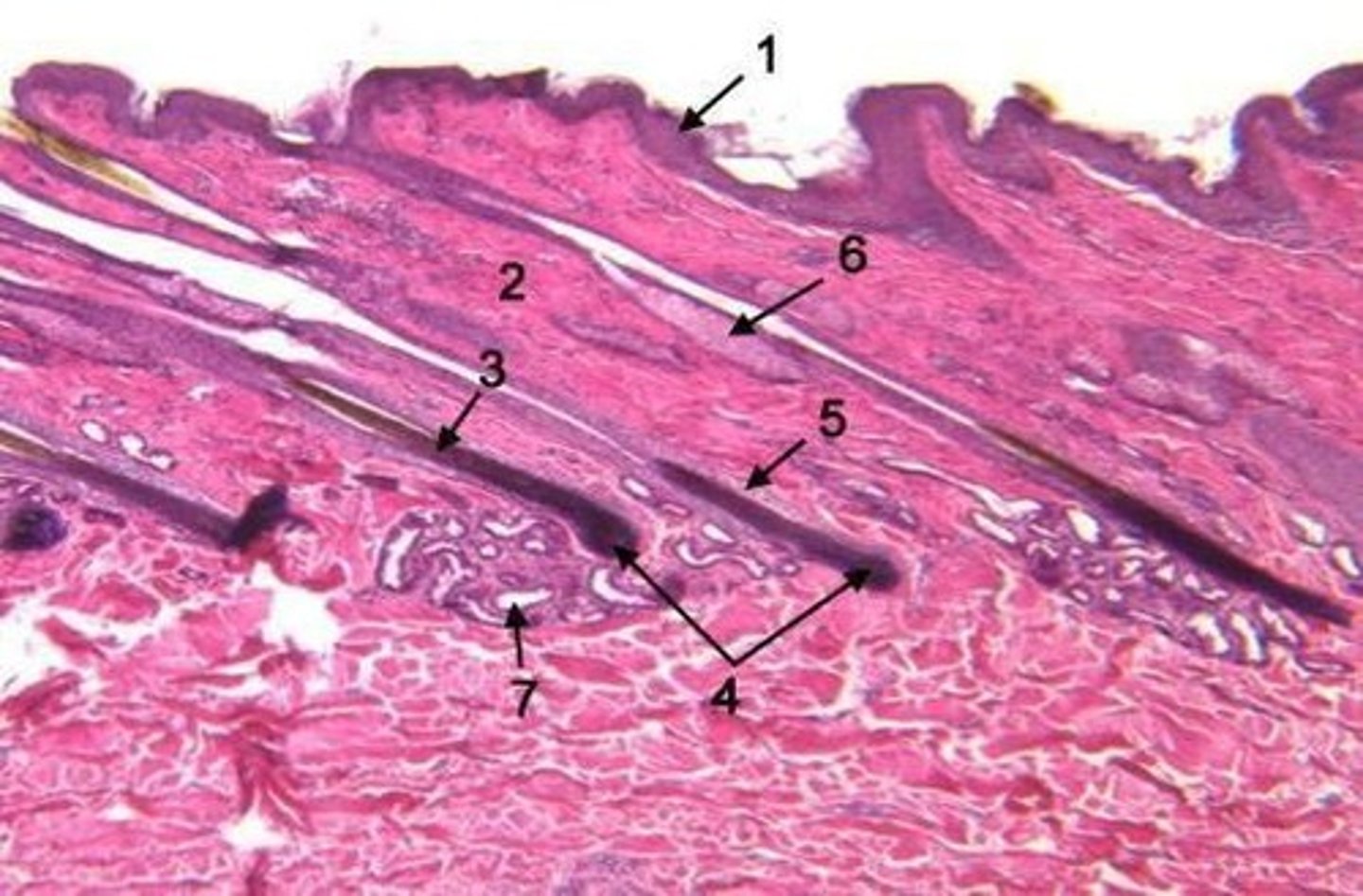
Avian skin
Skin structure in birds, magnified 40x.
Feather pulp
The core structure of a feather.
Barbs
Pigmented structures that branch from the feather shaft.
Feather follicle
The skin structure from which a feather grows.
Dermis
The layer of skin beneath the epidermis.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of skin.
Hair
A keratinous strand consisting of a shaft and root.
Guard hairs
Coarse, visible hairs that provide pigmentation.
Undercoat
A denser layer of hair providing insulation.
Hair vs Fur vs Wool
Hair is a basic term; fur is short and dense; wool is from sheep.
Hair density
650,000-2.6 million hairs per square inch.
Exocrine glands
Glands that secrete substances through ducts.
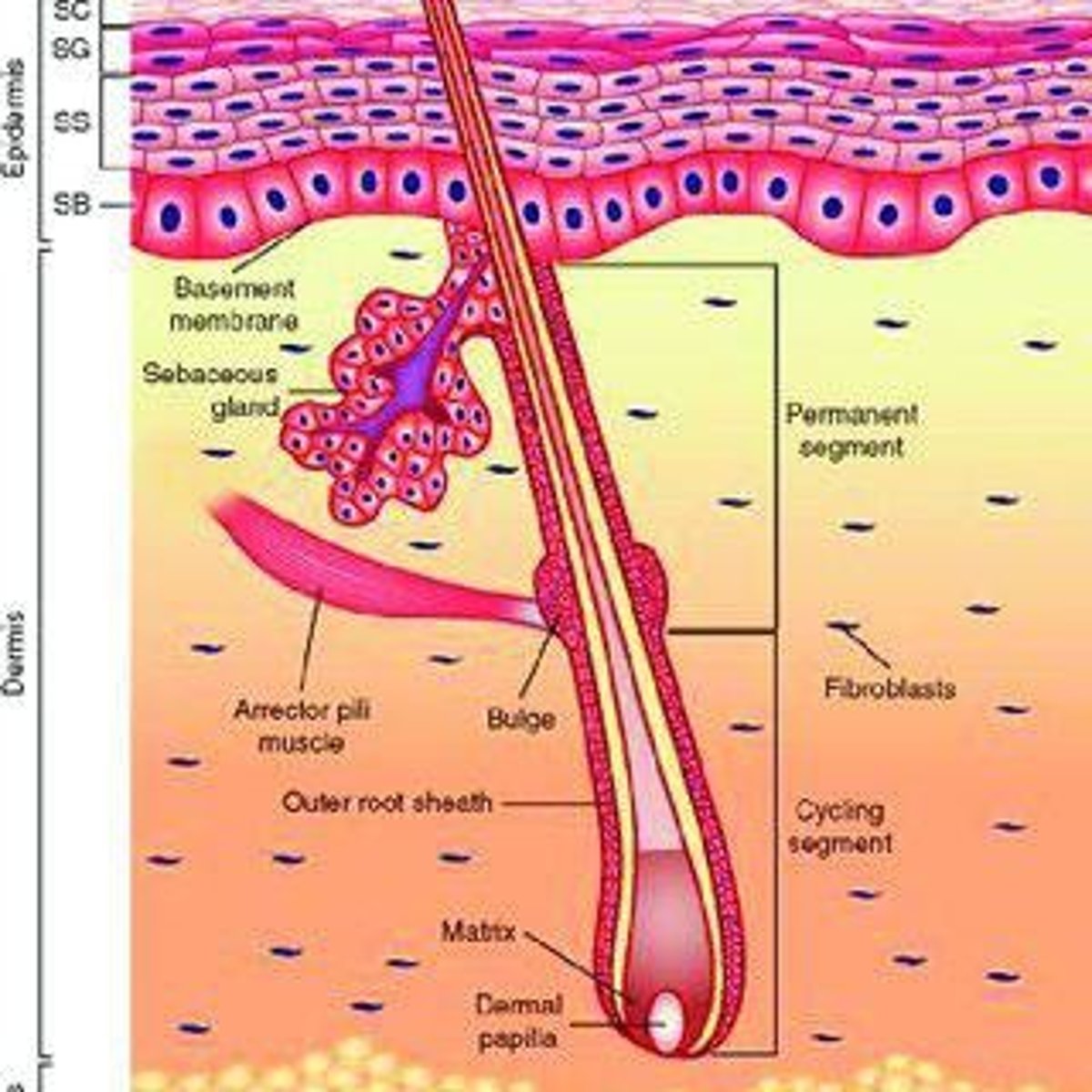
Sebaceous glands
Oily glands that provide waterproofing.
Meibomian glands
Glands that produce oil for the eyelids.
Eccrine glands
Sweat glands not associated with hair follicles.
Apocrine glands
Sweat glands associated with hair follicles, producing viscous sweat.
Meibomian Gland Tumors
Common eyelid abnormalities in dogs, including adenoma or adenocarcinoma.
Schirmer Tear Test
A test to measure tear production in the eyes.
Hipposudoric Acid
A substance produced by hippos, referred to as 'blood sweat'.

Sweatiest Mammals
Mammals with apocrine glands, except humans who also have eccrine glands.
Mammary glands
Glands responsible for producing milk in mammals.
Streak canal
During dry (non-lactating) periods, epidermal lining the streak canal forms a keratin plug that effectively seals off canal.
Mastitis
Clinical significance related to the streak canal.
Anal Glands
Present in all carnivorous mammals, used for scent marking and predator deterrent, and can be subject to blockage or expression.
Domestic Ferret Pre and Post-op Perianal Tumor
Clinical significance related to anal glands.
Apocrine Gland Adenocarcinoma
Clinical significance related to anal glands.
Hooves, Claws, Nails
Keratinized structures at ends of digits.
Hooves
Generally surround distal digit and support body weight.
Nails/Claws
Emerge from dorsal portion and don't support body weight (generally).
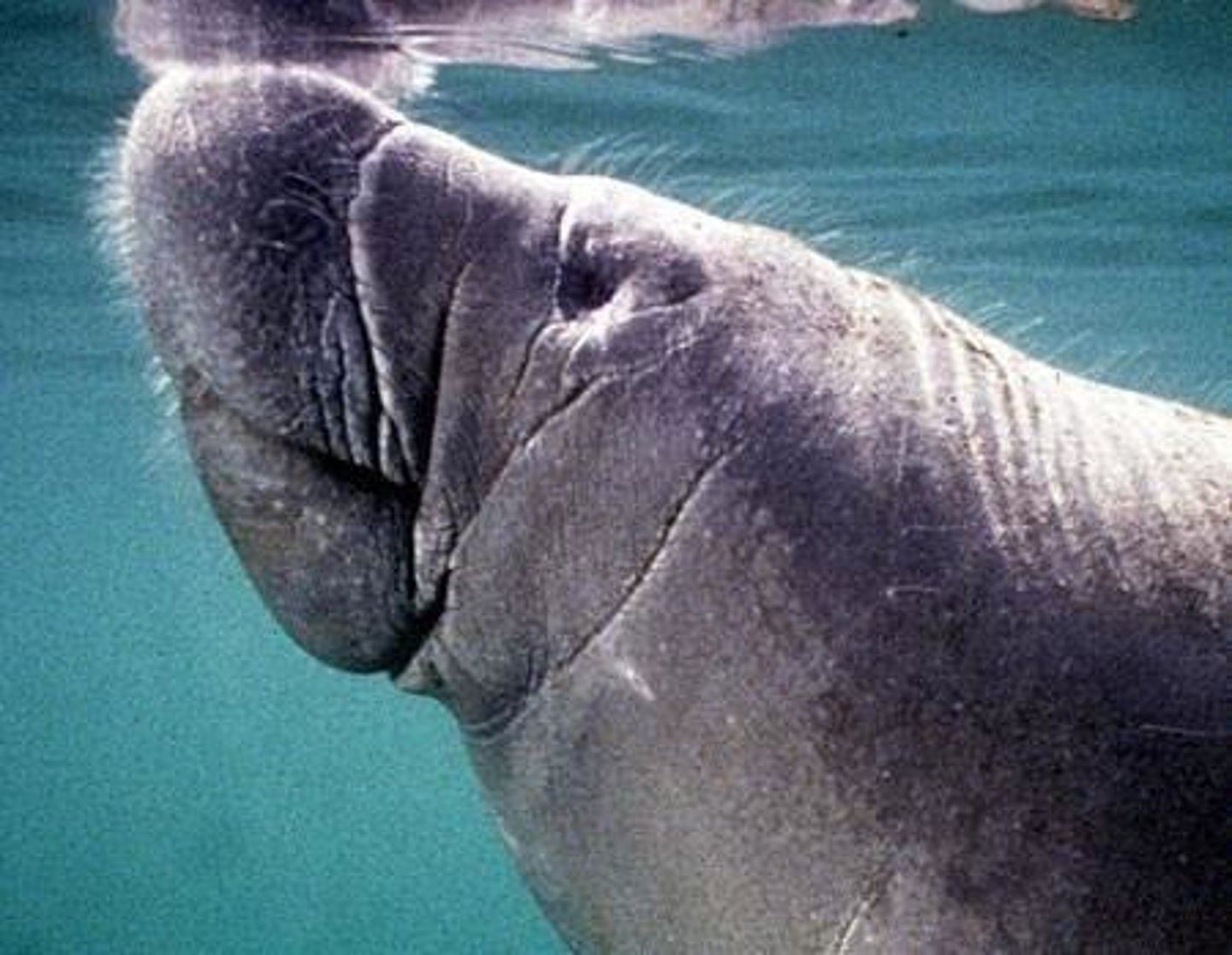
West Indian Manatee
Clinical significance related to overgrown hooves.
Corium
Approximately equivalent to dermis.
Onychectomy
Clinical significance related to the corium.
Horns
Keratinized covering with bone core, continued growth, and not branched.
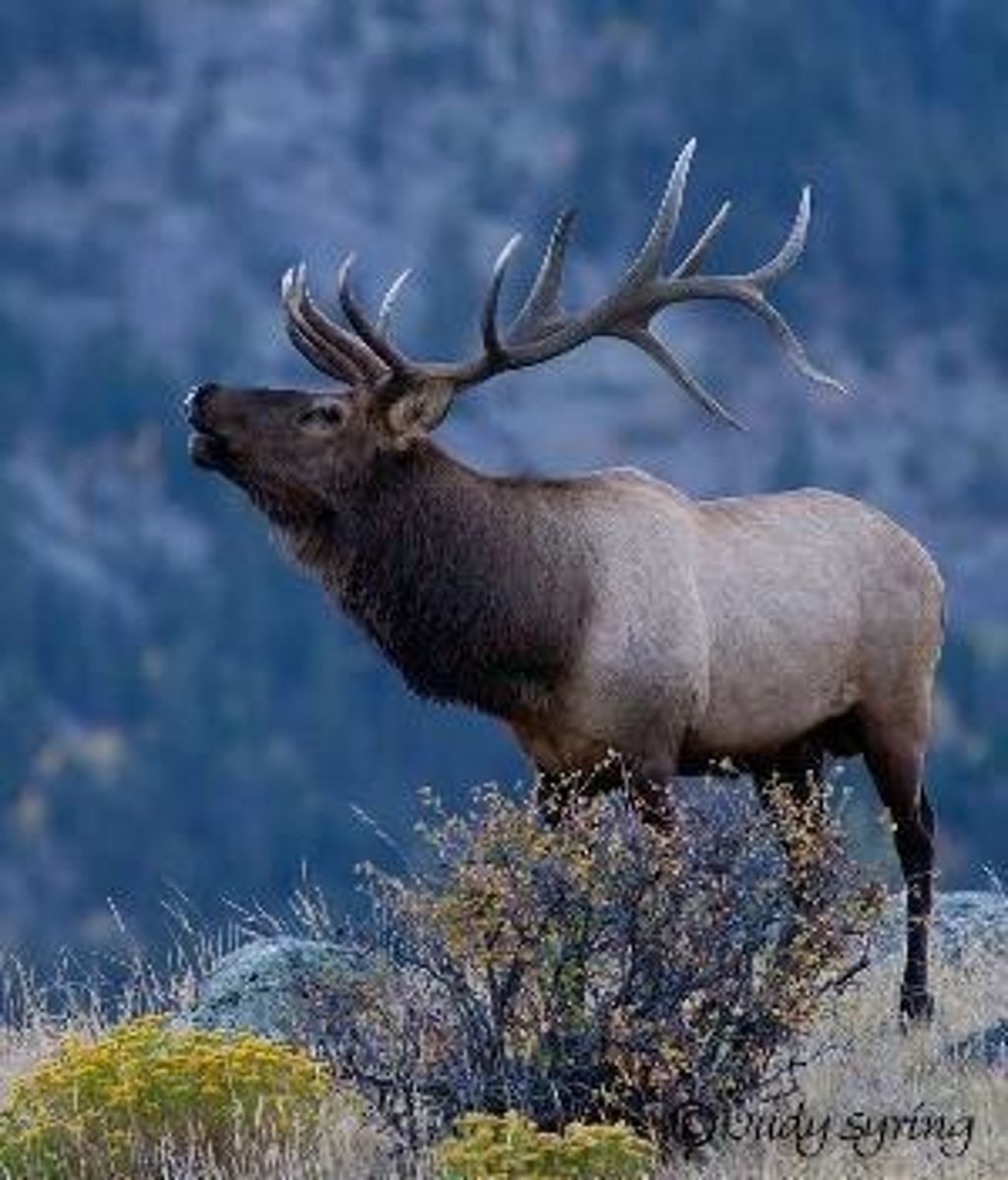
Antlers
Skin viable and is shed, as is bone core, with determinate growth then shed and branched.

True horns
Found in Bovids, can be male or female.
Cervids
Animals with antlers that undergo an annual cycle of growth, velvet phase, and shedding.
Antler Abnormalities
Clinical significance related to antlers, including conditions like 'Antleroma' and Perruque caused by interruption of androgens during velvet phase.
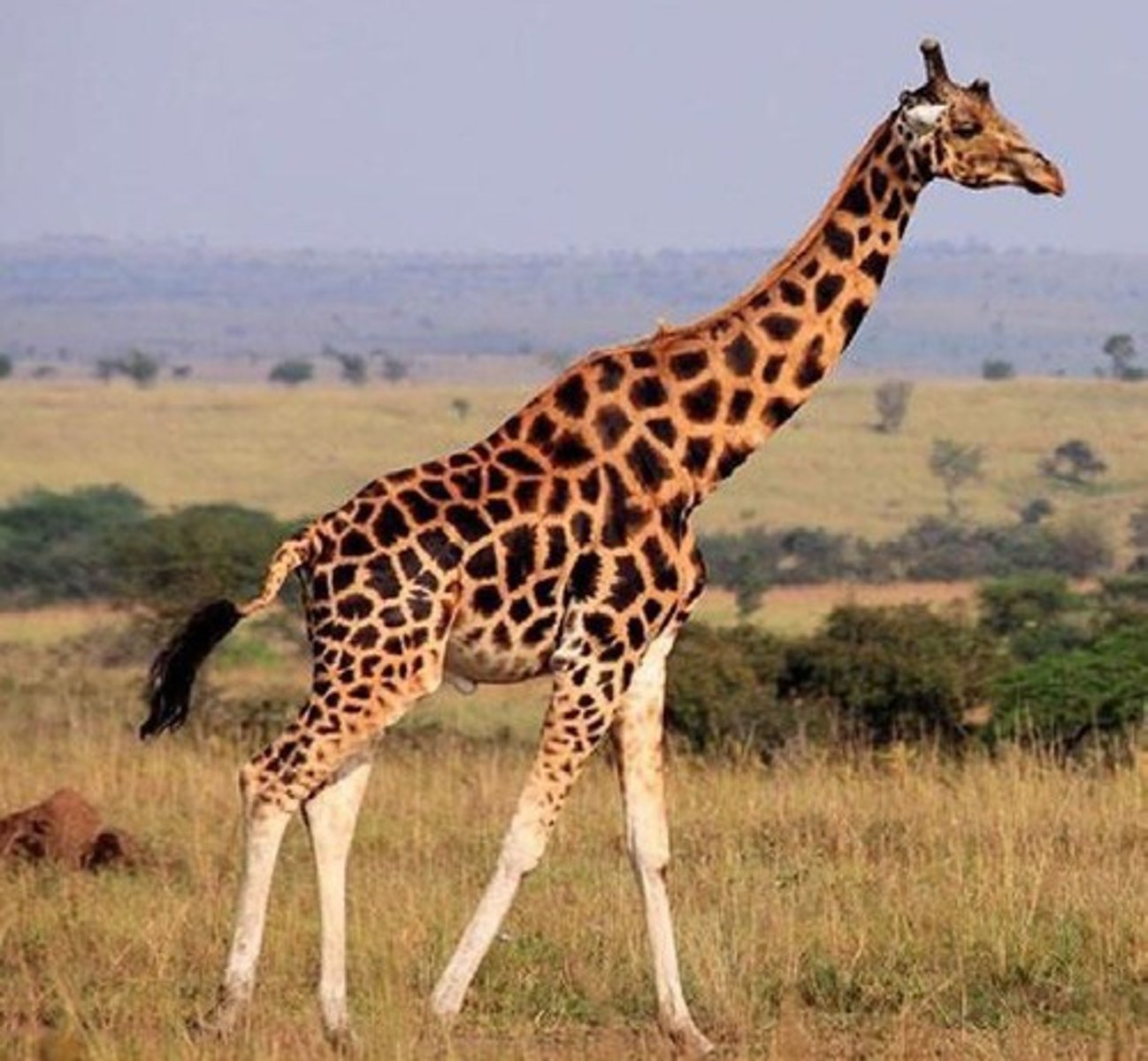
Horn-esque
Rhino 'horns' are keratin, no bone; Giraffe/Okapi have ossicones of ossified cartilage/skin.

Baleen
Plates of keratin grown from gums of upper jaw, built in strainer, referred to as 'whalebone' but not really bone.
Vibrissae
Highly sensory structures prominent in nocturnal species, only found in mammals.

Quills
Modified hairs, with porcupine quills potentially aiding in the development of less painful hypodermic needles.
Adaptations
Examples include Harbor Seals with 'lobes' in skin structure proposed to reduce drag.
Echidnas
Mammals with no teats, known for milk patches.
Male Dayak Fruit Bat
One of the few known occurrences of paternal lactation.
Hairless or Nearly
Refers to cetaceans (only a few guard hairs), elephants, and hippos, which have been artificially selected.
Fish scales
Originate from a bone-like composition layer of the skin and are covered by epidermis.
Reptile scales
Originate from a layer of the skin that contains keratin and may have underlying dermal bone (osteoderms) in some species.
Scutes
Larger scales that give rise to feathers.
Fish slime
Produced by unicellular mucous glands for antimicrobial protection, predator evasion, and osmoregulation.
Amphibian skin
Features cutaneous respiration with capillaries to the epidermis and multi-cellular glands that produce mucous or poison.
Reptile skin
Has fewer skin glands and increasing keratinization, with scales that are epidermal (scutes).
Ecdysis
May be complete or patchy in reptiles.
Skin defects/incision in reptiles
Reptile skin inverts when injured or incised.
Everting suture pattern
Used to close skin defects in reptiles.
Carapace
Formed by the fusion of ribs and the spinal column in turtles and tortoises.
Plastron
Formed by clavicles/interclavicle and gastralia in turtles and tortoises.
Melanin in scutes
Gives pattern to the scutes.
Avian integument
Lacks sweat glands and sebaceous glands, except for one big exception.
Feathers
Grow from feather tracts (Pterylae) and are absent in featherless areas (apteria).
Feather emergence
Involves shedding/grooming of the sheath, receding of the dermal core and artery/vein, and unfurling of the feather.
Broken feathers vs. cut
Differentiates between feather clipping and pinioning.
Evolution of feathers
Described in the Quarterly Review of Biology, detailing the evolutionary origin and diversification of feathers.
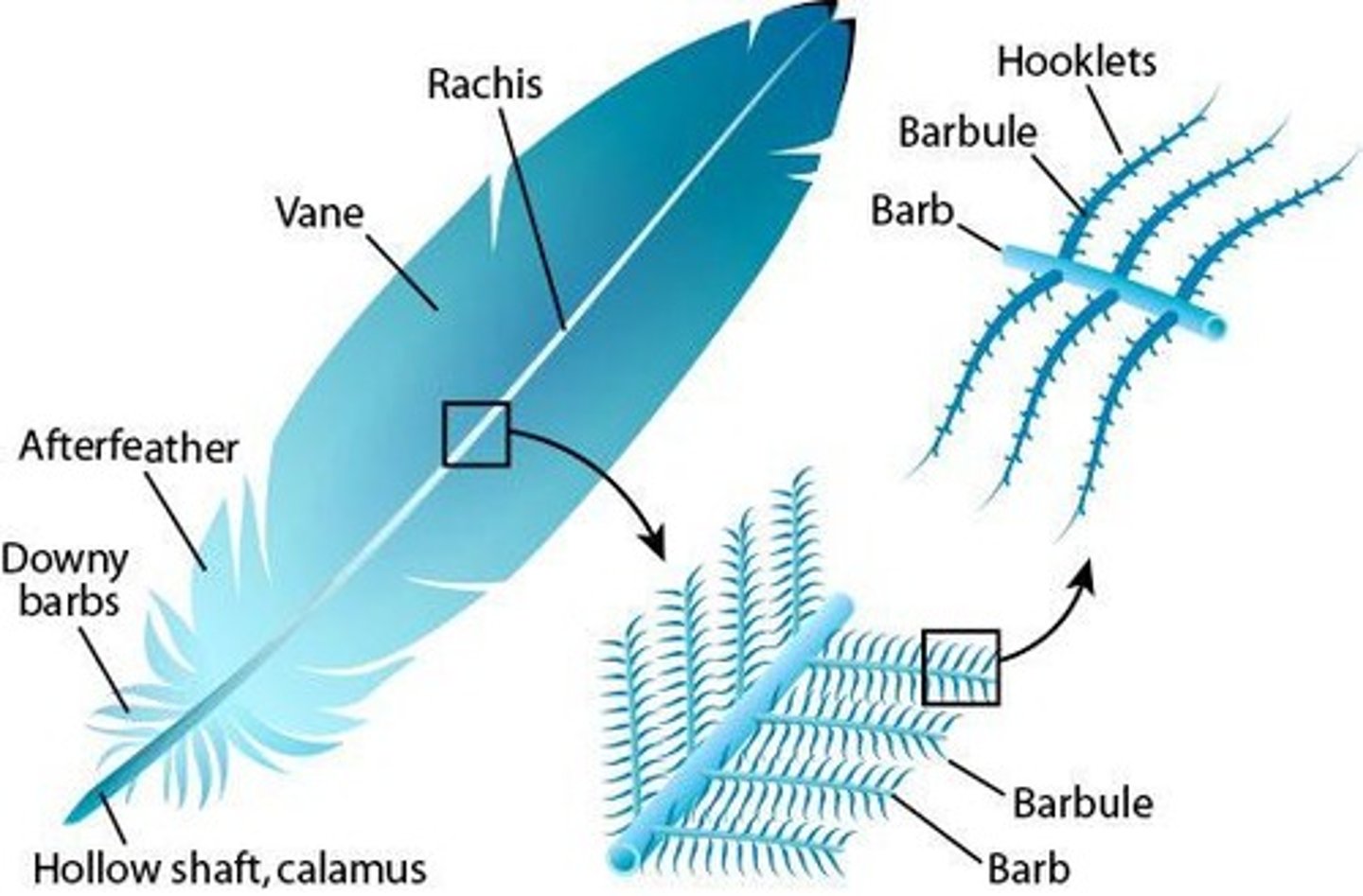
Calamus/Quill
The hollow base of a feather that anchors it to the bird's skin.
Shaft/Rachis
The central shaft of the feather that supports the vanes.
Vane
The flat part of the feather that extends from the shaft, consisting of barbs.
Barb
The branches that extend from the shaft of the feather.
Barbule
The smaller branches that extend from the barbs and interlock to form the feather's structure.
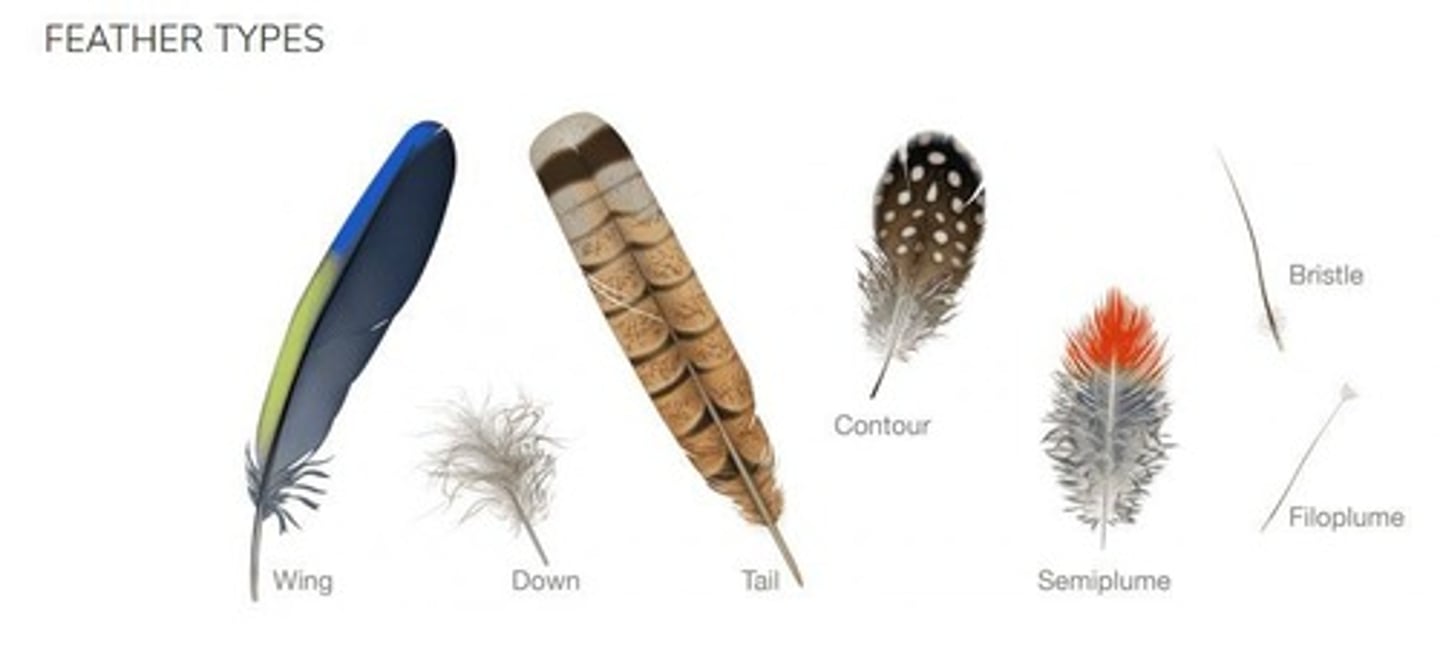
Contour Feathers
Feathers that cover the body, aiding in aerodynamics and often overlapping.
Bristles
Specialized contour feathers near the beak.
Down Feathers
Feathers that lack interlocking barbules, resulting in a fluffy texture.
Rictal Bristles
Specialized feathers that provide sensory feedback about wing position.
Flight Feathers
Feathers that are critical for flight, including primaries for thrust and secondaries for lift.
Filoplume
Sensory feathers that help detect the position of other feathers.
Primaries
The flight feathers attached to the manus that provide thrust.
Secondaries
The flight feathers attached to the ulna that provide lift.
Powder Down
Special feathers that never molt and continuously grow, breaking down into a talcum powder-like dust.
Synchronous/Catastrophic Molt
A type of molt observed in some birds where feathers are shed all at once.
Clinical Significance: Arrested Molt
Failure to molt, often observed in captivity due to various factors.
Melatonin Implant
A treatment used for issues related to arrested molt.
Pigmentation
The coloring of feathers due to various pigments such as melanins, carotenoids, and porphyrins.
Structural Color
Color that appears based on the angle and refraction of light, often seen in iridescent feathers.
Uropygial (Preening) Gland
A gland that produces a waxy substance for waterproofing and arranging feathers.
Clinical Significance: Preening Gland Impaction
A condition caused by poor diet, infections, or trauma affecting the preening gland.